unit #4b: brain & cranial nerves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
how many neurons does the brain have? how many synapses does the brain have?
* 86 billion neurons
* 150 trillion synapses
* 150 trillion synapses
2
New cards
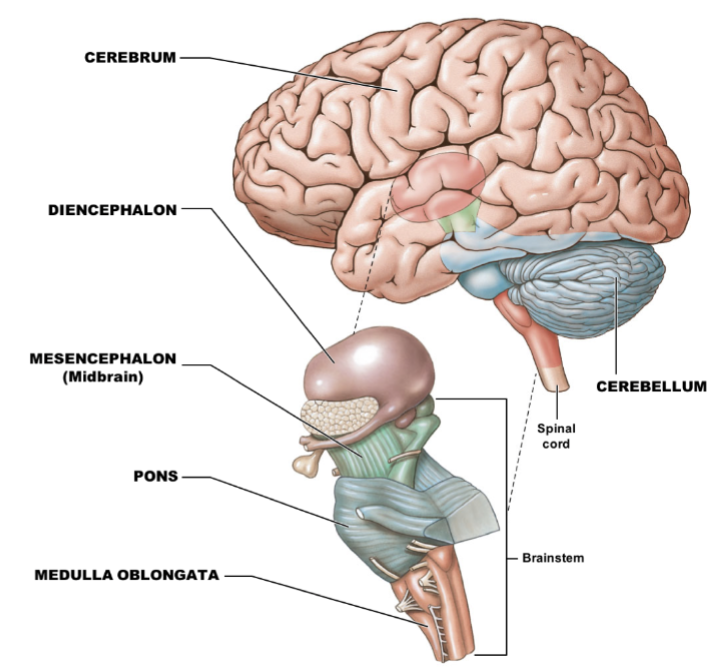
what are the 4 main regions of the brain? for one of the main regions, what are the 3 subregions?
1. cerebrum: largest part of brain
2. cerebellum: located posterior to pons
3. diencephalon: connects brainstem to cerebrum
4. brainstem
1. mesencephalon (midbrain)
2. pons
3. medulla oblongata: connects spinal cord to brain
3
New cards
what 5 parts are involved in brain protection?
* skull bones
* cranial meninges
* blood brain barrier
* cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
* blood supply
* cranial meninges
* blood brain barrier
* cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
* blood supply
4
New cards
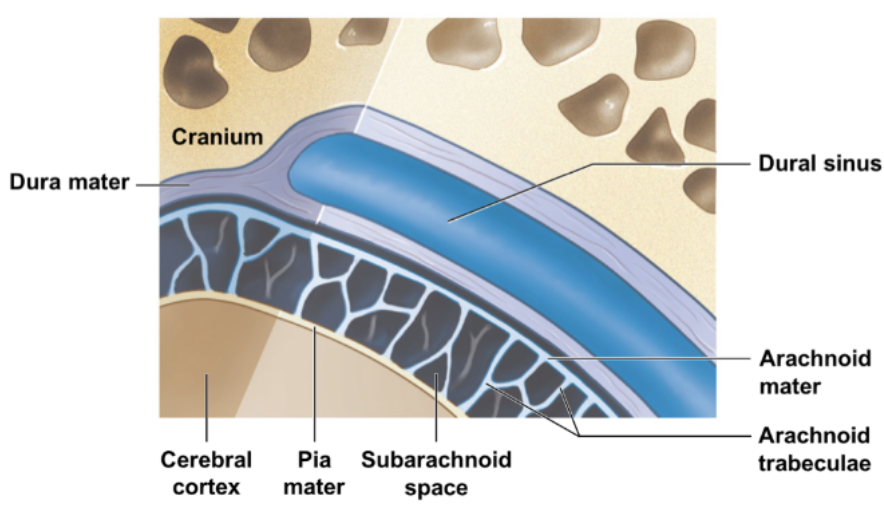
describe cranial meninges. what are the 3 layers, from superficial to deep?
