APAH: Ancient Greece
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
essential knowledge of Greek art
Greek art is characterized by a pantheon (more than one) of gods celebrated in large civic and religious buildings
Much ancient writing survives in the fields of literature law, politics, and business. These documents shed light on Greek civilization as a whole and on Greek art in particular.
greek art is studied chronologically according to changes in style
greek works are not studied according to dynastic rule, as in Egypt, but according to broad changes in stylistic patterns
greek art is most known for its idealization and harmonic proportions both in sculpture and in architecture
greek art has had an important impact on European art and architecture
greeks are a seafaring culture, will take over Mesopotamia and Egypt
gods serve as showing bad behavior, as what not to do
greeks traded heavily with Egypt
democracy comes out of Greece
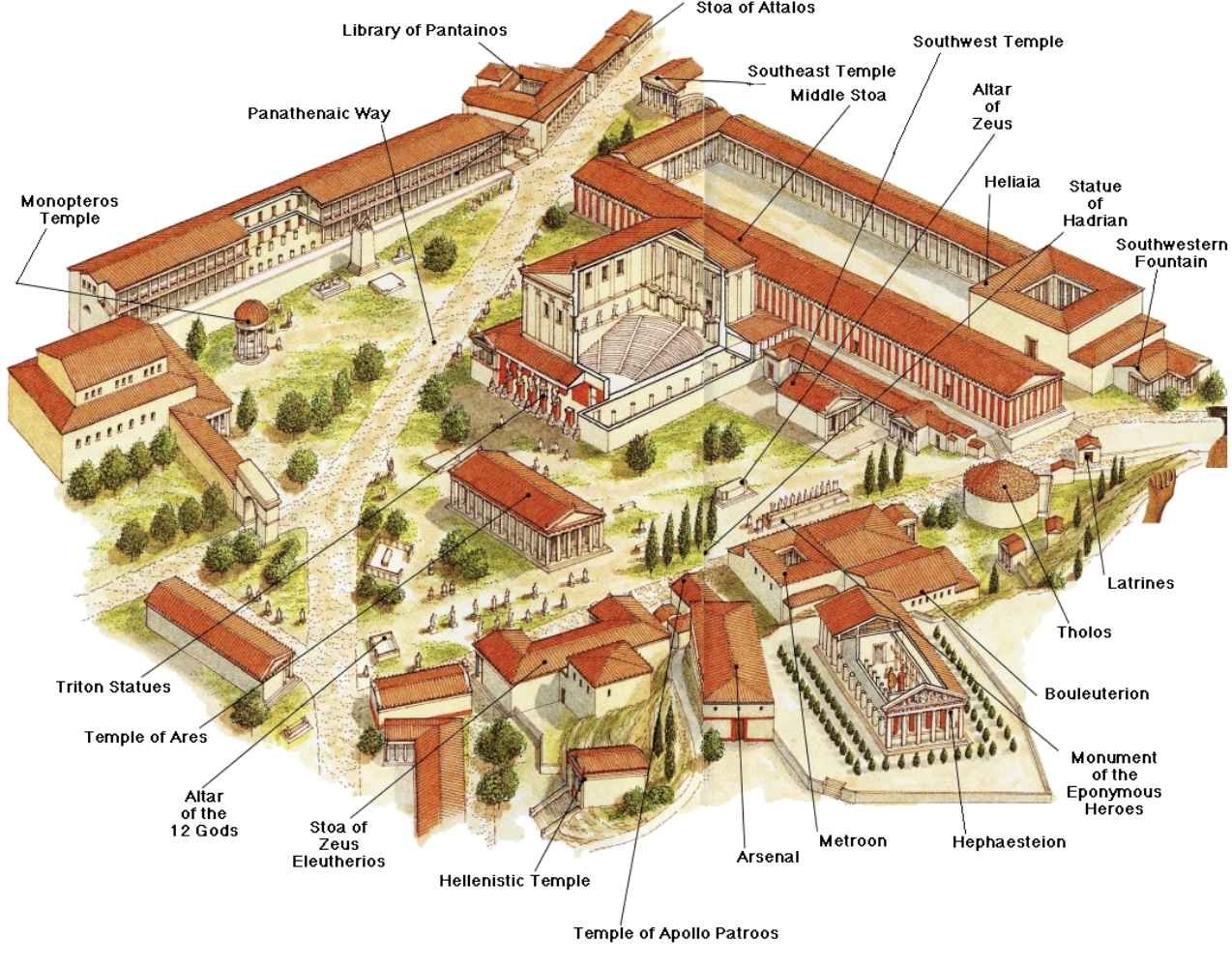
Athenian Agora:
limestone
first multifunction (plaza and city) center for people to meet (place for the people = democracy
setting for Panathenaic festivals and many altars for other greek gods
once a year all citizens held a parade, entering at the Dipylon Gate, walking up the holy side (Acropolis; sacred space) to give the statue of Athena a new garment (peplos) on her birthday
plaza was surrounded by a bouleterion (city hall) used by council, tholos temples (round temples/gazebos) and stoas (covered walkways with columns on one side and a wall on on the other)
rebuilt and remodeled numerous time across many periods
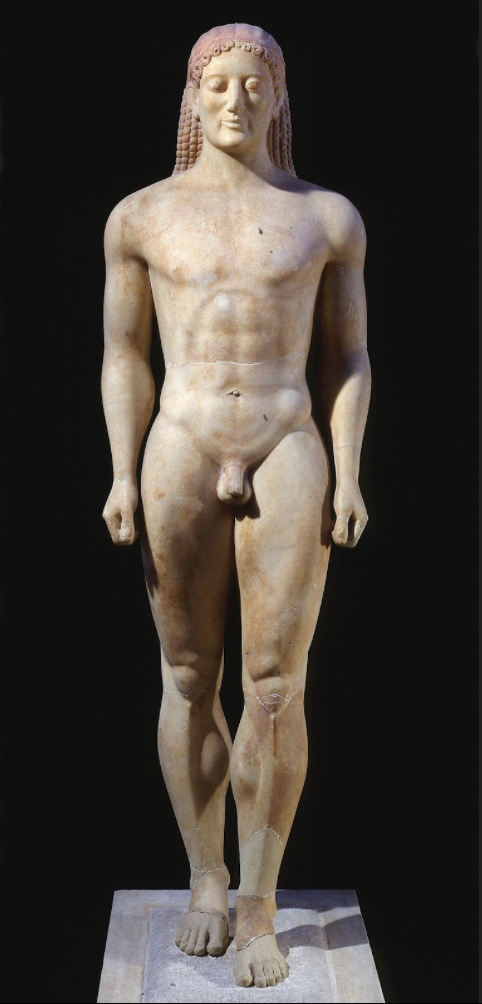

Anavysos Kouros: (Archaic)
marble and paint (was brightly painted)
heavily appropriates from Egyptian sculpture (square shoulders, 1 step forward)
funerary; a grave marker for a young man killed in battle
not a portrait; idealization of an ideal warrior
kouros: naked youth
rigidly frontal
idealizing democracy and sacrifice, not idealizing rich pharaohs in Egypt
“Archaic Smile”
Athens

