spine - TOS
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
areas of vulnerability that may cause TOS
- scalene triangle
- costoclavicular space
- pec minor space
scalene triangle borders
- anterior: anterior scalene
- posterior: middle scalene
- inferior: 1st rib
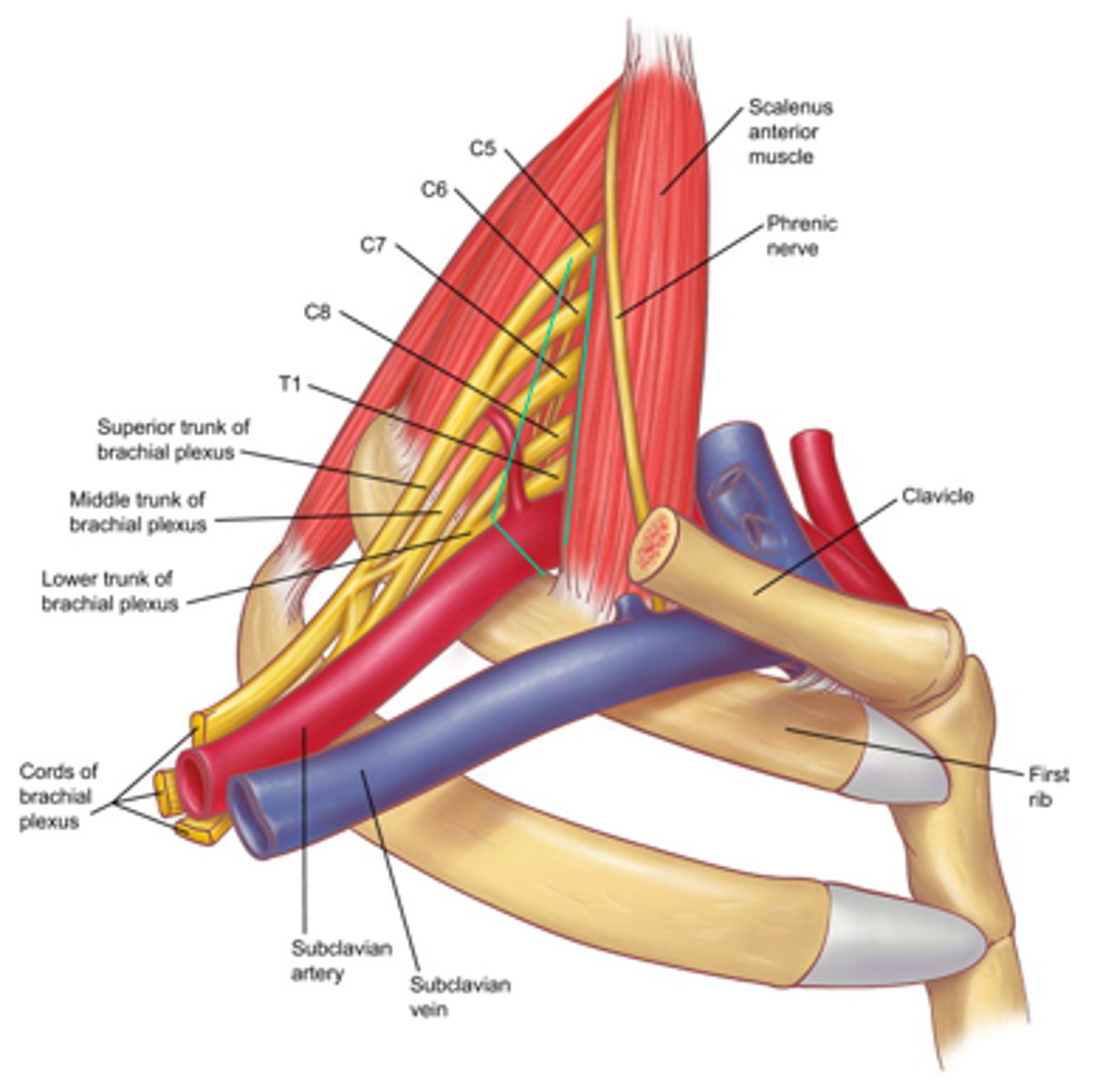
costoclavicular space borders
- anterior: clavicle (subclavius)
- posterior: medial 1st rib
- postlateral: scapula

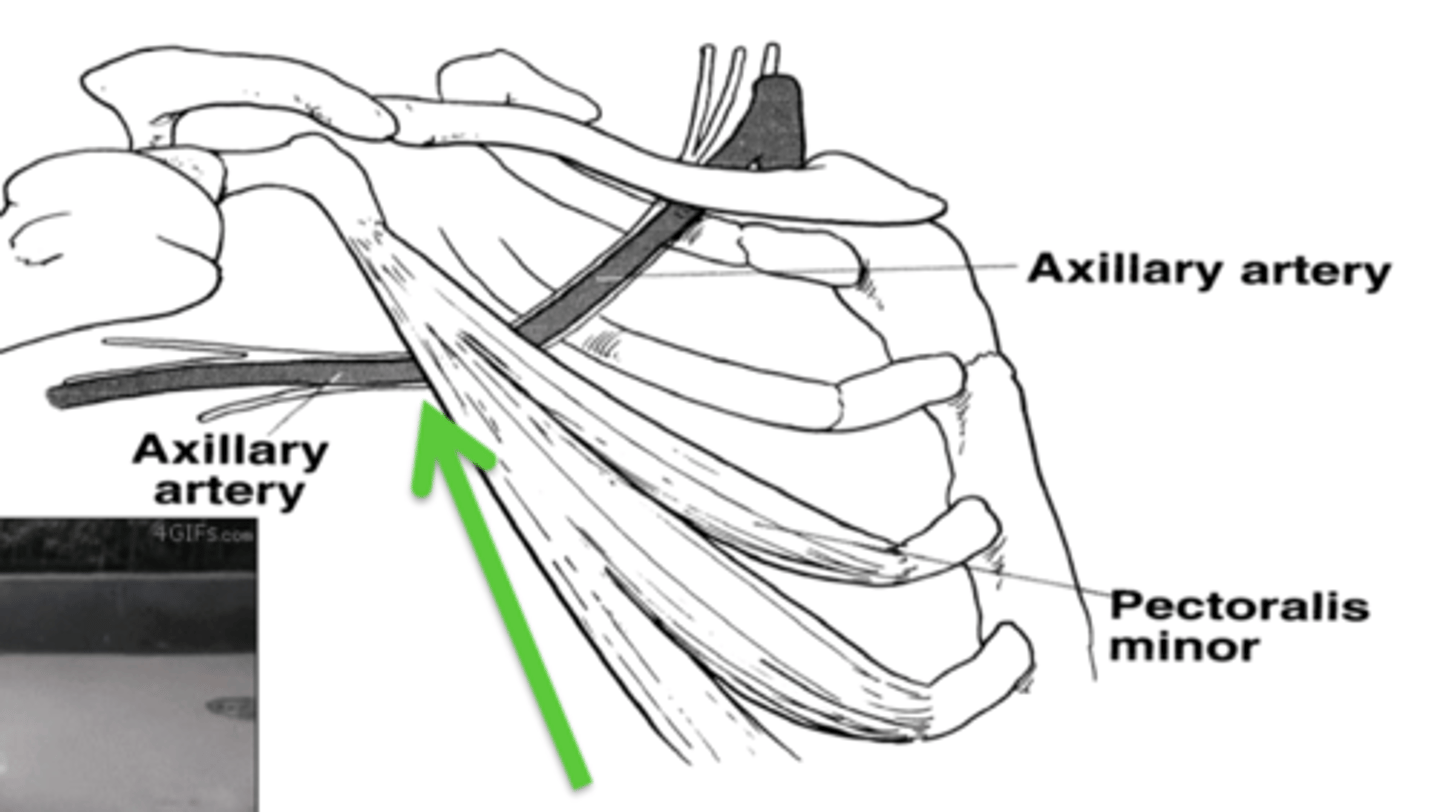
pec minor space
- anterior: pec minor
- posterior: chest wall
what happens if the scalenes become tight or spasm?
space closes/clamps down on nerves
why may sxs start if someone has TOS because of the scalene triangle and is working out
scalenes assist with deep inhalation
what may cause compression of the costoclavicular space?
heavy load on the shoulder
how does a tight pec affect the pectoralis minor space?
tips the coracoid forward & down and narrows the space
how does occupational repetition (painters, carpenters) cause TOS
chronic "hyperabduction" of UE
athletes may have hypertrophy of what muscles causing TOS
- scalene
- pec minor
what type of TOS us more common in competitive athletic men
vascular
sxs of TOS
- parathesias in fingers/UE
- weakness
- swelling/discoloration
- lifting/reaching overhead may aggravate
- diffuse pain in arm
- neck pain
- chest pain
- occipital HA
anatomical causes of TOS
- bony abnormalities: cervical rib, C7 TP longer, fx clavicle/1st rib
