Human Biology exam revision
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
Passive transport
Does not require cell energy
Active transport
Requires cell energy
3 processes for cell transport
1. Simple diffusion
2. Facilitated transport
3. Vesicular transport
Simple diffusion
A passive process resulting from the random movement of ions and molecules' osmosis is a special case of diffusion where water passes across the membrane
Facilitated transport
A process that requires special proteins in the cell membrane, either channel or carrier proteins.
May be passive or active
Vesicular transport
An active process in which materials are moved in membrane-bound sacs
Diffusion meaning
The spreading out of particles until they are evenly distributed.
Occurs with liquids and gases due to the movement of their particles
Concentration gradient
Greater the difference between concentrations, the steeper the gradient
Net diffusion meaning
The movement of liquids and gases from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, along a concentration gradient, until the concentrations are equal
Lipid soluble molecules
Diffuse through the lipid part of the membrane (phospholipid bi-layer)
E.g., Alcohol, fatty acids, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Water soluble molecules
Pass through channel proteins, providing they are small enough to fit through
E.g., Water or ions like sodium or calcium
Osmosis meaning
Diffusion of water across a semi permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration
Passive process
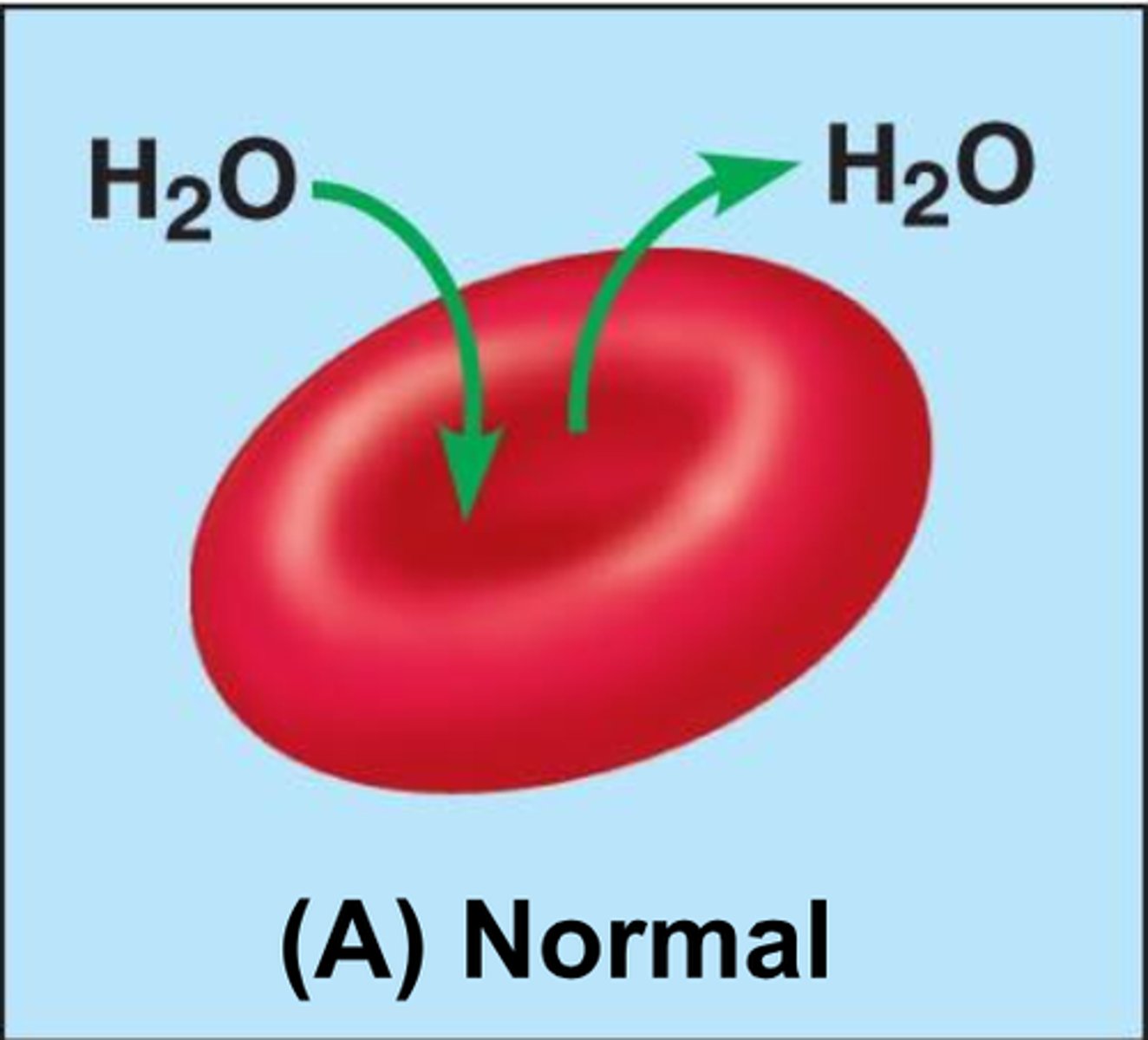
Isotonic solution
Has the same solute concentrations as another solution.
No net movement of water particles and the concentration on both sides.
