bio/biochem meow 1
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
concepts, questions, unsure/learn
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
The association observed experimentally between the expression of miRNAs and mRNAs in AR kidney transplants indicates that miRNAs regulate the expression of genes implicated in which type(s) of immune response(s)?
A. Adaptive immunity only
B. Humoral immunity only
C. Innate and cell-mediated immunity only
D. Adaptive and innate immunity only
A: adaptive immunity
involves B cells n T cells, memory cells (long lasting protection), SPECIFIC pathogen response
Humoral: antibody production, B cells (plasma n memory B cells), depend on helper T cells for full activation n B cell differentiation
cells involved in cell-mediated vs. humoral immunity, target, mechanism
cell-mediated:
cytotoxic T cells, helper T cells, memory T cells, natural killer cells
target: intracellular pathogens n cancer cells
mechanism: DIRECT cell killing, regulate immune responses
humoral:
B cells (plasma n memory), helper T cells
target: extracellular pathogens like bacteria/virus in blood n mucous
mechanism: produce antibodies = neutralize pathogens = help remove
cells involved in innate immunity, target, mechanism
macrophage, neutrophils, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, BEN, mast cells, monocyte
target: broad, non-specific range of pathogens
mechanism: immediate, non-specific, phagocytosis, inflammation
what are acetate, propionate, and butyrate examples of? glucose (mono n poly) to what in the GI tract via bacteria?
SHORT CHAIN FATTY ACIDS
disulphide bond vs phosphodiester bonds
disulphide bridge/bond
between 2 cysteine amino acids in close proximity on a polypeptide chain form COVALENT bond
phosphodiester bond
between 5’ phosphate and 3’ hydroxyl OH of deoxyribose sugar
Based on the passage, to which phylum does Enterobacter most likely belong?
A. Actinobacteria
B. Firmiculate
C. Bacteroidete
D. Proteobacteria
D:
passage said: TWO ** means highly INCREASED. also states CD impacted individuals have highly INCREASED gram negative Proteobacteria… since enterobacter is INCREASED, we can conclude that it belongs in this phylum.
paracrine n autocrine vs endocrine signalling
endocrine: transported by blood vessels to impact tissues all over
autocrine: secrete messengers that act on themselves, act locally
paracrine: secrete messengers that act on cells nearby, act locally
ALL: bind to receptors on or in cells
significance of protein glycosylation
CRUCIAL for structural conformation of protein, which determines if a ligand will activate its receptor
function in energy storage, adhesion, and intracellular trafficking, as well as signaling through cell-to-cell interactions
happens in endoplasmic reticulum n Golgi apparatus
can glycoproteins cross the plasma membrane on their own?
NO, usually too large n charged, polar, has a receptor on plasma surface
In an experiment in which IBU alone was administered to normal mice in order to determine whether long-term treatment with the analgesic can cause behavioral symptoms of depression, what would be the appropriate control group?
A. Normal mice treated with an SSRI
B. Depressed mice treated with IBU
C. Normal mice treated with a placebo
D. Depressed mice treated with cytokines
C:
C: CORRECT: shows baseline. mice without IBU vs. mice w IBU (Exp)
A: WRONG: SSRI decreased depression, so not effective to assess if IBU CAUSES it
B: WRONG: already depressed mice, IBU is testing on non-depressed mice. to insure that observed symptoms are CAUSED by IBU, must be non-depressed mice
D: WRONG: already depressed ^.
Which comparison best determines whether IFNγ is necessary for antidepressant-induced increases in the expression of p11?
Expression levels of p11 in:
A. wild-type mice versus IFNγ knockout mice, both treated with p11
B. wild-type mice versus IFNγ knockout mice, both treated with an SSRI
C. wild-type mice treated with IFNγ versus wild-type mice treated with an SSRI
D. wild-type mice treated with IFNγ versus wild-type mice treated with ibuprofen
B:
independent variable: IFNy given or not
dependent variable: p11 expression
subject: those on antidepressants, SSRI
How does the Unit Membrane Model differ from the Fluid Mosaic Model?
A. The location of proteins differs in the two models.
B. The Unit Membrane Model has a monomolecular layer of protein on each surface, while the Fluid Mosaic Model has a bimolecular layer of protein on each surface.
