hyphenated techniques
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what is nominal mass?
integer mass of ion made up of lightest stable isotopes of each element
what is exact monoisotopic mass?
mass of ion that is made of lights stable isotopes of each element
what is average mass?
mass of ion calculated using relative average isotopic mass of each element
what is isotopic abundance?
naturally occurring distribution of same element with different atomic mass
what are isobaric mass empirical formulae?
same nominal mass gut different exact monoisotopic masses
how is exact monoisotopic molecular mass calculated?
remember to subtract mass of electron
how to calculate intensity of M+1/intensity of M peak?
natural abundance of each +1 isotope (e.g 13C) x exact mass / lightest stable isotope x natural abundance
what does a full scan give? what type of analysis? 2D or 3D why?
maximum info
large volumes of data
don’t visualise as 3D as too complex
good for non targeted analysis
what is a total ion chromatogram?
integrates signal over all m/z values
what is a base peak chromatogram?
most intense m/z peak at each time point
what is extracted ion chromatogram?
collects full scan and extracts data for specific m/z
what is selected ion monitoring? advantages? what type of analysis?
only collect at specific m/z (don’t collect full scan)
collect many more data points = smoother chromatogram, less data generated
used for targeted analysis
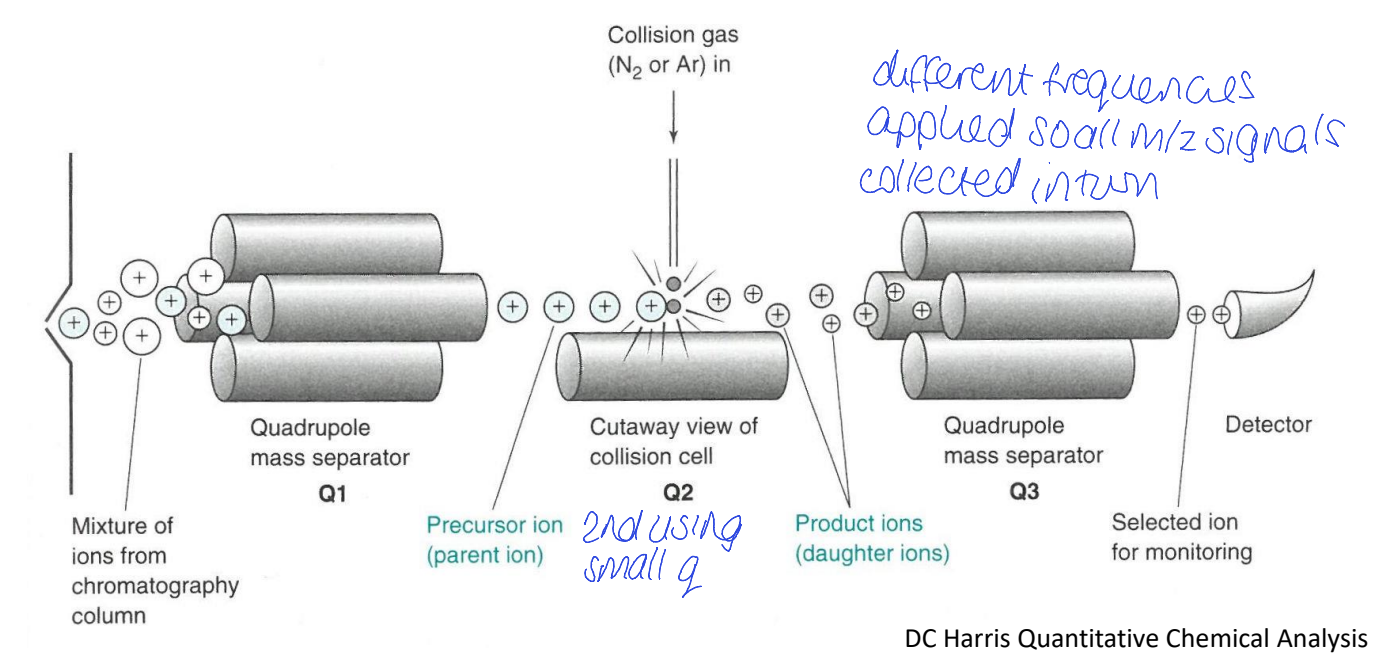
quadrupole MS
what is the principle of mass analysis? low or high res
filters ions by oscillating electric fields
low res
triple quadrupole MS (QqQ)
what is the principle of mass analysis?