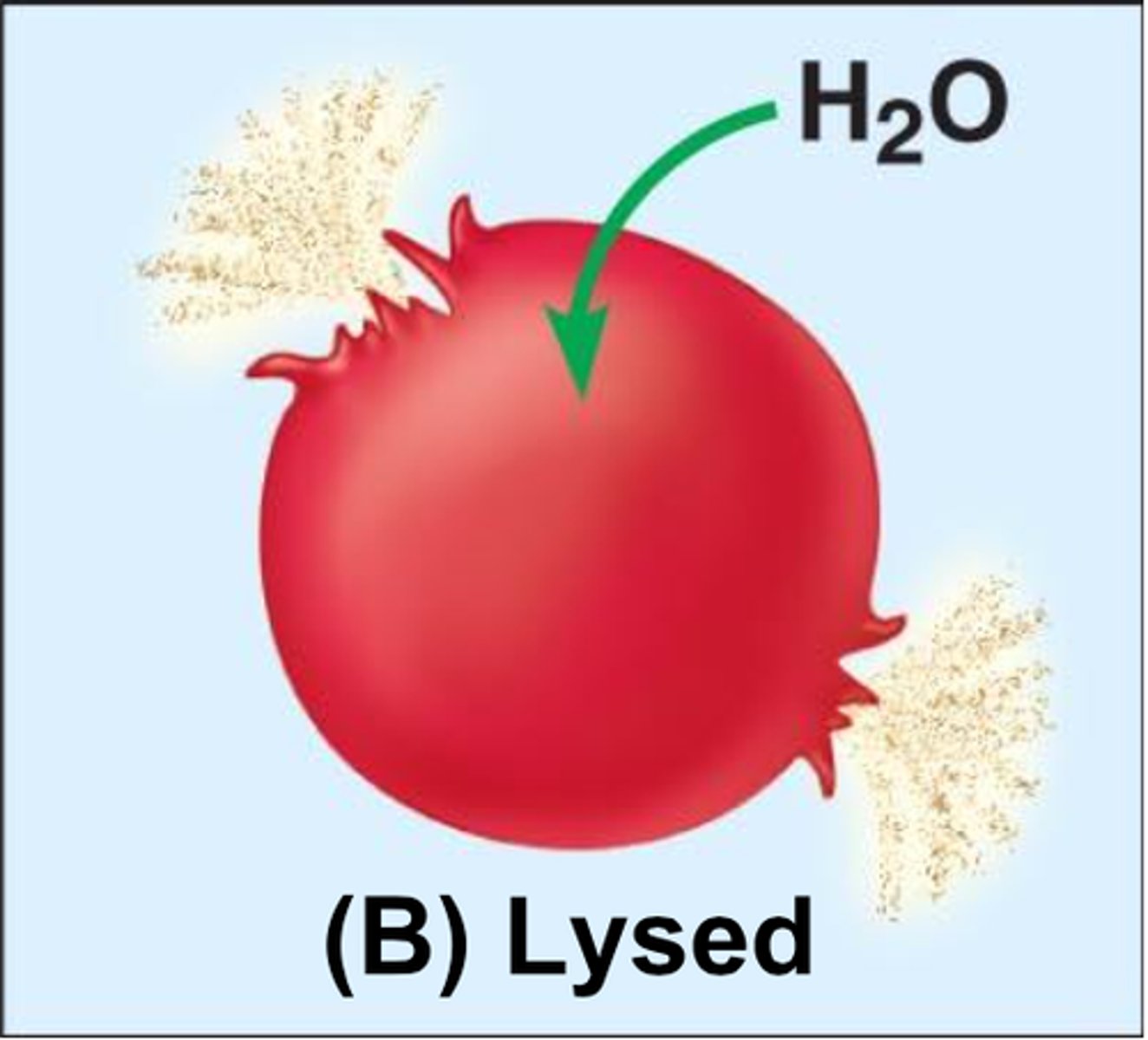
Hypotonic solution
Has a lower solute concentration than another solution. Water particles will move into the cell, causing the cell to expand and eventually lyse
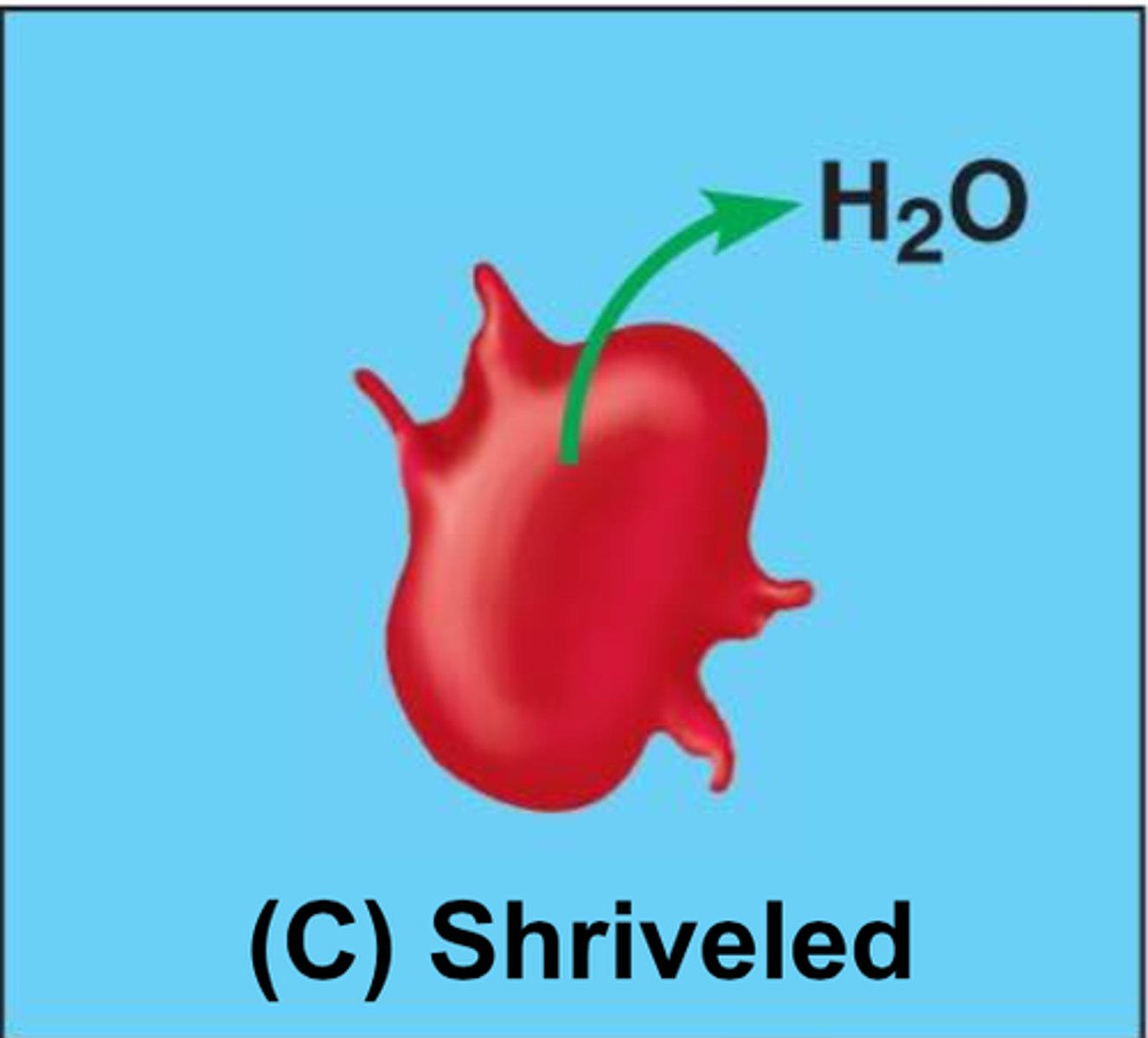
Hypertonic solution
Has a higher solute concentration than another solution. Water particles will move out of the cell causing it to shrivel
Carrier mediated transport
Molecules bind to carrier proteins to move across the membrane.