* cranial meninges: surround the brain & protect contact with the skull
* superficial to deep layers: dura mater → arachnoid mater → pia mater
* superficial to deep layers: dura mater → arachnoid mater → pia mater
5
New cards
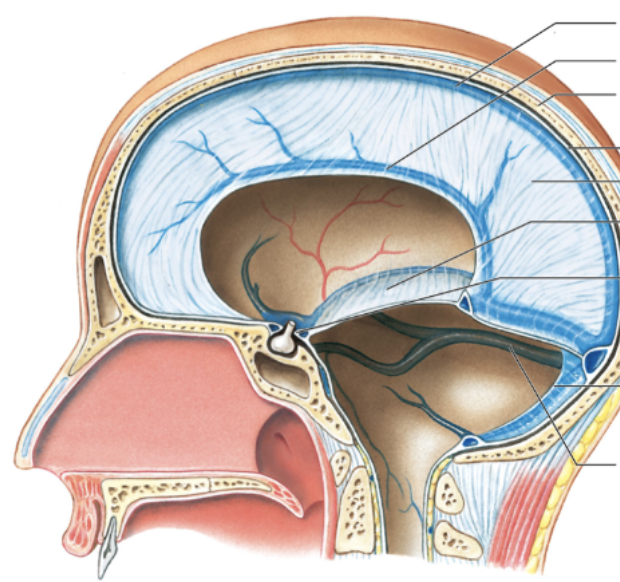
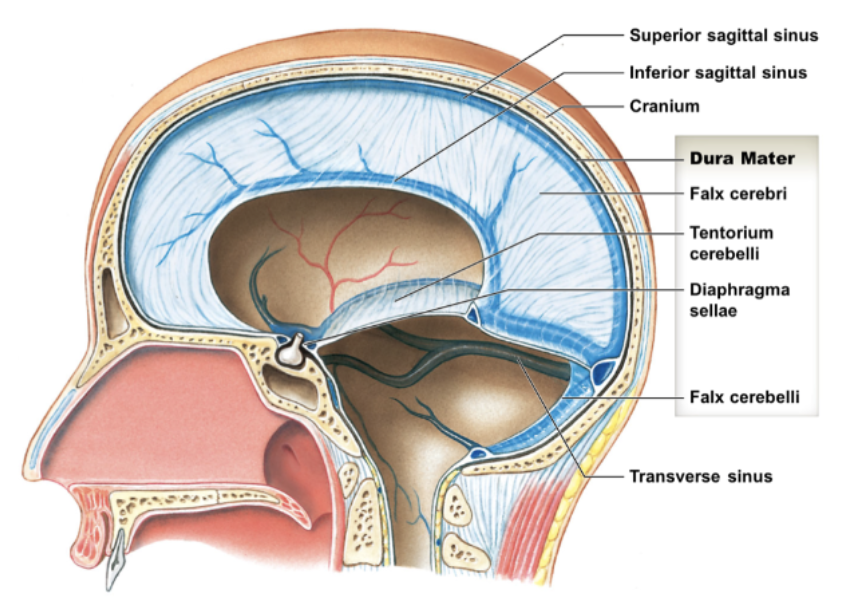
describe the dura mater. identify the 4 different parts of this layer.
* dura mater: tough, fibrous outer layer that connects to cranium and folds inward; holds dural sinuses
* dural sinuses: drain blood/CSF into internal jugular vein
\
* falx cerebri
* tentorium cerebelli
* falx cerebelli
* diaphragma sellae
* dural sinuses: drain blood/CSF into internal jugular vein
\
* falx cerebri
* tentorium cerebelli
* falx cerebelli
* diaphragma sellae
6
New cards
describe the falx cerebri of the dura mater. what does it attach to? what does it hold?
* falx cerebri: fold between R/L hemispheres
* attaches to crista galli
* holds superior sagittal sinus and inferior sagittal sinus
* attaches to crista galli
* holds superior sagittal sinus and inferior sagittal sinus
7
New cards
describe the tentorium cerebelli in the dura mater. what does it hold?
* tentorium cerebelli: surrounds occipital lobes at right angle to falx cerebri
* holds transverse sinus
* holds transverse sinus
8
New cards
describe the falx cerebelli of the dura mater. what does it divide?
* falx cerebelli: divides cerebellar hemispheres midsagittally, inferior to falx cerebri
9
New cards
describe the diaphragma sellae of the dura mater. what does it line? what does it surround? what bone does it anchor the dura mater to?
* diaphragma sellae: lines sella turcica, surround pituitary gland, anchors dura mater to sphenoid bone
10
New cards
describe the arachnoid mater. identify 2 notable parts of this layer.
* arachnoid mater: delicate middle layer just deep to dura mater
* notable parts: subarachnoid space, arachnoid granulations
* notable parts: subarachnoid space, arachnoid granulations
11
New cards
describe the subarachnoid space of the arachnoid mater. what is it made of, and what is it used for?
