The Origin of Species and Speciation Processes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Macroevolution
Origin of new taxonomic groups over time.
Microevolution
Genetic variation within a species across generations.
Biological species concept
Species defined by potential interbreeding and viable offspring.
Speciation
Process of forming a new species from existing ones.
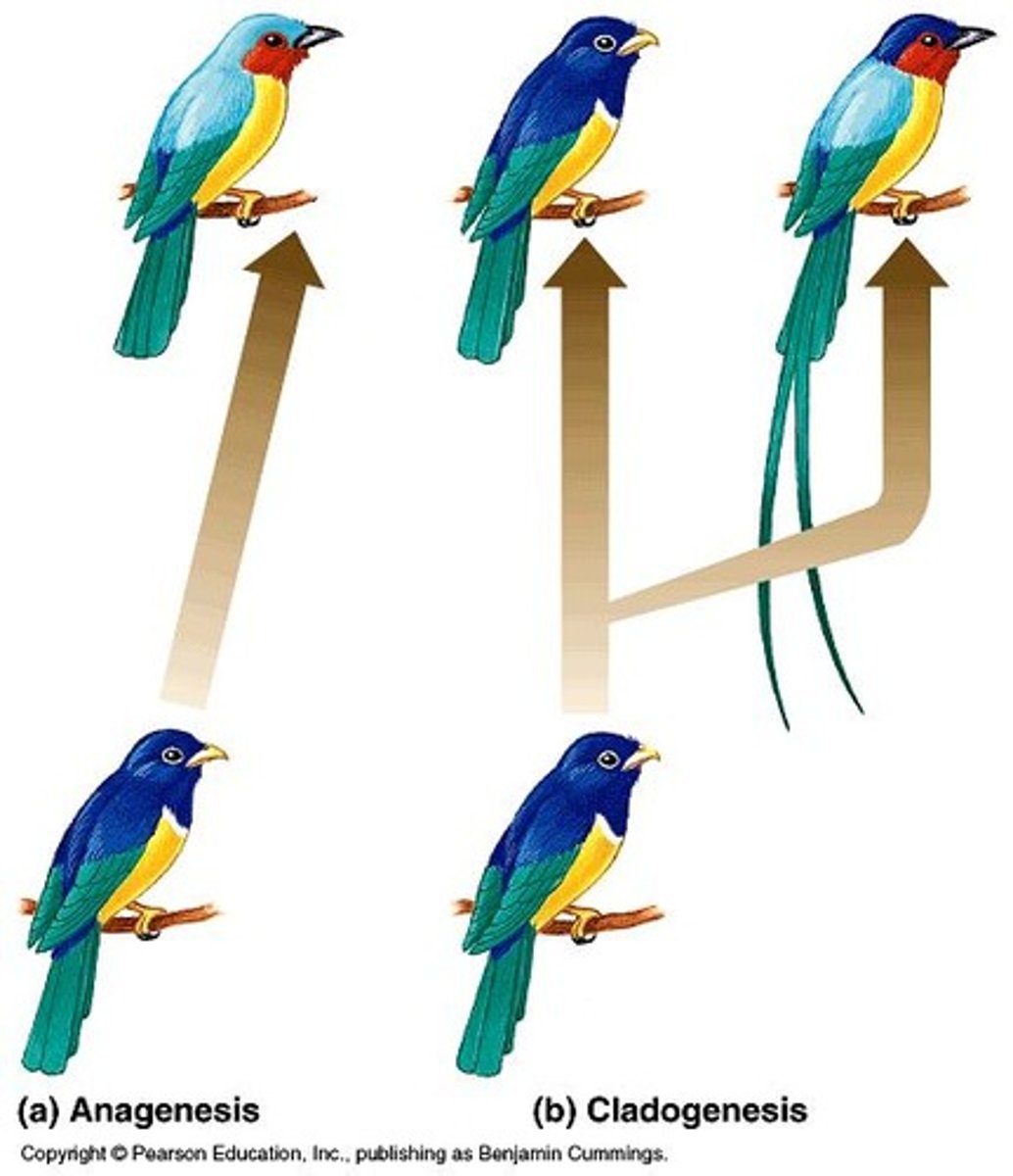
Anagenesis
Accumulation of traits transforming a population into a new species.
