Midterm Exam 1
1/267
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 7: Tuesday, October 7th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
268 Terms
_______ explains how and when life began on Earth
the emergent theory of life
the formation of Earth and the presence of an unstable atmosphere happened around _______
4.5 billion years ago
the presence of a stable hydrosphere happened around _______
4.2 billion years ago
prebiotic chemistry (natural chemical processes and pathways of early Earth) happened around _______
4.2-4.0 billion years ago
Pre RNA world happened around _______
4 billion years ago
RNA world happened around _______
3.8 billion years ago
(LUCA) First DNA/protein life occurred around _______
3.6 billion years ago
the diversification of life happened around _______
3.6 billion years ago-present
from the diversification of life, which 3 organisms emerged?
unicellular microorganisms, multicellular organisms, and organisms that can switch between unicellular and multicellular
multicellular organisms have specialized and interdependent cells because they evolved from _______
single-cell organisms
_______ keeps elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, argon, hydrogen, and helium (also found in Earth’s atmosphere and the universe) balanced in our body
hormone communication
our internal environment is 70% water, and compartmentalized into _______ and _______ fluid
intracellular and extracellular
our extracellular fluid is separated into _______ (in tissue) and _______ (in blood vessels, lymph vessels, and the cerebralspinal cord)
interstitial, inter-tubal
true or false: the external environment is dynamic (unstable) and uncertain
true
_______ is the internal regulation of the body in relation to to the external environment, and necessary for growth, survival, and reproduction
homeostasis