* subarachnoid space: created by arachnoid trabeculae, extending from superficial cranial arachnoid mater toward pia mater
* here, CSF circulates around CNS
* here, CSF circulates around CNS
12
New cards
describe the arachnoid granulations in the arachnoid mater. what is it’s purpose?
* arachnoid granulations: finger-like projections of arachnoid mater, through the dura mater and into superior sagittal sinus
* acts as a site for CSF to return to venous blood circulation
* acts as a site for CSF to return to venous blood circulation
13
New cards
describe the pia mater.
* pia mater: highly vascular, innermost layer that tightly attaches to the surface contours of the brain
14
New cards
describe the blood brain barrier (BBB). what substances are: freely passible, transported in, transported out?
* blood brain barrier (BBB): tight junctions between endothelial cells of blood vessels along astrocytes (main constitution); makes movement of molecules from blood into brain highly selective
* freely passible: oxygen, carbon dioxide; respiratory molecules
* transported into brain: glucose (metabolism)
* transported out brain: glycine (amino acid that acts as neurotransmitter)
* freely passible: oxygen, carbon dioxide; respiratory molecules
* transported into brain: glucose (metabolism)
* transported out brain: glycine (amino acid that acts as neurotransmitter)
15
New cards
which regions of the brain are more permeable? why?
* areas around: hypothalamus, pineal gland, posterior pituitary gland; allows diffusion of hormones into blood circulation
* choroid plexuses: formed by ependymal cells; filters blood and makes CSF
* choroid plexuses: formed by ependymal cells; filters blood and makes CSF
16
New cards
describe what ventricles are. identify the 3 ventricles of the brain.
* ventricles: hollow, fluid-filled spaces within brain that creates & circulates CSF; provides internal support for brain’s weight
* includes: lateral, third, fourth ventricles
* includes: lateral, third, fourth ventricles
17
New cards
describe the lateral ventricles. what are they separated by? how do they connect to the third ventricle?
* lateral ventricles: upper region, two big masses; one each located in cerebral hemispheres
* separated by: septum pellucidum
* connect to third ventricle by: interventricular foramen
* separated by: septum pellucidum
* connect to third ventricle by: interventricular foramen
18
New cards
describe the third ventricle. where is it located? how does it connect to the fourth ventricle?
* middle mass in relation to the ventricles
* located within: diencephalon
* connects to fourth ventricle by: cerebral aqueduct
* located within: diencephalon
* connects to fourth ventricle by: cerebral aqueduct
19
New cards
describe the fourth ventricle. where is it located? what does it continuously connect? this ventricle also has apertures. identify them and note what they connect to.
* lowermost region in relation to other ventricles
* located in inferior medulla oblongata
* has continuous connection to: spinal cord’s central canal
* has 2 lateral apertures and 1 medial aperture; connects to subarachnoid space
* located in inferior medulla oblongata
* has continuous connection to: spinal cord’s central canal
* has 2 lateral apertures and 1 medial aperture; connects to subarachnoid space
20
New cards
what are 3 functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
* fluid cushion
* suspends brain
* transports nutrients and wastes
* suspends brain
* transports nutrients and wastes
21
New cards
describe the formation of cerebrospinal fluid in 3 steps.
1. created in regions of all four ventricles by choroid plexuses (roof third ventricle extensions into lateral ventricles, roof of fourth ventricle)
2. ependymal cells filter blood thru active & passive transport mechanisms to absorb ions (Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻, HCO₃⁻, Ca²⁺) and nutrients; also secretes waste products
3. CSF is inside ventricles → free to pass in/out CNS tissues
1. flows thru ventricles, down spinal cord & into subarachnoid space before being returned to blood
22
New cards
list the order of CSF circulation.
1. lateral ventricles
2. interventricular foramen
3. 3rd ventricle
4. cerebral aqueduct
5. 4th ventricle
6. (two possible routes)
1. (most CSF) lateral & medial apertures
2. central canal of spinal cord
7. subarachnoid space
8. arachnoid granulations
9. superior sagittal sinus
10. internal jugular veins
23
New cards
describe the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. what does it connect? what are its 3 functions?
* lowermost region; connects spinal cord to brain
\
1. relays info to/from diencephalon, cerebrum, cerebellum, etc.
