Plant Bio Test 3
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Hormones
chemical messengers that regulate plant growth
most transported in phloem tissue (ATP)- ALL require expenditure of energy on part of plant for transport
interact with external environmental factors to determine growth (soil moisture/temp, day length, air temp, seasonality)
What do hormones control (6 things)
growth, seed germination, flowering, fruiting/seed production, shedding of leave, color change of leaves (breakdown of photosynthetic pigments)
2 broad categories of hormones
growth inhibiting: mostly fall/winter (certain times of year is not good)
growth promoting: mostly summer/spring
Auxins
first group of plant hormones described, GPH, produced in shoot tips, seeds, fruits, leaves, stems, NOT ROOTS
Auxin Effects
promote cell elongation, shoot elongation, production of wood, and fruit development.
inhibit bud development (produce new later shoots)
inhibit expression (droppings) of leaves, flowers, fruits
Cytokinin
originally detected in coconut milk
GPH
produced in seeds, fruits, and roots
Cytokinin Effects
promotes cell division, lateral bud development
inhibits leaf senescence/ change of color due to breakdown of pigments (especially chlorophyll)
Gibberellins/ Gibberellic Acid
many types (more than any other group)
GPH
found throughout plant, but concentrated in seeds
Gibberellins Effects
promotes stem elongation by stimulating cell division and elongation
promotes breakdowns of food reserves in germinating seeds: starch → glucose to be respired by cells to generate ATP for seed growth
adequate soil moisture
intake of water causes swelling and embryo hydration
embryo secrets gibberellins
transported to cells of another layer to secrete enzyme (alpha-amylase) for breakdown of endosperm →glucose (starchy stored food)
embryo is deciding the timing of germination
advantage of seed plants
Abscisic Acid (ABA)
GIH
found in large quantities in seeds, mature leaves, and dormant buds
ABA Effects
inhibits cell elongation
inhibits alpha-amylase production (curb early germination)
promote leaf senescence (loss of pigments)
promote production of storage carbs in seeds (keep endosperm from breaking down)
Ethylene
GIH but is actually gas from incomplete metabolism (not both ways in phloem)
Ethylene Effects
promote fruit ripening
promote abscission of leaves, fruits, and flowers
interacts with 3 GPH to determine cell size and shape (cells elongate too fast → weak cell walls)
Seed Germination
requires breaking of dormancy, combo of internal and external factors
typically over winter
Internal Factors for Seed Germination
hormones, stored food, H2O absorption, embryo swelling
External Factors for Seed Germination
sunlight, temp (air of soil), longer days (increased temps), soil moisture
Seed Germination Parts (3)
Seed Coat(s), embryo, and stored food
What happens as the seed coat cracks?
