HR Exam 2 Combined PDF
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Examples of training in the workplace
Formal classes
• Customer service classes • Conflict management seminars • Leadership and management workshops • Software classes • Sexual harassment prevention training • Safety training sessions • Workplace ethics, policies and procedures
Communities of Practice
• Professional development seminars (Lunch & Learns)
Mentoring • Formal and informal
Linked to organizational needs
1. Better task behavior leading to successful operational outcomes
2. Reduced expenses, fewer mistakes, safer workers
3. Better employee retention, more motivation and commitment
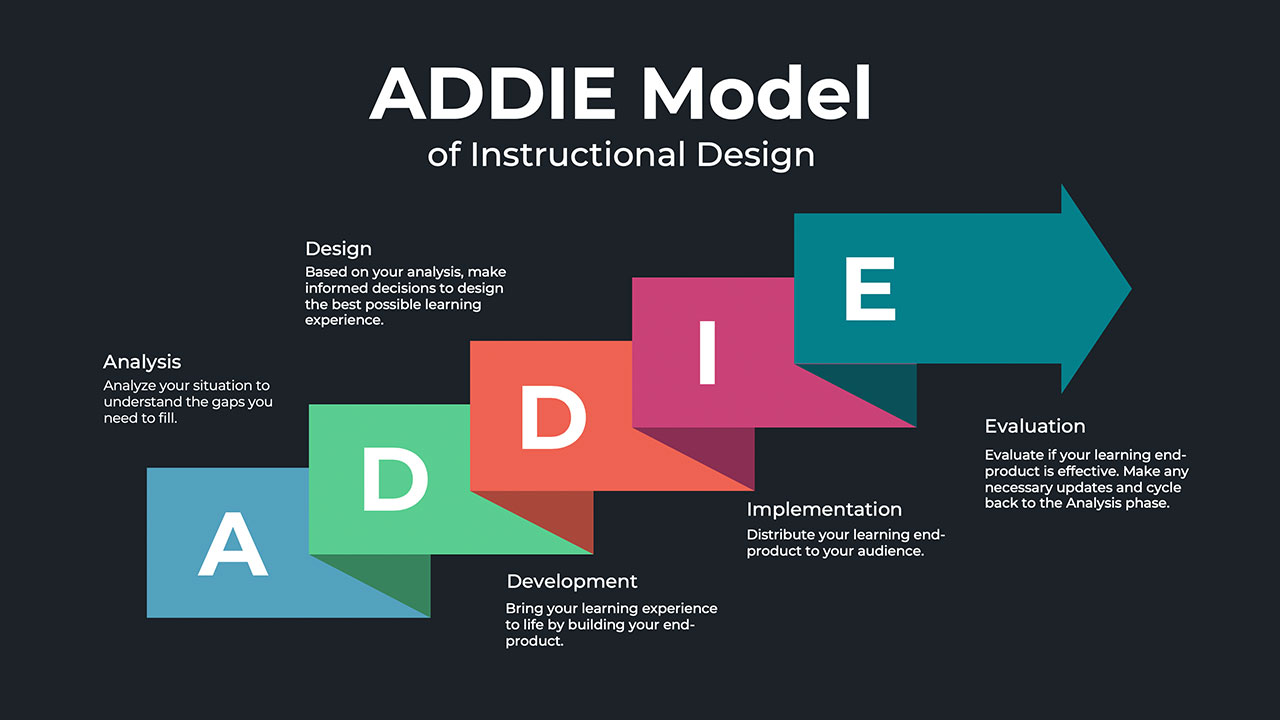
ADDIE model of instructional design
Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation
Needs Assessment
The process of evaluating the organization, individual employees, and employees’ tasks to determine what kinds of training, if any, are necessary.