Cladogenesis
Branching evolution creating new species from an ancestral species.
Isolation
Separation of populations preventing interbreeding.
Prezygotic barriers
Prevent mating or fertilization between different species.

Habitat isolation
Species occupy different habitats, limiting encounters.
Behavioral isolation
Unique mating signals prevent interbreeding between species.
Temporal isolation
Species breed at different times, preventing mating.
Mechanical isolation
Anatomical incompatibility prevents successful mating.
Gametic isolation
Sperm and egg must recognize each other for fertilization.
Postzygotic barriers
Prevent hybrid offspring from developing or reproducing.
Reduced hybrid viability
Hybrids fail to develop properly, aborting early.
Reduced hybrid fertility
Hybrids are sterile, unable to produce viable gametes.
Hybrid breakdown
First-generation hybrids are fertile, but next generation is not.
Ecological species concept
Species defined by ecological niche and resource use.
Pluralistic species concept
Species maintenance factors vary, including reproductive isolation.
Morphological species concept
Species defined by unique structural features.
Genealogical species concept
Species defined by unique genetic histories and DNA.
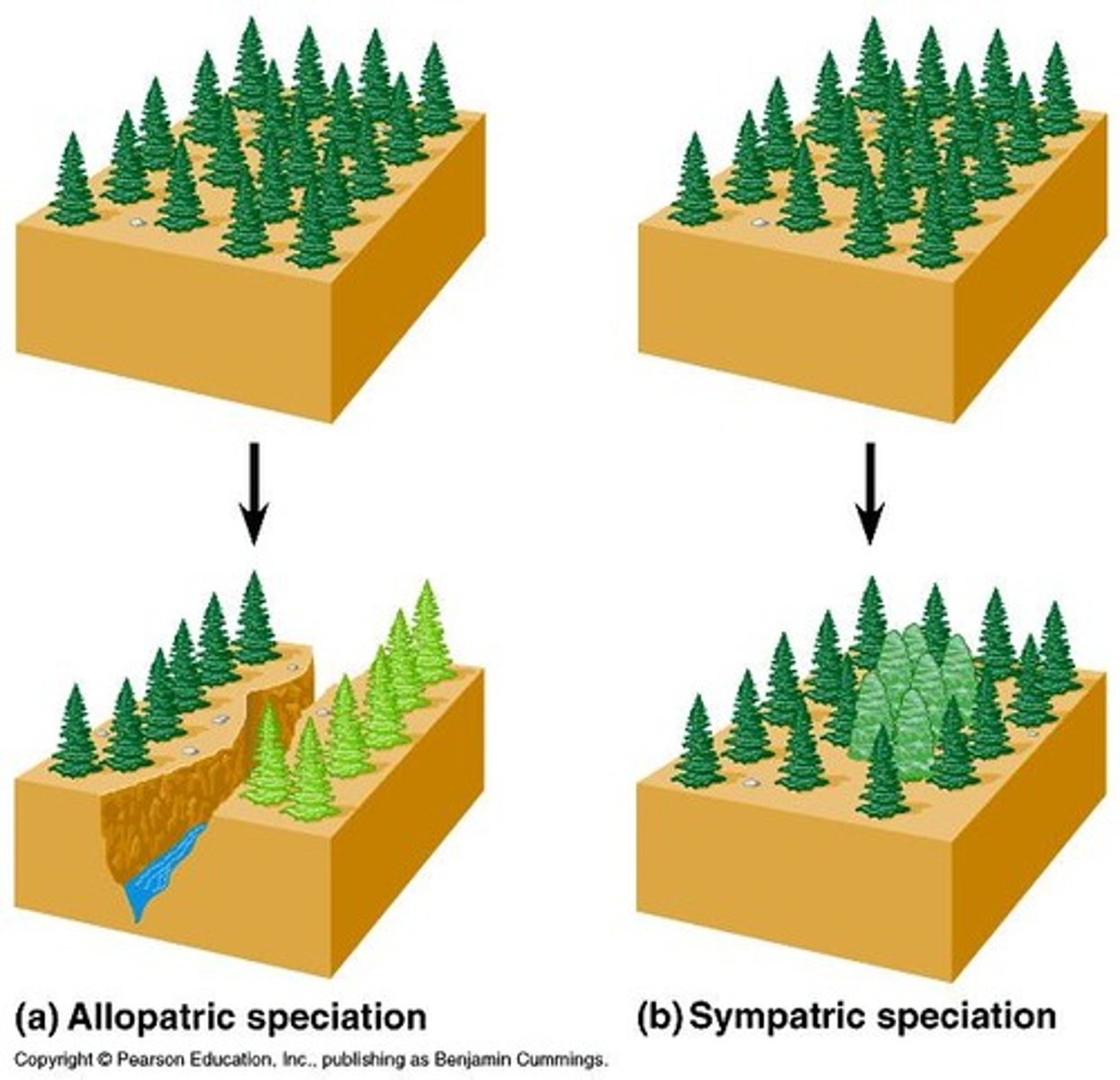
Allopatric speciation
Speciation occurring in geographically isolated populations.