- muscle abnormalities: scalenes (insertion anomaly, hypertrophy, minimus present, BP passes through ant scalene)
cervical rib is an extra rib coming off
C7
what cords of the brachial plexus may a cervical rib compress?
C8 and T1
true or false: tumors can cause TOS
true
vascular TOS can be either ____ TOS or ____ TOS
- arterial
- venous
neurological TOS can be either ____ or ____ TOS
- true neurological
- symptomatic
why is neurological TOS more common than venous or arterial TOS?
nerves are more sensitive to compression than vascular structures
onset of arterial TOS
- spontaneous/acute
- young adults with hx of increased UE activity
arterial TOS signs/sxs
- pain in hand
- pallor
- claudication
- loss of pulse
- coldness and cold intolerance
- parathesias usually stem from arterial emboli
how to dx arterial TOS
- signs and sxs
- doppler US/angiography
venous TOS onset
- spontaneous
- males with increased UE activity/high level athletes
signs/sxs of venous TOS
- UE swelling
- cyanosis
- feeling of heaviness
- parathesia in fingers/hand (due to swelling)
venous TOS is not caused by what space?
scalene triangle
dx of venous TOS
- signs and sxs
- venous studies, venography
cause of neurogenic TOS
hx of neck trauma
signs/sxs of neurogenic TOS
- pain, parathesia, numbness, and/or weakness in the hand, arm, and shoulder
- neck pain
- occipital HA
- loss of dexterity
- cold intolerance
- raynaud phenomenom (sympathetic overactivity)
neurogenic TOS is usually caused by what nerve roots?