_______ feedback loops bring interval levels back to their baseline
negative
_______ feedback loops push internal levels past their baseline in order to communicate a necessary message
positive
_______ is a chemical messenger that coordinates the activities of diferent cell groups in reponse to environmental changes
hormone
true or false: hormones have specific chemical structures that fit into target cell receptors
true
true or false: one endocrine organ can only control its own function
false. One endocrine organ can control the function of other endocrine organs
true or false: a single hormone can induce multiple biochemical responses in its target cell, or multiple hormones can perform the same function
true
during this type of chemical communication, chemicals are sent out of endocrine glands via endocrine cells/glands
endocrine communication
_______ may become specialized to coordinate cellular activity and maintain homeostasis
endocrine cells
_______ consisits of a mass (parenchyma) of secretory cells, connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves
encorine glands
true or false: endocrine glands can be within tissues of exocrine glands/organs, transient, or produce one/more than one hormone
true
true or false: every cell in our body can only produce one chemical
false. every cell in our body can produce the same chemicals, but for some this ability is turned off for specialization
during this type of chemical communication, chemicals bind to receptors on cells next to each other
paracrine communication
during this type of chemical communication, chemicals bind to receptors on the surface of the cell that releases them
autocrine communication
during this type of chemical communication, chemicals bind to receptors inside the cell that release them, but they remain inside the cell
intracrine communication
soluble, secreted signaling polypeptides capable of instructing specific cellular responses ina biological environment are called _______
growth factors (GF)
during this type of chemical communication, chemicals are released in the brain adn act on the body
neural communications
neurons release these chemicals into tbe bloodstream, which act on distant target organs
neurohormones
neurons release these chemicals at synapses to communicate directly with neighboring neurons
neurotransmitters
neurons release these chemicals that modify the effect of neurotransmitters
neuromodulators
_______ are used between same-specicies organisms to communicatephe
pheromones
_______ are used between different-species of organisms
allomones
true or false: current hormones evolved from chemicals that served a neurocrine/paracrine function
true
_______ focues on body fluids to diagnose illnesses (blood, yellow bile, black bile, phlegm)
Hippocrates’s humoral hypothesis
_______ found that loss of testes in men and birds led to voice and size changes, and less aggression
Aristotle
_______ observed differences between ductile and ductless glands
Thomas Warton
_______ suggested that thyroid gland secreted substances into blood
Fredrik Ruysch
_______ developed radioimmunoassay to measure hormone levels in blood/body fluids
Rosalyn Yalow
_______ and _______ developed immunometric and biological assays to enable the discovery of nerve and epithelial growth factors
Rita Levi-Montalicini and Stanley Cohen
_______ used transgenic and gene knockout animals to enable precise testing for effects of hormones and receptors
Richard Palmiter