2. houses autonomic centers for regulating cardiovascular & respiratory functions
1. cardiovascular centers & respiratory rhythmicity centers
3. regulates digestive system activities
\
1. relays info to/from diencephalon, cerebrum, cerebellum, etc.
2. houses autonomic centers for regulating cardiovascular & respiratory functions
1. cardiovascular centers & respiratory rhythmicity centers
3. regulates digestive system activities
24
New cards
describe pons of the brainstem. what does it connect? what does it regulate?
* middlemost region; connects cerebellum to brainstem
* regulates somatic and visceral motor centers
* regulates somatic and visceral motor centers
25
New cards
describe the mesencephalon (midbrain) of the brainstem. what does it process and where? what does it initiate?
* uppermost region
* processes visual and auditory info in corpora quadrigemina (superior + inferior colliculi)
* initiates reflexive somatic motor responses
* processes visual and auditory info in corpora quadrigemina (superior + inferior colliculi)
* initiates reflexive somatic motor responses
26
New cards
what are the 3 regions of the diencephalon?
* epithalamus
* thalamus
* hypothalamus
* thalamus
* hypothalamus
27
New cards
describe the epithalamus of the diencephalon. what does it contain? what gland is featured, and what does it secrete (which regulates what?)?
* most distal region of diencephalon, forming roof of 3rd ventricle
* contains choroid plexus & pineal gland
* pineal gland: secretes melatonin (day-night cycle regulation)
* contains choroid plexus & pineal gland
* pineal gland: secretes melatonin (day-night cycle regulation)
28
New cards
describe the thalamus in the diencephalon. what does it make up? what is it interconnected by? what is its function?
* two thalami make up walls of third ventricle
* interconnected via interthalamic adhesion
* relays & processes sensory info projected to cerebellum
* interconnected via interthalamic adhesion
* relays & processes sensory info projected to cerebellum
29
New cards
describe the hypothalamus of the diencephalon. what does it make up? what does it connect to (via what?)? what is it located by? what are 3 of its functions?
* region below thalamus
* makes up floor of 3rd ventricle
* connects to pituitary gland (sits on sella turcica) via infundibulum
* located by: optic chiasm (point of crossing over of the medial optic nerve fibers)
\
1. produces hormones
2. controls emotional/appetite states (hunger, thirst, sexual desire)
3. regulates autonomic functions (body temp., blood pressure)
* makes up floor of 3rd ventricle
* connects to pituitary gland (sits on sella turcica) via infundibulum
* located by: optic chiasm (point of crossing over of the medial optic nerve fibers)
\
1. produces hormones
2. controls emotional/appetite states (hunger, thirst, sexual desire)
3. regulates autonomic functions (body temp., blood pressure)
30
New cards
describe the cerebellum. what is it composed of, and what separates it? what is the outer region called, and what are its folds called? what is the inner white matter that branches within it?
* composed of two hemispheres
* separated by vermis
* outer region: cerebellar cortex, composed of numerous folds: folia
* inner white matter: arbor vitae
* separated by vermis
* outer region: cerebellar cortex, composed of numerous folds: folia
* inner white matter: arbor vitae
31
New cards
what are 2 functions of the cerebellum?
1. coordinates complex somatic motor functions
2. adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord
32
New cards
describe the cerebrum:
\
1. what is composed of, and what is it separated by?
2. what interconnects the two compositions?
3. what are the folds and ridges called of the outer region (give name)?
1. what is this outer region made of?
\
1. what is composed of, and what is it separated by?
2. what interconnects the two compositions?
3. what are the folds and ridges called of the outer region (give name)?
1. what is this outer region made of?
1. composed of R/L hemispheres, separated by longitudinal fissure
2. interconnected via corpus callosum
3. outer region (cerebral cortex) composed of gray matter, with folds (sulci) and ridges (gyri)
33
New cards
what are the 4 frontal lobes of the cerebrum? list and describe their specific function(s) (their specific cortex(es)). also, name and describe the “hidden” region of the cerebral cortex.
