C29 - Magnetic Fields
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
magnetic force
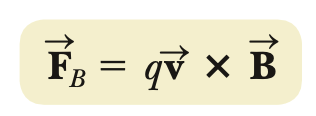
B = magnetic field vector
Lorentz force
the combination of magnetic and electric forces
magnetic force rules
proportional to velocity
proportional to sinθ
0 when moving || mag. lines
max. when moving ⟂ mag. lines
- & + particles are forced opposite ways
FB points ⟂ both v & B (x product)
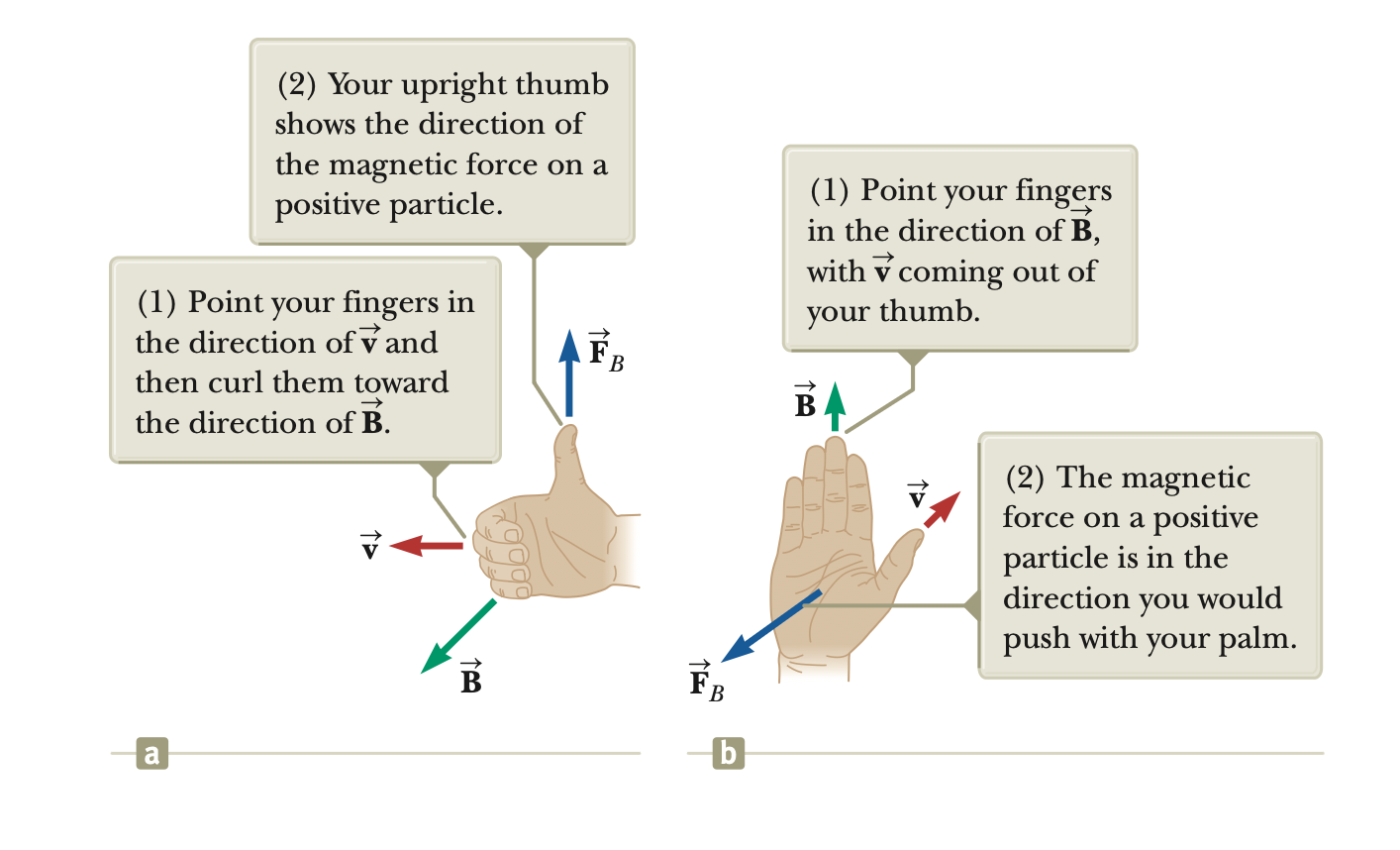
right-hand rules
magnetic force units
tesla (T = N/(A • m) = N/(C • m/s)))
circular motion in uniform magnetic field
r = mv/qB
ω = qB/m
cyclotron frequency
T = 2πm/qB
velocity selector
combination of Fe in one direction & FB in the other, allows for only specific velocities of particles to pass (& in a straight line)
v = E/B
mass spectrometer
separates ions based on mass-charge ratio along circular path
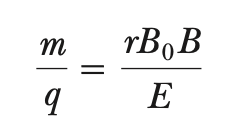
based on fixed velocity (from velocity selector)
cyclotron
first successful particle accelerator
alternating current + magnetic field moves particles in an increasingly larger & faster circular path by constantly swapping voltage
energy (particles exiting cyclotron)
(qBR)2/2m
magnetic force (on a current-carrying wire segment; uniform electric & magnetic fields)
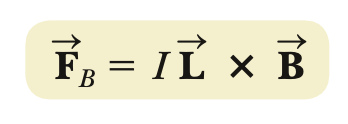
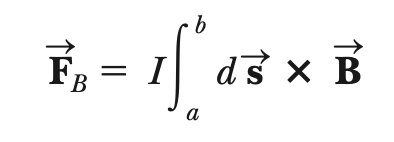
torque (on a current loop; uniform field)
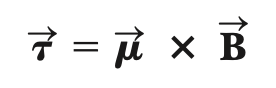
magnetic dipole moment
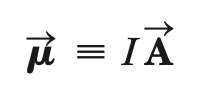
potential energy (current loop in a magnetic field)
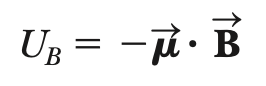
Hall effect
an electrical potential difference between the top and bottom of a current-carrying segment, induced by a magnetic field
Hall voltage
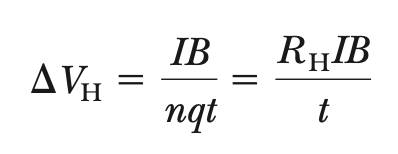
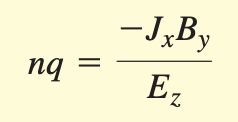
RH = 1/nq = Hall coeff.