Chapter 5 Reactions of ionic compounds | Chemistry for VCE Units 1 & 2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
ionic compound
a chemical compound that is held in place by ionic bonds
crystal lattice
a three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or ions that repeats to make up a compound
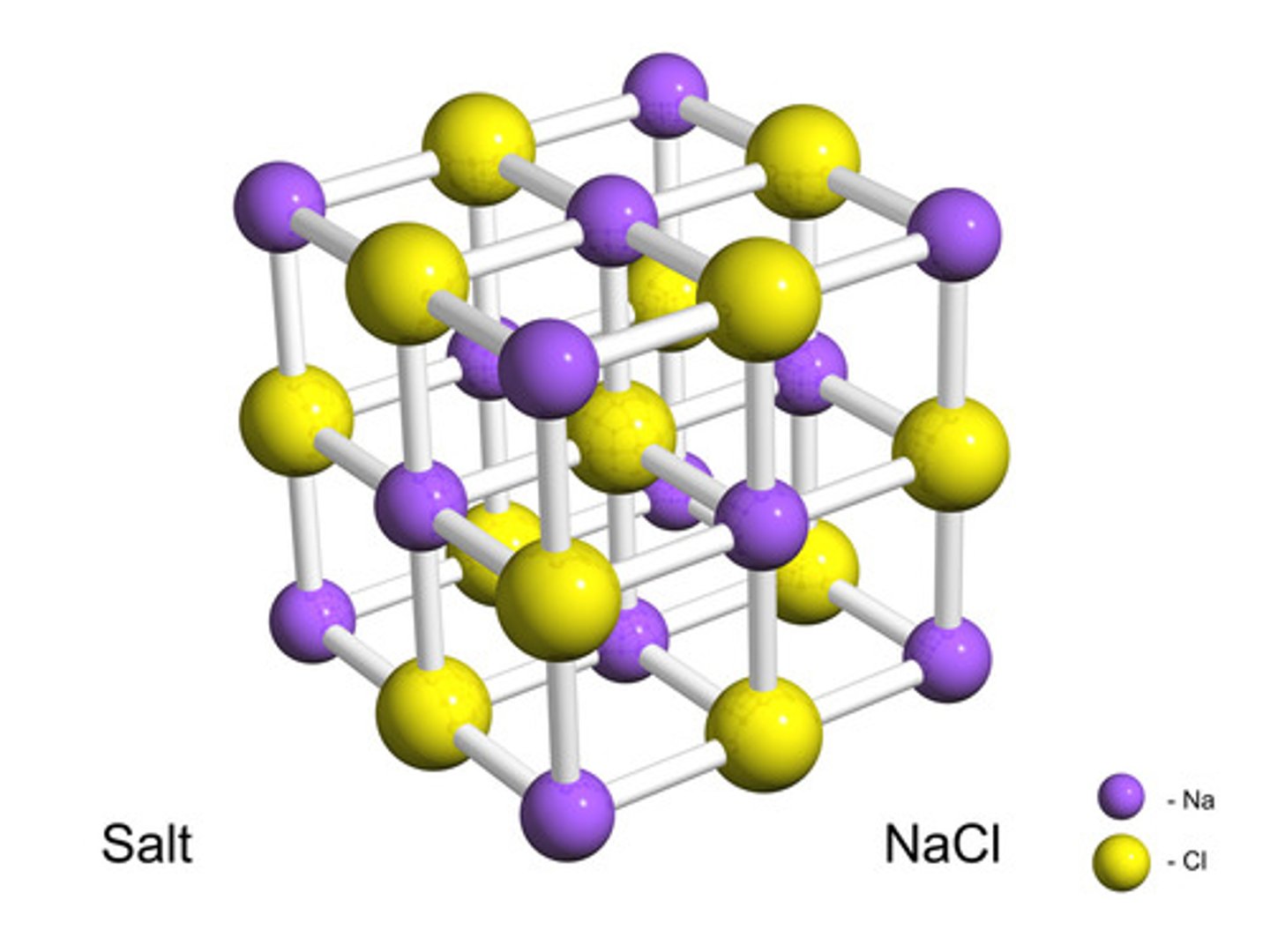
electrolyte
an electrically conductive solution that contains free moving charged ions
electron transfer diagram
