Optic Nerve
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
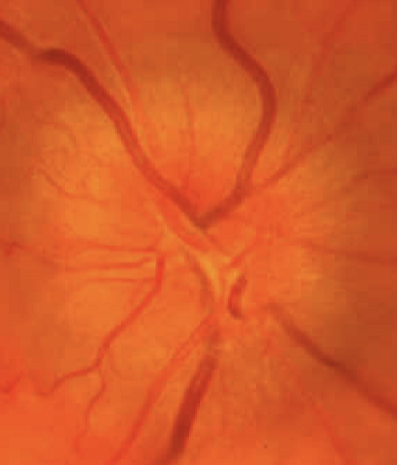
Optic Disc=nerve head
axons of the retina all converge here and exit the eye
1.5 in diameter
Retinal arteries and veins exit and enter here
Appearance of optic disc
Light yellowish-pink in color; nerve fiber layer is thickest just around the optic disc
What does the optic disk no contain?
photoreceptors
Physiologic cup
the depression in the center of the optic disc
Color is usually lighter than disc
Depth varies
Cup/disc ratio remains fairly stable in the absence of pathology
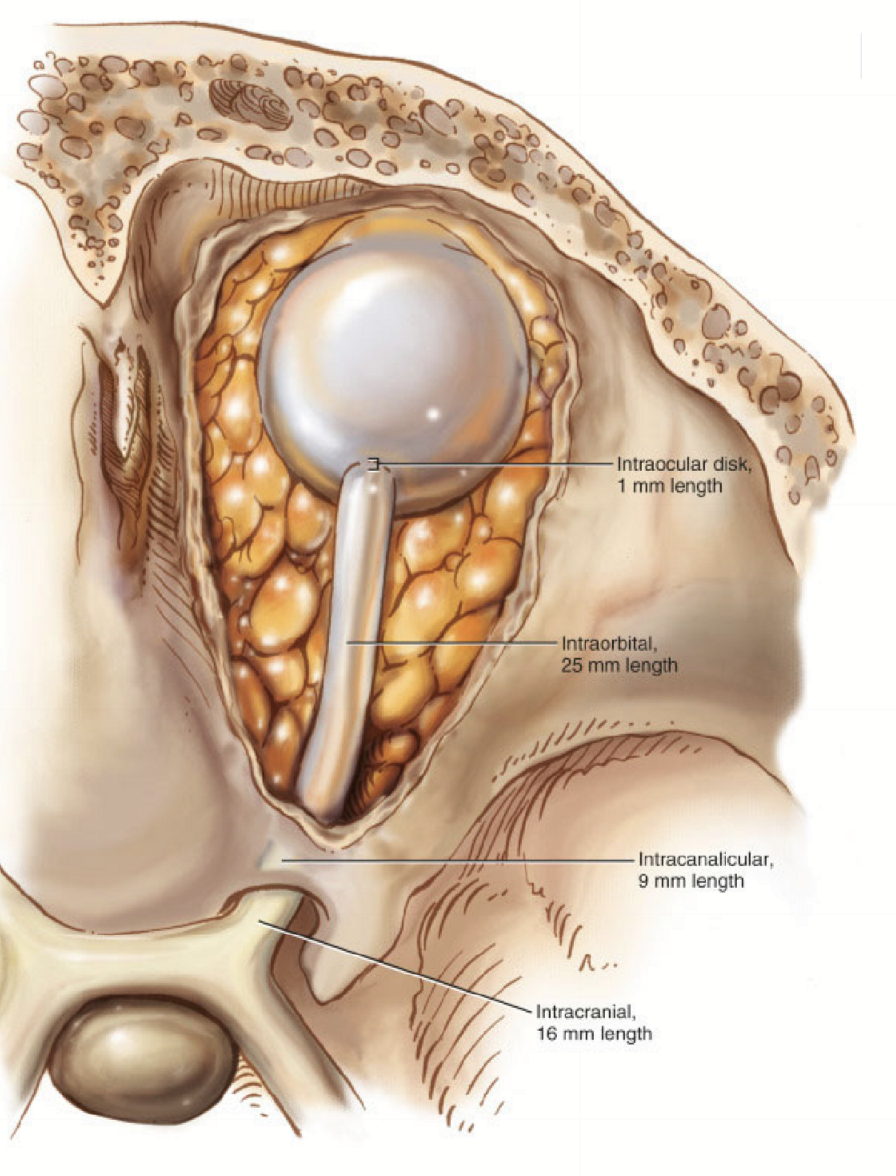
Nerve fibers sections:
intraocular
intraorbital
intracanalicular
intracranial
Where does most of the optic nerve fibers terminate at?