Shoot comes out, radicle emerges first
Seedling
result of cell reproduction (RAM or SAM) and increase in cell size
internal development: cells to tissues to organs to organism = Plant
Nutrient
substances metabolized by/incorporated into organism
What nutrients does photosynthesis need
CO2, H2O, K, N, Ca
Deficiency Symptoms
what happens in plants that receive too little of a nutrient
Essential Elements
play many roles in plant metabolism, often enzyme cofactors
Macronutrients
required in at least 1g/kg of plant dry mass
Micronutrients
‘trace’
required in at or less than .1 g/kg of plant dry mass
Limiting Factors of Nutrition
sunlight (photosynthesis), CO2 (photosynthesis), H2O (photosynthesis, elongation, and more), other mineral nutrients
How many essential elements must ALL plants have (some can have more)
16
What are the 16 essential elements
C, H, O from CO2 (air) and H2O (soil), 13 soil nutrients (absorbed dissolved in H2O through roots from soil, follow same path as H2O/xylem)
Soil Macronutrients (6)
Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), Phosphorus (P), Calcium (Ca), Sulfur (S), Magnesium (Mg)
Nitrogen
component of proteins, nucleic acids, chlorophyll
Potassium
osmosis and ion balance, open/close stomata (gas exchange)
Phosphorus
component of nucleic acids, ATP, phospholipids (‘gatekeeper’)
Calcium
component of cell wall (support)
Sulfur
component of proteins, coenzymes
Magnesium
component of chlorophyll, enzyme coactivator
Soil Micronutrients (7)
Molybdenum (Mo), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Chlorine (Cl), Boron (B), Iron (Fe)
Molybdenum
enzyme cofactor
Copper
enzyme cofactor
Zinc
enzyme cofactor
Manganese
enzyme cofactor, chloroplast membrane for O2 release with photosynthesis
Chlorine
split of H2O (generate electron energy), ion balance
Boron
enzyme cofactor, cell wall component, nucleic acid synthesis
Iron
enzyme cofactor, component of cytochromes (photosynthesis, cellular respiration), synthesis of chlorophyll
Most plants display sexual reproduction; what is this
2 gametes fuse to produce offspring with unique combination of genes
Plants undergo alteration of generations
2 multicellular life cycle stages: Diploid and Haploid
Diploid Life Cycle Stage
spore producing sporophyte by meiosis (2N to 1N)
Haploid Life Cycle Stage
gamete producing gametophyte via mitosis (1N to 1N)
Evolutionary Trends
sporophyte is larger and more complex where as the gametophyte is smaller and less complex
Moss
sporophytes are small and dependent on gametophyte
Flowering Plant
sporophyte larger, independent, more complex than gametophyte
dependent gametophyte are few-celled and within flowers
female is around 7 cell, male is around 2/3 cells
Flowers
only in angiosperms
all sizes, shapes, colors, and aromas
Essential Processes of Sexual Reproduction within the Flower
meiosis/cytokinesis (reduce chromosome #, 2N → 1N)