C8, T1
true neurogenic TOS is _____ where as symptomatic is ______ only
- objective
- subjective
true neurogenic TOS has parathesias ________ and are known as "______"
- during the day
- compressors
symptomatic neurogenic TOS has parathesias _____ and are known as "________"
- at night
- releasers (neural blood supply is restored)
true neurogenic TOS is confirmed through ___ whereas it is normal in symptomatic
EMG/NCV
cyriax release test
[neurogenic TOS]
- sitting, use of pillows/towels to produce passive shoulder elevation
- position held until sxs produced --> sxs decrease with time
*can use prior to sleeping to allow pt to sleep longer into the night prior to waking
Adson's Maneuver
- pt seated
- palpate radial pulse
- pt rotates had to side being test and extends neck
- PT abducts, extends, ERs shoulder
- have pt take deep breath and hold
- (+) = decrease in pulse vigor from starting position to final position and/or reproduction of sxs
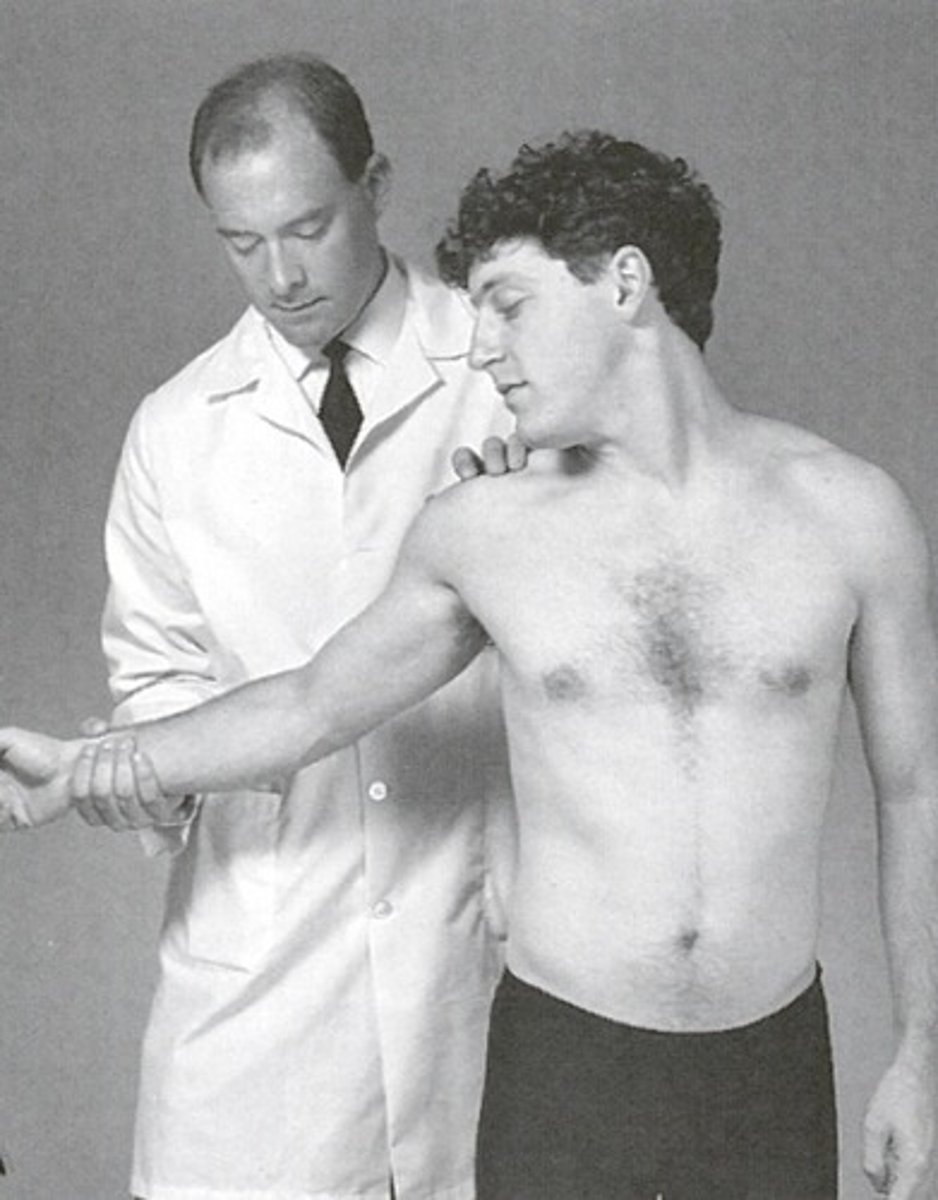
Adson's manuever engages the ______ which affects what space?