Peplos Kore: (Archaic)
marble and paint (was brightly painted)
not funerary; hand appearing out of sleeve was some sort of tribute or offering
peplos is the garment she’s wearing
breaks mold of archaic statuary with arm extending away from body
may have been representation of a goddess due to extended arm
Artemis (bow and arrow) or Athena
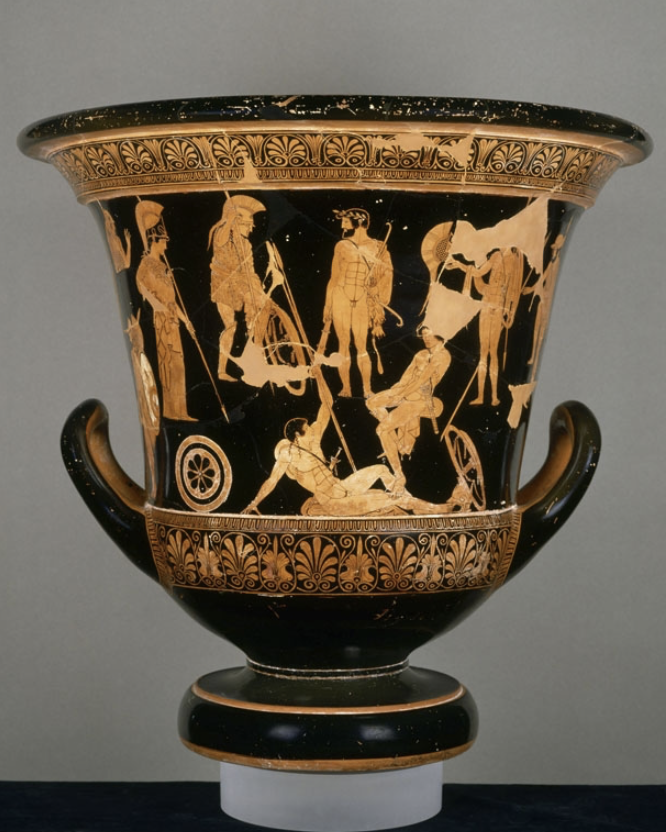

Niobides Krater: (Classical)
clay
found in Italy, showing greek trade
first time in greek vase paintings that the heads of the figures are not on the same level
Archaic: black figure technique (large figures in black on the natural red surface of clay)
Classical: Anokides introduces red figure technique (vases painted black and natural red surface of clay depicted the figures)
greek myth of killing of Niobi’s children
Niobi bragged about her fertility with 7 daughters and 7 sons
Leto heard the bragging, used her only two children (Artemis and Apollo) to kill Niobi’s children
other side could be Hercules surrounded by heroes and Athena, or warriors of Marathon placing themself under Hercules’ protection
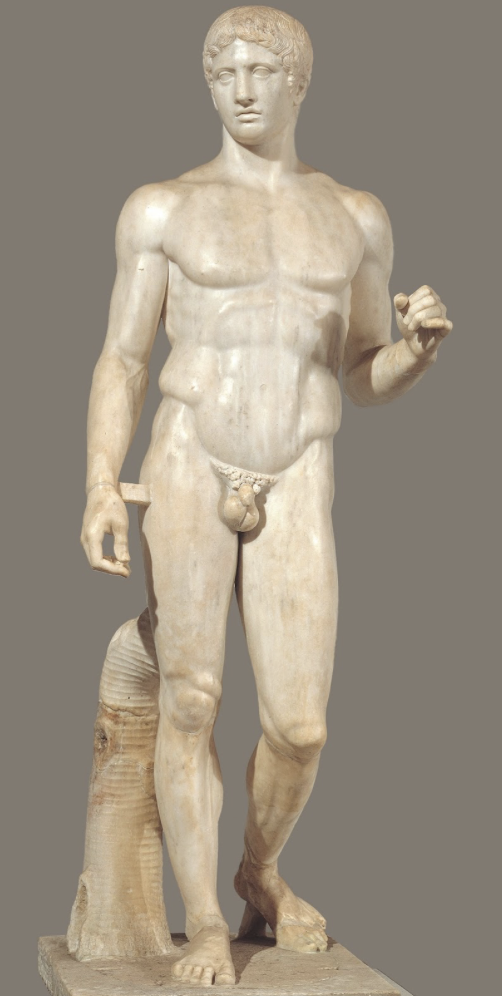