syngamy (fertilization, restore chromosome #, 1N egg + 1N sperm = 2N zygote
Ideal Flower
4 sets of highly modified leaves arranged in whorls at tip of highly modified stem
highly modified determinate (short term) shoot system
Whorls
Sepals, Petals, Stamens, Carpels
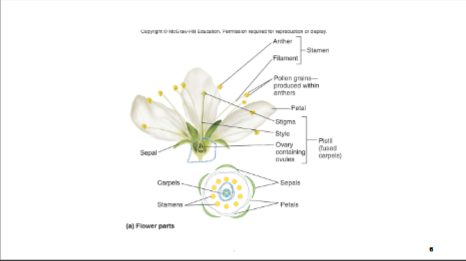
Whorls for Reproduction
Stamens and Carpels
Whorls NOT for Reproduction
Sepals and Petals
Sepals
make Caylx- All sepals, protect unopened flower
Petals
make Corolla- all petals, attract pollinators, contain color, smell, and nectar
Stamens
make Androecium- all stamens, male household, pollen (sperm)
Carpels
make Gynoecium- all carpels, female household, embryo sac (with egg)
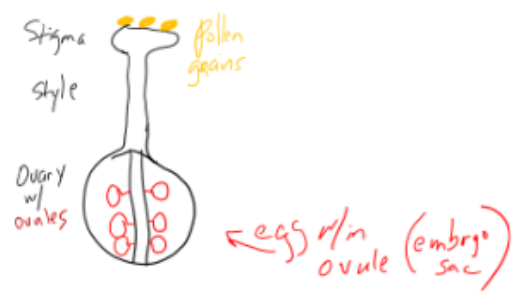
Pistil (fused carpels)
stigma, style, ovary with ovules, become seeds, ovary with fruit
What is a part of the sporophyte generation, is 2N, and is attached to the receptacle
Pedicel (flower stalk), Receptacle (enlarged tip of pedicel), and 4 sets of highly modified leaves
What is a part of the 1N gametophyte generation
Pollen (sperm) and Egg (within embryo sac)
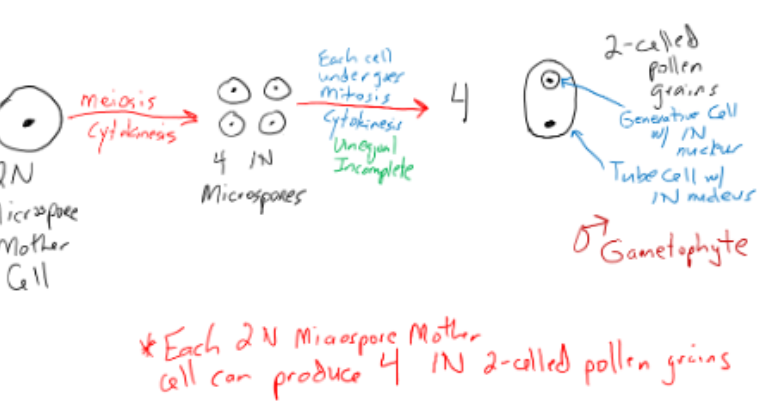
Pollen Formation (male side)
takes place within stamen
Anther
bilobed with 2 pollen chambers per lobe
c.s.- 2 N microspore mother cells
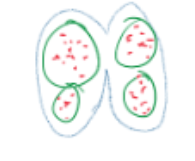
2N microspore mother cell within anther
2N cell undergoes meiosis and cytokinesis to create 4 1N microspores which then undergo mitosis and cytokinesis, but unequal and incomplete for some to create 4 2-celled pollen grain which contain a tube cell with a 1N nucleus and a generative cell with a 1N nucleus
EACH 2N MICROSPORE MOTHER CELL CAN PRODUCE 4 1N 2-CELLED POLLEN GRAINS
Pollination
transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of pistil
Self-pollination
transfer within same flower or between flowers of the same plant
Cross-pollination
transfer between flowers of different plants which causes genetic variation
Pollinating Agents
mechanisms used for transfer of pollen
Wind (small, lightweight pollen)
Water (with a few aquatic plants)
Animals (majority of plants, utilize ‘trick and reward’ system [nectar, color, aroma to attract animals])
Ovule Development (Female Side)
ovule = future seed, ovary = future fruit
enclosed within ovary of pistil (carpel), one to many ovules per ovary
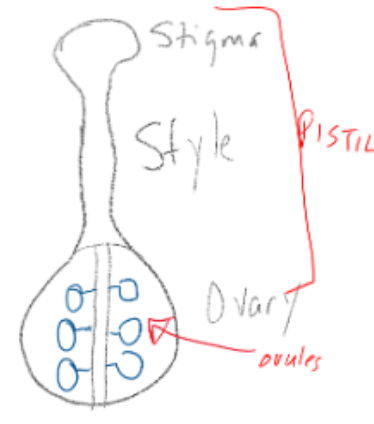
Ovule attached to the central axis or wall of hollow ovary
Always enclosed, only in angiosperms
Megaspore Mother Cell
within ovule is 1 large 2N cell
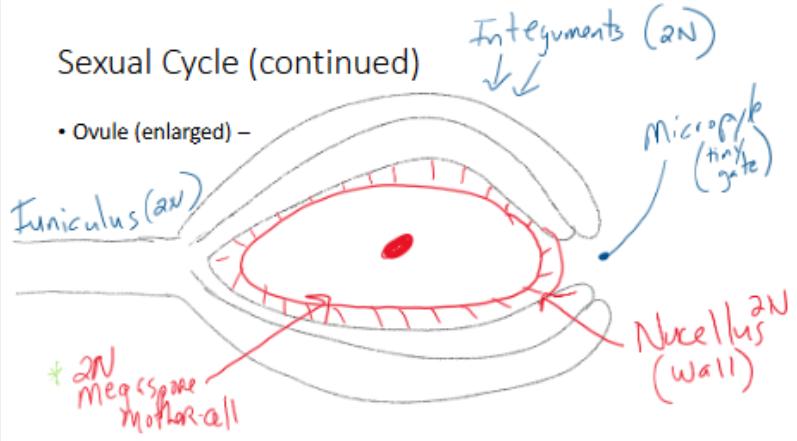
Megaspore Mother Cell
1 2N megaspore undergoes mitosis and cytokinesis to create 4 1N megaspores, 3 are degraded leaving 1 functional 1N megaspore, this undergoes series of 3 mitosis and cytokinesis all of which are incomplete and unequal which creates 8 1N nuclei that only have 7 cells
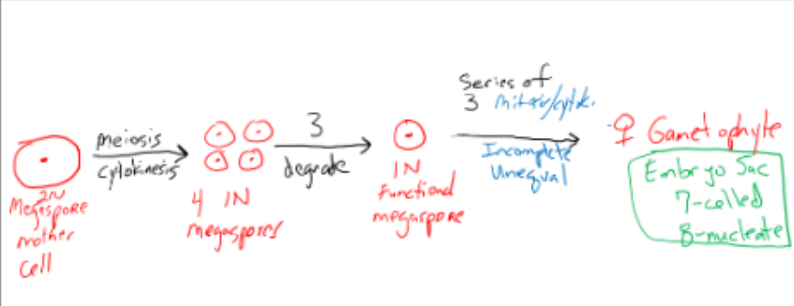