Lateral geniculate nucleus
Intraocular portion
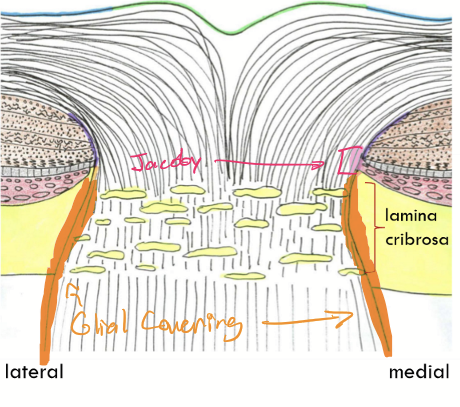
subdivided into three regions that are collectively referred to as the intraocular portion of the optic nerve
laminar region = lamina cribrosa = scleral fibers
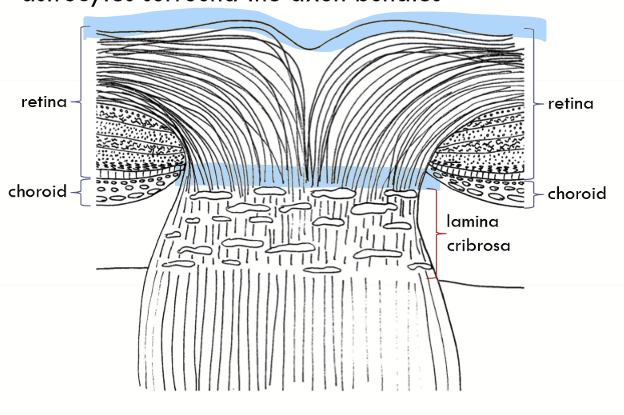
Prelaminar portion
the nerve head proper; astrocytes surround the axon bundles
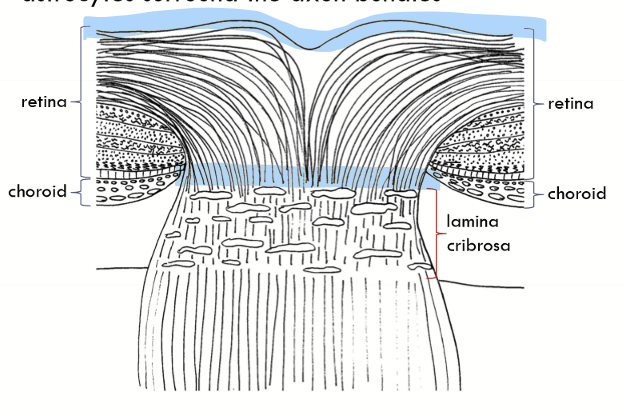
Postlaminar region
the first millimeter of the optic nerve just behind the eye;
axons bundles surrounded by more connective tissue;
Fewer astrocytes and more oligodendricytes
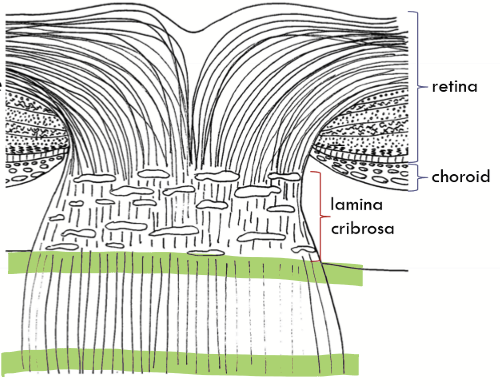
What do astrocytes divided the optic nerve from?