- scalenes
- scalene triangle
hyperabduction/Wright test
- palpate radial pulse
- passively "hyperabduct" the arm above head
- held for up to 2 mins
- (+) = pulse diminished and/or sxs reproduction
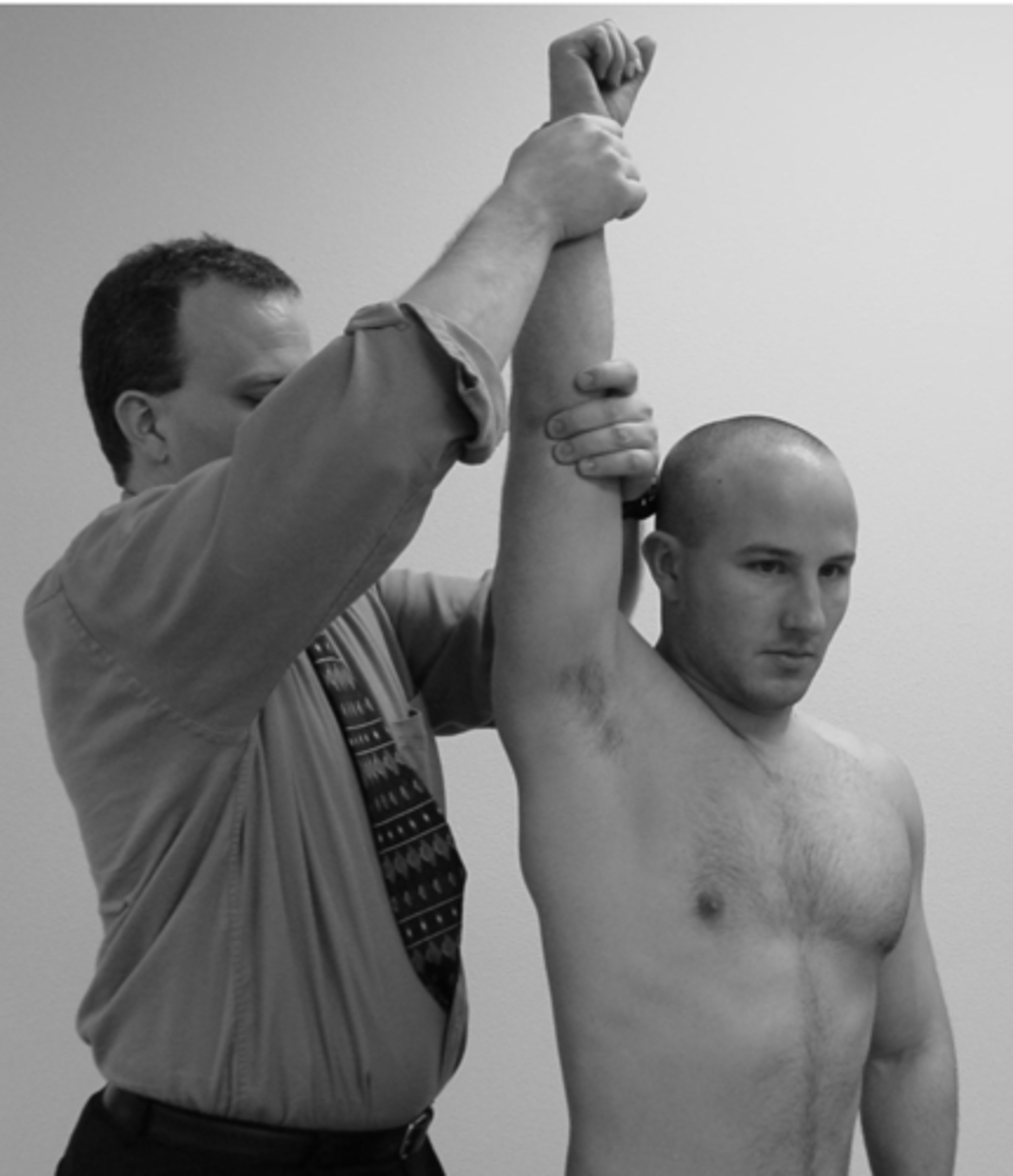
hyperabduction test compresses what spaces?
costoclavicular and pec minor spaces
allen test
- palpate radial pulse
- shoulder passively abd/ER to 90 with elbow flexed
- pt turns head away
- (+) = diminished radial pulse and/or reproduction of sxs
