Nuclear Processes
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science GACE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Unstable Isotope
An isotope with a a nucleus that breaks down over time through radioactive decay
Example.
C-14
Radioactive Decay
a process that changes the nucleus of an atom by emitting high-energy alpha, beta, and/or gamma particles
Nuclear Fusion
a process in which the nuclei of light elements, like hydrogen, fuse together to create the nuclei of heavier elements, like helium
Alpha Decay
The nucleus emits a particle with 2 protons and 2 neutrons, leaving the rest of the nucleus behind
Radioactivity
Term definition.
when an atom changes the number of protons in the nucleus and releases radiation
Term,Half-Life
Term definition.
The amount of time it takes for half of the isotopes in a sample to change
Term,Stable Isotope
Term definition.
An isotope with a nucleus that does not decay over time
Example.
C-12
Term,Beta Decay
Term definition.
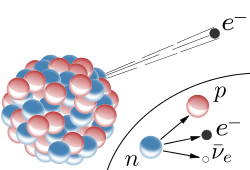
A neutron changes into a proton by emitting an electron and a neutrino from the nucleus; increases the positive charge of the atom.
Term,Isotope / Radioisotope
Term definition.
An atom with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus than other atoms of the same element
Term,Nuclear Fission
Term definition.

a process in which the nuclei of an atom is split, releasing a massive amount of energy.
Term,Nucleus (of the Atom)
Term definition.
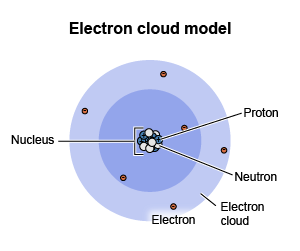
the positively charged, small, central core of an atom; made of protons and neutrons
Term,Gamma Decay
Term definition.
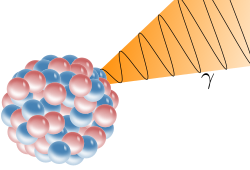
Electromagnetic energy is released from the nucleus in the form of a gamma ray. The atomic number and mass number of the isotope do not change.
Term,Proton
Term definition.

positively charged particle found in the nucleus of atoms
Radium-226 decays to radon-222 through:
alpha emission
Which of the following nuclear processes is an example of a beta emission?
234Th → 234Pa
Students in a class called Earth and Space Science are each given a paper cup filled with 100 small wooden disks. A black mark is stamped on one side of each disk. The following instructions are given to the students:
With all of the disks in the cup, gently shake the cup, and then dump its contents out onto a piece of paper.
Remove all disks with the black mark facing upward, count and record the number of remaining disks, and return them to the cup.
Repeat the gentle shake, dumping the contents, removing disks with the black mark showing, and recording the number of remaining disks until all disks are gone.
Which of the following topics is the teacher most likely introducing with this activity?
half-life of radioactive materials
Which of the following will give off energy if used as fuel in a fission reaction?
thorium (Th)
The beta emitter 13755Cs has a half-life of 30 years. After 25.5 years, 7 g remain. What was the original mass?
12.6 g
Polonium212 decays to lead208 through alpha particle emission. Which of the following correctly describes an alpha particle?
a positively charged particle with 2 protons and 2 neutrons
An isotope has a half-life of 3.00 hours. How many hours will pass before approximately 87.5% of the isotope has decayed?
9.00 hours