The blood retinal barrier from and the blood brain barrier
What does the sclera divide the optic nerve from?
the choroid (temporally)
Intermediary tissue of Kuhnt
composed of astrocytes; dividing line retina from optic nerve (purple area)
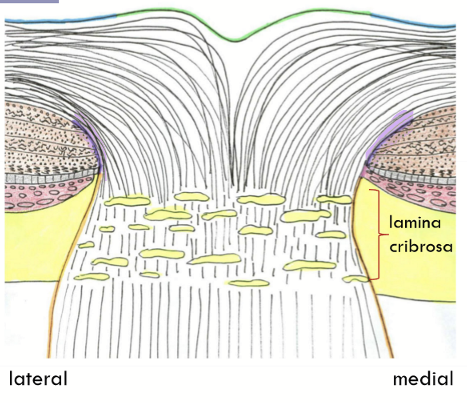
Border tissue of Jacoby
Found nasally only;
continuation of astrocyte covering;
glial covering continues the length of optic nerve
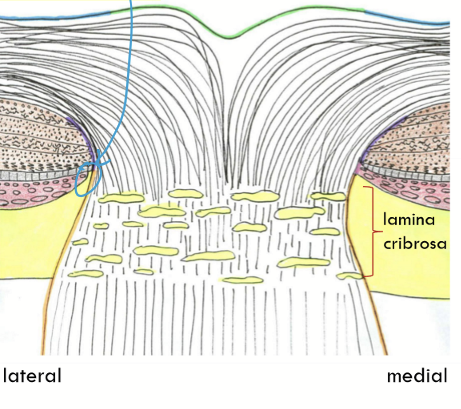
Marginal (border) tissue of Elsching
Found temporally only;
posterior termination of the choroid;
between the astrocytes surrounding the optic nerve and the stroma of the choroid
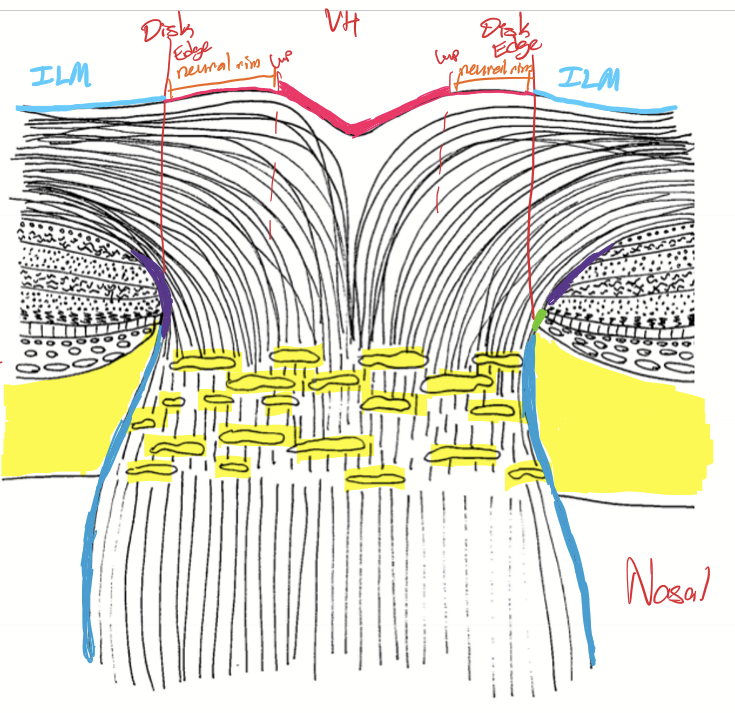