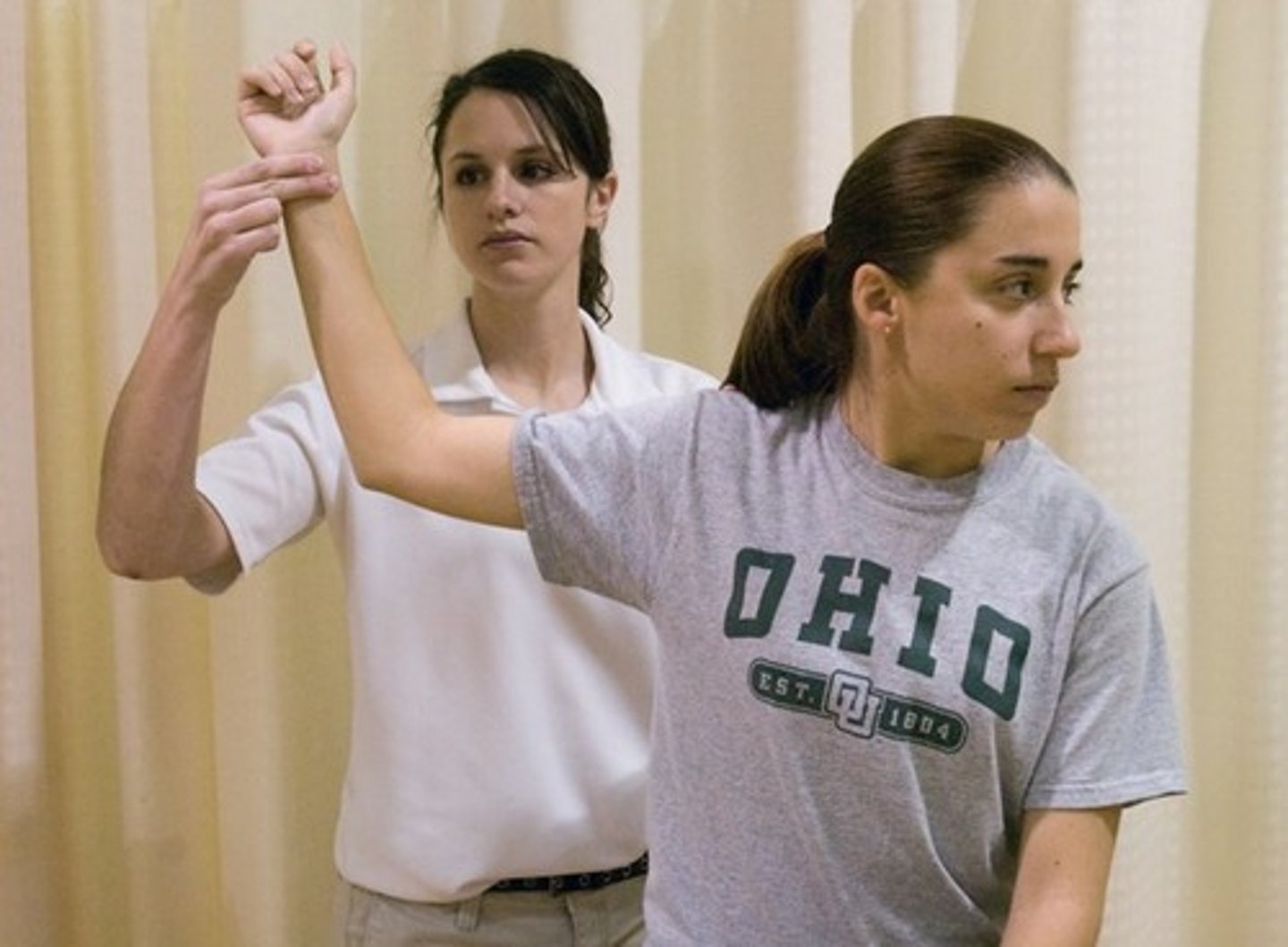
military press test (costoclavicular maneuver)
- palpate radial pulse (B) with arms at side
- pt retracts and depresses scapula while protruding chest
- position is held for up to 60 secs
- (+) = change in radial pulse and/or pain and parathesias
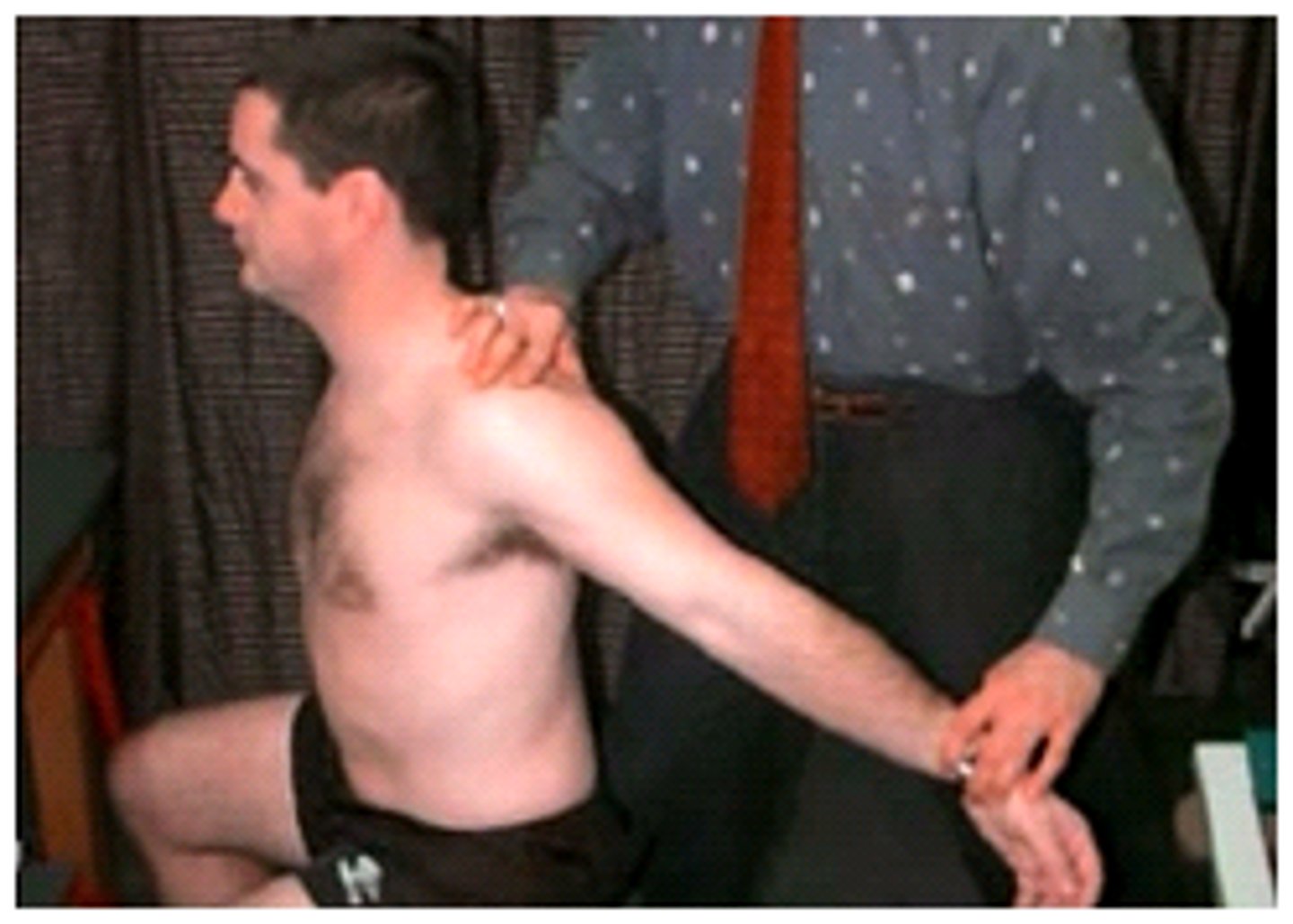
Roos Test (elevated arms stress test)
- pt abducts shoulders to 90 deg with full ER