Proteins are specific, they will only bind to a particular molecule. Carrier activity is regulated by substances such as hormones
Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion
- Passive
- Large molecules such as Glucose and Amino Acids
- the transported molecule binds to the carrier protein which changes shape and releases the molecule on the other side
- moves with the concentration gradient
Carrier mediated active transport
- active (requires energy in form of ATP)
- movement of substances against the concentration gradient (low to high)
- glucose, amino acids and some ions
Types of vesicular transport
- Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
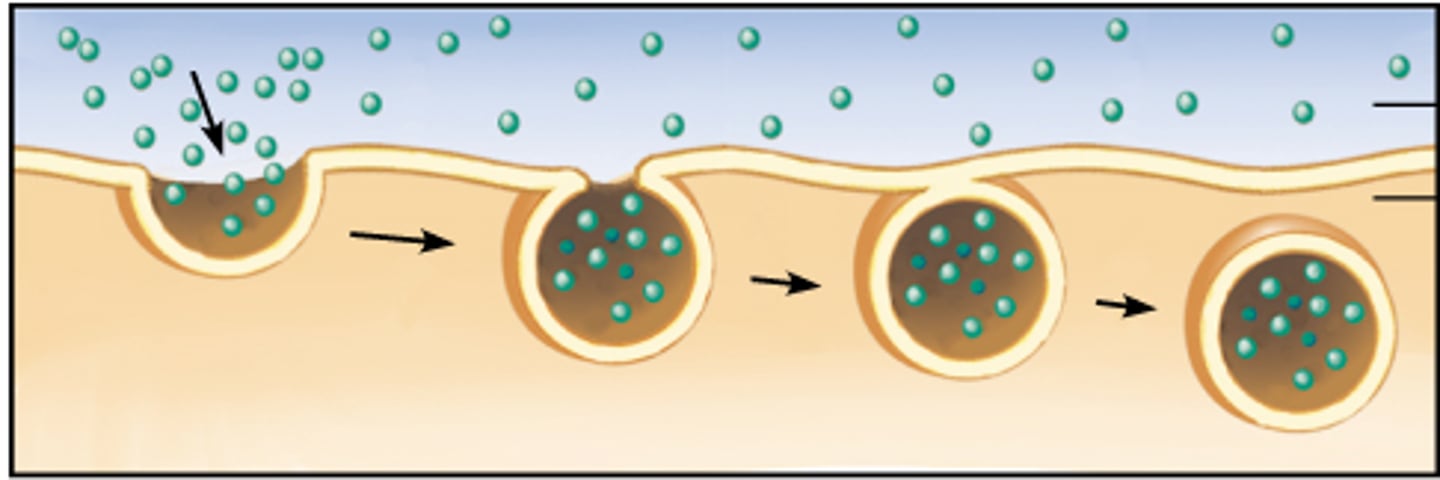
Endocytosis
Brings material into cell
Cell surrounds and encloses extracellular material. Vesicle then pinches off and is suspended in cell's cytoplasm
Phagocytosis
Cell eating, solids e.g., whit blood cells use phagocytosis to engulf bacteria
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking, liquids
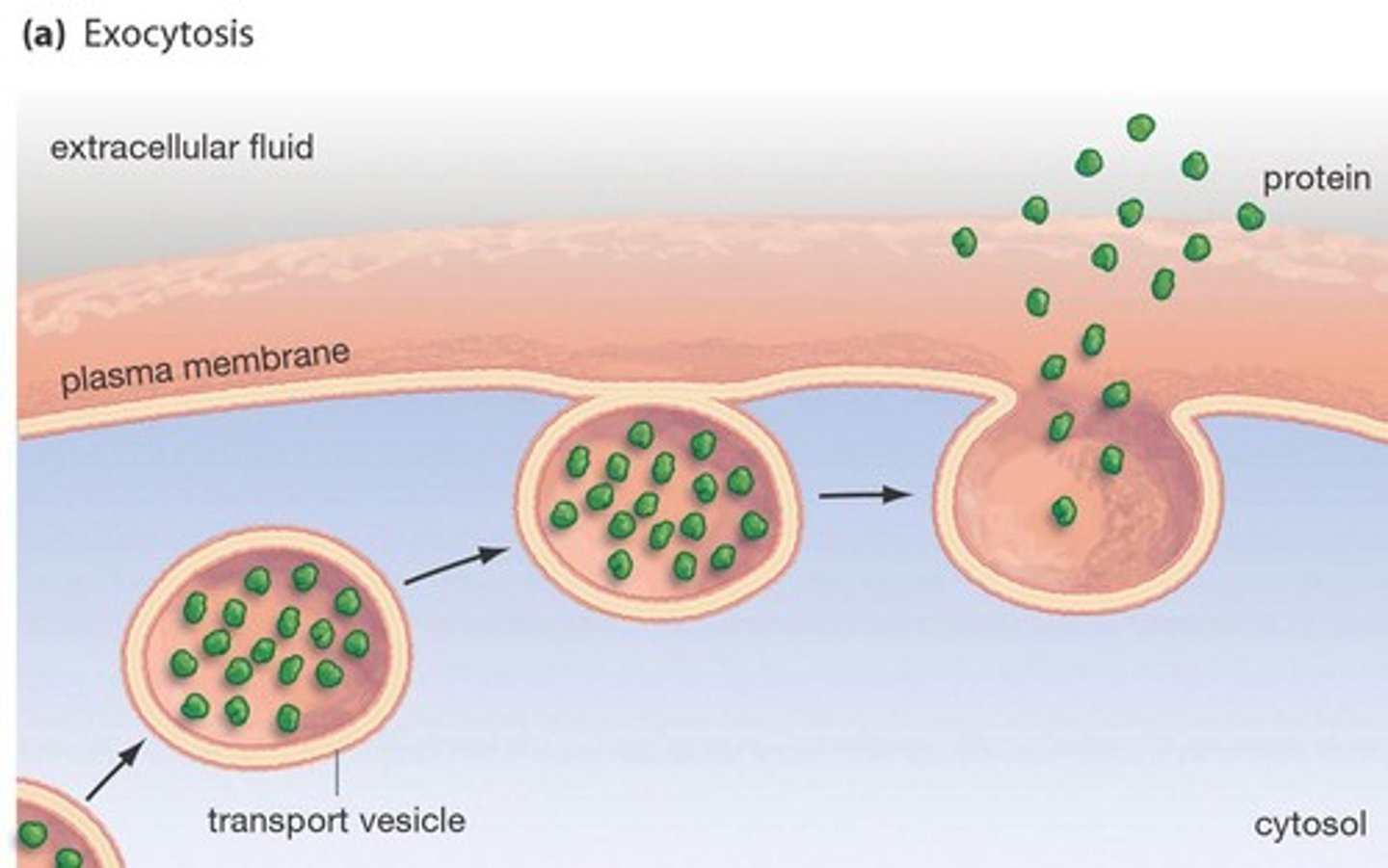
Exocytosis
Contents of vesicle are pushed out
Vesicle is formed inside the cell, migrates to the membrane and fuses with it, passing out the contents
Factors that affect the exchange of materials
- surface area to volume ratio
- concentration gradient
-physical and chemical nature of the materials being exchanged
Cell theory
all organisms are made of cells, which are the basic unit of life and arise from pre-existing cells
Cell membrane
- separate the intracellular fluid from the extracellular fluid
- made of phospholipid bilayer
- controls what enters and exits the cell
Nucleus
Contains genetic material, DNA
Nucleolus
- suspended in nucleoplasm
- role in protein synthesis, contains RNA
Nuclear membrane
separates nucleus from cytoplasm. contains pores for movement of molecules