low or high res
two quadrupoles + collision cell for MS/MS
low res
time of flight MS
what does it measure? high/low res?
measures time ions take to reach detector
high res
quadrupole time of flight MS
how does it work? low or high res
quadrupole for selection
time of flight for detection
high res
GC-MS
how do analytes leave the column?why?
what are the sources of ions?2
leave column at low conc in high temp gas = suitable for introducing into mass spec after species ionised
ions from electron impact or chemical ionisation
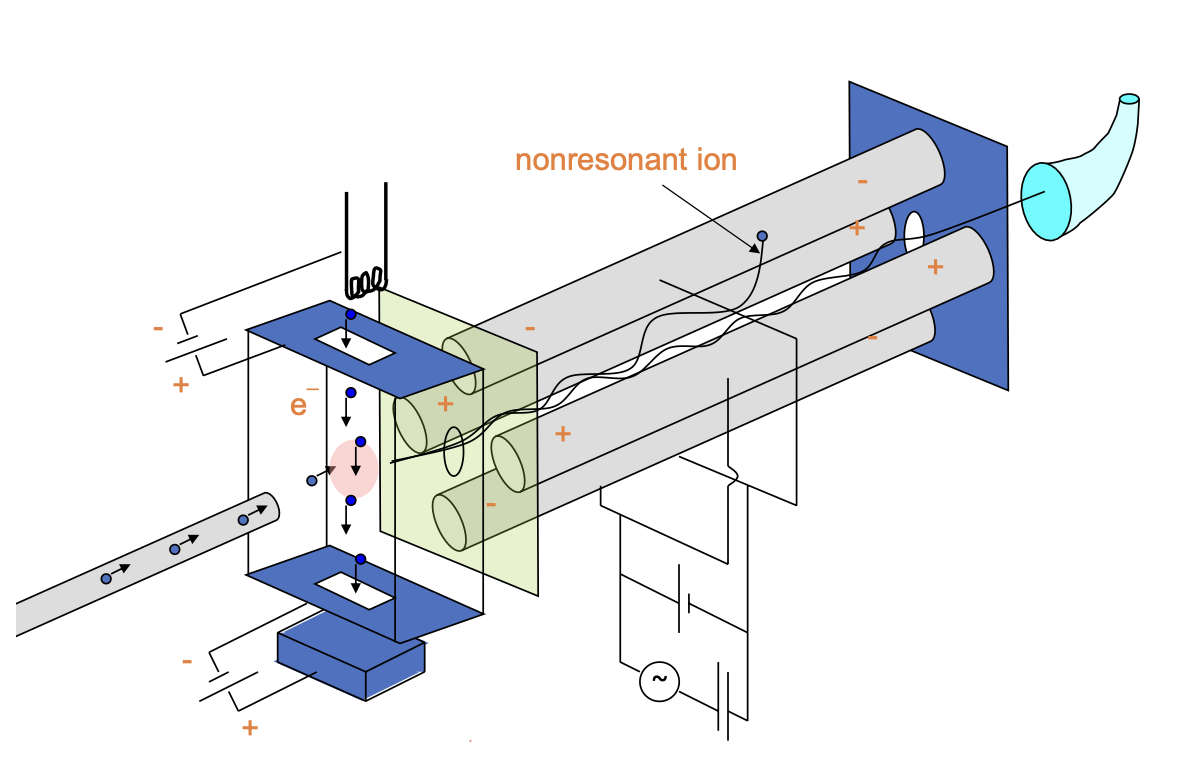
label this electron impact quadrupole mass separator
where does sample come from
how does sample become ionised, where?
what happens to electrons?
how does mass analyser work? what determines whether or not the ion reaches detector?
