3.1.12 - Equilibrium constant (Kp) for homogeneous systems
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What happens to Kc when the reactants and products are gaseous?
Kp is deduced
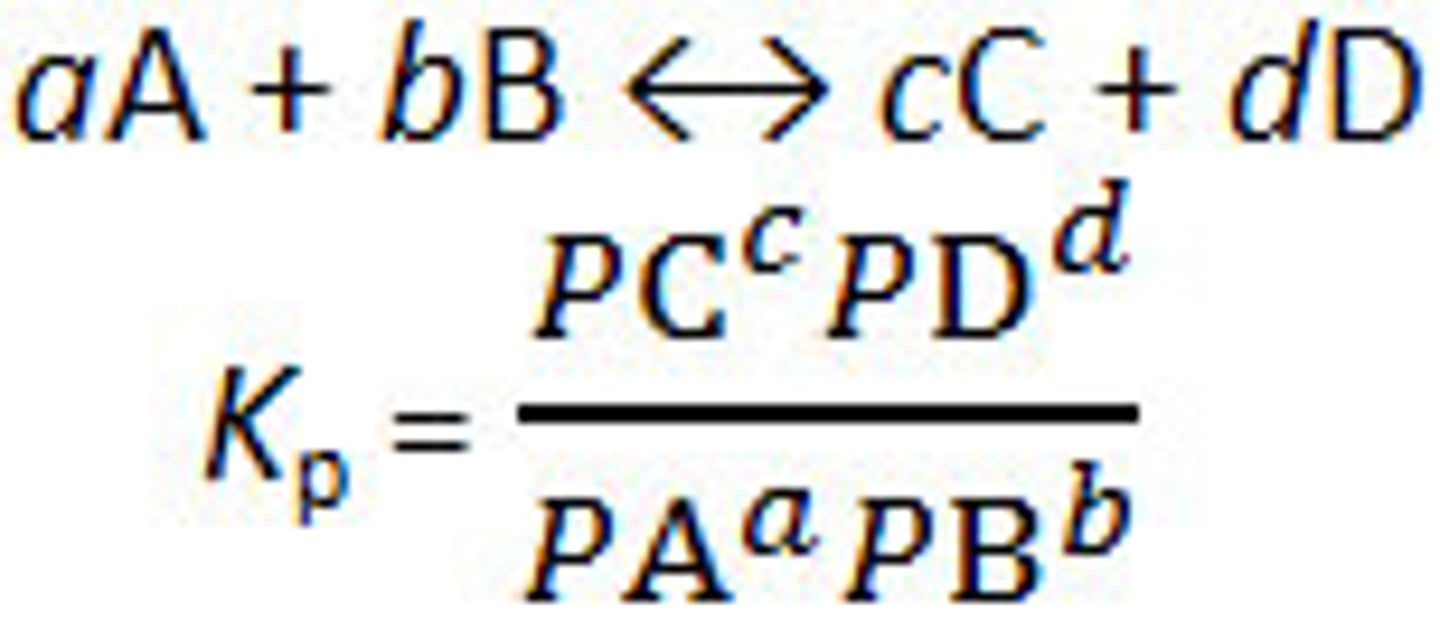
What does PaA stand for?
paA = partial pressure of A at equilibrium
What happens to solidsand liquids in Kp?
Solids and liquids are ignored in Kp equilibrium expression.
What changes Kp?
Kp of a reaction is constant and only changes if the temperature of the reaction changes.
How does temperature affect Kp in exothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions: increasing the temperature means more products and less reactants, the ratio of products to reactants decreases so Kp decreases.
How does temperature affect Kp in endothermic reactions?
Endothermic reactions- Increasing the temperature means less reactants and more products. This means the ratio of products to reactants increases so the value of Kp increases.
How is Kp affected by pressure?
Kp is not affected by any changes in pressure, because anu changes in pressure causes a shift of equilibrium which restores the value of Kp.
How is Kp affected by catalysts
Kp is not affected by a catalyst as it speeds up the forward and reverse reactions at the same rate.
Why is Kp used for gasses instead of Kc?
For reactions involving mixtures of gasses Kp is used as it is easier to measure the pressure than the concentration of gasses.
What is the partial pressure of a gas?
Partial pressure of a gas is the pressure that the gas would have if it was in the container all by itself.
How do you calculate the total pressure?
Total pressure = sum of all partial pressures.
How do you calculate the mole fraction?
Mole fraction= moles of a particular gas / total number of moles of all the gases in the mixture
How do you calculate the partial pressure?
Partial pressure = mole fraction * total pressure