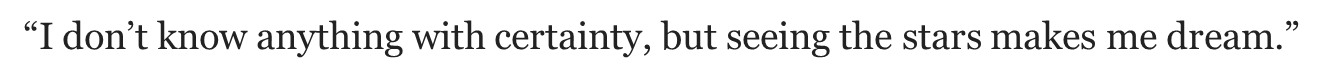AA - WEEK 2 : OVERVIEW OF HUMANITIES AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE ARTS IN TODAY’S DIGITAL AGE
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Humanities
Academic disciplines that study human society and culture (e.g., Philosophy, Literature, History, Religion, Arts, Languages).
Arts
Human activities involving visual, auditory, and performing creations to express beauty, emotions, and ideas.
Why Study Humanities
Develops (1) understanding of human experience, (2) critical thinking, (3) communication skills, and (4) ethical reflection.
Fundamental Principles of Humanities
Belief that human nature is good, individuals have free will, humans strive for self-actualization, reality is subjective, and people are responsible for themselves and others.
Nature of Art
A universal form of expression that reflects emotions, ideas, society, and imagination; meaning is subjective.
Functions of Art
These are the roles of art
Personal Function of Art
Expresses emotions and ideas.
Social Function of Art
Unites communities or raises awareness of issues.
Political Function of Art
Critiques or supports political ideologies.
Cultural Function of Art
Preserves heritage and traditions.
Economic Function of Art
Generates employment and commerce.
Mural Art
A form of art often used for social or political commentary.
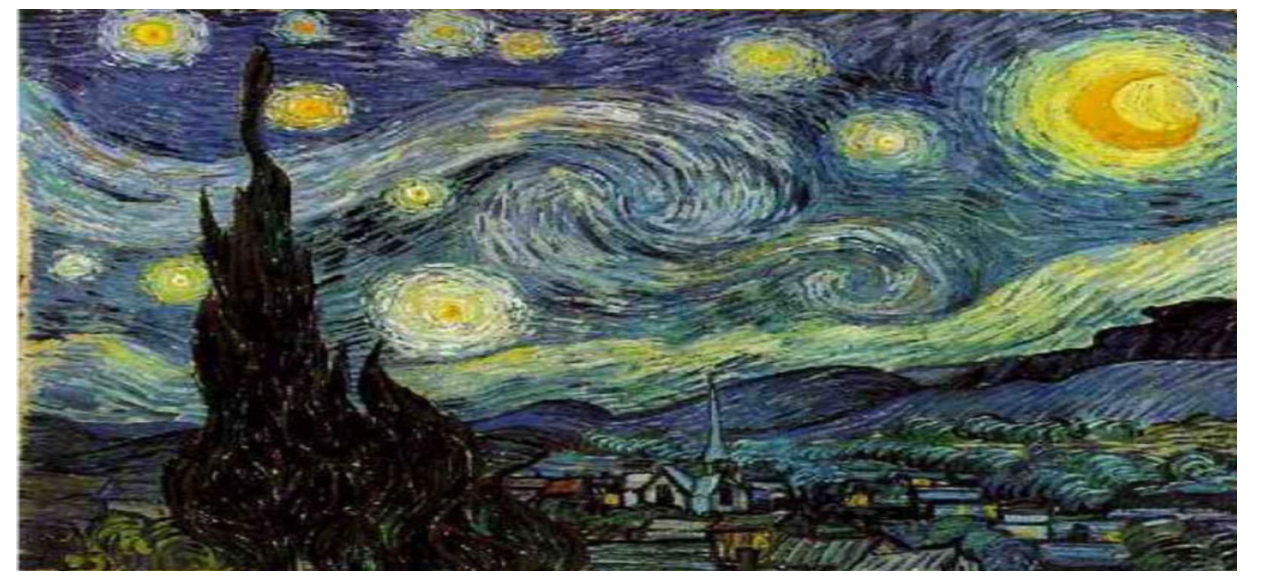
Starry Night (Van Gogh)
A painting symbolizing how art inspires dreams and emotions, reflects the subjective nature of meaning in art.

Subjectivity of Art
What is meaningful to one person may be trivial to another.
Mimesis [ Art Philosophy ]
Art as imitation of life (Plato, Aristotle).
Expressionism [ Art Philosophy ]
Art as expression of emotions (Tolstoy).
Formalism [ Art Philosophy ]
Art judged by form, style, and structure rather than content (Bell, Greenberg).
Institutional Theory [ Art Philosophy ]
An object becomes art through societal or institutional recognition (Danto); e.g., Duchamp's Fountain (urinal in an art exhibit).
Artists
Individuals who create primarily for creativity, expression, and intellectual or aesthetic purposes.
Artisans
Skilled creators of functional yet beautiful objects, focusing on craftsmanship and tradition.
Artists
Create primarily for expression, focusing on beauty, emotions, and ideas; examples include paintings, sculptures, and songs; output may not have practical use.
Artisans
Create functional yet beautiful objects, focusing on craftsmanship, skill, tradition, and usefulness; examples include baskets, furniture, and pottery; output has everyday use.