Internal limiting membrane of Elsching
Innermost covering of disk
Continuous with retinal internal limiting membrane
Contains the central meniscus of Kuhnt
Intraorbital optic nerve
extends to the apex of the orbit
surrounded by EOM, fat, and astrocytes
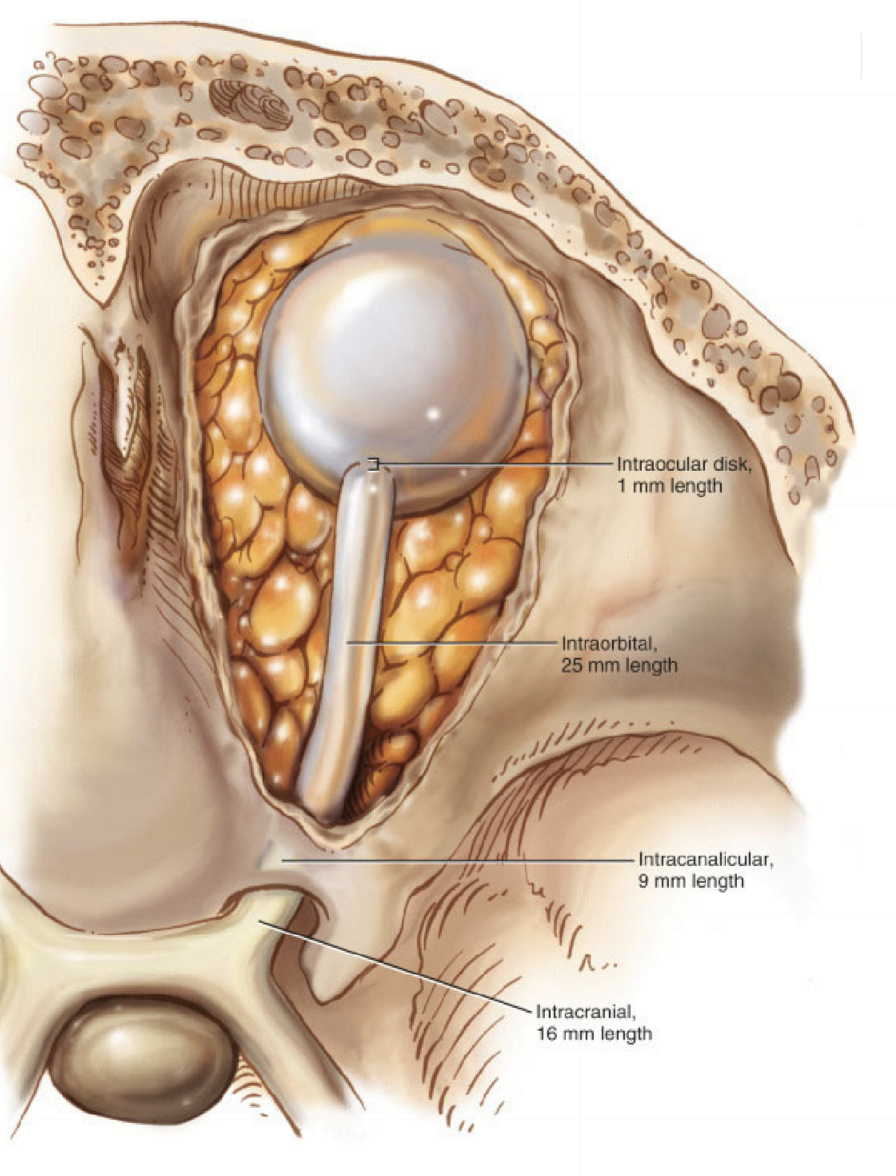
Intracranial Optic Nerve
The part of the optic nerve as it travels through the optic foramen
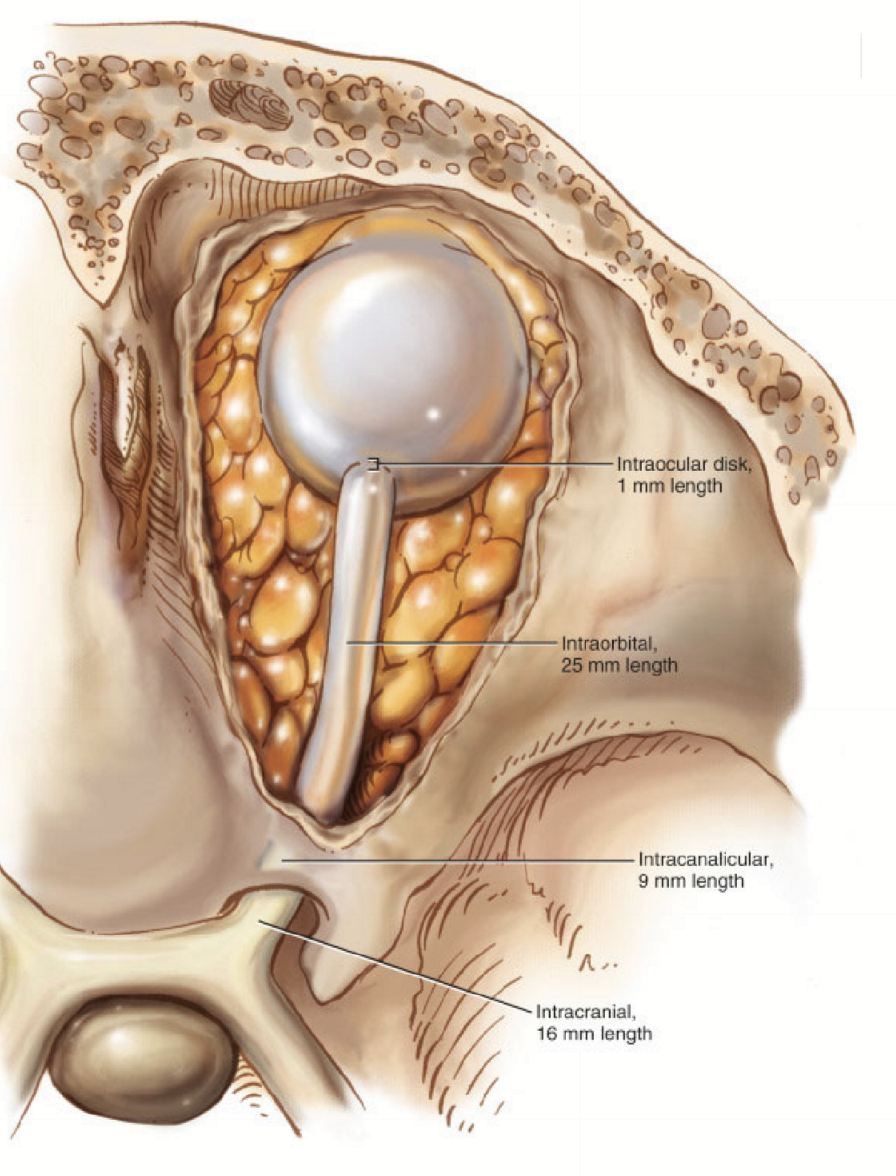
Intracranial optic nerve
From the optic foramen to the chiasm
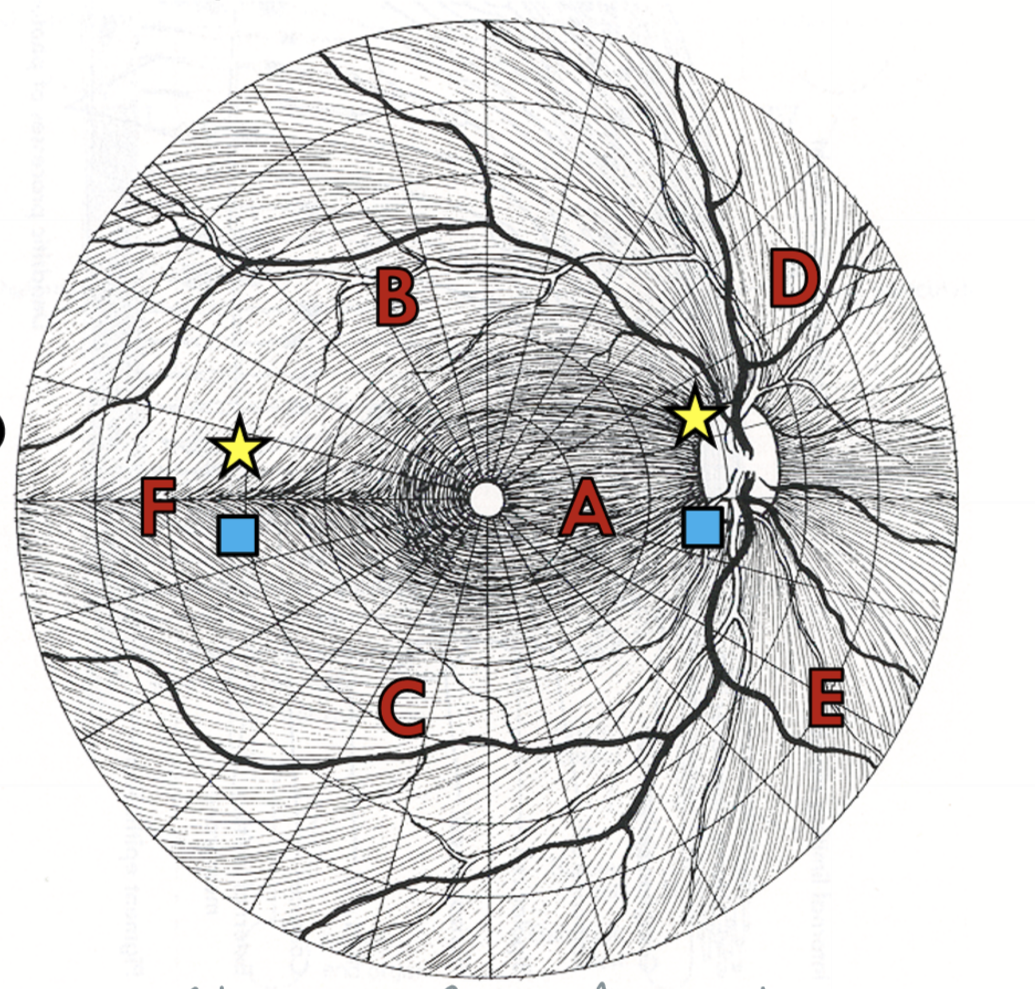
Nerve fiber orientation
maculopapillary bundle = between the macula and optic nerve (A)
superior arcuate fibers = fibers above the the horizontal raphe and macula (B)
