economics week 7b - market failures (externalities)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
are markets efficient?
at the equilibrium in a competitive market, marginal benefit = marginal cost, resource allocation is efficient (max total benefit is achieved), a competitive market produces the efficient quantity.
note
demand curve is the buyers marginal benefit, supply curve is the sellers marginal cost.
marginal benefit = marginal benefit only at competitive equilibrium
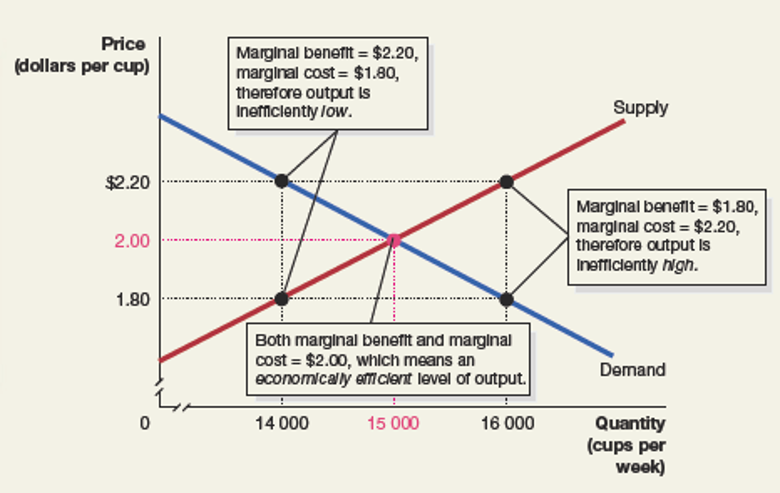
market failure
when the market produces too much or too less (inefficient outcome), this is known as the market failure.
externality
a benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service.
positive externality
when a production or consumption activity benefits someone who is not directly involved with the activity and who do not pay for it.
negative externality
when a production or consumption activity imposes costs on someone who is not directly involved with the activity and no compensation is paid.
4 types of externalities
positive and negative externalities in production
positive and negative externalities in consumption
effect of externalities
economic efficiency is reduced as externalities lead to a divergence between:
private and social benefits
private and social costs
private cost
the cost borne by the producer of a good/service.
social cost
the total cost of producing a good or service, including both the private cost and any external cost. (private cost + external cost).
private benefit
the benefit received by the consumer of a good or service.
social benefit
total benefit from consuming a good or service, including private benefit and external benefits.
negative externalities in production
the social cost of the production activity is greater than the private cost of production.
marginal social cost = marginal private cost + external cost
policies for negative externalities in production
taxes imposed on production equals to the cost of the externality.
aim of the tax is to internalise a negative externality
other government policies to deal with negative externalities
government tells firms what they must do, pollution taxes/tradable permits.
negative externalities in consumption
due to external cost, the social benefit of the consumption activity is less than the private benefit of consumption
msb < mpb
deadweight loss occurs
private market overproduce.
positive externalities in consumption
due to external benefit, social benefit from the consumption activity is > than the private benefit from the activity.
msb = mpb + external benefit
msb > mpb
consumption occurs at a level that is lower than the socially efficient level, and the price is lower than the socially efficient price.
deadweight loss occurs
private market will underproduce
policies for positive externalities in consumption
financial subsidy (payment) could be provided by government to consumers, equal to the value of the externality. will cause consumers to internalise the externality.
positive externalities in production
MSC < MPC
overall social cost (real cost to the society) < private cost due to external benefits.
products occurs at a level lower than the socially efficient level, and price is higher than the socially efficient price.
private market underproduces
deadweight loss
policies for positive externalities in production
financial subsidy could be provided by the government to the firms to increase supply. Subsidy aim is to internalise positive externality.