- pt then opens and closes the hand slowly for up to 3 min
- (+) = sxs of pain, parathesias, heaviness, dropping of arm for relief
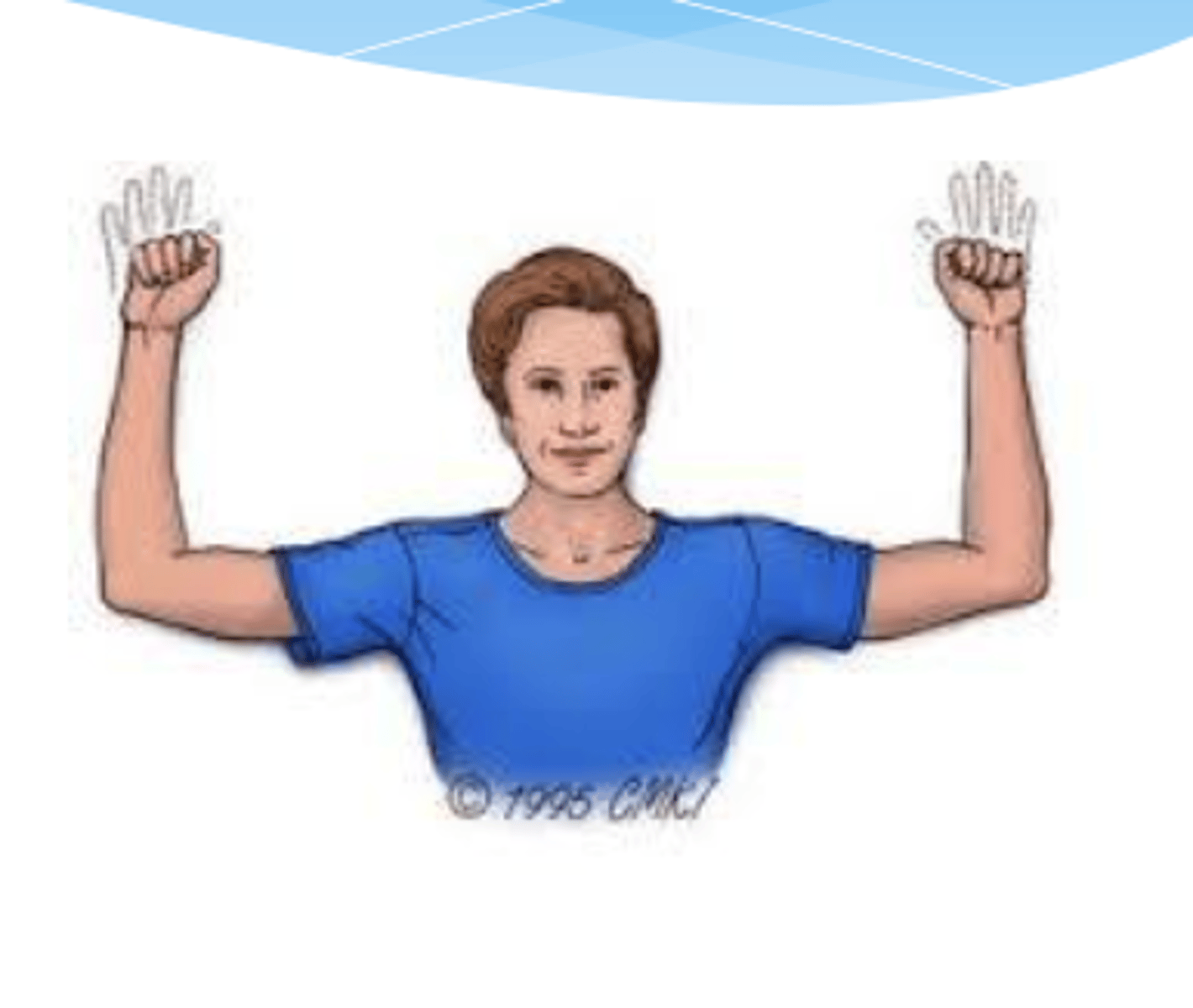

tinel sign
- percussion of supra- and/or infraclavicular areas
- (+) = replication of tingling
- Erb's point = 2-3cm above clavicle, site of upper trunk of BP
clinical test clustering
- adson + wright pulse
- adson + wright pain
- adson + Roos
- wright (pain) + Roos
what is the problem with ULTT?
