cell organelle and transport
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
visualize cell
light microscopy - no dyes
fluorescence microscopy - fluorescence dyes
excitation and emission filter
electron microscopy transmission TEM - higher magnification and resolution (englargement and definition - closest spacing of 2 lines)
internal structures
vaccum needed, no light source
scanning electron microscopy SEM - surfaces
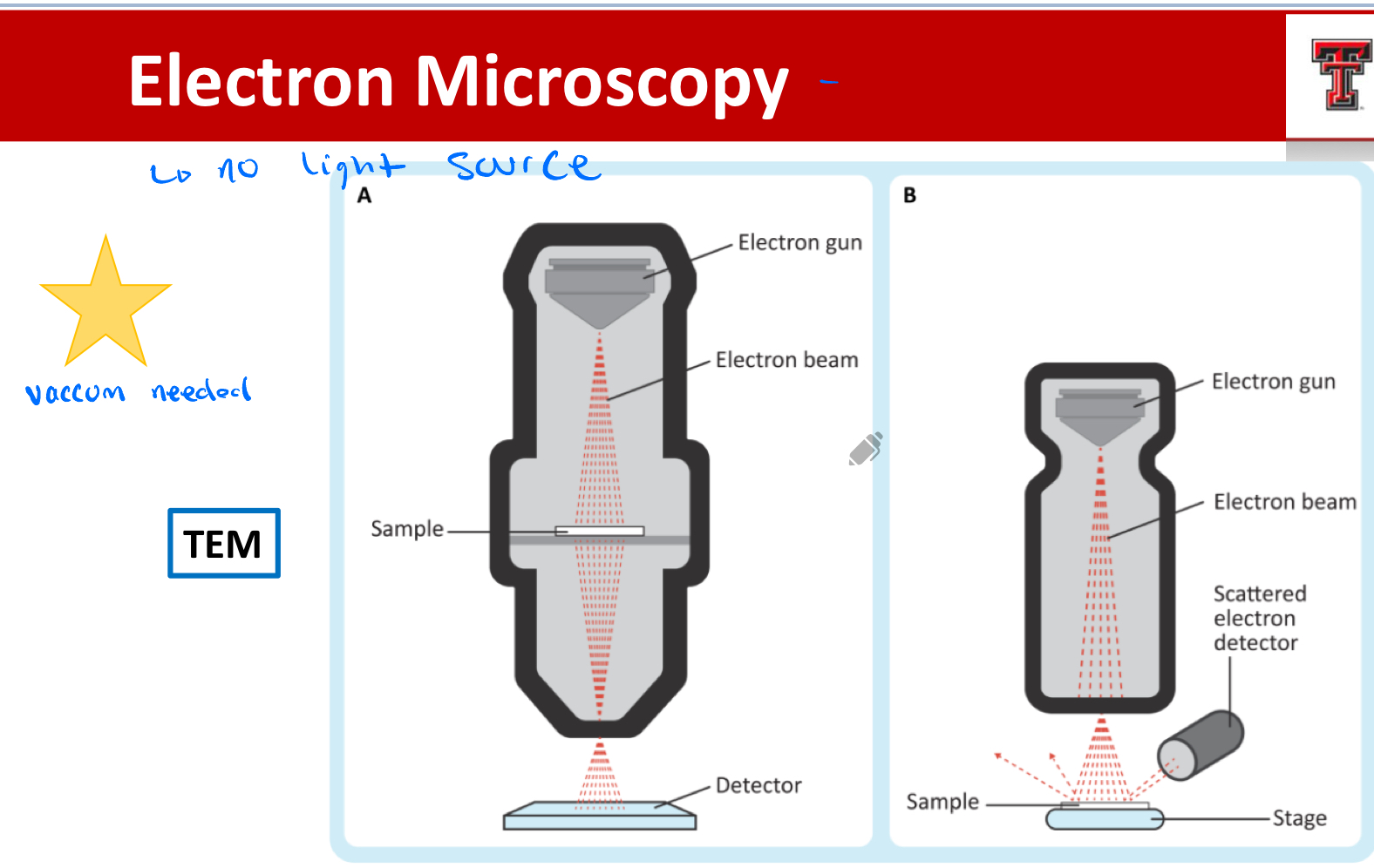
microscope to visualize specific structures that need to be differentiated?
visualize details of the surface of a bacteria ?
visualize internal organelles in higher mag and resolution
fluorescence microscope to targetr different structures
SEM - scanning electron microscope
TEM - transmission electron microscope
domains of living word
eubacteria - prokaryotes
bacteria
archaebacteria - prokaryotes
archaea
eukaryotes
has organelles and includes animal, plant, fungi(yeast), and protist cells.
virus vs bacteria
virus- not alive, needs host, no antibiotics, RNA/DNA
bacteria -alive, antibiotics, DNA, reproduced by binary fission
smooth ER
rough ER
free ribosomes
synthesis of lipids, Ca 2+ storage
translation of mRNA —> membrane associated proteins or for secretions out cell
translation of mRNA into cytosolic proteins
lysosome
endosome
proteosome - quality control
peroxisome - housekeeping
intracellular degradation
cell uptake of cholesterol, removal of receptions from plasma membrane, uptake of small molecules+water, internalization of large particles
degradation of intracellular proteins
detoxification of substances
phosphatidylserine - PS
normally, protein is on the inner membrane side of the plasma membrane
during apoptosis/cell death, PS will flip to the outside layer
to signal for macrophage engulfment and promote the clearance of dying cells.
plasma membrane
phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, carbs
have transporters bc of hydrophobic properties of the tails
pumps, channels, receptors, linkers, enzymes, structural proteins