Inferior arcuate fibers = fibers below the horizontal raphe and macula (C)
Superior radiating bundle = Nasally and superior to the optic nerve (D)
Inferior radiating bundle = Nasally and inferior to the optic nerve (E)
Horizontal raphe = F
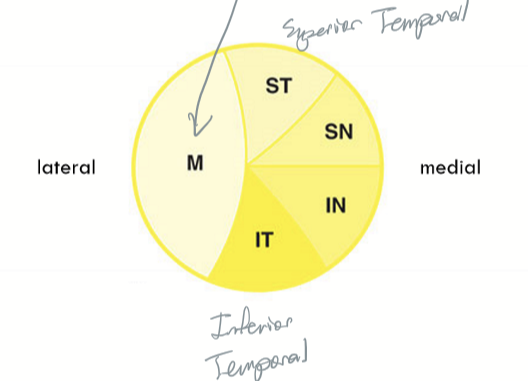
Optic nerve fiber orientation at optic disc
Maculopapillary fibers comprise of the temporal third of the optic disc
Optic nerve fiber orientation approaching optic chiasm
macula in the center, superior and inferior remain oriented correctly
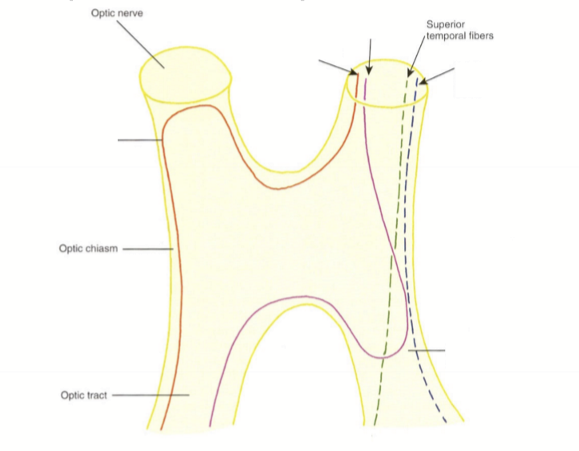
How does the superior temporal fibers enter and exit the optic chiasm?