not specific (but good for differential dx)
during pec minor stretching slight tingling is ok but
should go away when you stop stretching
pec minor stretch: push coracoid ______ and inferior angle _____
- posterior
- anterior
cervical rotation lateral flexion test
- assess 1st rib mobility
- pt seated
- PT passively rotates head away from the affected side and SB towards the affected side
- block trunk rotation
- (+) = SB movement is notably decreased with hard end feel --> hypomobile 1st rib
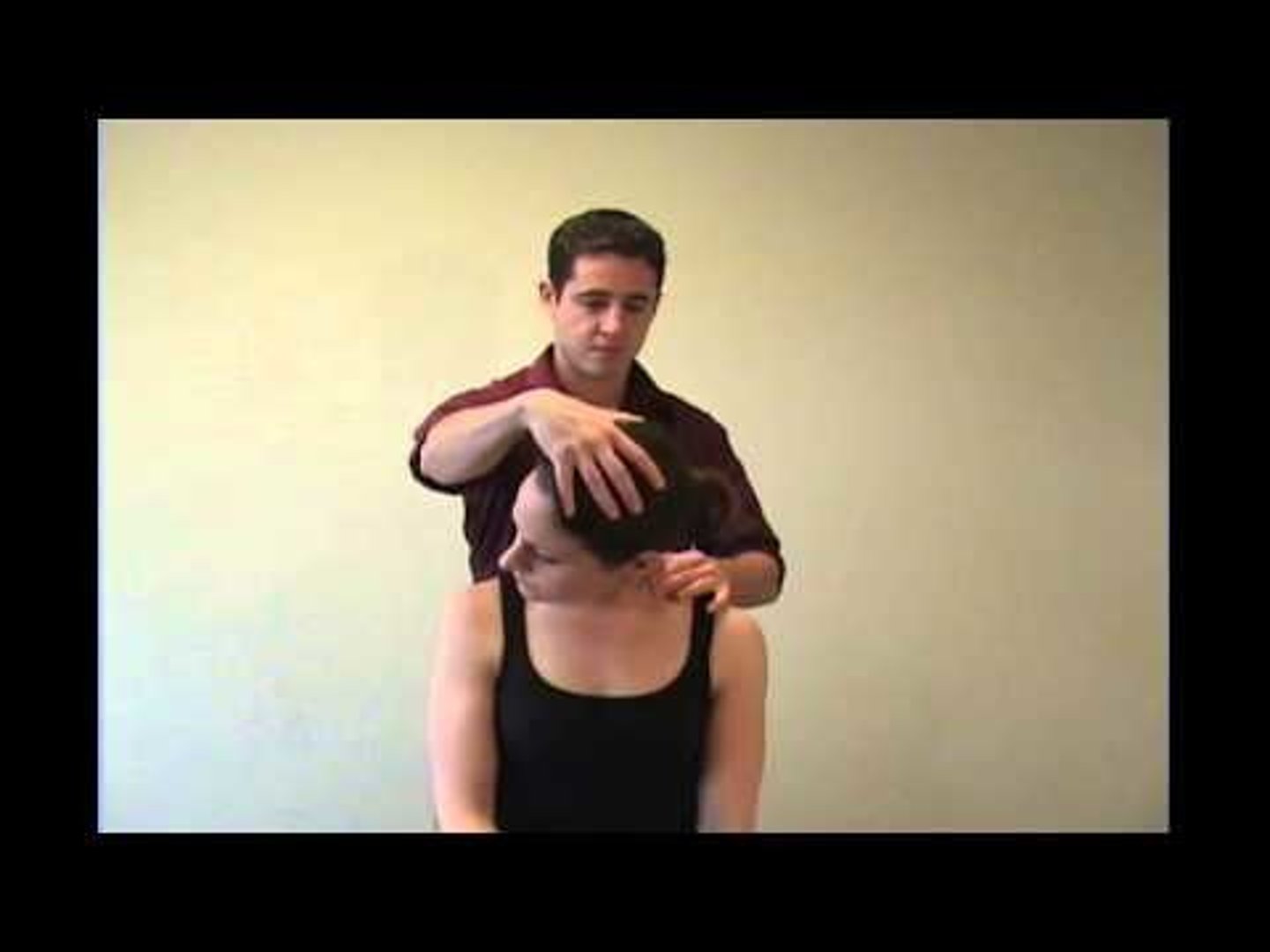
1st rib evaluation/mob supine
- pt supine
- PT uses radial hand/2nd MCP on cranial surface of 1st rib in a direction towards contralateral hip
- assess movement and end feel
- combine with inhalation

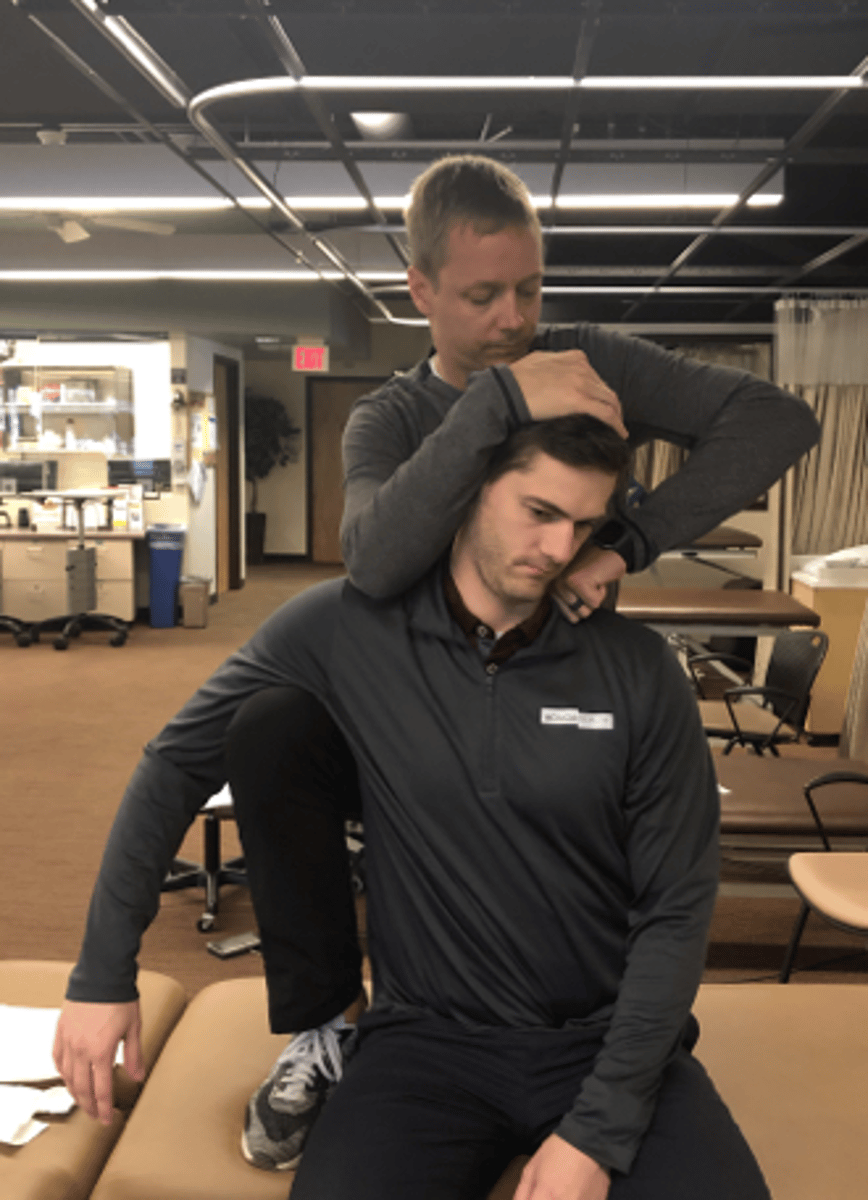