hormones, neurotransmitters, neurohormones, pheromones, and allomones are considered ______ because they dont fit into receptors so they’re modified to work and create new chemicals
ligands
true or false: polar hormones are amino acid based
false. polar hormones are cholesterol based
true or false: non-polar hormones are cholesterol based
false. non-polar hormones are amino acid based
true or false: water soluble hormones are polar and can’t pass through the membrane, so they need extracellular receptors
true
true or false: fat soluble hormones are non-polar and can pass through the membrane, so they need intracellular receptors
true
enzymes alter the shape of _______ to create hormones
precursors
the precursor for epinephrine, norepinephrine, doapmine, triiodothyronine, and thyroxine is _______. they are _______ or ________ soluble
tyrosine. fat or water
the precursor for testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, cortisol, aldosterone, and vitamin D is a _______. they are _______ soluble
steroid. fat
the precursor for oxytocin, vasopressin, insulin, and secretin is a _______. they are _______ soluble
peptide/protein. water
_______ is an environmental factor that may alter how chemical signals act on DNA to determine which segment is transcribed
epigenetics
_______ regulates other genes by secreting a regulatory protein
regulatory gene
_______ is affected by the regulatory proteins secreted by the regulatory gene (promotor)
regulatory sequence
_______ help genes be expressed at the right time
transcription factors
the _______ has a signal peptide directing it to the Golgi apparatus, where it’s folded into a _______
pre hormone, signal protein
in the Golgi apparatus, the prehormone is processed into a _______ once enzymes remove the signal protein and carbohyrdates are added
prohormone