Ribosomes
- site of protein synthesis, where amino acids are joined to make proteins
- most attached to endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
- pairs of parallel membranes that connect cell membrane with nuclear membrane
- provide surface for chemical reactions
- storage and transport of materials through channels
Golgi body/apparatus
- positioned near nucleus and surrounded by vesicles
- modify and package proteins in vesicles for secretion
- vesicles formed by endocytosis
Mitochondria
- release energy for the cell through cellular respiration (anaerobic and anaerobic)
- folds of the inner membrane produce large surface area
Lysosomes
contain enzymes that breakdown molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, as well as old organelles and materials not need in the cell
Functions of the cell membrane
- physical barrier
- regulates the passage of materials
- sensitive to changes
- helps support the cell
Functions of the cell membrane - physical barrier
separates the contents of the cell (intracellular) with the outside of the cell (extracellular) that have different compositions
Functions of the cell membrane - regulates the passage of materials
selectively/differentially permeable, controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell (maintains homeostasis)
Functions of the cell membrane - sensitive to changes
first part of the cell affected by any changes in the extracellular fluid (has receptors that are sensitive)
Functions of the cell membrane - helps support the cell
is attached to the cytoskeleton
Fluid mosaic model
Cell membrane structure
Fluid refers to the molecules which it is made up of are constantly changing position, and it is said to be mosaic because it is composed of many different kinds of molecules.