1st rib mob sitting

radiculopathy vs TOS
- radic relieved with distraction
- dermatomes & myotomes
- Spurlings
what peripheral neuropathies should you rule out if you suspect TOS?
- carpal tunnel
- ulnar nerve entrapment (Guyon tunnel & cubital tunnel)
how do systemic diseases cause double crush syndrome?
- lowers the threshold for a nerve compression
(obesity, RA, alcoholism, DM, thyroid disease, neuropathies)
30-50% of neurogenic TOS cases are associated with
a peripheral nerve entrapment
surgical interventions for TOS are only considered after failed conservative treatment for _____ weeks
8-12
surgical interventions are more likely done for what type of TOS?
vascular
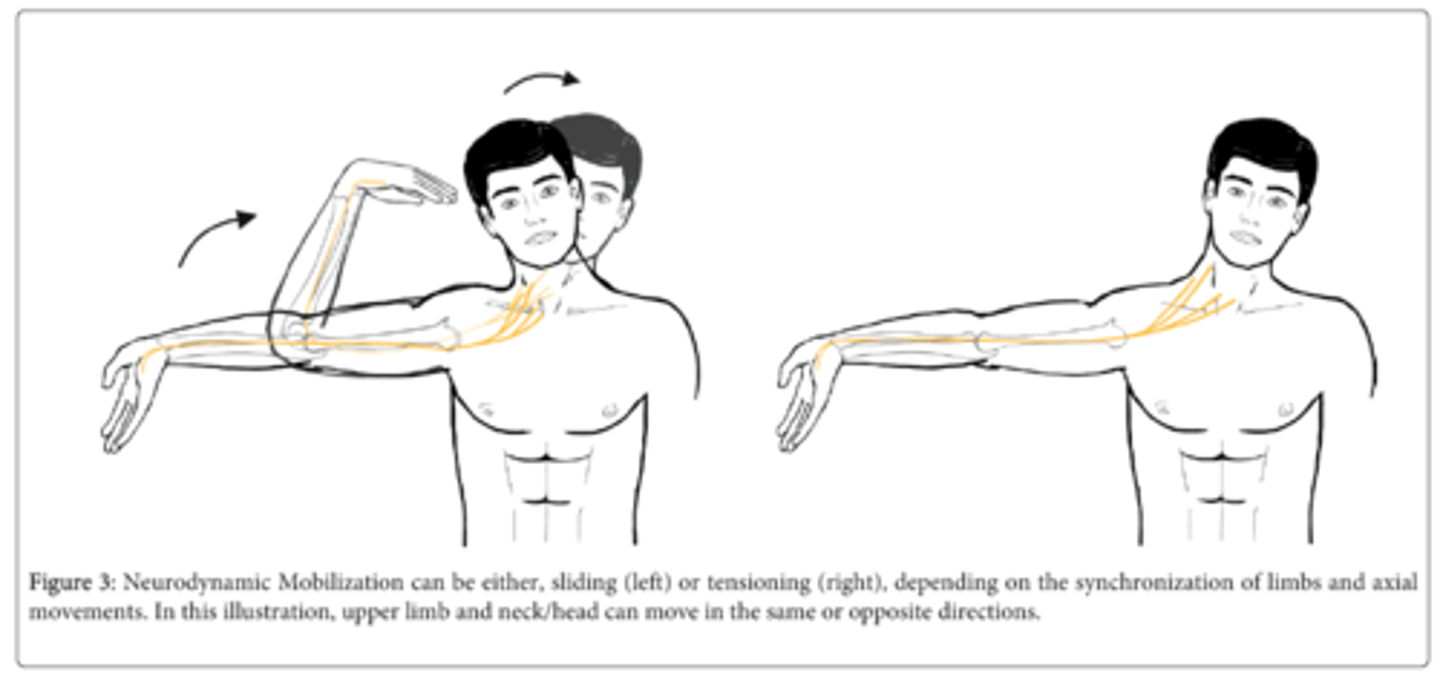
why are sliders better than tensioners?
greater movement with sliders