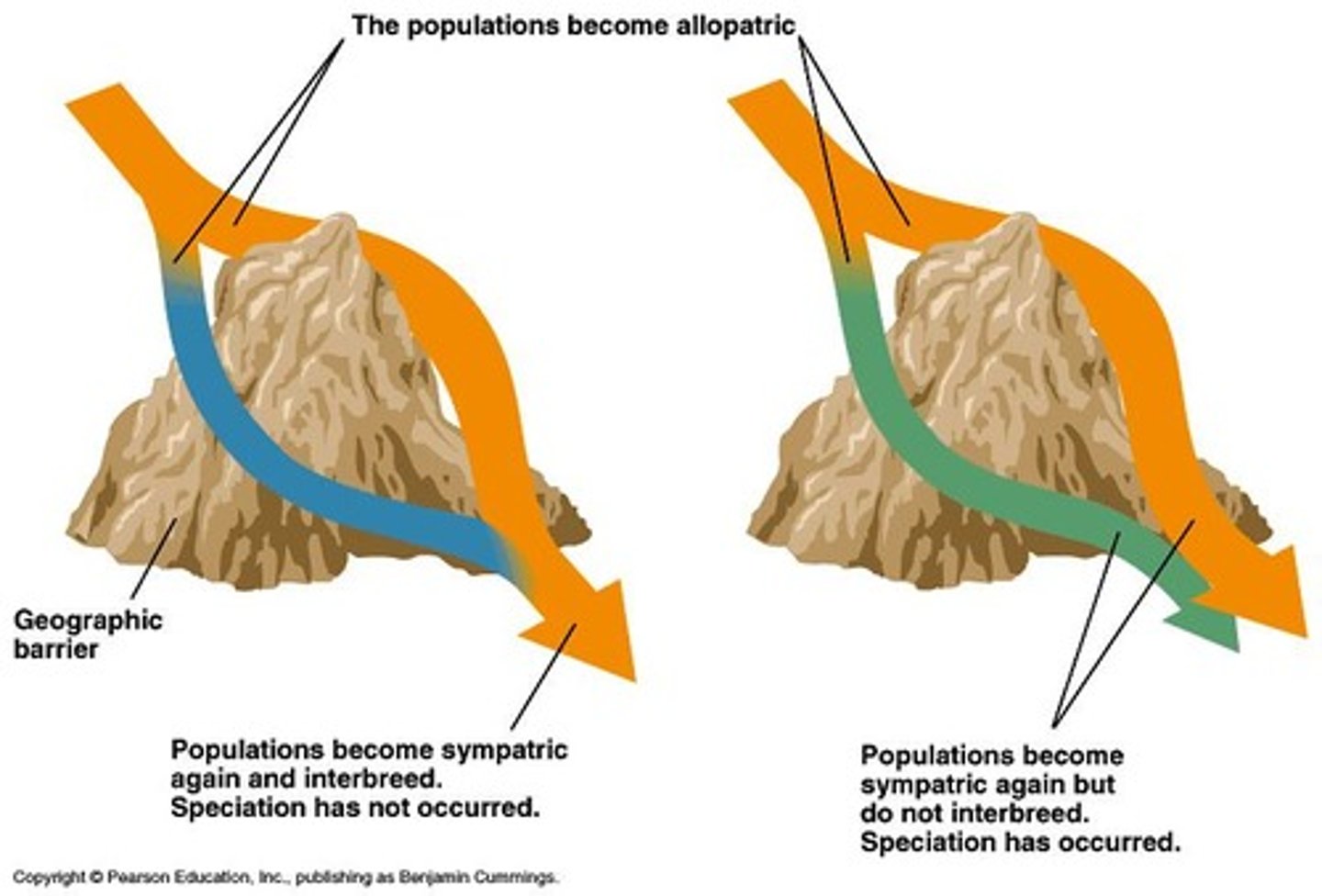
Sympatric speciation
Speciation occurring in overlapping geographic populations.