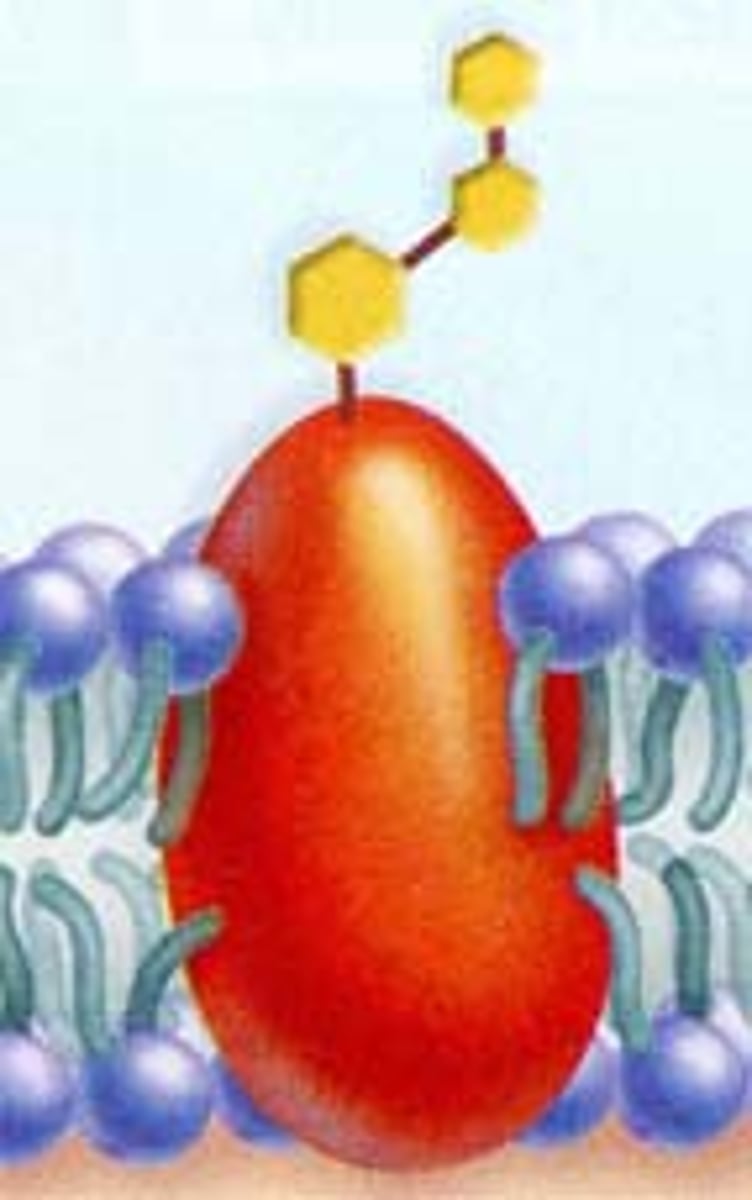
Proteins in the cell membrane
- channel proteins
- carrier proteins
- receptor proteins
- cell identity markers/recognition proteins
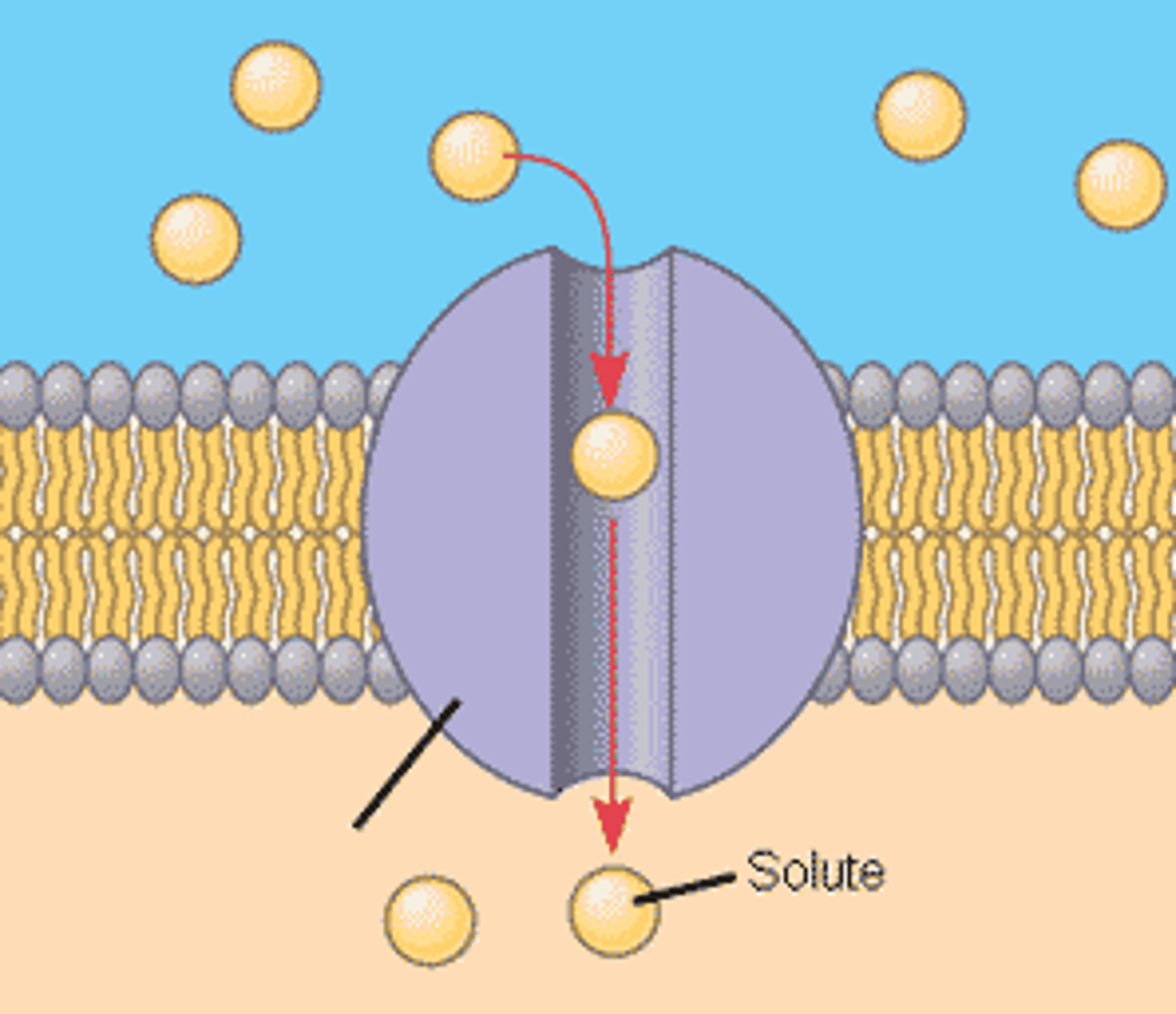
Channel proteins
form a channel through the membrane for smaller molecules to pass through, used for simple diffusion
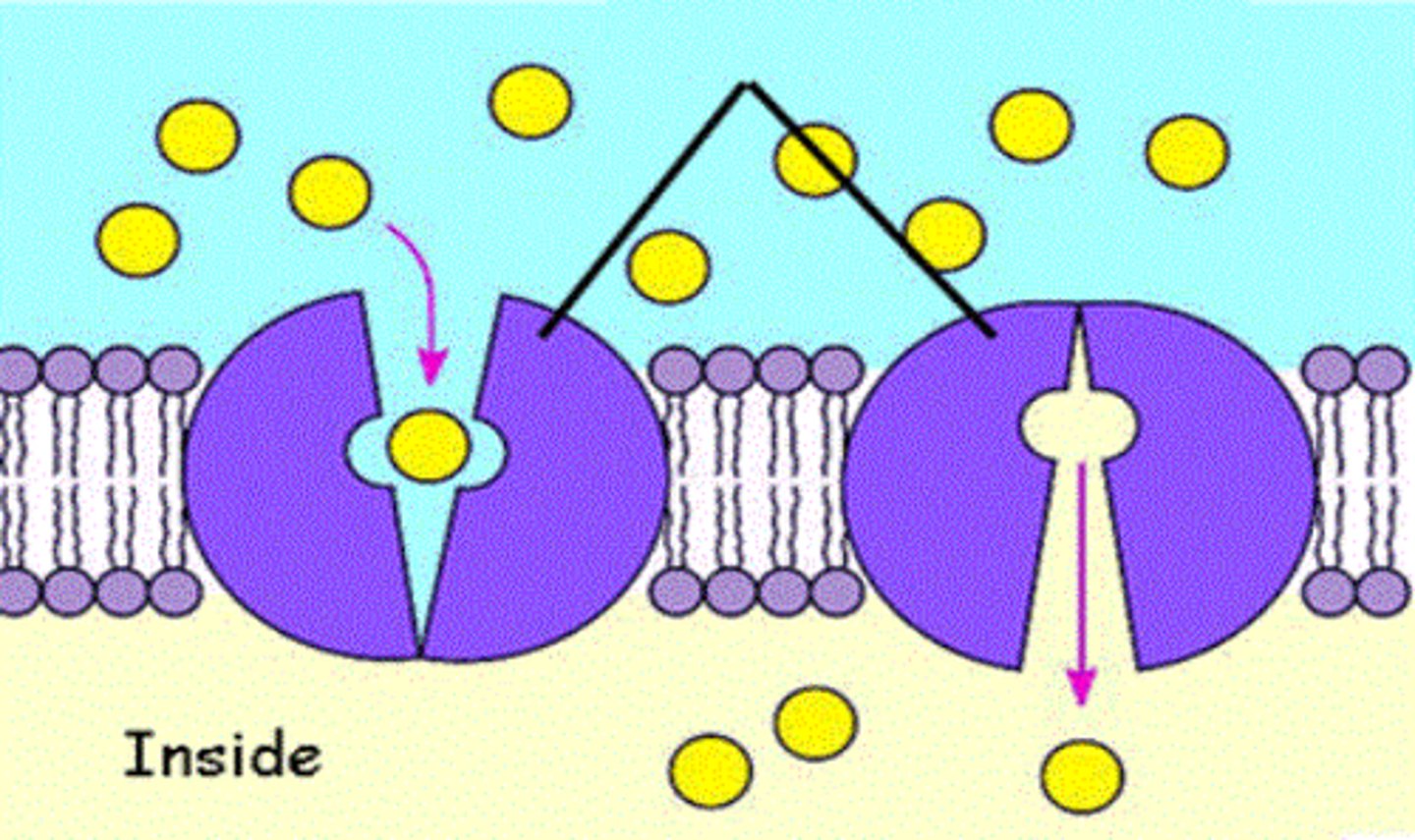
Carrier proteins
binds to larger molecules and help them move across the membrane, used for facilitated diffusion and active transport
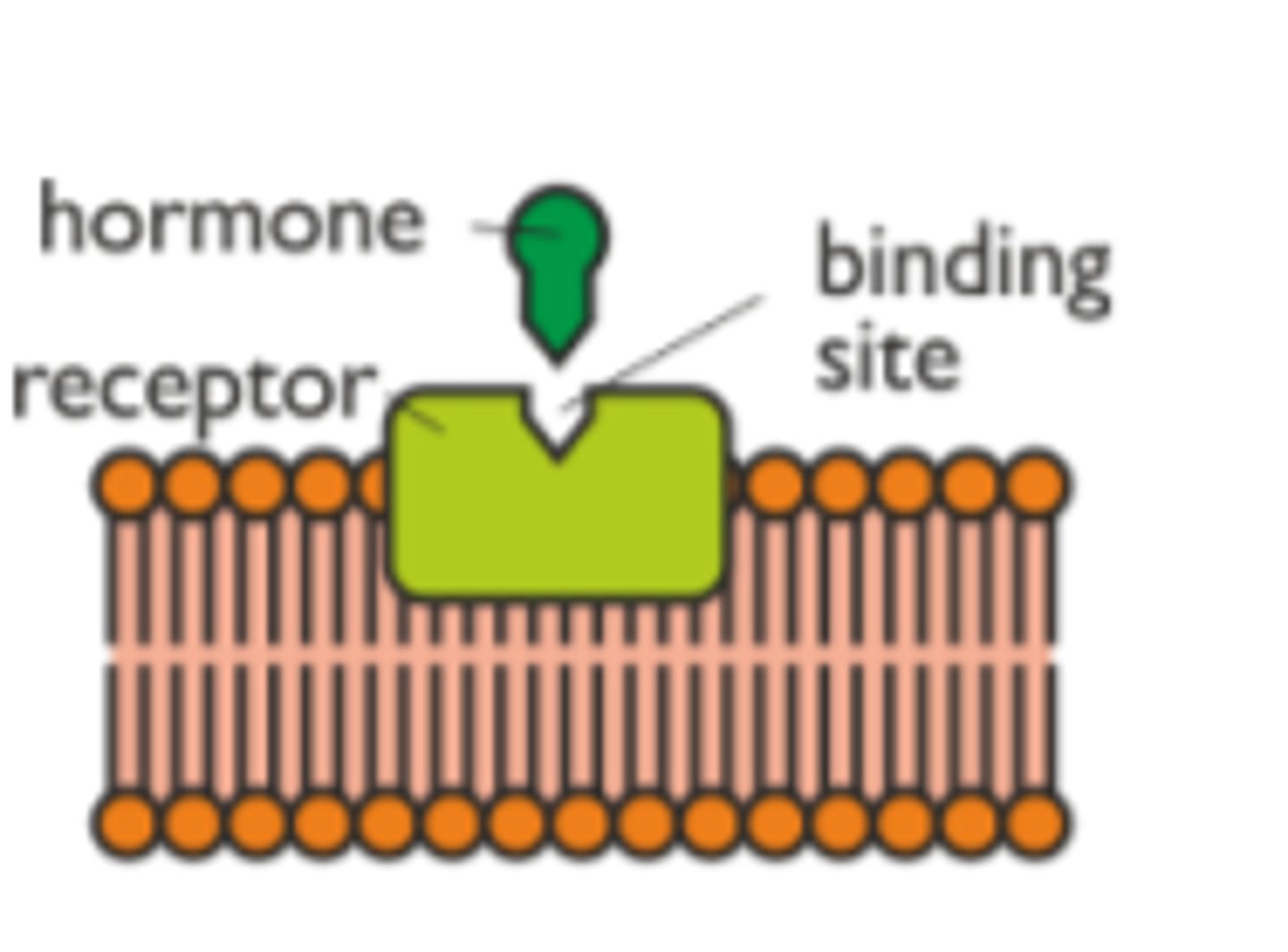
Receptor proteins
molecules outside the cell can bind to them o cause change within the cell
each type of receptor will only bind with one particular molecule - lock and key model
Recognition proteins