constant voltage and radio freq alternating voltage
causes electrons to spiral through 4 rods. radio freq determines which electrons reach the detector - others collide with quads and are lost
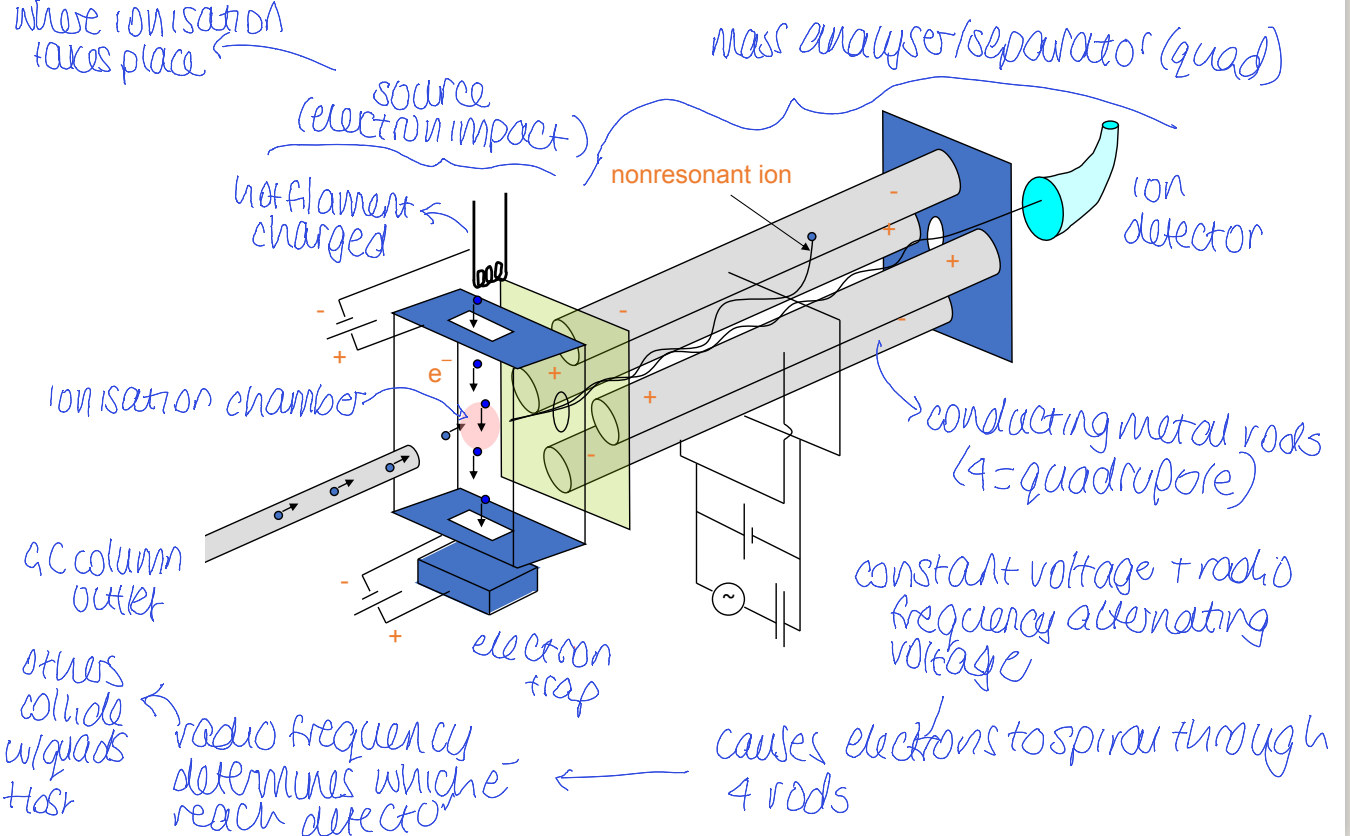
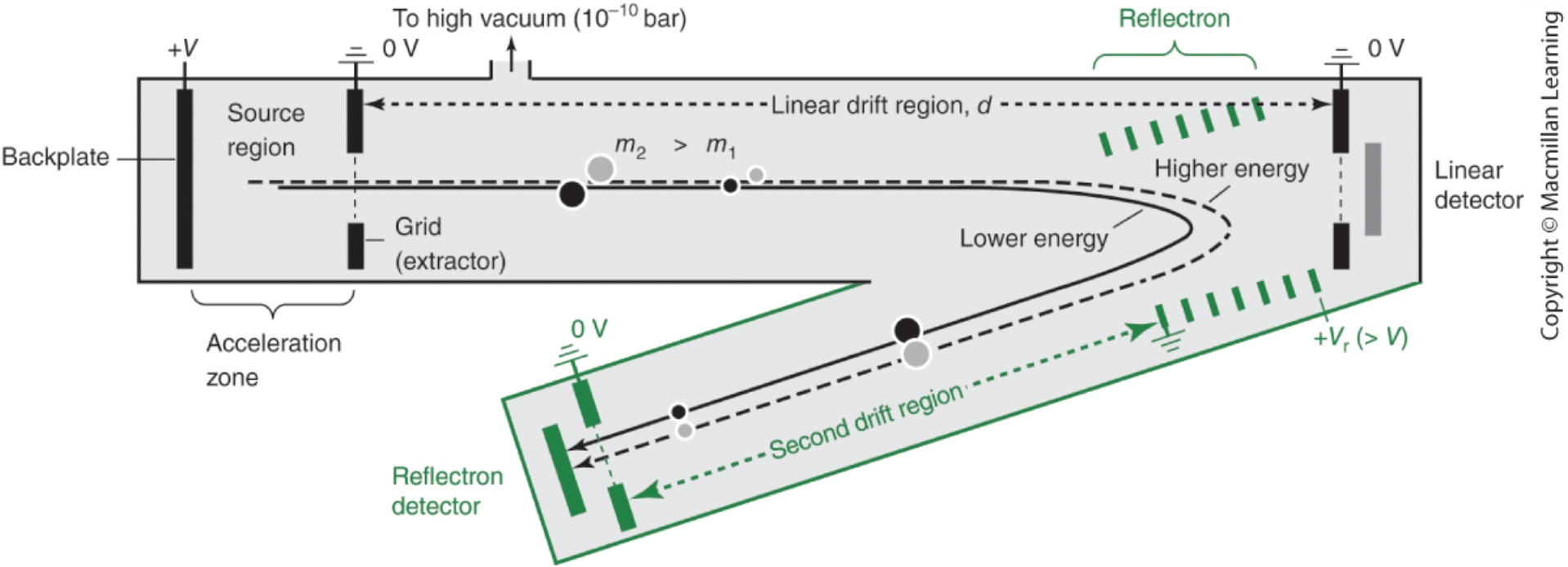
time of flight mass separator
why is tube bent?
how does the reflection detector improve resolution?
ions have same m/z but different kinetic energy depending on where they are
