Chapter 7: Flexible Budgets, Variances, and Management Control
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a Variance?
The difference between actual and expected (i.e., budgeted) amount
What does a Favorable Variance result in?
Higher operating income relative to budgeted amount
What does Unfavorable Variance result in?
Lower operating income relative to budgeted amount
What do managers need to determine the cause of?
Variances
What is the Variance Hierarchy?
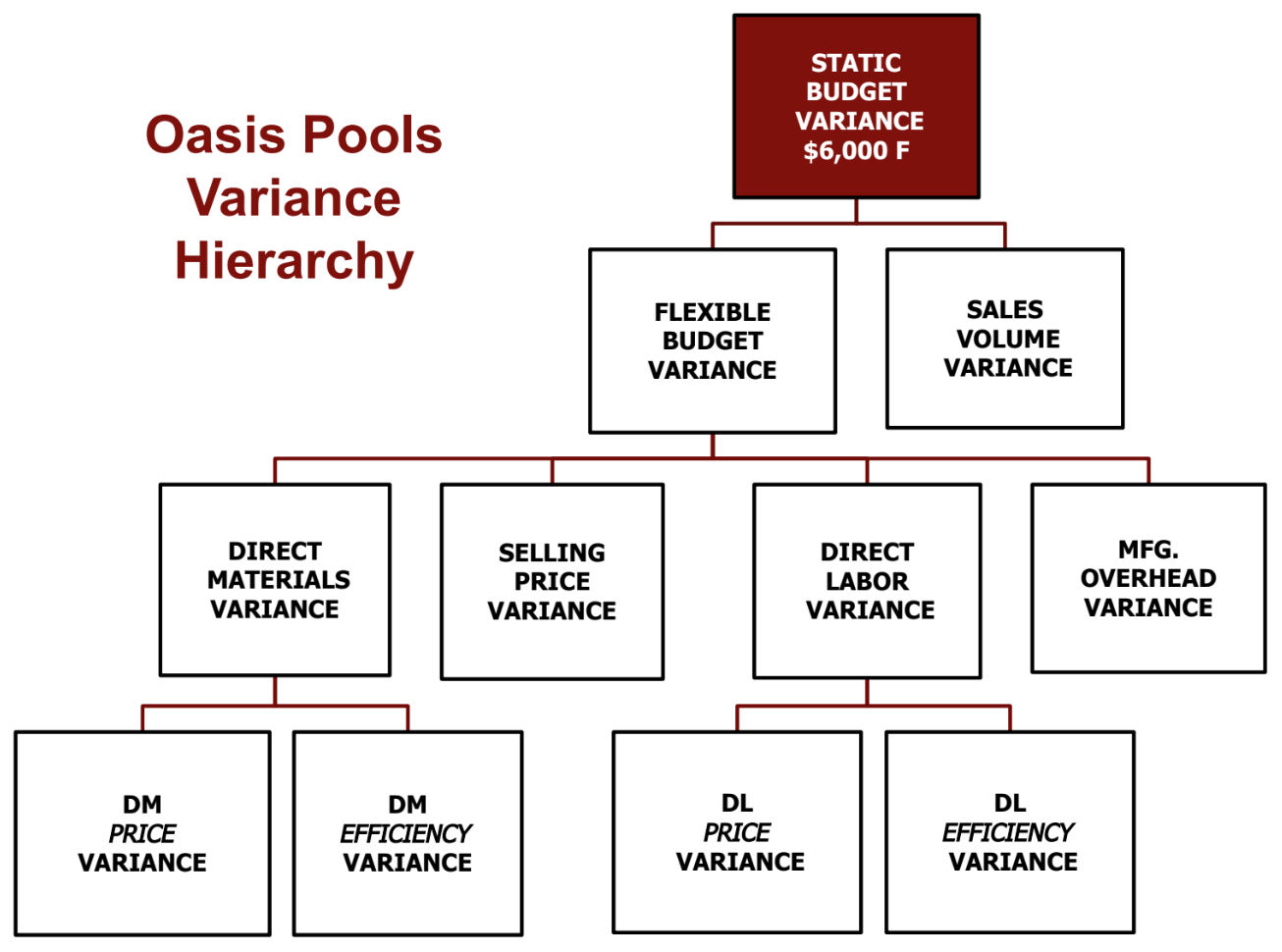
What is a Static (Master) Budget based on?
The output planned at the start of the budget period
What does Static mean?
Before the period
What does Flexible mean?
After the period
What does the Flexible Budget shift?
Budgeted revenues and costs up and down based on the actual level of activity
What is the formula for the Sales Volume Variance?
Master Budget Contribution Margin * (Actual Units Sold - Units Budgeted to be Sold)
What information must managers first determine for DM & DL Variances?
Actual Data: Actual Quantity, Actual Price
Standards (Budgeted Data): Standard Quantity, Standard Price per Unit
What question does Price Variance aim to answer?
Given the actual quantity of material used (labor incurred), how did the difference (i.e., variance) in price affect income?
What is the formula for Price Variance?
AQ * (AP - SP)
How do you know when the Price Variance is Favorable?
If AP < SP
What are some potential reasons for price variance?
For Direct Materials: Change in market price due to supply/demand bought, quality of materials, unexpected discount, etc.
For Direct Labor: Used more senior people to do work, more overtime hours, etc.
What question does Efficiency Variance aim to answer?
Given the standard price of the material (labor), how did the difference (i.e., variance) in quantity affect income?
What is the formula for Efficiency Variance?
SP * (AQ - SQ)
What are some potential reasons for efficency variance?
For Direct Materials: more spoilage than expected, people using more materials, etc.
For Direct Labor: used more skilled or senior workers who know what they’re doing, workers rushed through the work, heavier capital investment, etc.
How do you know when the Efficiency Variance is Favorable?
If AQ < SQ
What makes it difficult to determine the responsibility for a particular variance?
Interaction among variances often occur
What can variances in one part of the value chain be due to?
Root causes in another part of the chain
What is the formula for the Sales Price Variance?
(Actual Sales Price per Unit - Budgeted Sales Price per Unit) * Units Sold
What are managers needed to evaluate?
Size of the variance (both the absolute and relative amounts)
Costs and benefits of further investigation
What is an important note on favorable variances?
It is often important to investigate significant favorable variances as well as significant unfavorable variances
What are Perfection Standards?
Only attainable under near perfect conditions
What are Practical Standards?
Tight standards, but still attainable
What is Benchmarking?
The continuous process of comparing levels of performance against the best levels of performance in competing companies
How can variances be extended?
To include comparison to other entities