The process of identifying what employees need to learn • To do their jobs successfully • To grow in their careers • For the organization to achieve its goals
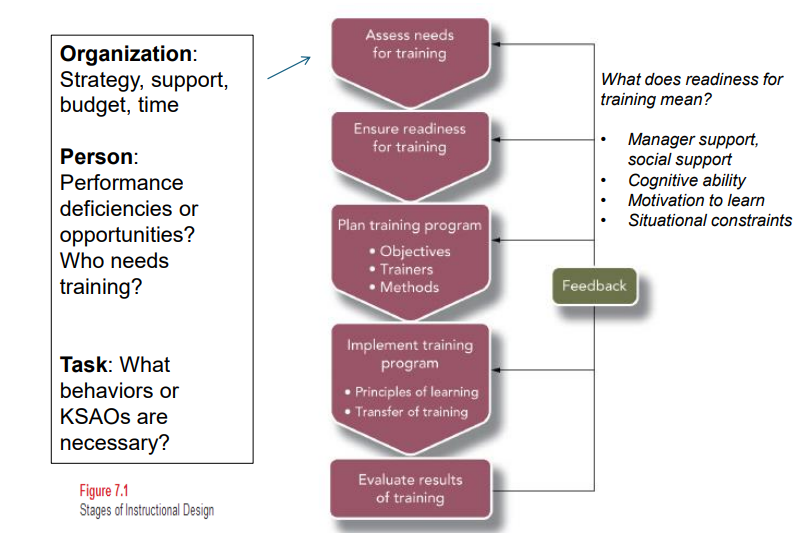
Linking Training to Organizational Needs: Instructional Design Process
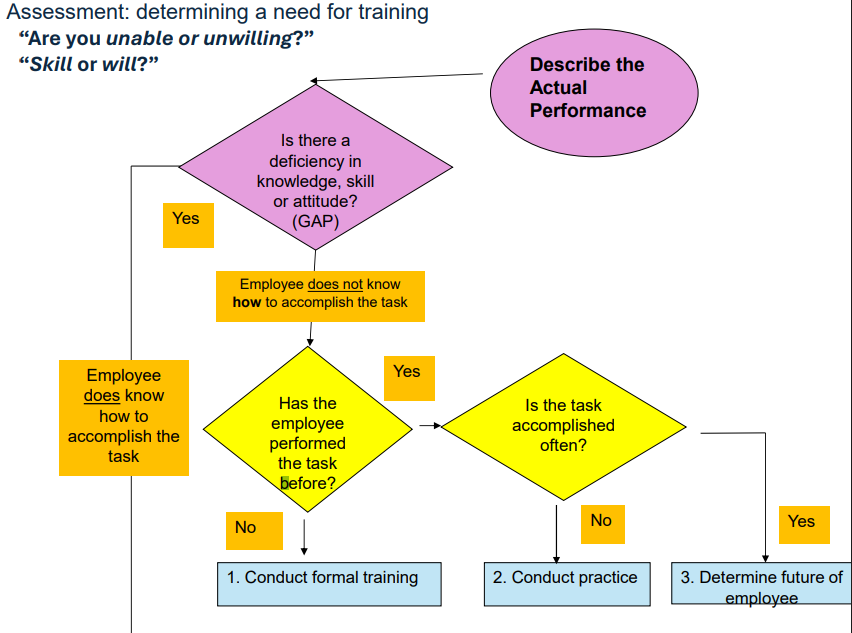
Assessment (aka gap analysis): determining a need for training / explain a performance deficiency
What does the assessment answer?
“Are you unable or unwilling?” “Skill or will?”
Diversity training is often ineffective. How to make if effective?
Social Accountability- Diversity task forces and diversity managers drive accountability. When people know they might have to explain their decisions, they are less likely to act on bias.
Contact- Working side-by-side breaks down stereotypes
Engagement- When managers actively help boost diversity in their companies, they begin to think of themselves as diversity champions. Mentoring is another way to engage managers.
Metrics- Collecting and analyzing data on diversity over time, comparing those numbers to the numbers at other organizations, and sharing them with key stakeholders/companies
Training needs assessment
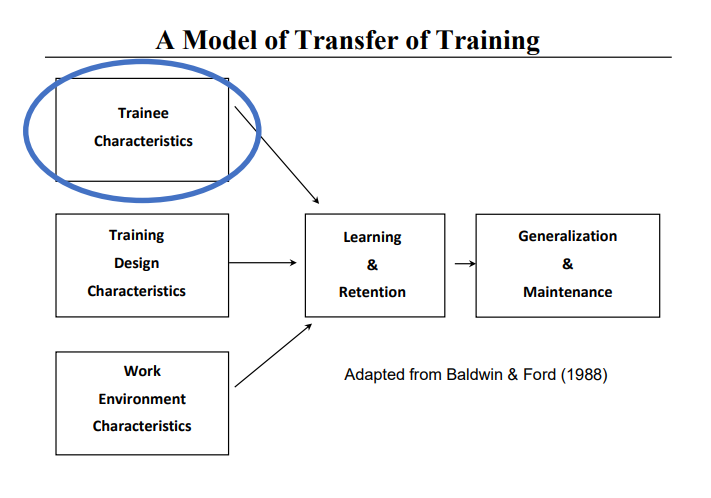
Learning transfer occurs when people apply concepts/skills learned in training to actual work situations • Transfer is the ultimate measure of training success • Without transfer, training investments fail to deliver value
Goal of people management
To drive the right behaviors to achieve strategy and organizational goals
Instructional Design
A process of systematically developing training to meet specified needs.