C. The Unit Membrane Model has one layer of phospholipids, while the Fluid Mosaic Model has two layers.
D. The Unit Membrane Model contains dissolved protein, while the Fluid Mosaic Model is coated with a monomolecular layer of protein on each surface.
A:
UMM: proteins form monomolecular layer OUTSIDE n INSIDE bilayer, NO penetration.
FMM: proteins inserted inside bilayer
BASICS: transformation vs transduction vs conjugation
transFORMATION: transfer genetic material environment —> bacteria
transDUCTION: nucleic acids virus —> cells. During the assembly of new bacteriophages (virus), fragments of bacterial DNA are mistakenly packaged into phage capsids. The phages then inject this DNA into new host cells.
conjugation: EXCHANGE nucleic acids between bacteria
fatty acid chain length, saturation, membrane fluidity, and cholesterol
RIGID N LOW FLUIDITY:
lots Van Der Waal forces, LONGER chains, saturated
cholesterol INCREASES fluidity
PERMEABLE N HIGH FLUIDITY:
less Van Der Waal forces, SHORTER chains, unsaturated
cholesterol DECREASES fluidity
coding, noncoding, template, mRNA transcript: differences, TOP to BOTTOM
coding/non-template/SENSE strand @ top. SAME nucleotide sequence as mRNA transcript, but the latter has uracil instead of thymine
NON-coding/template/ANTI-sense strand @ bottom. mRNA codes from this. both mRNA n sense strand have the OPPOSITE sequence as this
mRNA transcript @ in between. SAME nucleotide sequence as CODING/non-template/sense strand except w uracil.
where do transcription factors bind?
enhancer or promotor regiion
enterocyte function
intestinal cells that produce ENZYMES that digest carbs, specifically, disaccharides like LACTOSE
A particular diploid organism is heterozygous in each of 3 unlinked genes. Considering only these 3 genes, how many different types of gametes can this organism produce?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
D: 8
2³ = 8
gametes are HAPLOID. organism has 2 options (heterozygous) for each gene, and limited to one allele. 3 gene spots in the haploid chromosome with possibility of 2 alleles each. so 2×2×2
ABC, ABc, AbC, aBC, Abc, aBc, abc, abC
if a was HOMOZYGOUS, then 2² = 4. ABC, AbC, ABc, Abc since only 1 option in homozygous
Which type of reaction has a Keq > 1 and is kinetically fast?
Exergonic with low activation energy level
isoelectric focusing
Separates proteins based on their pIs n uses an electric field and a pH gradient which causes proteins to stop moving at a pH equal to their pI
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction where enzyme concentration is held constant and substrate concentration is relatively low, which kinetic parameter will increase with the addition of more substrate?
(Note: Other than substrate concentration, assume no other changes to reaction conditions.)
A. KM
B. kcat
C. Vmax
D. V0
D:
KM, the rate constant of a reaction, does not change with changes in substrate concentration.
Kcat is the reaction turnover number and does not change with changes in substrate concentration.
Vmax is the maximum velocity of a reaction and is a constant property which does not change with the addition of more substrate.
V0 is the initial velocity of an enzymatic reaction. At low concentrations of substrate and constant enzyme concentration, adding more substrate will increase V0 until the maximal velocity is reached.
what is the ratio of the cationic (+) to anionic (–) functional groups in a protein at its pI? what about the net charge of the cationic (+) and anionic (–) functional groups?
RATIO at its pI isoelectric point is always ONE 1
NET charge at its pI isoelectric point is ZERO
ionophores
compounds that bind to ions and facilitate their movements across membranes
gel filtration vs. ion exchange chromatography
gel filtration is done by SIZE of proteins
ion exchange chromatography is done by CHARGE difference of proteins
3 amino acids w beta branches
isoleucine, valine, threonine
TIV
reduced carbonyl
alcohol group
oxidized aldehyde or ketone
carboxylic acid (extreme for ketone)
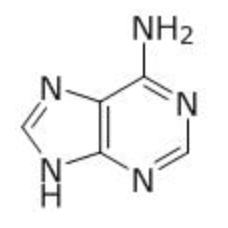
what molecule is this
adenine, purine
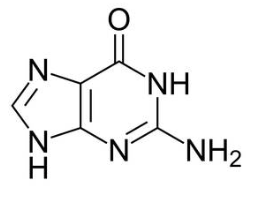
what molecule is this
guanine, purine
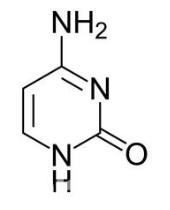
what molecule is this
cytosine, pyrimidine
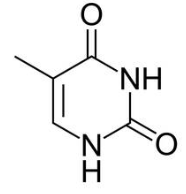
what molecule is this
thymine, pyrimidine
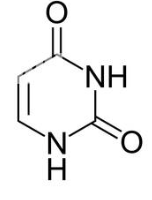
what molecule is this
uracil, pyrimidine
what happens to the pOH and [OH-] as you go from a HIGHLY acidic environment to a less acidic one?