the hormone and enzymes are moved into secretory vesicles and excreted out of the cell via _______
exocytosis
true or false: hormones and steroids are stored in secretory vesicles within glands where they're produced
false. only hormones are stored in secretory vesicles within glands where they're produced
what two chemicals are involved in exocytosis to release hormones from vesicles?
ATP and Ca²+
during hormone release, the donor membrane forms vesicles and carries hormones inside and the v-SNARE proteins (coding) tell it where to go. this step is known as ________
budding
during hormone release, the vesicle travels on the cytoskeletal filament via motor proteins (has ATP attached), which pulls it to the right location. this step is known as _______
movement
during hormone release, the vesicle approaches the acceptor membrane so tethering factors and complexes can hold it in place while v-SNAREs on the vesicles and t-SNAREs line up. this step is known as _______
tethering
during hormone release, the vesicle and acceptor membrane fuse so the vesicle can release out of the cell, or in another compartment. this step is known as _______
fusion
_______ are synthesized and immediately absorbed through the membrane
steroid hormones
true or false: hormones circulate in the bloodstream freely in small concentrations, or attached to carrier proteins
true
true or false: hormones bound to carrier proteins can be broken down
false. bound hormones can’t be broken down. separation from carrier proteins is required for hormone effect and destruction
the time it takes for hormone concentration in blood to be reduced by half is the_______
half life
hormones can be broken down by _______, _______, or _______
the liver, kidneys, or muscles (other tissues)
in the liver, a _______ or _______ is added to hormones so they can become more water soluble and leave via urine