Embryo Sac
female gametophyte, 8 nucleate, 7 celled structure
7 cells in the embryo sac
3 antipodal cells (1N): opposite end from micropyle
1 central cell with 2 large 1N nuclei (polar nuclei)
2 synergid cells (1N): micropyle end on outside
1 Egg (1N): middle at micropyle end
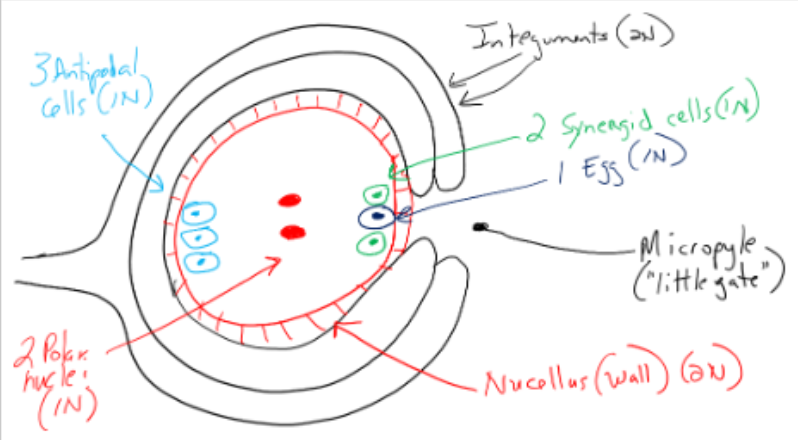
Syngamy
1N egg + 1N sperm = 2N zygote (single cell, fertilized egg)
Pollen Grain Germination
tube cell forms pollen tube, generative cell divides by mitosis and cytokinesis to produce 2 1N sperm
Syngamy Steps
pollen tube enters micropyle of ovule, digest nucellus
pollen tube delivers sperm to location of egg
pollen tube enters 1 synergid, releases its contents, synergid ruptures
tube nucleus degrades, 2 sperm release into large central cell
micropyle closes up
fertilization!
Double Fertilization/Fusion
both sperm fuse with other nuclei
1N egg + 1N sperm = 2N zygote (fertilized egg)
1N sperm + 2 1N polar nuclei = 3N primary endosperm cell
all other cells in embryo sac reabsorbed
Post Fertilization (within ovule)
2N zygote grows by mitosis/cytokinesis into 2N multicellular embryo
3N primary endosperm cell grows by mitosis/cytokinesis into 3N multicellular endosperm (nutritive tissue for embryo)
indie ovule: 2N integuments harden to form seed coats
Post Fertilization, not just inside ovule
ovule with 2N zygote matures into seed with 2N multicellular embryo and ovary enlarges with sugars and H2O into fruit (mature ovary) with enclosed seeds (mature ovules)
Seed Dispersal (seeds enclosed within fruit)
wind, water, animals (majority)
Seed Germination
seed with 2N embryo enters period of dormancy which is broken by combination of internal and external (environmental) factors
Radicle (1st root) emerges and grows down
Shoot emerges and grows up
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
building block of life (contains info to build an organism)
made up of 4 nucleotides
4 Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
A=T, G=C
Genotype
genetic information of a trait, sequence of nucleic bases
Phenotype
physical expression of trait
Central Dogma (don’t think we have to know this term, but helpful to know)
DNA (can replicate) → (transcription) RNA → (translation) Protein
Dominant vs Recessive
visible vs masked
How Many Alleles Per Gene
Each individual has 2
Homozygous
2 copies of same allele (AA or aa)
Heterozygous
2 different alleles (Aa)
Dominant Allele vs Recessive Allele
uppercase vs lowercase
Punnett Square AA x aa
100% Aa (hetero)
Phenotypic Ratio: 1:0
Genotypic Ratio: 0:1:0
Punnett Square Aa x Aa
AA, 2 Aa, aa
Phenotypic Ratio: 3:1
Genotypic Ratio: 1:2:1
Independent Assortment
traits/genes assort independently of one another
Mutations
change in order/structure of genetic information (DNA)
provides genetic variation
Example of a Mutation
Albinism in animals
Rare recessive mutation where pigment is removed from fur