Chapter 2: Market Forces - Supply & Demand
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Applied Business Economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is Demand?
The buyers side of the market (Consumer side)
What is Quantity Demanded (QD) ?
The amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at each price.
EX. At price =$2, the QD of beer is 500 on Friday night
What is the Law of Demand?
Price and Quantity Demanded are inversely related.
As Price goes UP, QD goes DOWN
As Price goes DOWN, QD goes UP
Why are demand curves downward sloping?
Because the Law of Demand
Typically a firm is concerned with the _____________________, which measures the buying plans for the entire population of potential consumers in the market
Market Demand Curve
How is the Market Demand Curve Derived?
It is derived from individual consumer demand curves using horizontal summation.
What leads to an Increase/Decrease in QD ?
A change in that own goods price causes movement ALONG the demand curve
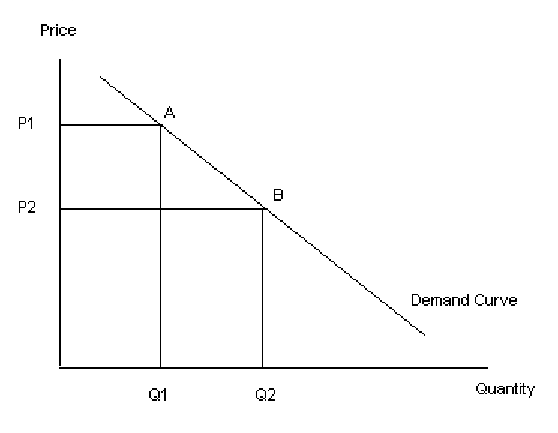
What are the 5 factors that lead to an Increase/Decrease in Demand?
Income
Prices of Related Goods
Advertising & Consumer Taste
Number of Buyers/Population
Consumer Expectations
All these factors will lead to a SHIFT of the DEMAND CURVE
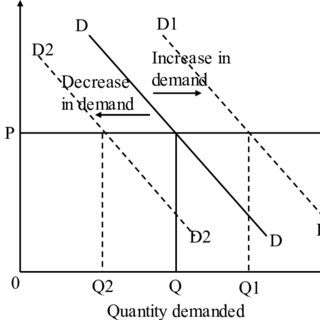
When referring to income what must you consider about the good?
If it is a Normal Good or Inferior Good
What is a Normal Good?
A good whose demand increase (shifts right) when consumer income increases
A good whose demand decreases (shifts left) when consumer income decreases
When income increases a person would rather travel buy plane (Normal Good), than by bus (Inferior Good)
What is an Inferior Good?
A good whose demand decrease when income increases
A good whose demand increase when income decreases
What must be considered when looking at the prices of related goods?
If they are substitutes of compliments
What is a substitute good?
When an increase in the price of one good increases the demand for another good
EX. Pepsi and Coke
If the price of Pepsi goes UP, then the Demand for Coke will go UP
If the price of Pepsi goes DOWN, then the Demand for Coke will go DOWN
What is a compliment good?
When an increase in the price of one good decrease the demand for the other good
EX. Hot dogs & Hot dog buns
As the price of hot dogs goes UP, the demand for hot dog buns goes DOWN
As the price of hot dogs goes DOWN, the demand for hot dog buns goes UP
How does advertising and consumer tase affect the demand curve?
As advertising INCREASES, Demand INCREASES
As advertising DECREASES, Demand DECREASES
How does the number of buyers/population affect the demand curve?
As # of buyers/population INCREASES, Demand INCREASES
As # of buyers/population DECREASES, Demand DECREASES
How does consumer expectations affect the demand curve?
If consumers think prices will increase in the future, we see an increase in current demand
As prices INCREASE, Current Demand will INCREASE
What is Supply?
Supply is about the sellers side of the market (producers side)
What is Quantity Supplied?
The amount of product/service that suppliers are willing and able to sell at each price.
What is the Law of Supply?
As Price Increases, QS Increases
As Price Decrease, QS Decreases
How do you Aggregate the Supply Curve?
Horizontal Summation - using individual supply curves
What leads to an Increase/Decrease in Quantity Supplied?
A change in that own goods price
What are the 6 factors that to an Increase/Decrease in Supply?
Input prices
Technology
Number of Sellers
Government Regulations
Producer Expectations
State of Nature
All these factors lead to a SHIFT in the Supply Curve
What is the affect of input prices on the supple curve?
As Prices of Inputs INCREASES, Supply DECREASES
As Prices of Inputs DECREASES, Supply INCREASES
EX. When the price of sugar increases, producing ice cream becomes less profitable and the supply of ice cream decreases
What is the affect of technology on the supple curve?