Doryphoros (Spear Bearer): (Classical)
Polykleitos
Polykleitos made formula for human form: The Canon (based on Phythagoras)
roman marble copy of a greek bronze original
lost wax technique:
forms sculpture with wax, puts it in a box open at the top, box filled with plaster, wax inside melted, then turn plaster upside down to fill with bronze
distinct from Archaic for being more nature with contrapposto pose (putting our weight on one side then switching to the other)
considered ideal male form by Spartans (warrior + athlete)
found in Pompeii in an athletic/recreational complex (people would work out and aspire for his perfect figure)
held spear in left hand
not intended to look at the viewer (stoic and contemplative)
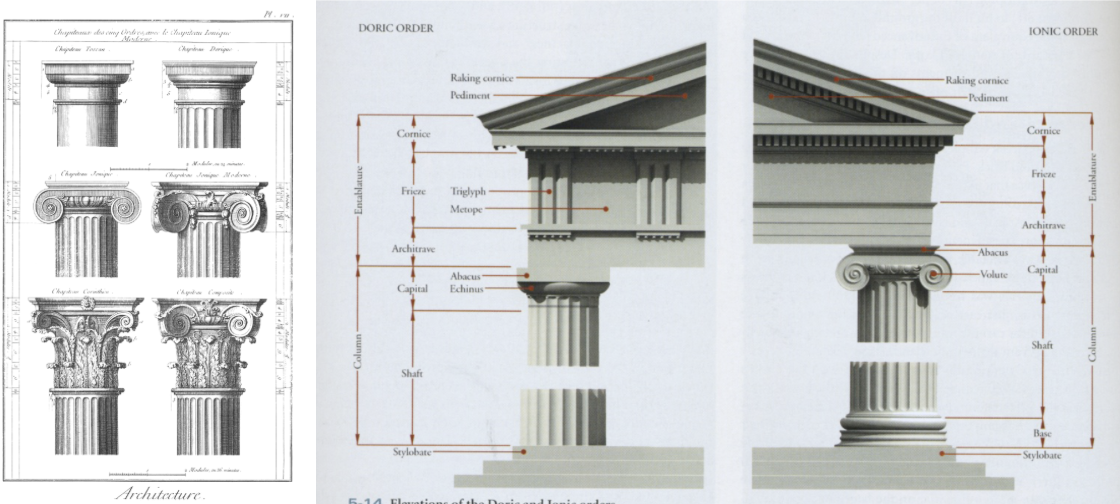
Greek architecture (capitals + structure)
Doric/Tuscan: top row
most strong
fluting: indents in columns
frieze: three long stones → metope (image telling a story) → three more stones…
Ionic: second row
looks like a scroll
smooth frieze, no metope or stones
Corinthian: last row
least strong
most decorative
stylobate: foundation of building (could be stairs)
pediment: triangle roof-top
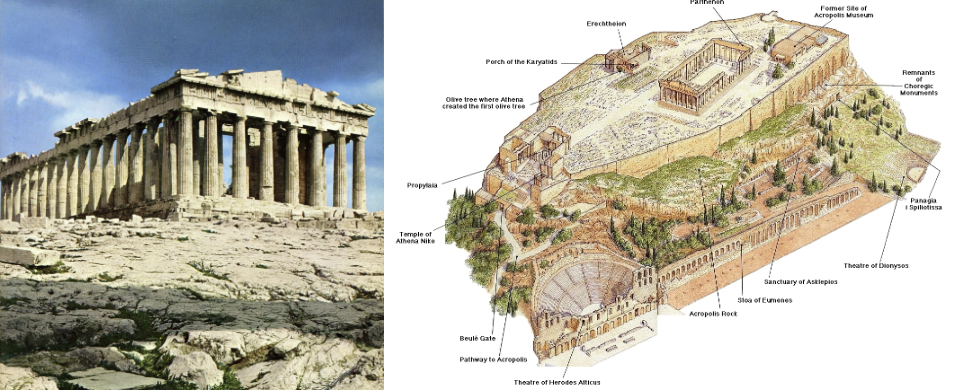
Acropolis/Parthenon: (Athenian Agora; Classical)
Marble
1st sacred space in Europe (hypostyle hall)
interior has ionic order (built later), outside is doric order
architects: Iktinos (made doric) and Kallikrates (made ionic)
patron: citizens of Athens through leadership of Pericles
originally built in archaic, destroyed when Persians sacked Athens
Delian League: Pericles used funds donated by all greek city states incase Persians returned
cela had massive gold and ivory statue of Athena that is lost
greeks skilled at geometry and algebra, shown in design of Parthenon (to connect with the divine)
no right angles
when ottomans took over Greece they blew apart the inside
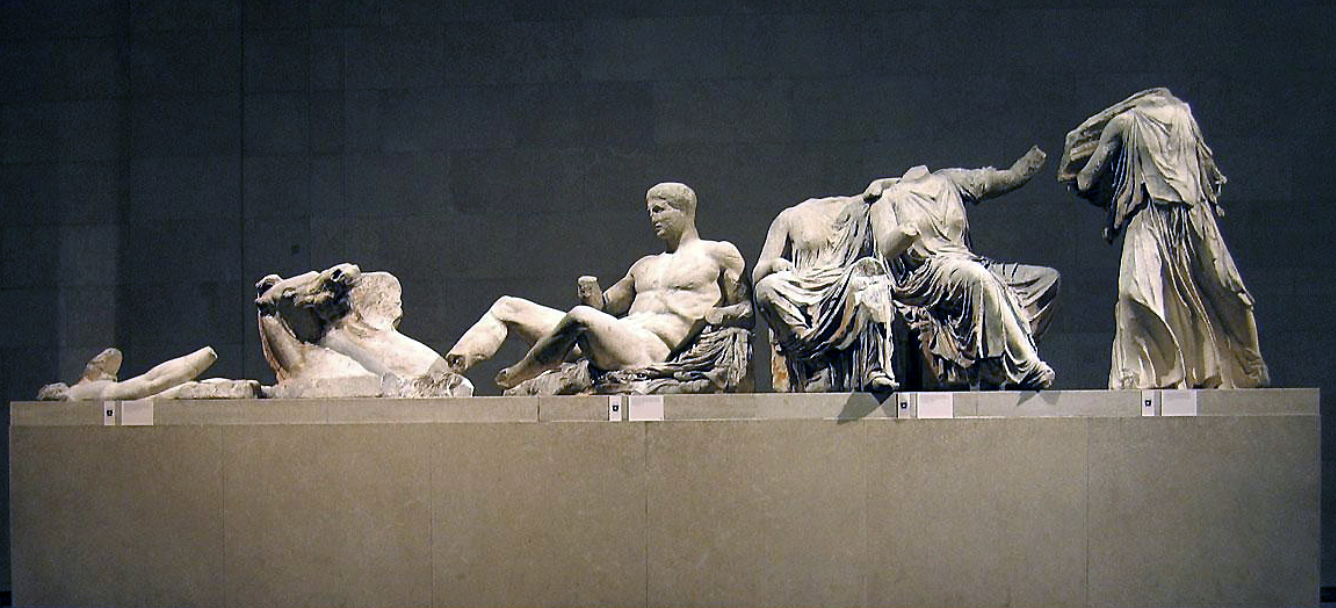

Helios, Horses, and Dionysos: (Parthenon; Classical)
east pediment of the Parthenon
marble
may have been sculpted by Phidias
story of birth of Athena
born from the head of Zeus, other deities are watching
Dionysus: god of wine and leisure (bachelor, unmarried man)
seated figures: goddesses Demeter and Persephone
numerous contrapposto poses
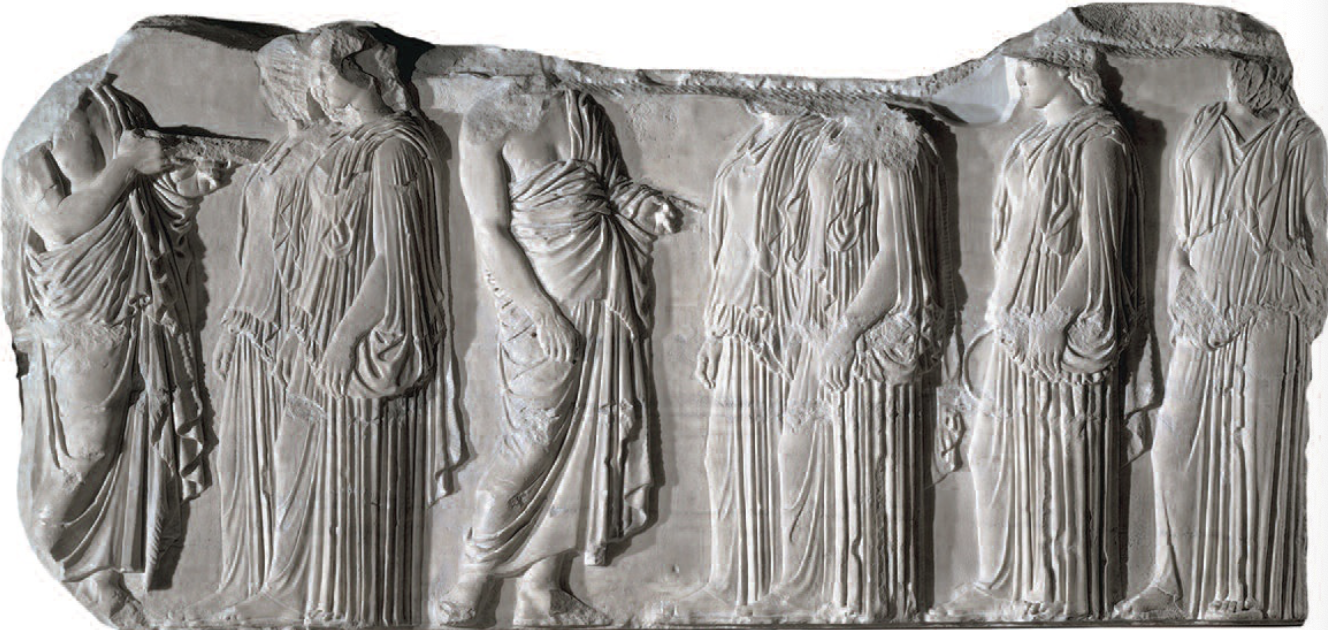