They enter the anterior anterior chiasm temporally, pass through the chaism nasally, and exit the ipsilateral optic tract nasally
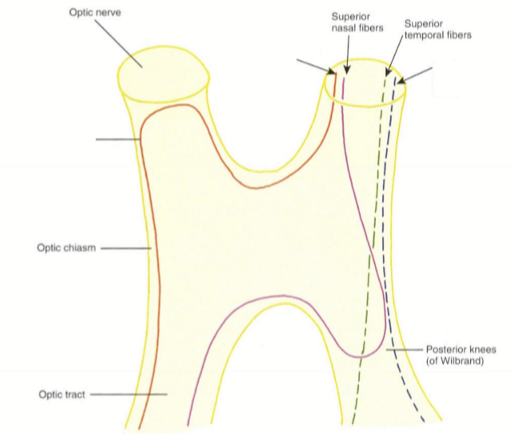
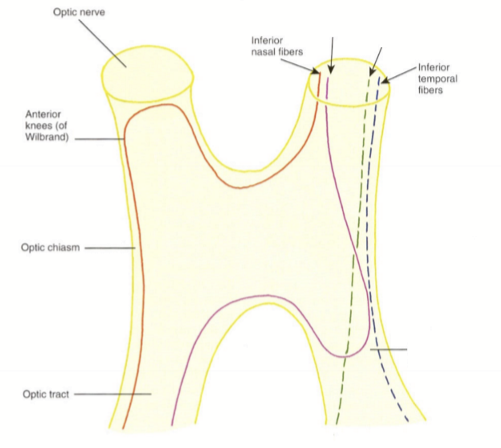
How does the superior nasal fibers enter and exit the optic chiasm?
They enter the anterior chiasm nasally, pass through the chiasm temporally, bend into the ipsilateral optic tract (forming posterior knees of Wilbrand) and then exit the contralateral optic tract nasally
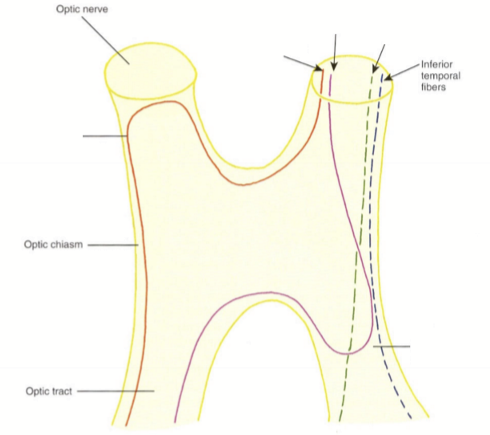
How does the inferior temporal fibers enter and exit the optic chiasm?
They enter the anterior chiasm temporally, pass through the chiasm temporally, and exit the ipsilateral optic tract temporally
How does the inferior nasal fibers enter and exit the optic chiasm?
They enter the anterior chiasm nasally, cross into the opposite side of the chiasm (bending into the terminal end of the contralaterla optic nerve to form the anterior knees of Wilbrand) pass through the opposite side of the chaism temporally, and exit the contralateral optic tract temporally
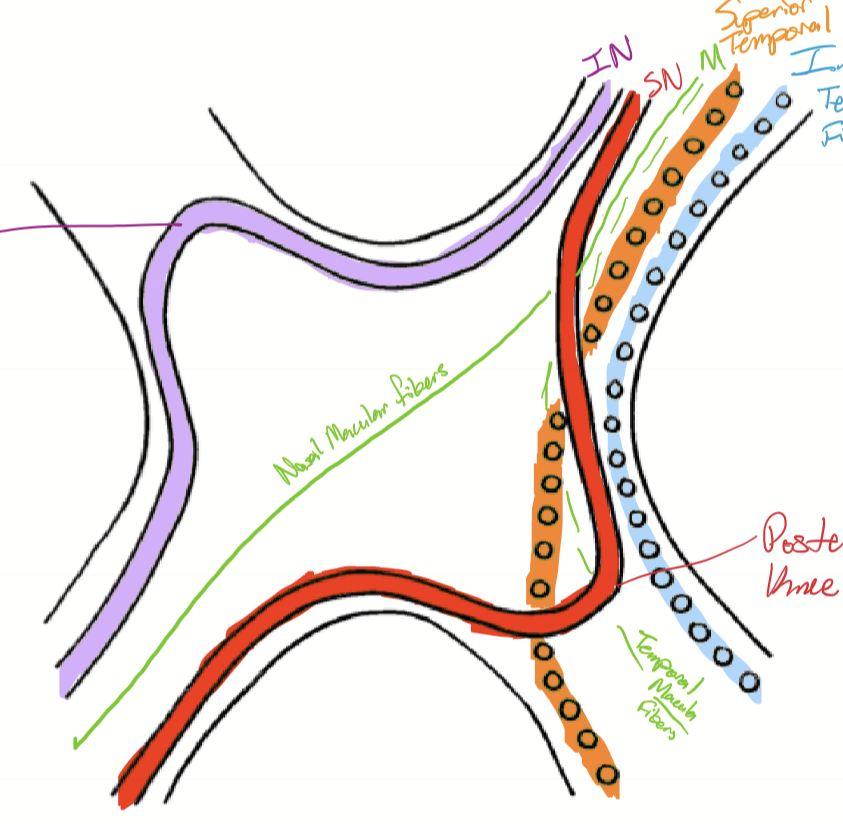
How does the nasal macular fibers enter and exit the optic chaism?