As Technology INCREASES, Supply INCREASES
Technology can’t go backwards so it can’t decrease
EX. The invention of the ice cream machine reduced the firms costs and the supply of ice cream increases
What is the affect of the number of sellers on the supple curve?
As the # of sellers INCREASES, Supply INCREASES
As the # of sellers DECREASES, Supply DECREASES
EX. If J’s Creamery went out of business, the supply of ice cream in Lubbock would decrease
What is the affect of government regulations on the supple curve?
As Gov. Reg. INCREASE, Supply DECREASES
As Gov. Reg. DECREASES, Supply INCREASES
EX. If taxes increase, supply goes down
EX. If subsidies increase, supply increases
What is the affect of producer expectations on the supple curve?
If prices are expected to INCREASE, Current Supply DECREASES
If prices are expected to DECREASE, Current Supply INCREASES
What is the affect of state of nature on the supple curve?
EX. If a flood/drought kills crops, Supply decreases
What is Market Equilibrium?
EQBM in a competitive market is determined by the interaction of both supply and demand
The competitive market EQBM occurs at a price where QS = QD
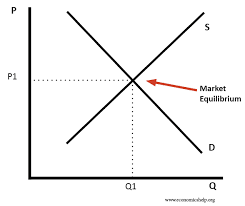
What is the “market clearing price” ?
The equilibrium price
What happens if the price is below the EQBM?
There will be a temporary shortage because of excess demand QD > QS
Buyers will pay more to get it (driving up price)
Sellers will want to supply more
Market forces push price and output back to EQBM levels
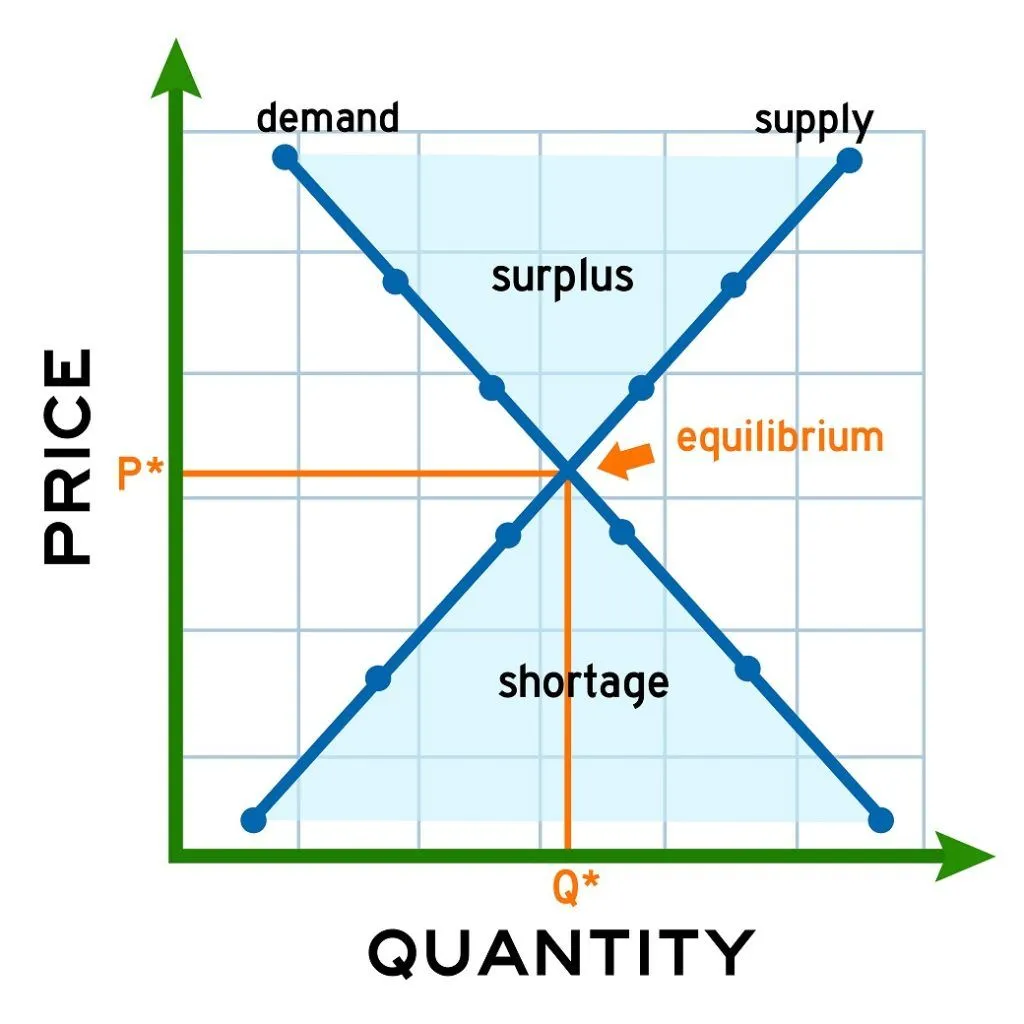
What happens if the price is above the EQBM?