identifies the cell to prevent attack by the body's immune system
have a carbohydrate group projecting out of the cell which acts as ID tags, allowing the cell to be recognised
Types of tissue
- epithelial
- connective
- muscle
- nervous
What is a sarcomere made up of?
actin and myosin
How is oxygen carried?
3% dissolved in the plasma of blood
97% is attached to haemoglobin molecules in erythrocytes
What is oxyhaemoglobin?
Haemoglobin when bonded to oxygen
CO2 transport
7-8% dissolved in the plasma and carried as a solution
22% combines with the global part of the haemoglobin molecule to form Carbanimohaemoglobin
70% is carried in the plasma as Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-)
How is the Bicarbonate ion formed?
Result of COs reacting with H20 when it is diffused into the blood forming carbonic acid.
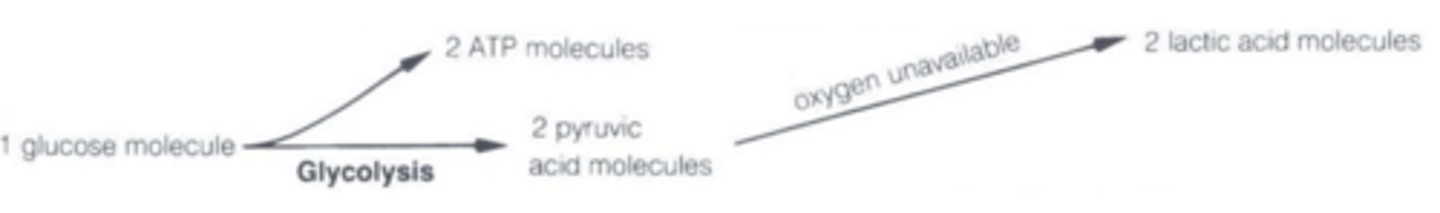
Anaerobic respiration equation
Aerobic respiration equation
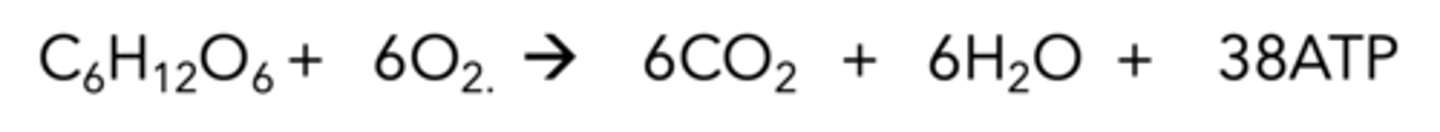
Cellular respiration equation
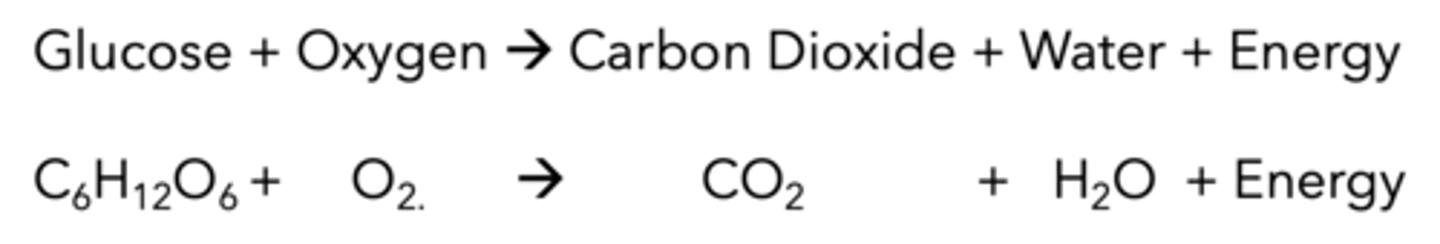
Metabolism definition
all the chemical reactions that take place in cells
Processes of metabolism
Catabolism
Anabolism
Catabolism
Breaks large molecules into smaller ones
- releases energy
- e.g., cellular respiration
Anabolism
Builds smaller molecules up into larger ones
- requires energy
- e.g., protein synthesis
6 groups of nutrients
- water
- carbohydrates
- lipids
- proteins
- minerals
- vitamins
What's a carbohydrate?