Plaque of Ergastines: (Parthenon; Classical)
portion of inner ionic frieze of the Parthenon
marble
depicts Panathenaic Procession held every year to honor Athena
in the procession the people of Athens enter at the Dipylon Gate and end at Athena, giving her a new peplos
Ergastines: women in Athens who wove Athena’s peplos
unique: human event (not deities) shown in the temple
depicting six Ergastines greeted by two priests
Isocephalism: all the heads are at the same level
viewed from the floor; figures become more three dimensional at higher parts of the relief
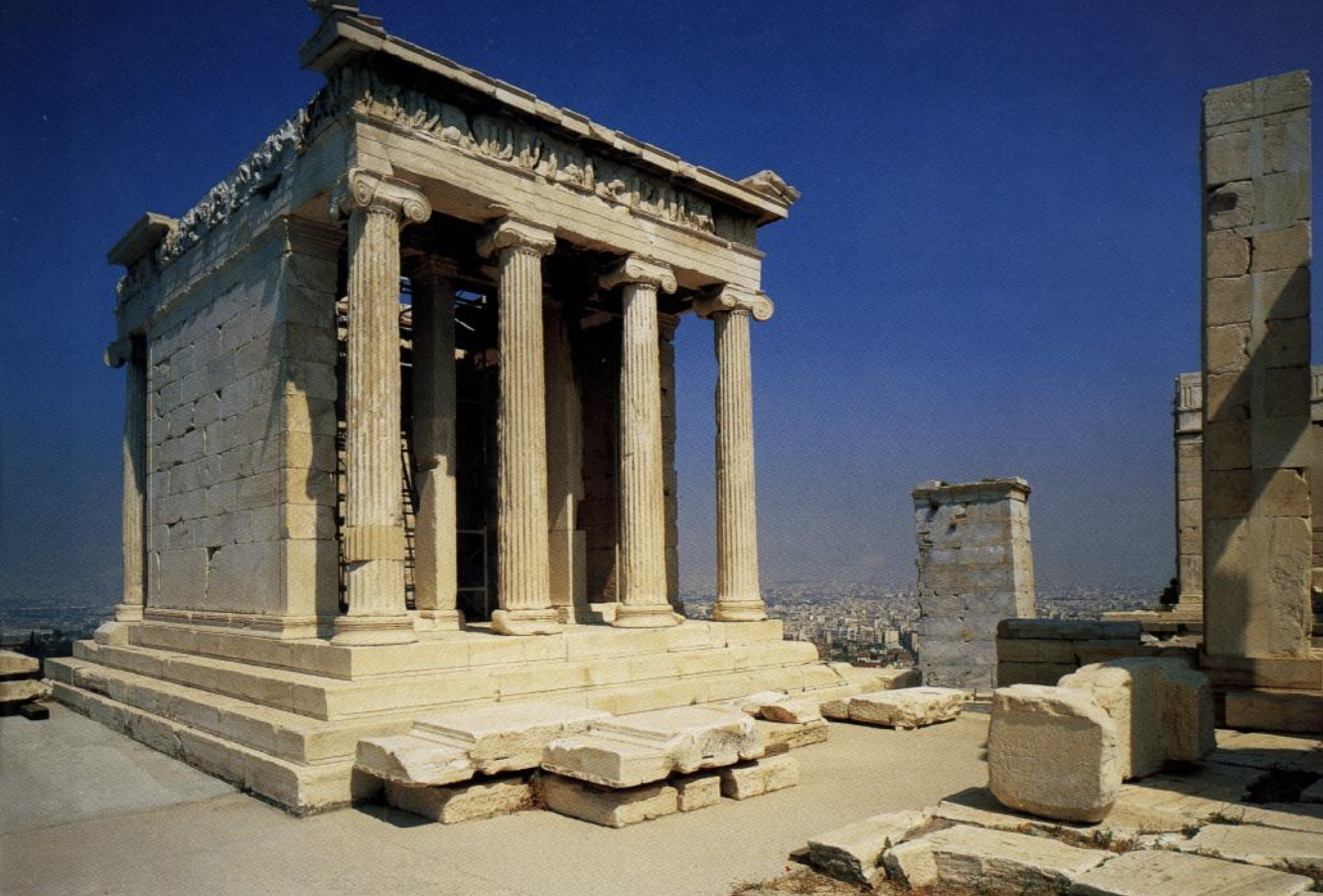

Temple of Athena: (Parthenon; Classical)
Kalikrates
Marble
At Acropolis to commemorate the “victory” over the Persians in the Battle of Marathon
Ionic period was firmly in place, columns and frieze (built when Parthenon was finished or close to)
Inside is a wood sculpture of Athena, dressed in new peplos in Panathenaic procession
many sculptures of Nike (victory)
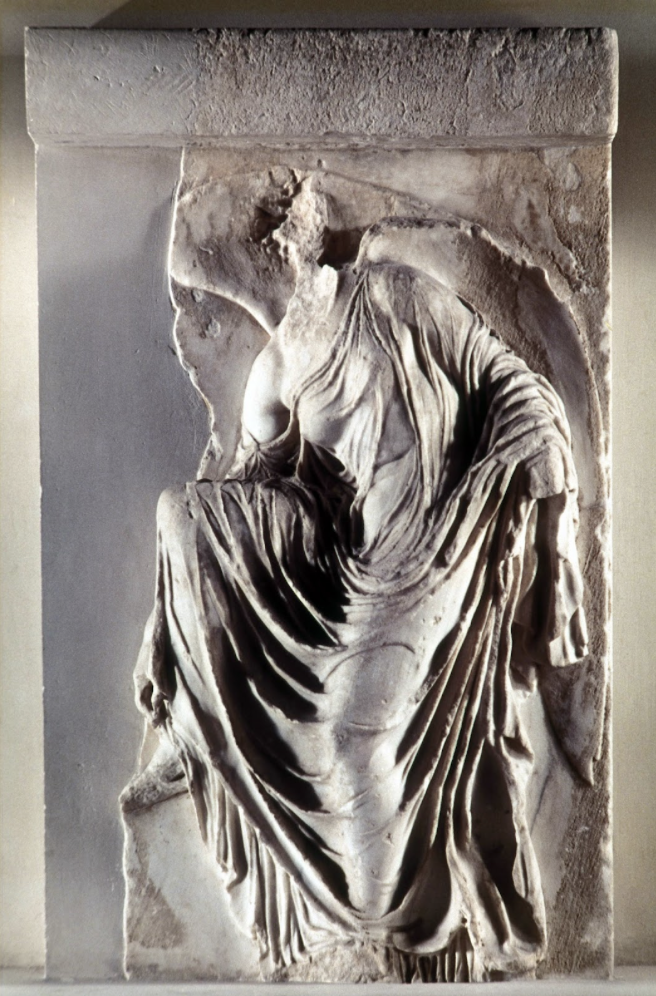

