hematology
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
structure of blood
Blood is composed of : 40% cells and 60% plasma
All blood cells develop in bone marrow
The cells that in the blood are
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
Platelets
hematology
the study of blood
hematopoiesis
formation and development of blood
hemoglobin
a pigment that contains iron and when it picks up oxygen, it gives a red color
antigen
the virus, bacteria, anything disease causing
when working w blood, the proper PPE to wear is
gloves
when working with stains you should wear ____ and _____ and work in a well ventilated area
goggles and gloves
true or false - stains are hazardous to skin and eyes
true, inform instructor of accidents immediately and rinse with water
where should used slides be disposed of
broken glass box
where should used blood tubes and pipets be disposed of
biohazard bag
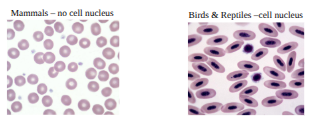
erythrocyte (RBC)
The most abundant blood cell, contain hemoglobin
Function - transport O2 throughout the body
leukocytes (WBC)
Colorless (white) cells capable of movement that provide body defense
Five types
Granulocytes - have granules in cytoplasm
1. Neutrophil
2. Basophil
3. Eosinophil
Agranulocytes - no granules in cytoplasm
4. Lymphocyte
5. Monocyte
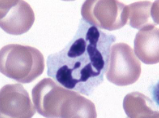
neutrophil
function - to stop or slow down foreign organisms
They work by:
Phagocytosis - to eat bacteria and dead cells
Bacteriocidal - to kill bacteria
How they get to infection site:
Sticky and can migrate through vessel walls
Release chemicals to signal other neutrophils to infection site
How they get to infection site:
Sticky and can migrate through vessel walls
Release chemicals to signal other neutrophils to infection site
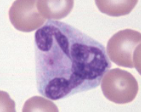
basophil
Function -
Phagocytosis
Act against allergic reactions
Produce heparin and histamine
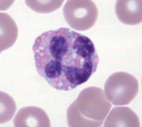
eosinophil
Functions -
Moderate the inflammatory response
Phagocytosis
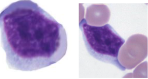
lymphocyte
Plays a vital role in immunity
T-cells (memory cells) - cells are sensitized to an antigen, remember that antigen and fight it off next time
B-cells - divide to form many cells to fight an antigen
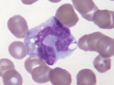
monocyte
Largest blood cell, irregular shaped nucleus
Function is phagocytosis
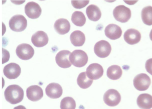
thrombocyte
Also called platelets
Function -
Hemostasis (clotting) - stop bleeding by sticking to damaged vessels and clumping together, release proteins that help form a clot