- Main source of energy for cells
- Made up of monosaccharides
What is a monosaccharide?
Simplest form of sugar
E.g., glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccarides
2 monosaccarides
E.g., sucrose, maltose, lactose
Polysaccarides
Many monosaccharides
E.g., glycogen, cellulose, starch
What's a protein?
Made up of many amino acids (100 or more).
Amino acids are made of peptide bonds
- dipeptide is 2 or more
- polypeptide is 10 or more
What's a lipid?
Broken down into fatty acids and glycerol
Includes fats and oils
Triglyceride of the most common fat that is stored in the body
Nucleic acids
Large molecules that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Phosphorus
Made up of nucleotides which have a nitrogen base, sugar and phosphate.
Provide no energy for the cell rather are essential in forming DNA and RNA
Inorganic compounds
- water
- minerals
- vitamins
Why is water important in metabolism?
It is the fluid in which other substances are dissolved. Some chemical reactions occur in water
Why are minerals important in metabolism?
They may be a part of enzymes, function as cofactors for enzymes or be a part of substances, such as adenosine triphosphate, that are involved in metabolism
Why are vitamins important in metabolism?
Act as coenzymes for many chemical reactions in metabolism
Ways energy is used by the cell
- Building complex molecules
- Cell division and growth (mitosis)
- Movement of organelles
- Movement of whole cell
- Maintaining cell organisation
- Active transport
- Transmission of nerve impulses
What is glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytosol
- First phase of the breakdown of glucose
- Does not require oxygen
- Forms 2 pyruvic acid molecules (pyruvate) and 2 ATP
- Larger molecule is being broken down (catabolism)
Blood clotting steps
1. Vasoconstriction of blood vessels
2. Platelet plug
3. Coagulation/blood clotting
First step of blood clotting - vasoconstriction of blood vessels
- smooth muscle in walls of small arteries that have been injured or broken constrict to reduce blood flow
Second step of blood clotting - platelet plug
- damage to the inside of the vessel walls causes them to become rough, causing platelets to stick
- sticking platelets attracts more platelets, building a plug
- platelets release substances that act as vasoconstrictors which enhance and prolong the constriction of the damaged vessels
Third step in blood clotting - coagulation
- formation of blood clot involves number of chemical suctances or clotting factors that are present in the plasma
- results in the formation of fibrin
- fibrin forms a mesh that traps blood cells, platelets and plasma
- is known as the clot or thrombus
After formation of the blood clot
- network of threads becomes denser which pulls the edges of the damaged vessel together
- known as clot retraction
- clear yellow fluid called serum is squeezed out of the cut
- clot dries and scab is formed over the wounds to prevent entry of infecting micro-organisms
Tissue of the heart
Cardiac muscle
What's the pericardium?
Membrane that holds the heart in place, allowing it to beat and preventing overstretching
Atrioventricular valves
Valves between the atria and ventricles.
Flaps of thin tissue held down by tendons called chordae tendinae and attach to the papillary muscles
Tricuspid and Mitral (bicuspid) valves
Where are red blood cells produced?
Red bone marrow
Lymphatic system main function
To collect the excess fluid that escapes the blood capillaries and return it to the circulatory system
How is lymph moved through lymphatic vessels?
Smooth muscle, skeletal muscle and valves
Smooth muscle contracts to push lymph along vessel
Skeletal muscles provide additional force by also contracting
Valves close when pressure drops to prevent back flow
Lymph nodes
1-25 mm bean shaped structures that occur at intervals along the lymph vessels
In the neck, armpits, groin, alimentary canal
Mastication
Process of chewing food, breaking it down into smaller particles
Semilunar valves
Prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles
Located at the start of the aorta and pulmonary artery
Pulmonary and Aortic valves
Functions of the circulatory system
- Transport of O2 and nutrients to cells
- Transport of CO2 and wastes away from cells
- Transport of chemical messengers (hormones)
- Maintain pH of body fluids
- Maintain body temperature
- Maintain water content and ion concentration
- Protect against disease causing microorganisms
- Clotting when blood vessels are damaged
Pulmonary Circulation
To the lungs to gain oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and then back to the heart
Systemic Circulation
Delivers oxygen to the rest of the body then takes waste CO2 back to the heart
Structure of erythrocytes
No nucleus
Circular and biconcave shape - flattened in the middle on both sides.
Flexible and increases surface area for oxygen to bind while still allowing room for haemoglobin molecules
Where are red blood cells destroyed?
Liver and spleen
Types of white blood cells
- Neutrophils
- Monocytes
- Lymphocytes
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
Neutrophils
Most common type of leucocytes, contains enzymes to digest pathogens
Monocytes
Form from other cells, including macrophages that engulf pathogens and aged or damaged cells by phagocytosis
Lymphocytes
Involved in immune response
Basophils
Responsible for allergic reactions, producing heparin and histamine to defend the body against parasites and bacteria
Eosinophils
Lead to inflammatory responses, they respond to larger parasites such as worms
Thrombocyte
Very small fragments of cells
Form a scaffold for the coagulation of the blood to form a clot in injured blood vessels
Artery structure
Smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Pressure in arteries
Is variable, increases as blood is pumped through artery and then decreases as the ventricles relax again