Nike Adjusting her Sandal: (Temple of Athena; Parthenon; Classical)
marble
high relief
very deep drapery, looks as wet, revealing the body
embodies characteristics of Classical sculpture
her balance is achieved through exaggerated contrapposto pose
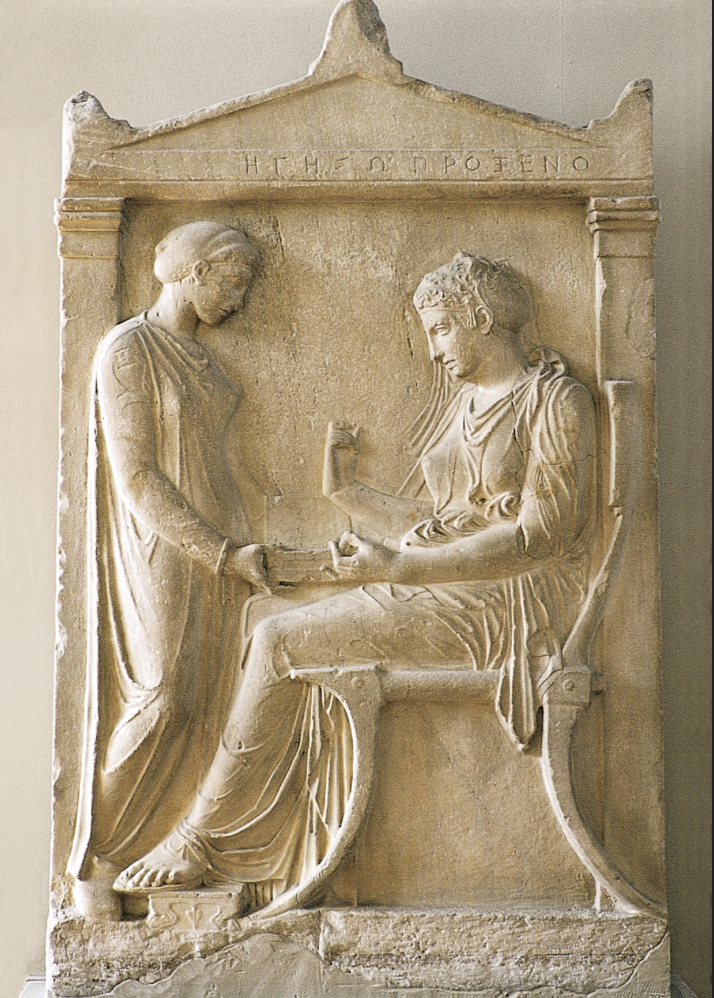

Grave Stele of Hegeso: (Classical)
Kallimachos
Dipylon cemetery, Athens
marble and paint
funerary in classical period (very different from Kouros)
regular woman’s gravestone, but comes from high status family
honors her and her father from the writing at the top (status of women)
she’s being depicted in a house (women’s place was in the home)
greek woman couldn’t leave without a charperone
women who did go out alone = prostitutes
Hegeso = seated woman examining a piece of jewelry brought by a servant (not visible, originally painted)
significance: what is not shown
Dipylon cemetery included sculptures of men outdoors, engaging in professions (hunting, athletics, warfare)
hellenistic art
320-30 BCE
Greek culture spreads out from the Balkan Peninsula into Asia and Africa
blending of Greek classical art with art from the east (Turkey, Iraq,Iran)
diffusion of greek culture through trade, Alexander the Great, and the Roman Empire
art shows movement, emotion, childhood, old age
shows wide range of human condition when classical sculpture only embraced stoic youthful
Greek, but dramatic!
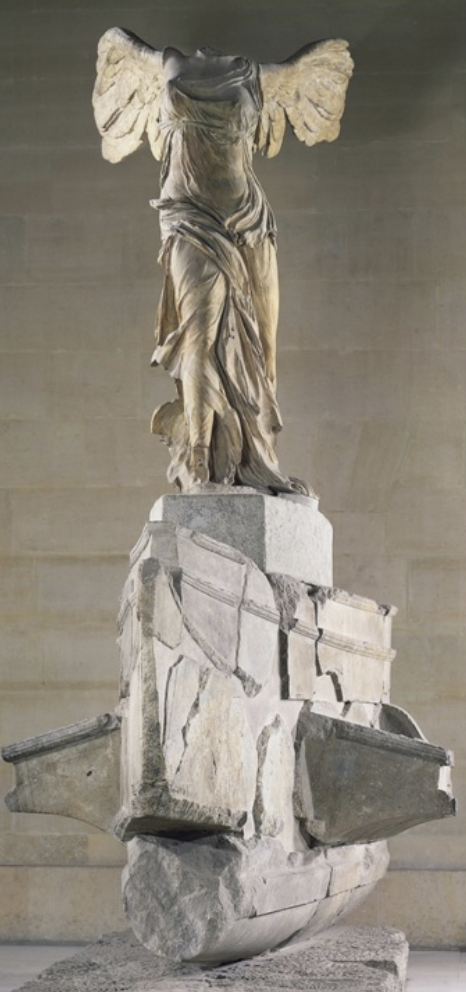