a visual representation that shows the movement of electrons between atoms and/or molecules
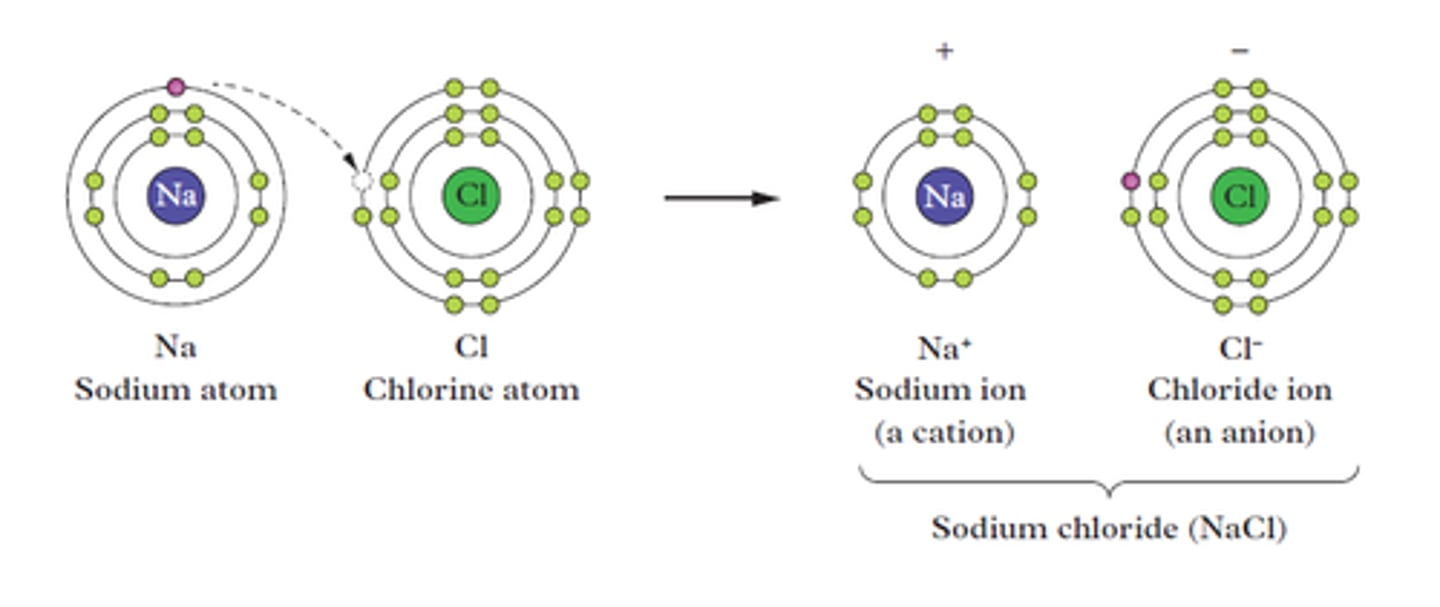
monoatomic
made from one type of atom
polyatomic
made from more than one type of atom
empirical formula
the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound
hydrate
an ionic compound that has water molecules surrounding the charged ions
dissociate
break apart into smaller atoms, ions or molecules
net ionic equation
a chemical equation in which electrolytes in aqueous solutions are expressed as dissociated ions
