Unit 2 Population Key Terms Flashcards
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP HUG Population Unit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Density
Frequency of a feature on a piece of land
Concentration
Extent of a feature on a piece of land
Arithmetic Density
Total number of objects in an area
Population / Land area
Physiological Density
Number of people supported by a unit area of farmable (arable) land
Population / Arable land
Agricultural Density
Ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
Population of farmers / Arable land area
Child Mortality Rate (CMR)
Total number of deaths in children under 5 years old out of 1,000 live births
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Total number of deaths in a year out of 1,000 people
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
Total number of live births in a year out of 1,000 living people
Age-Sex Distribution
On the X-axis of population pyramids
% female displayed on the right
% male displayed on the left
On the Y-axis of population pyramids
Age cohorts of usually 5 years
Oldest at top, youngest at bottom
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of humans that an environment can sustainably support
Census Tract
A small, relatively permanent statistical subdivision of a country used for collecting data
Depency Ratio
Measure used to indicate the ratio of people in the “dependent” (“non-working” or “unproductive”) ages compared to those who are working
Dependents: Ages 0-14 and 65+ years compared the economically productive people (15-64)
Doubling Time
The number of years to double population assuming a constant rate of increase
Rule of 70: 70 / growth rate % = Doubling Time
Exponential Growth
A population increasing at a steady rate, causing growth to become faster and faster over time
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
Number of deaths of infants under one year old out of 1,000 live births per year
Per 1,000 people rather than a percentage
Low in developed countries
High in developing countries
Life Expectancy
Average number of years a person is expected to live
Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR)
Number of female deaths out of 100,000 live births per year
Complications with childbirth, pregnancy, or the puerperium
Natural Increase Rate/Natural Rate of Increase
Percent by which a population grows in a year
((CBR - CDR) / 1000) x 100 = NRI
Replacement Rate
The average number of children a woman must have to replace herself and her partner to keep the population stable
Total Fertility Rate
Average number of babies a woman will have during childbearing years (15-49)
Urban Density
The concentration of people, jobs, or buildings within a city
People / Unit of land area
Zero Population Growth
A state where a population’s size remains stable
Births + Immigrants = Deaths + Emigrants
Demographic Momentum
The continued growth of a population even after fertility rates have declined
Large percent of the population still in their productive years
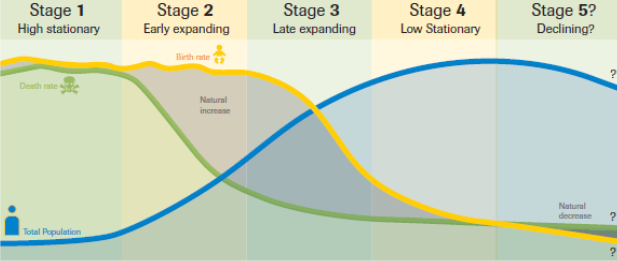
DTM Stage 1 - High Fluctuating
BR: High
DR: High
NIR: Low and fluctuating
Development: Very low
Where?: Pre-industrial, very low income countries (LIC)
Uncontacted tribes
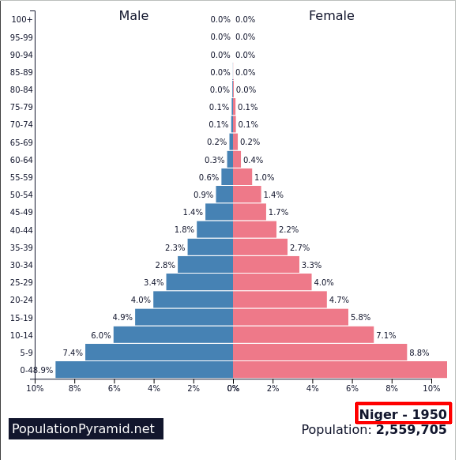
DTM Stage 2 - Early expanding/Youthful
BR: High
DR: Decreasing rapidly
NIR: Rapid Increase
Development: Low (LIC) — Indicates beginning of industrialization / healthcare access
Where?: LDCs like Sub-Saharan Africa, Afghanistan
Lots of other developing countries
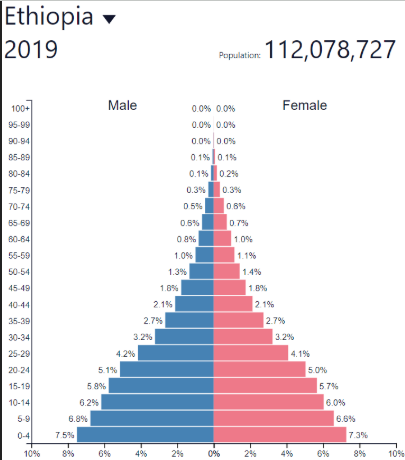
DTM Stage 3 - Late expanding
BR: Decreasing rapidly
DR: Decreasing more slowly/low
NIR: Increasing but more slowly
Development: Low to medium — “Newly Emerging Economies” (NEE)
Where?: Much of the developing / developed world
DTM Stage 4 - Low fluctuating/Stable
BR: Low
DR: Low
NIR: Low and fluctuating
Development: High/very high (HDCs)
Where?: Post-Industrial countries
Europe, North America, etc…
DTM Stage 5 - Decline
BR: Very low (Below DR)
DR: Low
NIR: Low; decreasing slowly
Development: Very high (HDCs)
Where?: Russia, Japan
Some other European countries
Demographic Transition Model
Demography
The scientific study of human populations examining their size, composition, and distribution across space
Neo-Malthusian
Mid 1900s
All of the same beliefs as Malthus, but believed that technology could not save us
Thomas Malthus
Claimed that the population grew faster than the food supply
Would cause a great famine
Theory and Reality of Malthus
Food production increased over the last 90 years (Faster than Malthus thought)
Model predicted that world population would quadruple over 50 years
Not even India’s population growth out-passed food
Point of Crisis = Critical Capacity
The moment when a population’s growth surpasses the environment’s ability to sustain it
Leads to severe imbalance and potential societal collapse
Epidemiologic Transition
A theory explaining how a population’s health threats change as a country develops
Infectious diseases and famines —- Chronic degenerative diseases
Population Pyramid
Graphical representation showing the distribution of various age groups in a population
Males on left, females on right
Youngest at bottom, oldest at top
Sustainable Growth Theory
An economic approach that balances economic development with environmental stewardship and social equality
Ensures that current needs are met without compromising future generations
“Baby Boom”
A period of significant increase in birth rates
“Baby Bust”
A period of declining birth rates that is followed by a “Baby Boom”
Cohort
A group of people who share a common characteristic, experience, or time period
Birth year, migration, etc…
Ecumene
Permanent human settlement
Nonecumene
Uninhabited area
Underemployment
When there is an abundance of skilled labor, but a shortage of suitable job opportunities
Infanticide
The intentional killing of an infant
Cultural reasons, gender imbalance issues, or unwanted children
Genocide
The deliberate and systematic killing of a racial, ethnic, religious, or national group
Pro-Natalist Policies
Countries with low birth rates
Japan, Denmark, Singapore
Anti-Natalist Policies
Countries with high birth rates
China’s One Child Policy (1970s-2015)
India’s Forced Sterilization (1960s-1970s)
Pandemic
A disease that spreads across a wide geographic area and affects a large percent of the population
Epidemic
Unexpected and large outbreak of a disease in a specific population or region exceeding what is normally expected
Primary Economic Activities
Agriculture, Natural resource extraction
LDCs / periphery
Stage 2/3
Secondary Economic Activities
Manufacturing
Developing countries
Stage 3
Tertiary Economic Activities
Goods and services
HDCs
Stage 4/5