They enter the anterior chiasm centrally, and cross to the other side of the optic chiasm, entering the contralateral optic tract centrally. The fibers merge with superior and inferior temporal fibers.
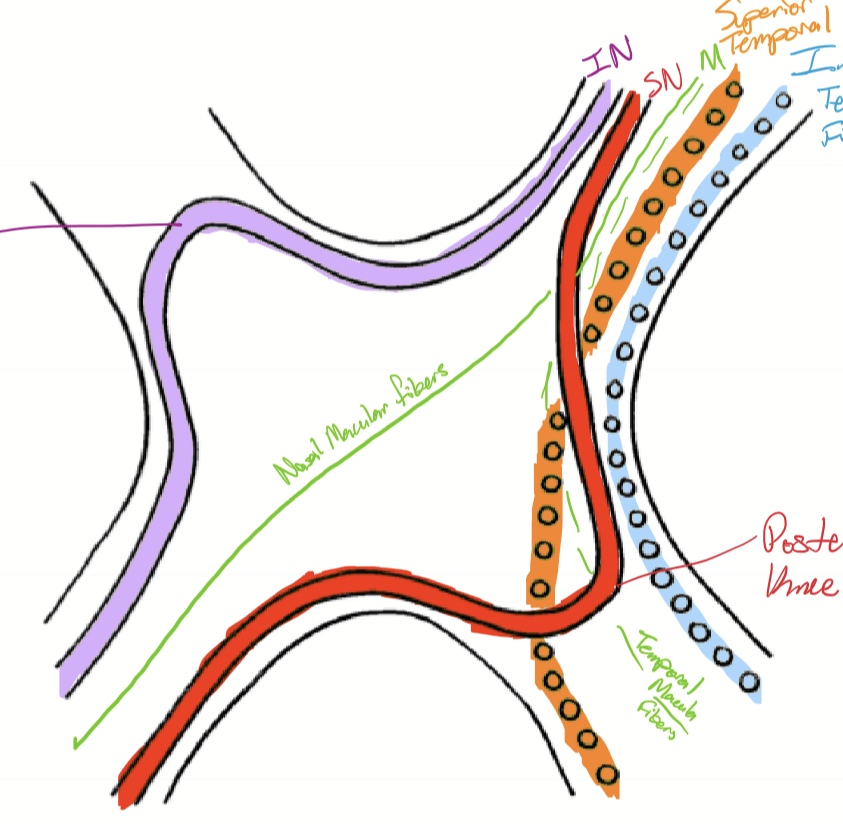
How does the temporal macula fibers enter and exit the optic chaism?
They enter the anterior chiasm centrally, and exit the chiasm on the ipsilateral optic tract centrally. The fibers cross the superior-posterior aspect of the chiasm before exiting the contralateral optic tract.
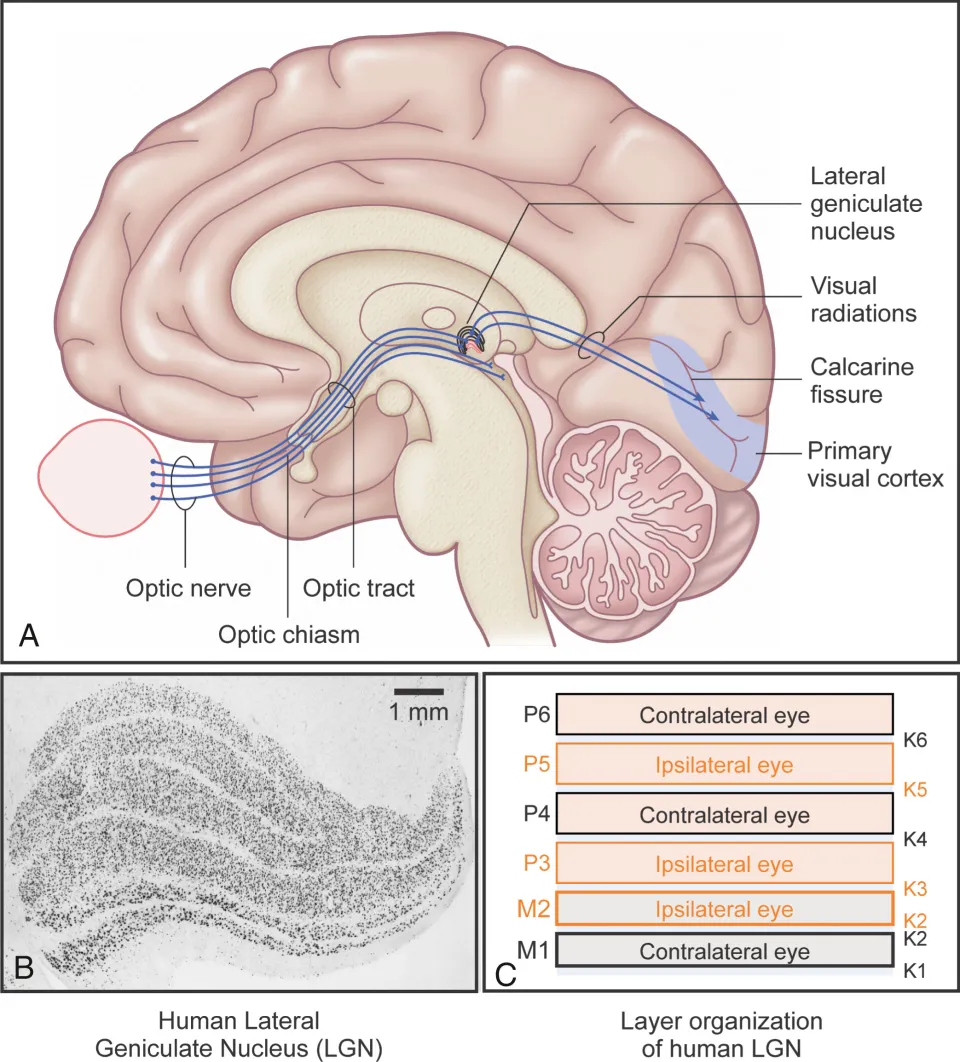
What does each optic tract contain?