precipitation reaction
a reaction between two soluble ionic substances that forms an insoluble product
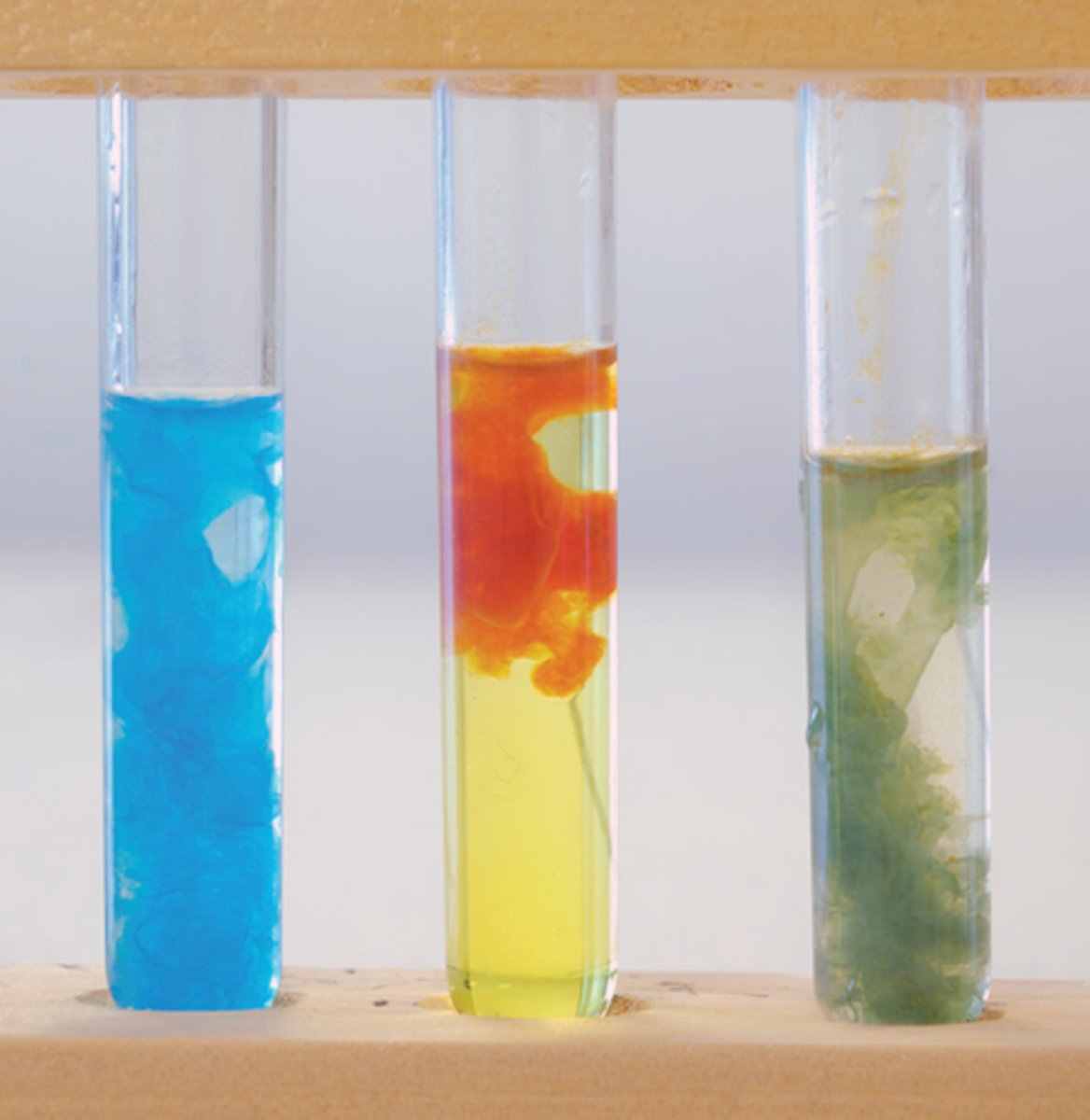

precipitate
the solid product formed from a precipitation reaction
spectator ion
an ion that does not participate in a reaction and has the same state and oxidation number as both a reactant and product
double displacement reaction
a chemical reaction that occurs when two reactants exchange cations or anions to form two new products