tube is bent so they arrive together, otherwise would arrive at different times
refocuses accelerated ions
where is electron lost from in electron impact? (oxygen)
HOMO - non bonding orbital centred on O or lone pair
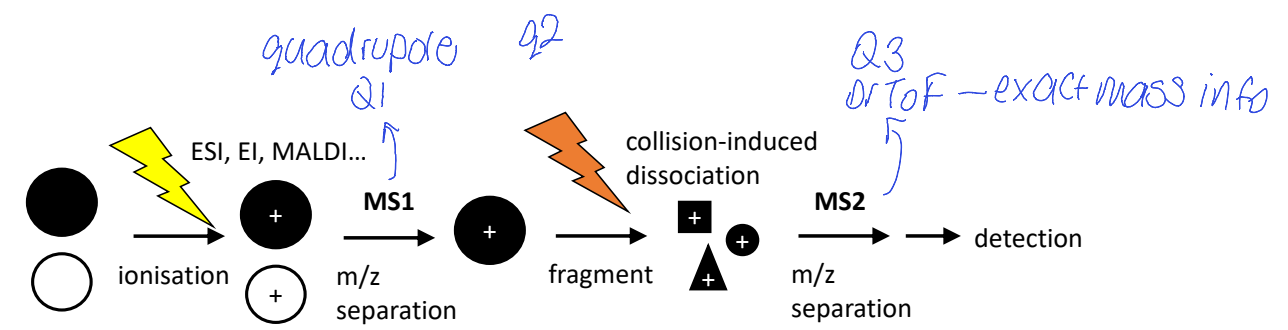
show general steps of ms/ms mass analysers (how many are there?), show how sample changes form and is sorted
what is selective reaction monitoring?