the ipsilateral temporal fibers and the contralateral nasal fibers.
Where does most of the optic tract fibers terminate at?
most continue to the lateral geniculate nuceus (LGN), with some fibers leaving prior to the LGN.
Optic nerve sheath isa continuous with what part of the brain?
the meningeal sheaths of the brain
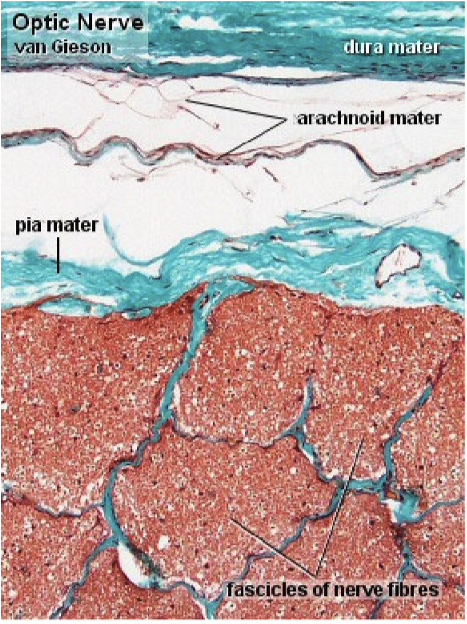
What are the layers of the optic nerve sheath?
Dura mater
external layer
fuses with outer layers of sclera and Tenon’s capsule
Arachnoid mater (LCT Matrix)
Pia mater
thin and vascular, lots of astrocytes
Subarachnoid space
continuous with sub-arachnoid space of brain
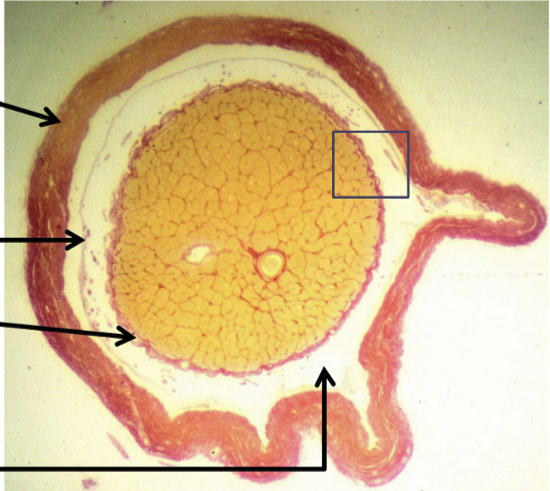
How are the optic nerve fibers organized?
Organized into fascicles:
Anterior to lamina cribrosa
fascicles surrounded by astrocyte from neuroglial sheath surrounding optic nerve
Posterior to lamina cribrosa
additional layer of CT sheath is added
nerve fibers become myelinated
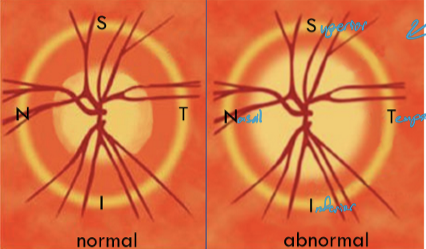
Papilledema is caused by what?
an increase intracranial pressure, resulting in edema of disc. Is an urgent situation
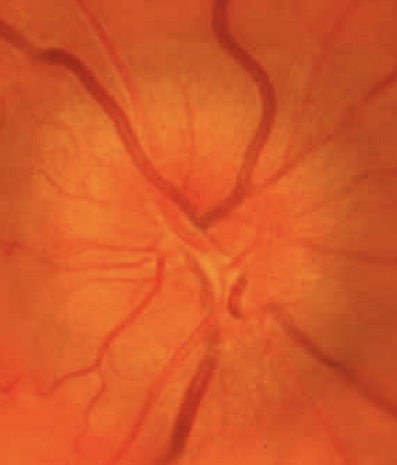
How does the papilledema appear?
elevated disc
margins blurred
loss of physiologic cup