Nike of Samothrace: (Hellenistic)
marble
found in situ on Island of Samothrace (close to Turkey)
found in a fountain with a boat like shape, meant to be the statue on the bow of a boat
wet drapery look meant to imitate the water on the bow of a boat or from the fountain
appears as if the wind was in the wings; slight twist in contrapposto pose as Nike lands her feet on the bow while adjusting for wind
monumental in size
right arm could have held a victory crown
major greek naval battle occurred off of Samothrace, this sculpture may be commemorative of that victory
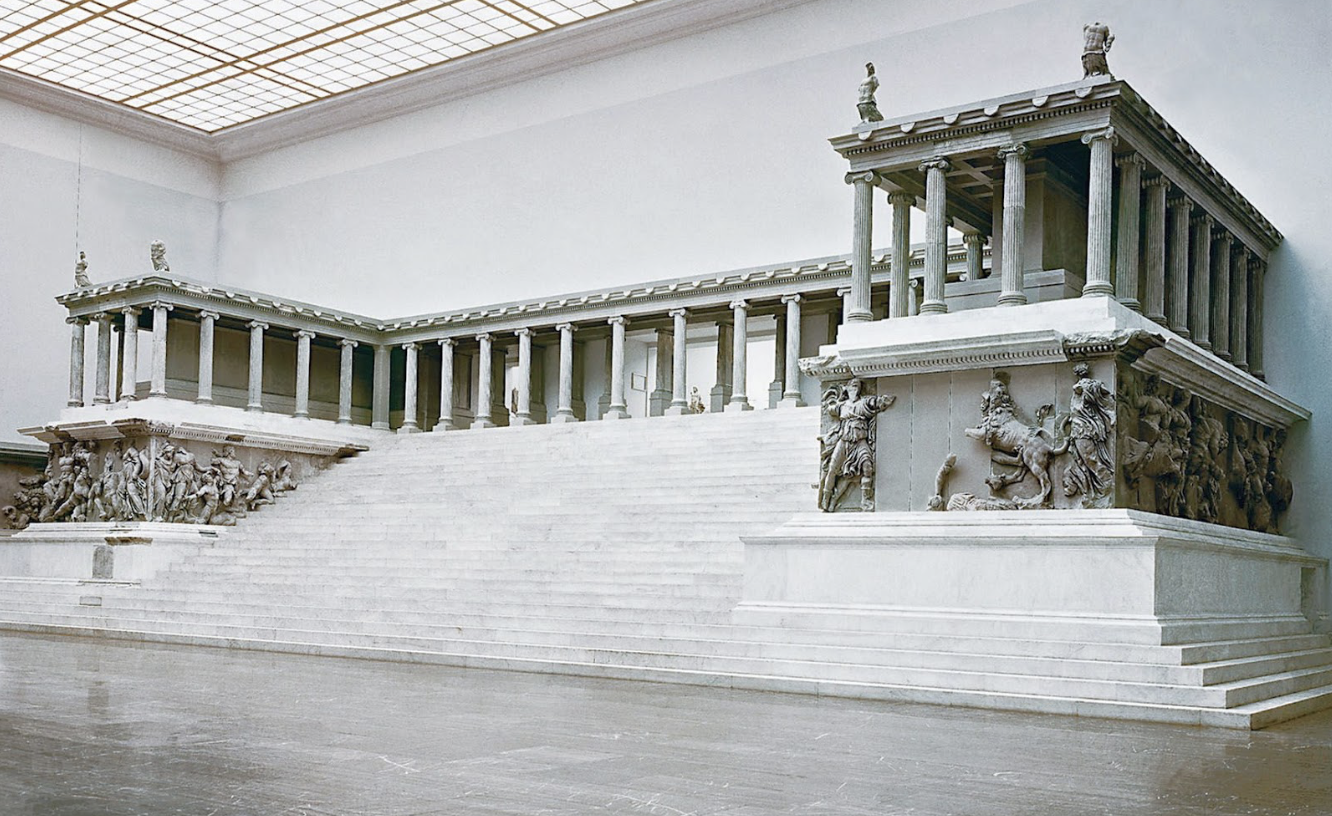

Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon, Coastal Turkey: (Hellenistic)
marble
narrative
sacred space
dramatic and steep flight of stairs leading to platform where fires burn in honor of Zeus (sacrifices and offerings made)
ionic order throughout, telling story of story of Zeus and Athena wraps around the monument
superiority of the Greek Gods to original gods
one religion replacing a local religion
propaganda to locals
only portion that is original is the frieze, temple is a recreation
in Berlin today
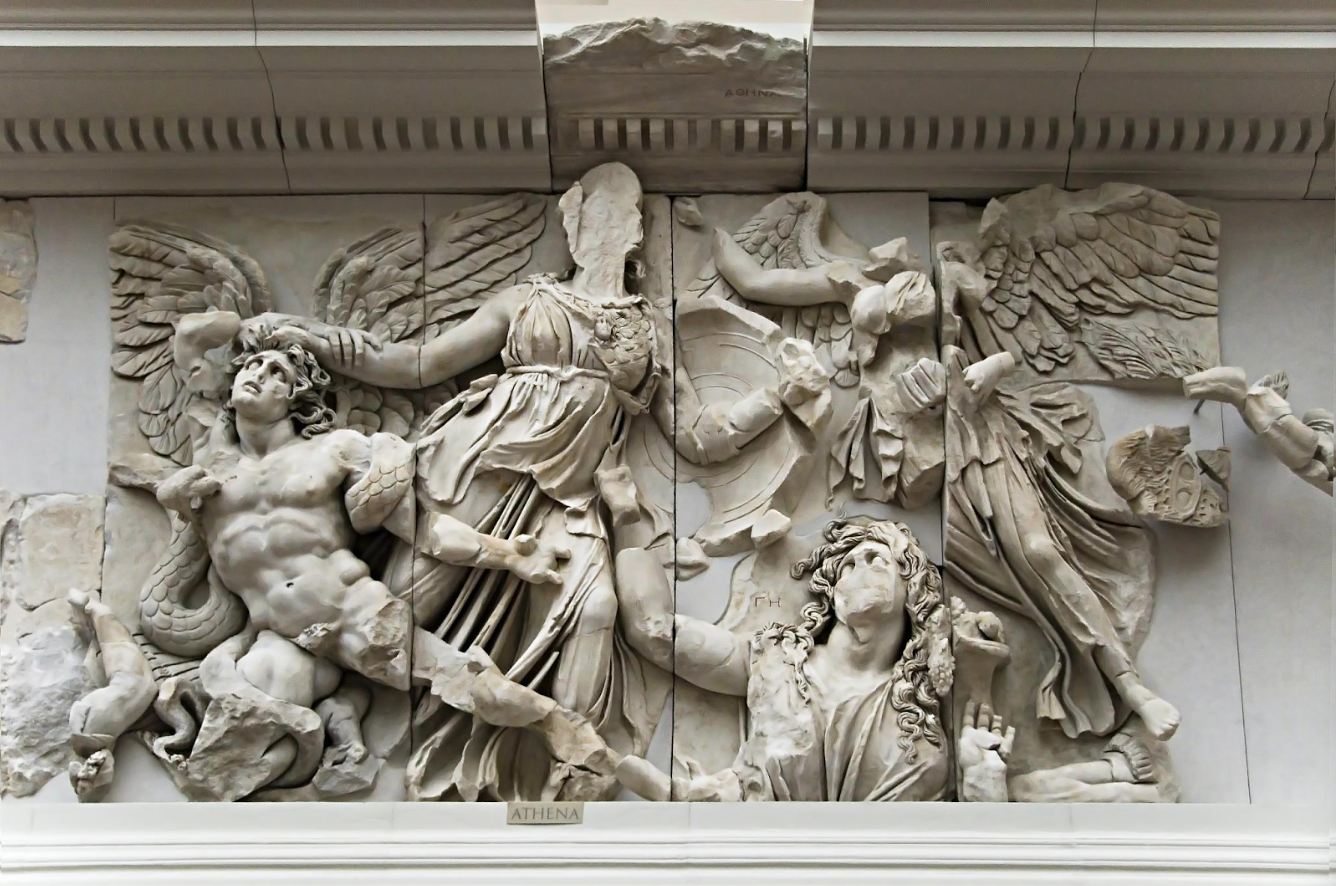