* frontal lobe: anterior region from central sulcus
* primary motor cortex: control of skeletal muscle
* parietal lobe: posterior region from central sulcus to parieto-occipital sulcus
* primary sensory cortex: perception of senses
* occipital lobe: posterior region from parieto-occipital sulcus
* visual cortex: perception of vision
* temporal lobe: inferior region from lateral sulcus
* auditory and olfactory cortex: perception of sound and smell
\
* insula: deep to temporal lobe
* sense of taste (gustation)
* primary motor cortex: control of skeletal muscle
* parietal lobe: posterior region from central sulcus to parieto-occipital sulcus
* primary sensory cortex: perception of senses
* occipital lobe: posterior region from parieto-occipital sulcus
* visual cortex: perception of vision
* temporal lobe: inferior region from lateral sulcus
* auditory and olfactory cortex: perception of sound and smell
\
* insula: deep to temporal lobe
* sense of taste (gustation)
34
New cards
what are higher-order functions? in what areas are they involved in? what are the 3 higher-order functions in the cerebrum?
* higher-order functions: complex interconnections between cerebral cortex and other brain regions, involving both conscious and unconscious processing, called integrative centers
* language areas, prefrontal cortex, hemispheric lateralization
* language areas, prefrontal cortex, hemispheric lateralization
35
New cards
describe the language areas higher-order function. what 2 areas are included, and what are their specific roles?
* includes Wernicke’s area for language comprehension
* and Broca’s area for speech production
* and Broca’s area for speech production
36
New cards
describe the prefrontal cortex higher-order function of the cerebrum.
* coordinates info from cortical regions to perform abstract functions
* ex. consequences of actions, temporal relationships, anxiety/frustration
* ex. consequences of actions, temporal relationships, anxiety/frustration
37
New cards
describe the hemispheric lateralization higher-order function of the cerebrum. what does the left vs. right brain specialize in?
* specialization of functions by each cerebral hemisphere
* left: analytical tasks (reading, math, decision making)
* right: interpretive tasks (smell & taste recognition, emotional comprehending in music/art, understanding 3D relationships)
* left: analytical tasks (reading, math, decision making)
* right: interpretive tasks (smell & taste recognition, emotional comprehending in music/art, understanding 3D relationships)
38
New cards
what 3 fiber types allow the central white matter of the cerebrum to connect cortical regions to each other?
* association fibers
* commissural fibers
* projection fibers
* commissural fibers
* projection fibers
39
New cards
describe the association fibers in central white matter of cerebrum. what are 2 subtypes of this fiber?
* association fibers: connect cortical regions within same hemisphere
* arcuate fibers: connect gyrus-to-gyrus
* longitudinal fasiculi: connect frontal lobe to other lobes
* arcuate fibers: connect gyrus-to-gyrus
* longitudinal fasiculi: connect frontal lobe to other lobes
40
New cards
describe the commissural fibers in central white matter of cerebrum. what are 2 examples that exude this?
* communicate info between hemispheres
* corpus callosum
* anterior commissure
* corpus callosum
* anterior commissure
41
New cards
describe the projection fibers in central white matter of cerebrum.
* communicate info to/from cerebrum and other brain regions + spinal cord
42
New cards
what are basal nuclei of the cerebrum? what are its 2 functions? what 3 parts are included in this?
* inner gray matter of the cerebrum
* controls subconscious adjustment and modification of voluntary motor commands
* ex. walking or preparing body for other movements
* caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
* controls subconscious adjustment and modification of voluntary motor commands
* ex. walking or preparing body for other movements
* caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
43
New cards
describe the limbic system. list and describe the 3 parts that fall under it.
* components from diff. brain regions that control memory processing, emotional state & drive creation (maternal instinct, etc.)
* hippocampus: learning and memory
* fornix: connects hippocampus to hypothalamus
* mammillary bodies: control eating movements
* hippocampus: learning and memory
* fornix: connects hippocampus to hypothalamus
* mammillary bodies: control eating movements
44
New cards
how many cranial nerves are there?
12
45
New cards
list all 12 of the cranial nerves in the following format: name (Roman numeral), function, general function.
1. olfactory (I), sensory, sense of smell
2. optic (II), sensory, sense of vision
3. oculomotor (III), motor, eye movement
4. trochlear (IV), motor, eye movement
5. trigeminal (V), both, sense of forehead/eyelids/ mouth & movement of mastication muscles
6. abducens (VI), motor, eye movement
7. facial (VII), both, sense of taste & movement of facial muscles
8. vestibulocochlear (VIII), sensory, sense of hearing and balance
9. glossopharyngeal (IX), both, sense of taste & movement of swallowing muscles
10. vagus (X), both, sense of neck and throat & movement of speech muscles
11. accessory (XI), motor, head/shoulder movement
12. hypoglossal (XII), motor, tongue movement