Visual Arts
Art forms such as painting, sculpture, and photography.
Literary Arts
Written art forms such as poetry, drama, and novels.
Performing Arts
Live artistic expressions such as music, dance, and theater.
Applied Arts
Practical art forms such as architecture, design, and fashion.
Media Arts
Modern art forms using technology, such as film and digital arts.
Art Appreciation
The process of understanding and evaluating artworks through five steps:
S1 : Describe [ Steps in Appreciating Art ]
Identify the elements used.
S2 : Analyze [ Steps in Appreciating Art ]
Examine how the elements convey meaning.
S3 : Contextualize [ Steps in Appreciating Art ]
Consider historical and cultural background.
S4 : Interpret [ Steps in Appreciating Art ]
Derive subjective meaning and personal response.
S5 : Judge [ Steps in Appreciating Art ]
Evaluate aesthetics and overall impact.
Describe
Identify what you see in the artwork—colors (bright, dark), shapes (circles, squares), lines (straight, curvy), texture (smooth, rough), and materials (paint, wood, fabric).
Analyze
Examine how the elements work together. Ask how colors, shapes, and lines create mood, emotion, or message.
Contextualize
Look at the story behind the artwork—time, place, culture, history, and the artist's life. Context deepens meaning.
Interpret
Express what the artwork means to you personally. Reflect on emotions, connections to your life, and the artist's possible intent.
Judge
Evaluate the artwork's impact. Is it beautiful, powerful, meaningful, or inspiring? Art's value lies in the impression it makes, not just in appearance.
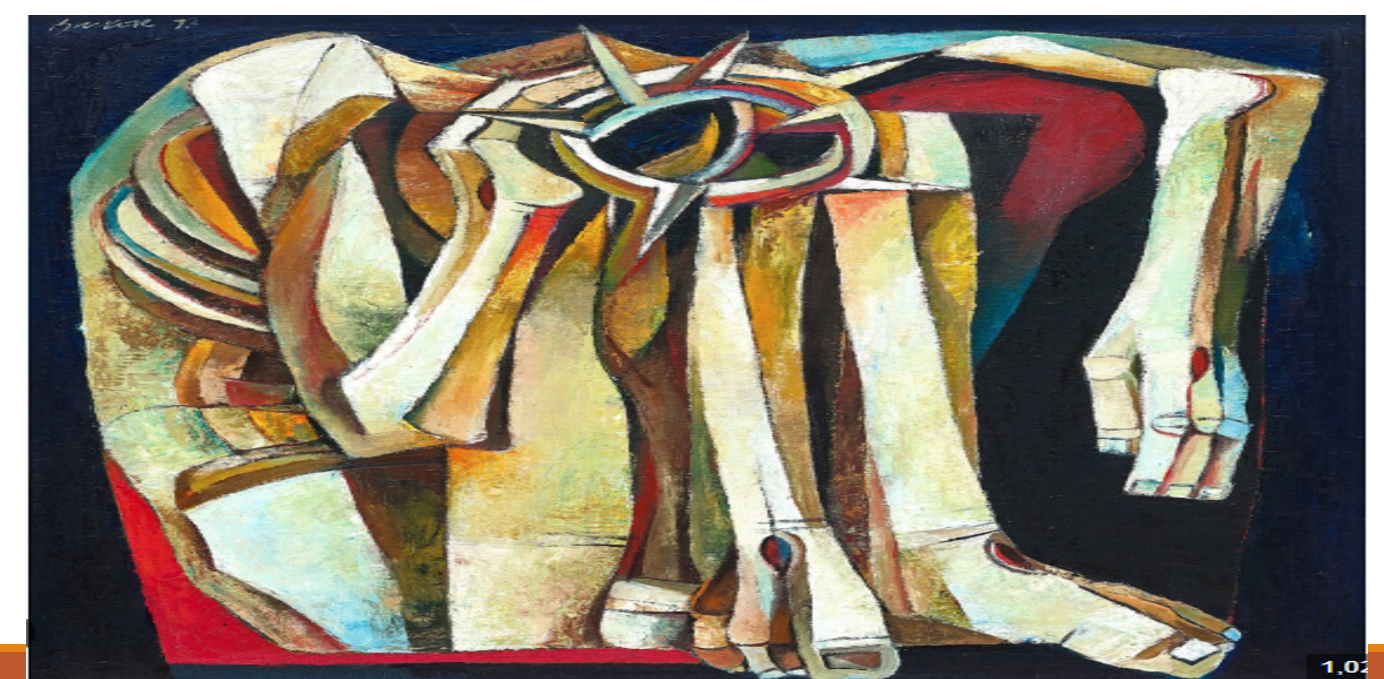
Ang Kiukok Pieta
"Crown of Thorns"

Appreciating Art 5 Step Acronym
D.A.C.I.J
Van Gogh’s Starry Night Quote
“I don’t know anything with certainty, but seeing the stars makes me dream.”