measures peak due to a specific daughter ion of a specific parent ion
even more selective and less noise
what are the two things a mass analyser could do to only allow specific m/z through
selective reaction monitoring
selecting parent ion and scan spectrum of daughter ions
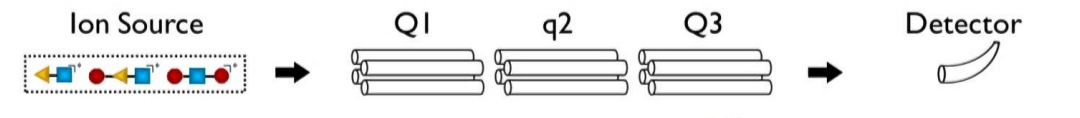
show triple quadrupole for GC-EI / LC-ESI?
show how parent ions become daughter ions, and how the mass separators sort the parent ions, and then the daughter ions
how are all m/z signals collected in turn?
for these general steps
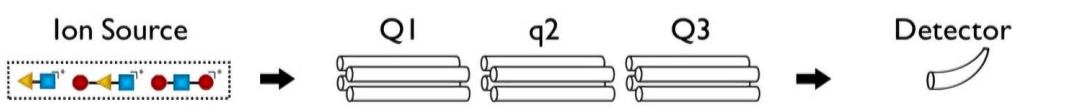
product ion scan - what is allowed through Q1? what is q2? what does Q3 do?
what is chromatogram and mass spec and what does it show?
only particular m/z ratio allowed through Q1
collision induced dissociation for q2
all allowed through Q3
chromatogram - peaks due to compounds with precursor ion
all fragment ions of precursor ions

for these general steps
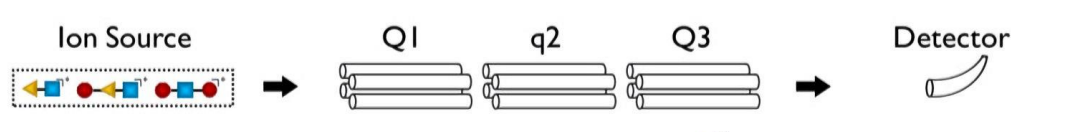
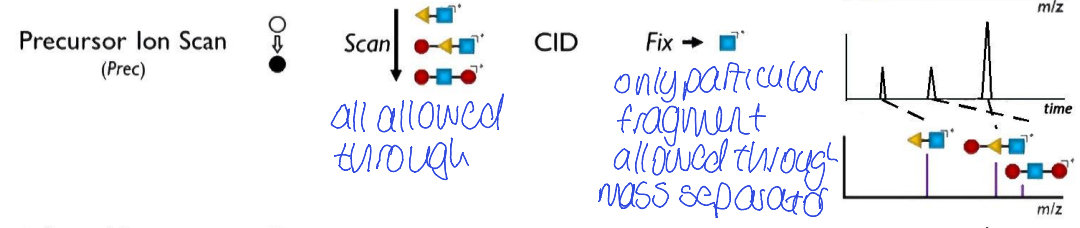
precursor ion scan - what is allowed through Q1? what is q2? what does Q3 do?
what is chromatogram and mass spec and what does it show?
Q1 - all allowed through
collision induced dissociation for q2
only particular fragment allowed through mass separator for Q3
chromatogram - peaks due to all compounds giving product ion
all precursor ions with same product ion
for these general steps
selective reaction monitoring - what is allowed through Q1? what is q2? what does Q3 do?
what is chromatogram and mass spec and what does it show?