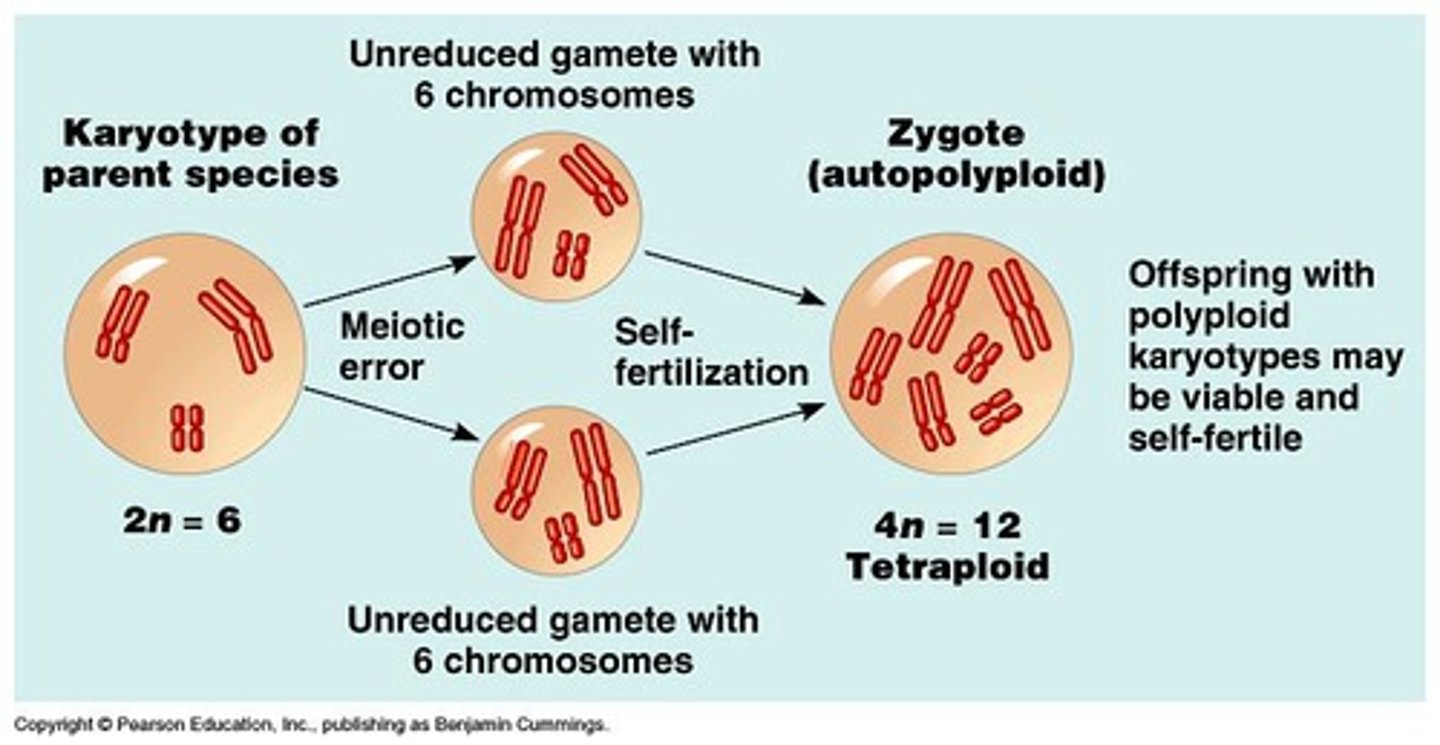
Polyploidy
Condition of having more than two sets of chromosomes.