HIGH acidic = LOW pH… transition to LOW acidic… HIGH pH
this means LOW pOH, which means HIGH [OH-]
electrolytic vs galvanic cell
electrolytic: DECOMPOSITION, non-spontaneous, delta G>0, endergonic, electric current supplied
galvanic: DECOMPOSITION, SPONtaneous, delta G<0, exergonic, electric current produced (opposite of electron flow)
purpose of a boiling chip
provide nucleation sites so the liquid boils smoothly without becoming superheated or bumping
3 common metals that form green precipitate, n why
chromium, iron, nickel
transition metals, partly filled D orbitals
acid + metal carbonate —>
—> salt + water + CO2
resonance effect vs inductive effect
is a molecule more or less stable when a side group is ionized and can form hydrogen bonds with another side group?
more stable
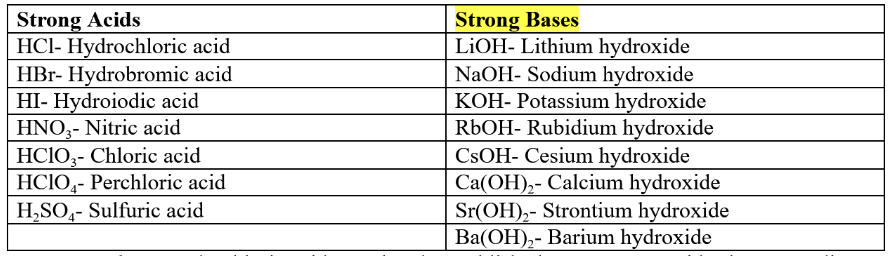
strong acids n bases
What is the sum of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in strontium–90?
mass number 90 = pro + neutrons
atomic number 38 = pro and electrons
sum = mass number + 38 electrons = 128
A lower-than-normal blood pressure will cause what effect on the rate of plasma clearance of Substance A?
low BP = LOW glomerular filtration rate aka how fast the filtrate moves through system = MORE time for water reabsorption = DECREASE RATE of plasma clearance n urine output
3 properties of DNA in prokaryotes
circular DNA
double-stranded DNA
NO telomeres
fermentation in prokaryote vs eukaryote
PROKARYOTE: pyruvate —> alcohol
EUKARYOTE: pyruvate —> lactic acid
NADH to NAD+
DNA mismatch repair system 4 steps
detect mismatch
endonuclease enzyme cleaves mismatched nucleotide n ADJACENT ones
DNA polymerase replaces n adds correct nucleotides
DNA ligase forms phosphodiester bonds n seals the nicks
KEY WORDS associated w these 3:
endocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
endo - inward budding
phago - extend n engulf
pino - invagination, non-receptor binding
lipid rafts facts 3
cholesterol rich
contain a higher concentration of the phospholipid sphingom
Signalling hotspots that LONG transmembrane proteins (LATERAL migration) can live in
peroxisome
have REDOX enzymes
help keep oxidation of cell (make H2O2 hydrogen peroxide)
protein secretory pathway, explain it
mRNA sent to cytosol to be translated
ribosomes detect special signal sequence for secretory proteins n then are sent to RER to have post-translational modifications
protein packaged into vescicles = sent to golgi
golgi processes n packages proteins —> sent to fuse w membrane n become receptor proteins
kinetochore is…
metaphase
where the spindle fibres made from microtubules connect to
does inhibiting lysosomal trafficking impact viral protein processing?
NO because lysosomes play a part in inhibiting ENTRY of viruses but once they are inside, lysosomal function is to degrade MACROMOLECULES not proteins