Q1 - one m/z ratio allowed through
collision induced dissociation for q2
only one fragment allowed through Q3
chromatogram = peaks due to specific compounds with specific precursor/product ion combo
precursor/product ion pair being monitored

what must the analyte be for GC? 2
what does derivatization increase? how?
analyte must be volatile and thermally stable
increases volatility - replace polar groups with non polar to lower BP and increase vapour pressure
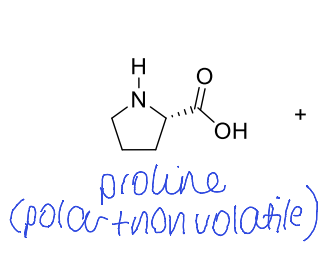
how could you make this less polar to increase volatility?
replace COOH with methyl ester group
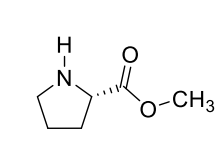
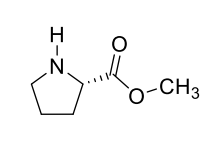
how could you make this less polar to increase volatility?
can no longer form H-bonds
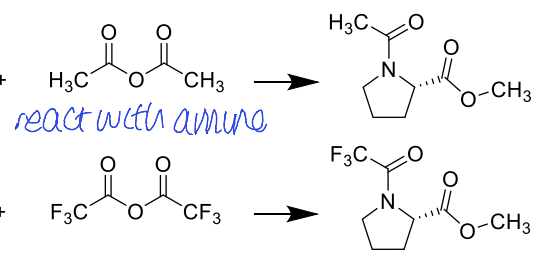
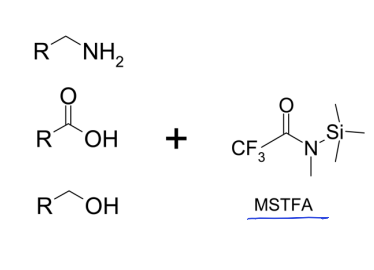
how could you make this less polar to increase volatility?
silylation

why are silyl are fluoroalkyl compounds more volatile than alkyl ones?
intermolecular forces are weakened
what state must instrument sample be when injected for GC, GC-MS or GC-MS/MS?
gas or solution of analyte in volatile solvent that isn’t water
how is sample of aqueous solution prepared for GC, GC-MS, GC-MS/MS?2
solvent extraction with immiscible organic solvent into which analyte partitions
solid phase extraction and elution with organic
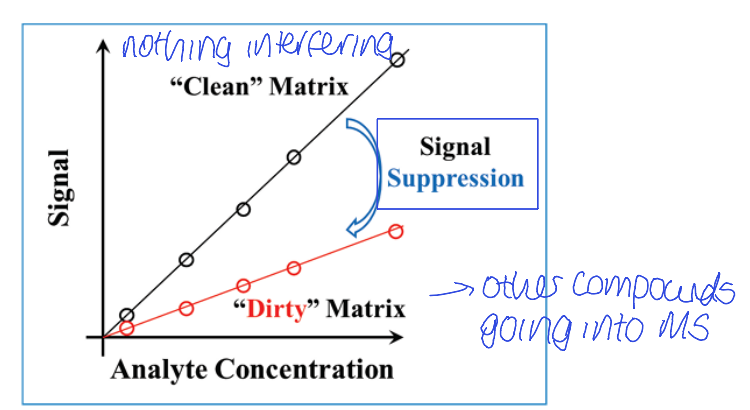
how does ionisation change with purity? what doe this mean about MS signal?
what is this effect called? show graph
analytes ionise more efficiently when pure
bigger signal in MS than if it co-elutes with other species (suppressing ionisation)
matrix effect
why is an internal standard better than an external standard for GC/LC-MS?
what is used as an internal standard? why?
due to changes in response factor of instrument
deuterated form of analyte is used as it is affected by ionisation suppression in exactly same way as the analyte
when is internal standard added? why
what is it now called?
before all work up steps
allows for losses during sample prep process
surrogate standard
when choosing a deuterated internal standard,
why should you use more than one D? what about for molecules with Cl?
acidic or basic group considerations?
single D in place of H increases m/z by 1 so overlaps with peaks due to isotopic partners (13C)
for Cl, avoid 2xD due to isotopic partners, and for 2 Cl avoid 4xD
don’t put D on an acidic or basic group as it may be exchanged during work up and chromatography
what is multiple reaction monitoring?