Adaptive radiation
Rapid evolution of diverse species from a common ancestor.
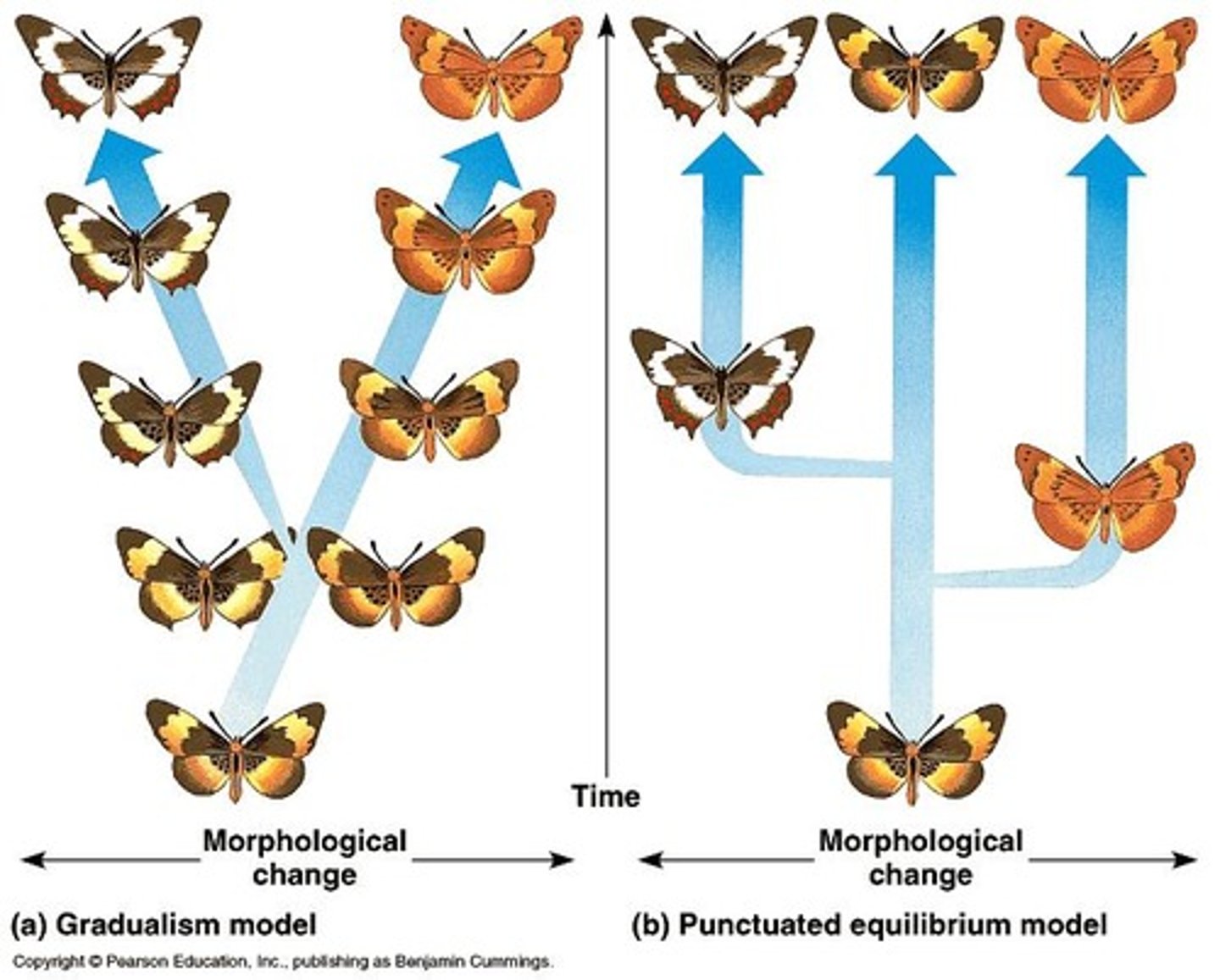
Gradualism model
Evolutionary change occurs gradually over time.
Punctuated equilibrium
Rapid evolutionary changes followed by long stability periods.
Exaptations
Structures evolving for one purpose but serving another.
Differential reproduction
Variation in reproductive success based on environmental factors.