Learning Management System (LMS)
An online application that automates the administration, development, and delivery of training programs.
Organization Analysis
A process for determining the appropriateness of training by evaluating the characteristics of the organization.
Person Analysis
A process for determining individuals’ needs and readiness for training.
Task Analysis
The process of identifying the tasks, knowledge, skills, and behaviors that training should emphasize.
Employee Readiness for Training
A combination of employee characteristics and positive work environment that permit training.
E-Learning
Receiving training via the Internet or the organization’s intranet.
Electronic performance support system (EPSS)
Computer application that provides access to skills training, information, and expert advice as needed.
On the Job Training (OJT)
Training methods in which a person with job experience and skill guides trainees in practicing job skills at the workplace.
Apprenticeship
A work-study training method that teaches job skills through a combination of on-the-job training and classroom training.
Internship
On-the-job learning sponsored by an educational institution as a component of an academic program.
Simulation
A training method that represents a real-life situation, with trainees making decisions resulting in outcomes that mirror what would happen on the job.
Classroom training
a trainer lecturing a group
Experiential Programs
training programs in which participants learn concepts and apply them by simulating behaviors involved and analyzing the activity, connecting it with real-life situations
Adventure Training
a teamwork and leadership training program based on the use of challenging, structured outdoor activities
Cross Training
team training in which team members understand and practice each other's skills so that they are prepared to step in and take another member's place
Team Leader Training
Training in the skills necessary for effectively leading the organization’s teams.
Coordination Training
team training that teaches the team how to share information and make decisions to obtain the best team performance
Action Learning
training in which teams get an actual problem, work on solving it and commit to an action plan, and are accountable for carrying it out
Transfer of Training
On-the-job use of knowledge, skills, and behaviors learned in training.
Communities of Practice
Groups of employees who work together, learn from each other, and develop a common understanding of how to get work accomplished.
Orientation
Training designed to prepare employees to perform their jobs effectively, learn about their organization, and establish work relationships.
Onboarding
Ongoing process that aims to prepare new employees for full participation in the organization.
4 goals of onboarding
Compliance- understand company policies, rules and regulations
Clarification- understand job and performance expectations
Culture- understand company history, traditions, values, norms, and mission
Connection- understand and develop working and interpersonal relations
Best/Worst Practices for Training
Best: practice testing and distributed practice
Worst: summarization, highlighting, rereading
Work Environment Characteristics
• Learning climate • Organizational support •Compliance v. voluntary participation • Framing (e.g., congrats on being recognized vs. you are required to attend) • Opportunity to practice trained skills • Training reputation (program, trainers, outcomes) • Trainee participation in training decisions
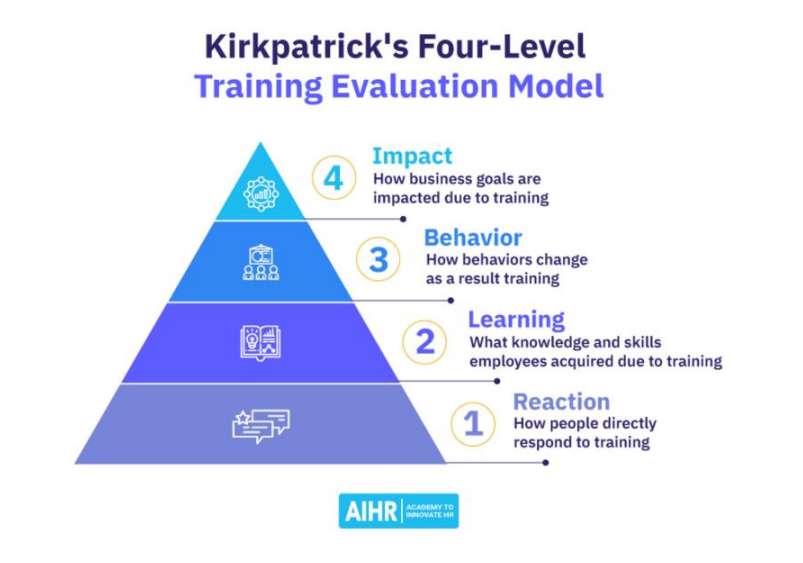
Kirkpatricks Four Level Training Evaluation Model