like SRM, but more than one parent daughter combination
how does sample come out of chromatography column in LC, and how must it be prepared for MS
leave column at relatively high conc in liquid
need to remove a lot of liquid to do MS
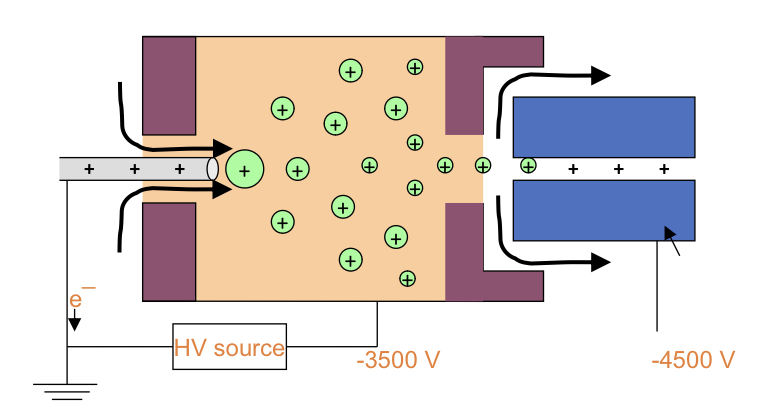
electrospray ion source for LC-MS
label
how is solvent removed
how are analytes ionised
how are ions separated, how do ions change
where do ions go after
charged droplets spray into drying chamber where they repel each other
ions shrink as solvent evaporates
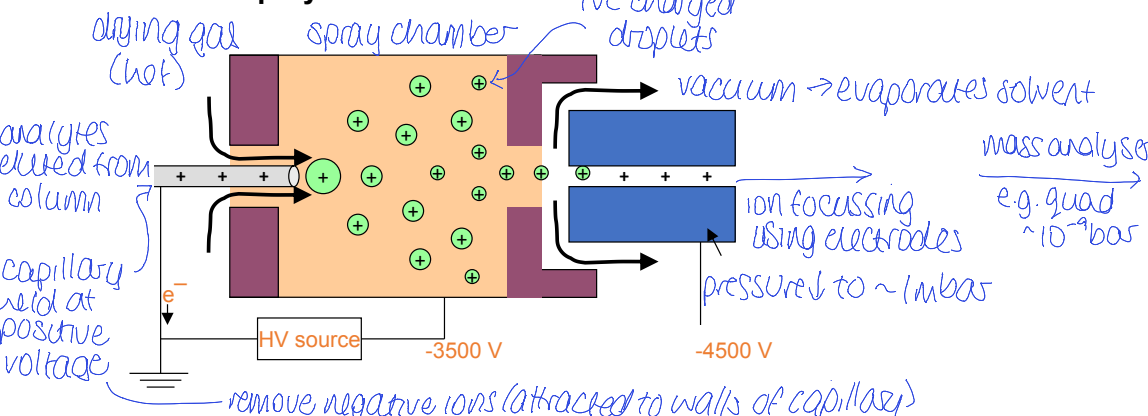
how does electrospray ion source change in a glass capillary
solvent evaporates completely and leaves only gas phase ions
what are the three different modes of operation for LC-MS?
what can you use for these three?
full scan(3D output)
general detector - total ion chromatogram or base peak chromatogram
selective detector - selective ion monitoring, extracted ion chromatogram
what is base peak for positive ionisation?3
what are the sources of these ions?
M+ (if inherently cationic/zwitterionic)
MH+
MNa+
H+ from water and Na+ from traces in water/tubing
what is base peak for negative ionisation?3
M- if inherently anionic/zwitterionic
(M-H+)-
adducts e.g. MCl-
mobile phase requirements for electrospray ionisation 3
need enough water to support ionisation but not too much as it is harder to evaporate
no involatile additives
MP acidified (source of H+ for MH+ ion) - e.g. with formic acid (HCOOH)
where does collision induced fragmentation often occur (ie which bond breaks)
at a single bond between carbon and electronegative element
what form must instrument sample be in when injected into instrument for reverse phase HPLC
in a solution of analyte in mobile phase (water/ co solvent)
how is aqueous solution prepared for reverse phase HPLC (2)
direct injection
or solid phase extraction and elution with polar co solvent