Athena portion of Frieze: (Great Altar of Zeus and Athena; Hellenistic)
superiority of the Greek Gods to original gods
one religion replacing a local religion
propaganda to locals
Athena victorious over a giant named Alkyoneos while his mother watches
Alkyoneos being dragged up the stairs to worship Zeus
Nike appears from behind to lay a victory crown on Athena’s head
deeply carved, high relief, dramatic tension in body and faces
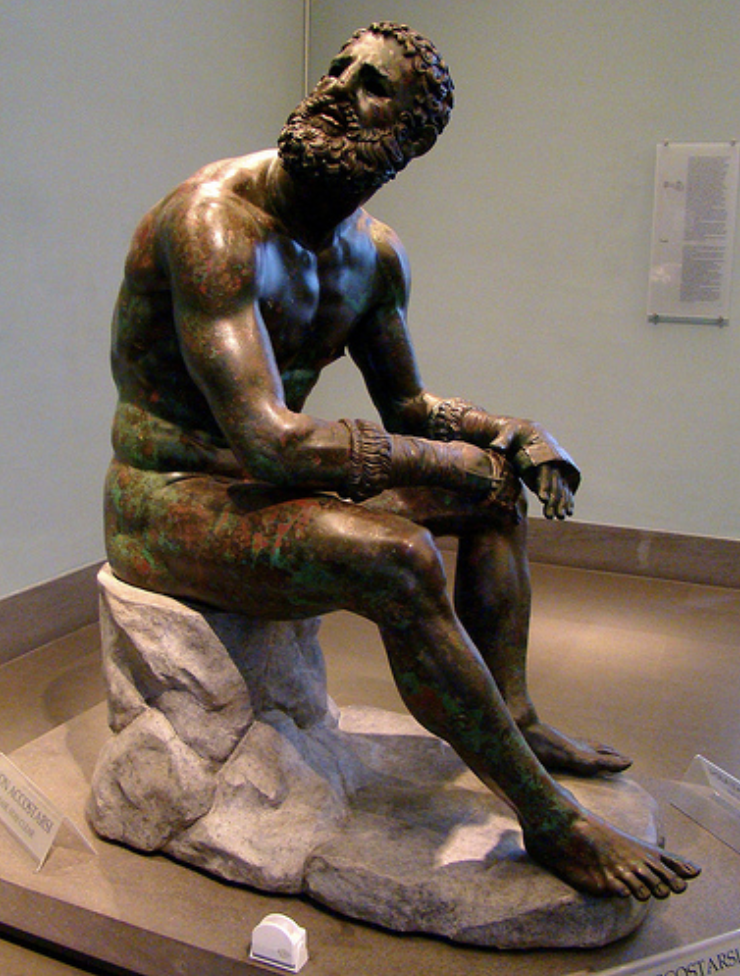

Seated Boxer:
bronze; one of very few Greek bronzes to survive
shows an aged boxer looking up at his opponent in defeat
smashed nose, blood runs in copper drips onto his face and arms
copper used as highlights on lips, nipples, straps on gloves, wounds on head
great emotion, agony of both physical and emotional defeat (don’t see that emotion in Classical)
ancient romans most likely brought the sculpture from Greece to Rome
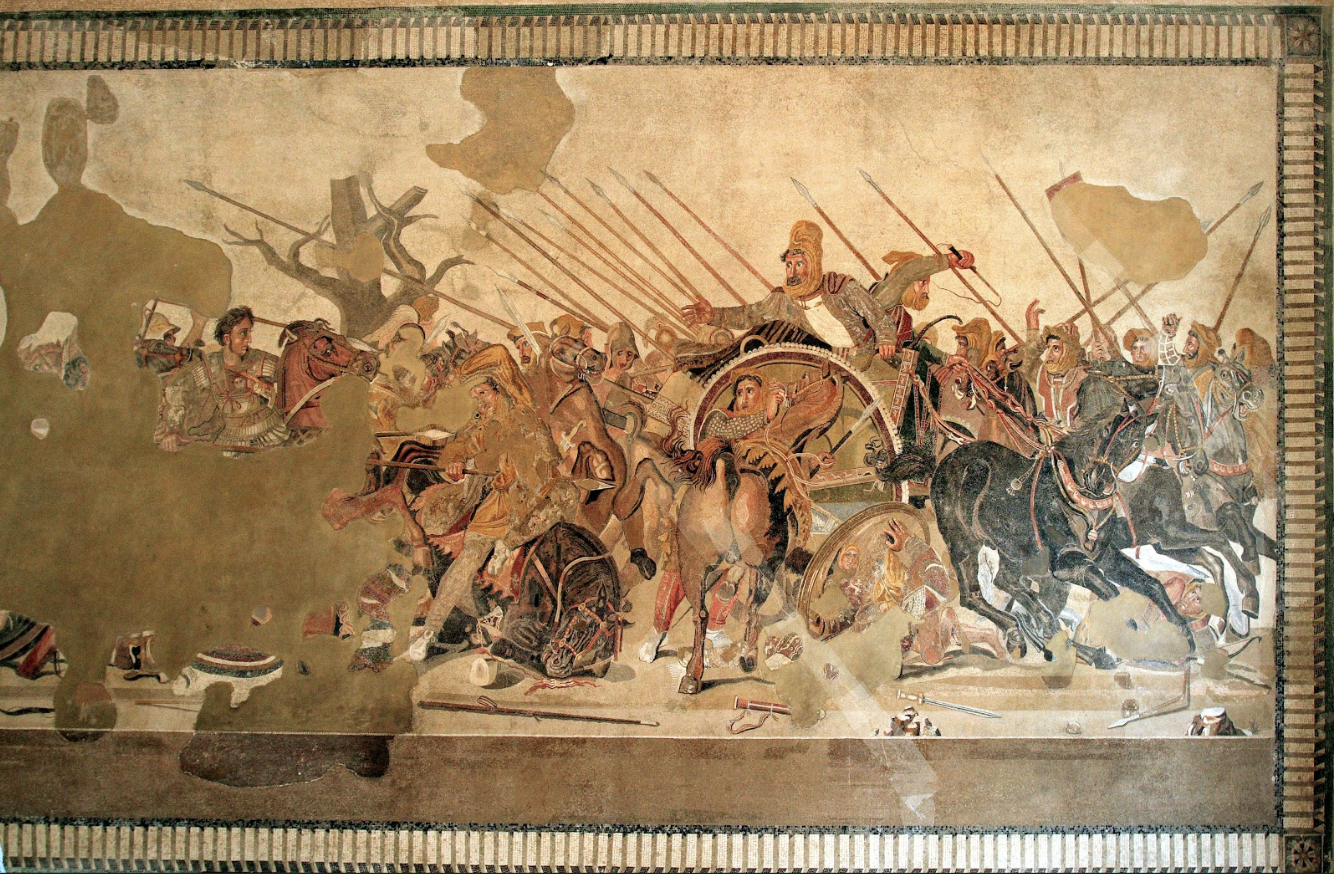