There will be a temporary surplus because QS > QD
Sellers will want to lower price to alleviate surplus (Driving price down)
Consumers will want to buy more
Market forces push price and output back to EQBM levels
How do you find the EQBM price and quantity?
Set QD = QS to find EQBM Price
Plug EQBM Price back into Demand or Supply Function and Solve for Q
What happens to eqbm price and eqbm quantity if there is an increase in demand?
Q increases , P increases (when in doubt, draw it out)
What happens to eqbm price and eqbm quantity if there is an decrease in demand?
Q decreases , P decreases (when in doubt, draw it out)
What happens to eqbm price and eqbm quantity if there is an decrease in supply?
Q decreases, P increases (when in doubt, draw it out)
What happens to eqbm price and eqbm quantity if there is an increase in supply?
Q increases, P decreases (when in doubt, draw it out)
What happens to Eqbm Price and Eqbm Quantity if there is an Increase in Demand and an Increase in Supply?
Affect on Price: Ambiguous
Affect on Quantity: Increase
What happens to Eqbm Price and Eqbm Quantity if there is an Decrease in Demand and an Increase in Supply?
Affect on Price: Decrease
Affect on Quantity: Ambiguous
What happens to Eqbm Price and Eqbm Quantity if there is an Decrease in Demand and an Decrease in Supply?
Affect on Price: Ambiguous
Affect on Quantity: Decrease
What happens to Eqbm Price and Eqbm Quantity if there is an Increase in Demand and an Decrease in Supply?
Affect on Price: Increase
Affect on Quantity: Ambiguous
What is a free market?
A market where no government or agency is forcing people to make things or buy things.
How do we measure consumer welfare?
By measuring
Consumer Surplus
Producer Surplus
What is consumer surplus?
It is the difference between the amount consumers would be willing to pay and the amount they actually pay.
CS is a way to monetize the benefit that consumers receive by participating in the market, compared to not
Where is CS located on the Supply and Demand Curve?
Above price, Below Demand
What is producer surplus?
It is the difference between the price producers actually receive and the price at which they are willing to accept to sell.
Can think of this as the difference between the price they get and the cost they incur to make it
PS is basically “variable cost price”
Where is PS located on the Supply and Demand Curve"?
Below Price, Above Supply
One way to evaluate the outcome in a market is whether it is ________.
Efficient
How do you know if an outcome is efficient?
An outcome is efficient if it is maximizing the total surplus.
What makes up total surplus?
TS = CS + PS
In general, _____________________ generate an efficient equilibrium outcome!
Unregulated competitive markets
What are two characteristics of unregulated competitive markets?
Gains from trade are maximized
All the transactions that should take place are taking place
Just because the eqbm. is efficient, does not necessarily mean it is equitable/fair
What is the definition of government regulations in markets?
The government sometimes intervenes in markets through regulation
EX. Price controls, Quotas, Taxes, etc.
What is a price floor?
When the government sets a minimum price at which a good/service can be sold in the market
Why would the government want to have a price floor?
To help suppliers in the market via higher prices
What must be true in order for a price floor to be effective?
The price floor must be about the market price.
In order see if a price floor is effective we need to measure ________.
Welfare
What is deadweight loss?
It is the welfare lost because a price floor is implemented. OR The reduction in total surplus that occurs as a result of a markets inefficiency.
What is a price ceiling?
The government sets a maximum price at which a good or service can be sold in the market.
EX. Rent Controls, Taxi Fares, Gasoline Prices
Why would the government want to implement price ceilings?
To help buyers/consumers in the form of lower prices
What is another way the government can impact markets?
Through taxes
What are the impacts of taxes on a per unit sales tax?
Taxes can be assessed on the buyers or sellers
both sides will typically share the burden of the tax
What is a tax incidence?
The division of the burden of the tax between the buyer and seller
What will happen if the government puts a tax on the sellers for $1.50 per cigarette pack?
Supply will decrease by the exact amount of the tax, $1.50
Suppose a tax of $1.50 is assessed to the buyers. What will happen in this scenario?
Demand will decrease by the amount of the tax, $1.50
Who pays the tax?
The burden of the tax depends on the relative “shape” of the supply & demand curve
Which ever curve is steeper, they will pay more of the tax
The steeper the curve the less price sensitive that side of the market is
Are sales taxes efficient?
No, because they create DWL
The bigger the tax, the bigger DWL
What is a subsidy?
just a negative tax
Implications are similar to taxes
Except, now we get an “inefficiency” (DWL) in the form of too much being produced