Alexander Mosaic From the House of Faun: (Hellenistic)
a Roman copy floor mosaic Pompeii
mosaics: small colored stones and shells to create a picture
complex interweaving of figures
battle between Alexander the Great and Darius III of Persia
Alexander at left, assured of his success
Darius reaches for Alexander but his charioteer commands retreat
Greek wall paintings no longer exist, so this Roman copy is the closest thing to the Greek genre
shows extreme attention to detail, emotion, directionality, multiple poses, foreshortening
connect to Persepolis
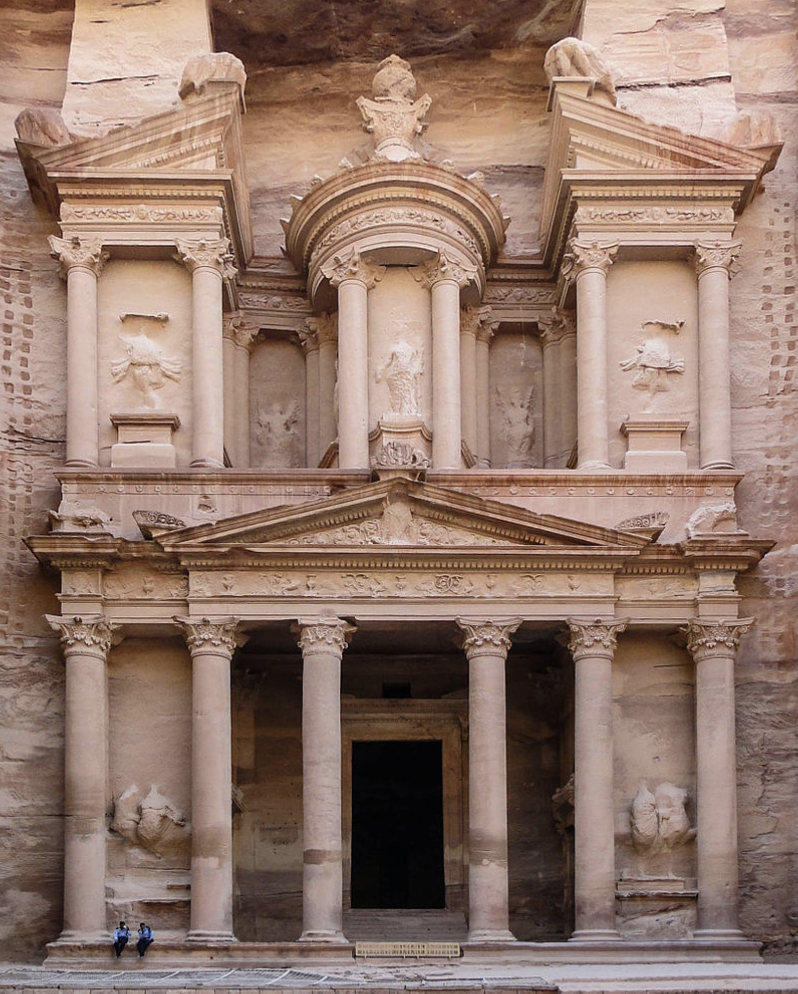

Tomb Named Al-Khazneh, “The Treasury”: (Hellenistic)
Nabataean Peoples
Jordan
Pre-Islamic/Greek influence
rock cut tomb
Hellenistic in style, both Greek and near eastern architecture
figurative sculpture adorns the tomb, Amazons, Isis (Egypt)
Greek/Roman influence on lower half
Tholos on upper floor, broken pediment (unique)
Corinthian columns, not evenly spaced
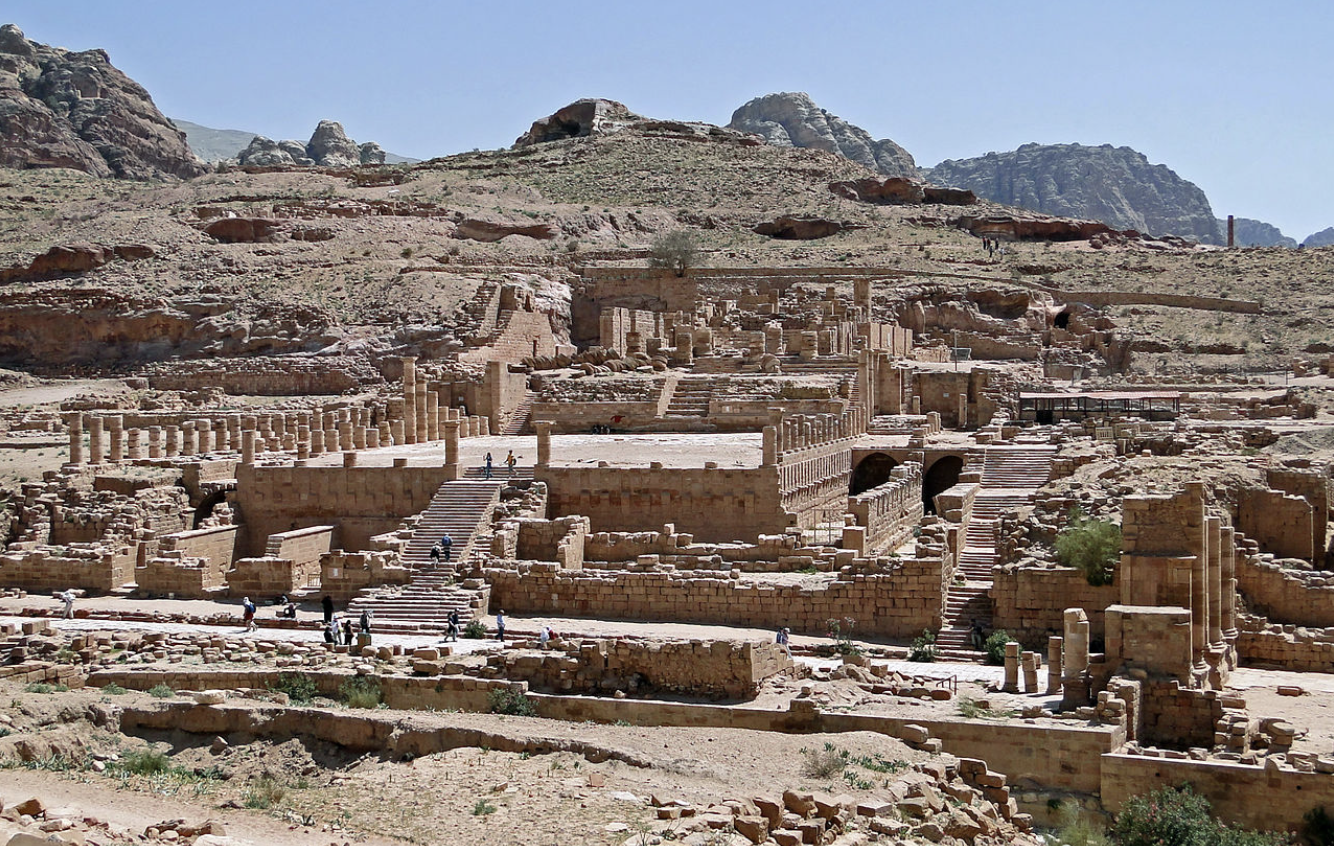

Great Temple of Petra: (Hellenistic)
Nabataean Peoples
Jordan
Pre-Islamic/Greek influence
cut rock
Hellenistic influence, but the culture is not necessarily Greek, influenced through trade
Patron: Aretha IV
Silk Road, merchant peoples
Dead buried in rock cut tombs on hillside behind temple
A combo Greek and Egyptian temple amongst a nomadic trading people showed the influence of Greek Hellenistic culture
well developed metropolis