sulfate group or acid
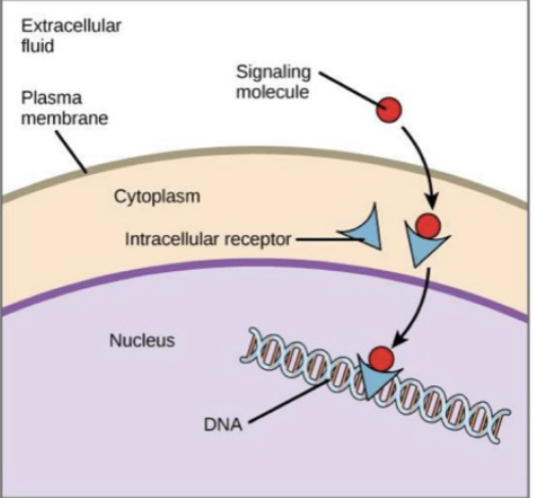
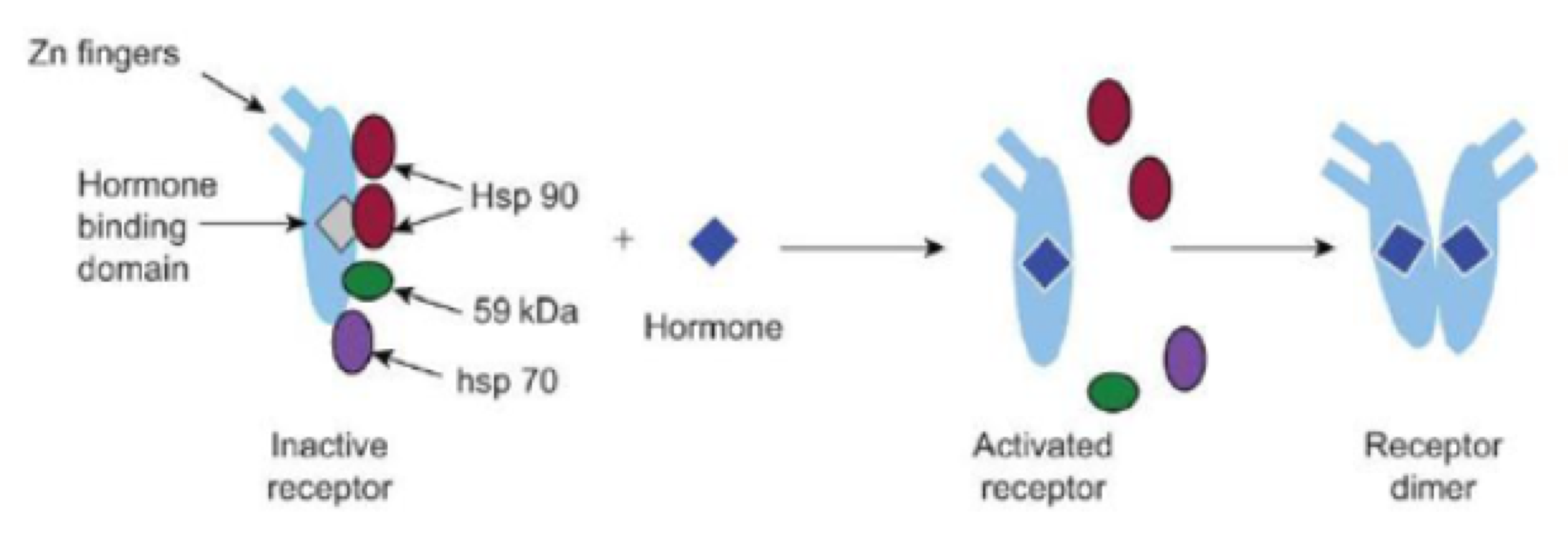
these receptors are inside the cell; non-polar (fat soluble) hormones bind here
intracellular receptors
these receptors are on the membrane and always need secondary messengers; polar hormones (water soluble) bind here
transmembrane receptors
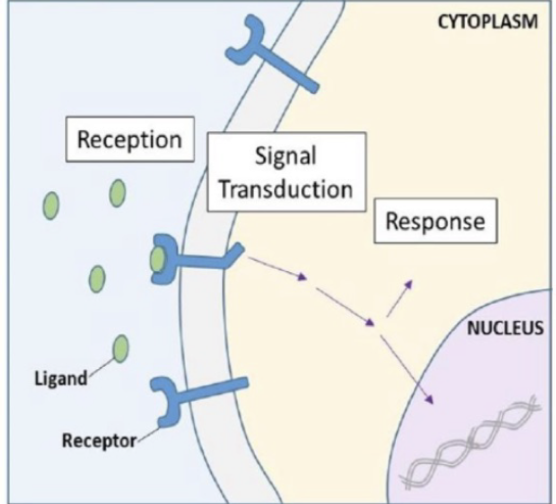
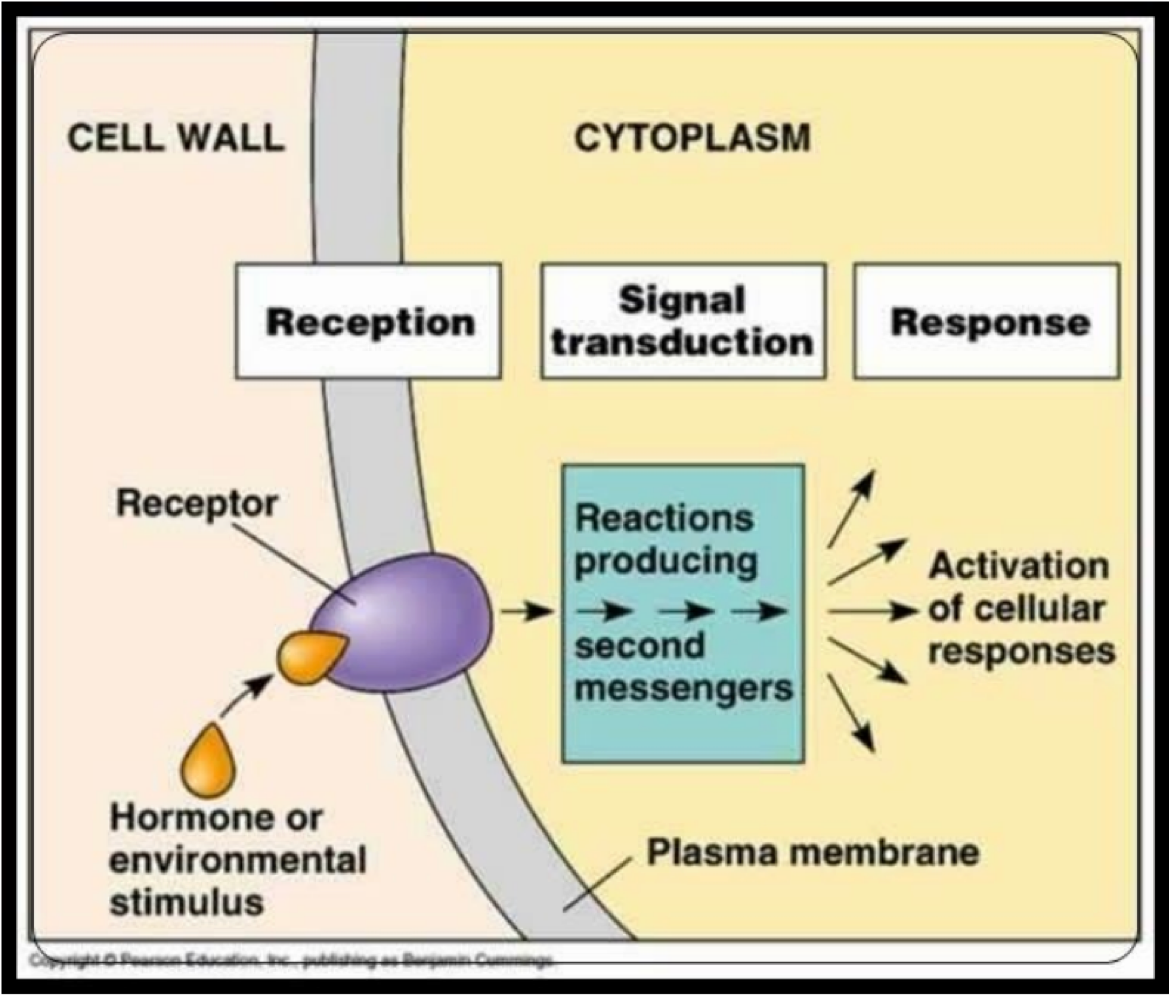
This process is involved in transmembrane receptors and converts the hormone message into a cellular response by changing the cell biochemistry
signal transduction
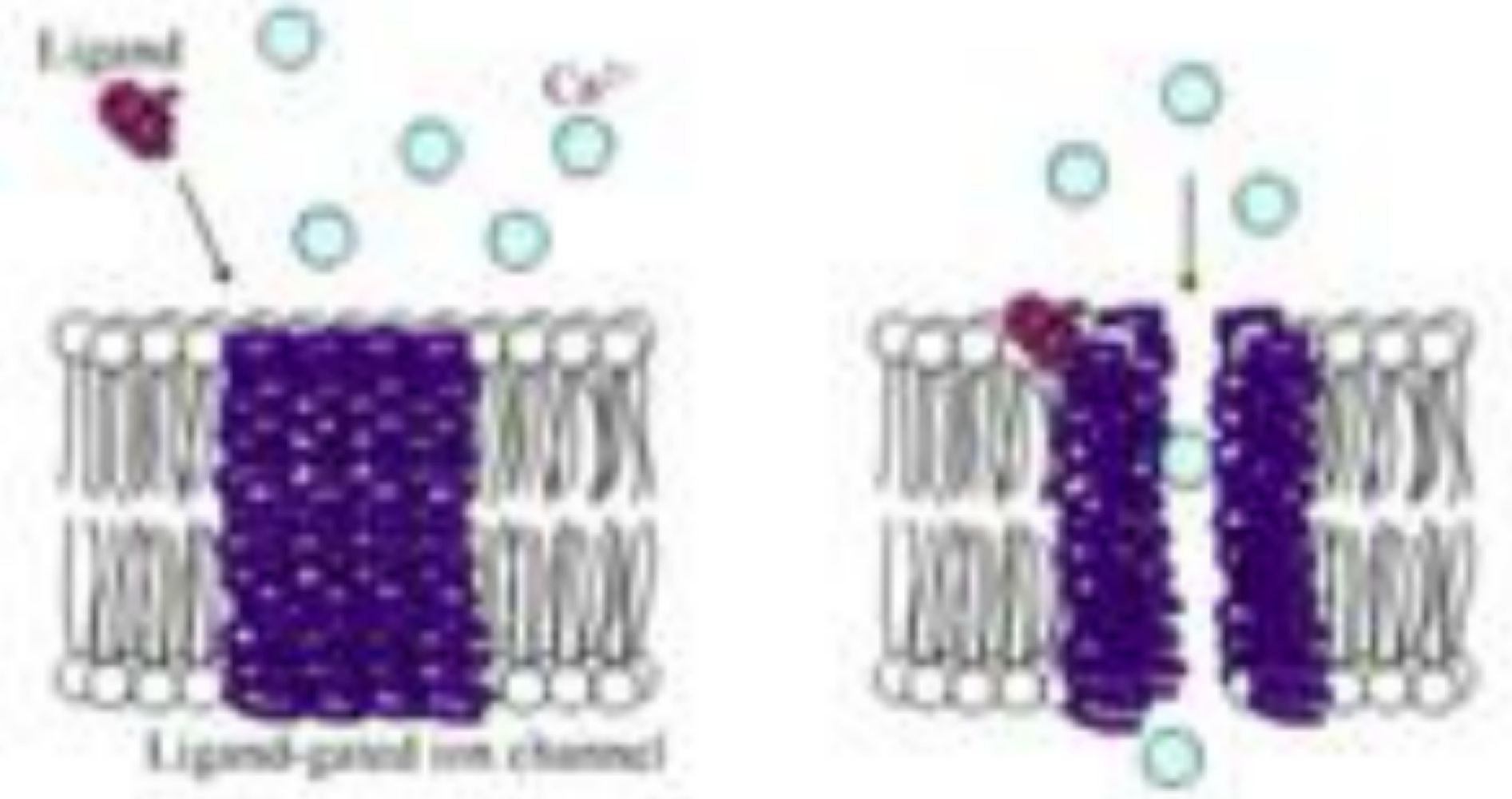
these receptors are transmembrane and open or close channels (sodium-potassium pump)
ionotropic receptors
true or false: in the ECF, there are a lot of sodium ions, but in the ICF, there are a lot of potassium ions (both cations)
true
true or false: in the ECF, there are a lot of hydrogen phosphate ions (HPO42-), but in the ICF, there are a lot of calcium ions (both anions)
false. in the ECF, there are a lot of calcium ions, but in the ICF, there are a lot of hydrogen phosphate ions (HPO42-)
these receptors can be intracellular or transmembrane (with or without enzymes), and initiate signaling pathways within the cell
metabotropic receptors
these receptors have enzymes in side (guanylyl cyclase, insulin)
intrinsic enzyme transmembrane receptors
these receptors have enzymes attached (g-protein)
enzyme-coupled transmembrane receptors
true or false: receptors are proteins/glycoproteins, located in the membrane, cytosol, or nucleus, and are categorized base don their derived-from gene
true
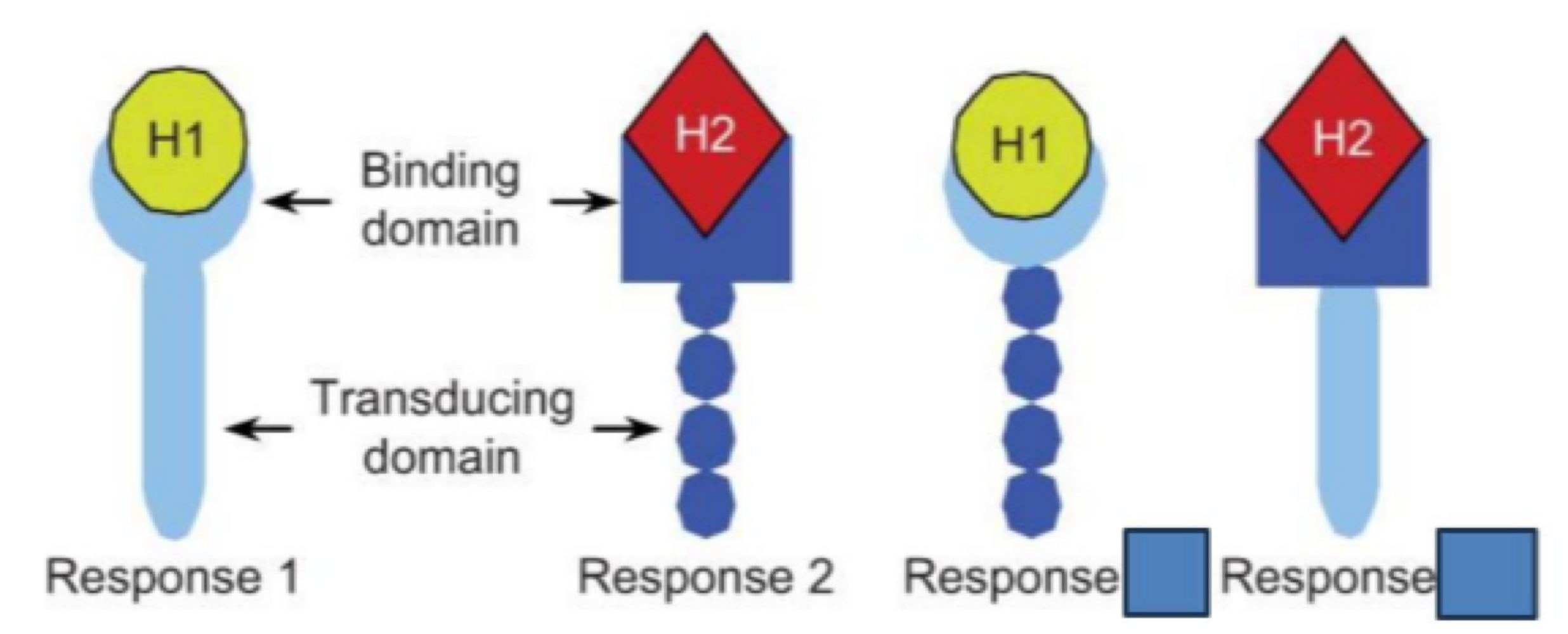
the _______ is where the hormone binds to the receptor
binding site
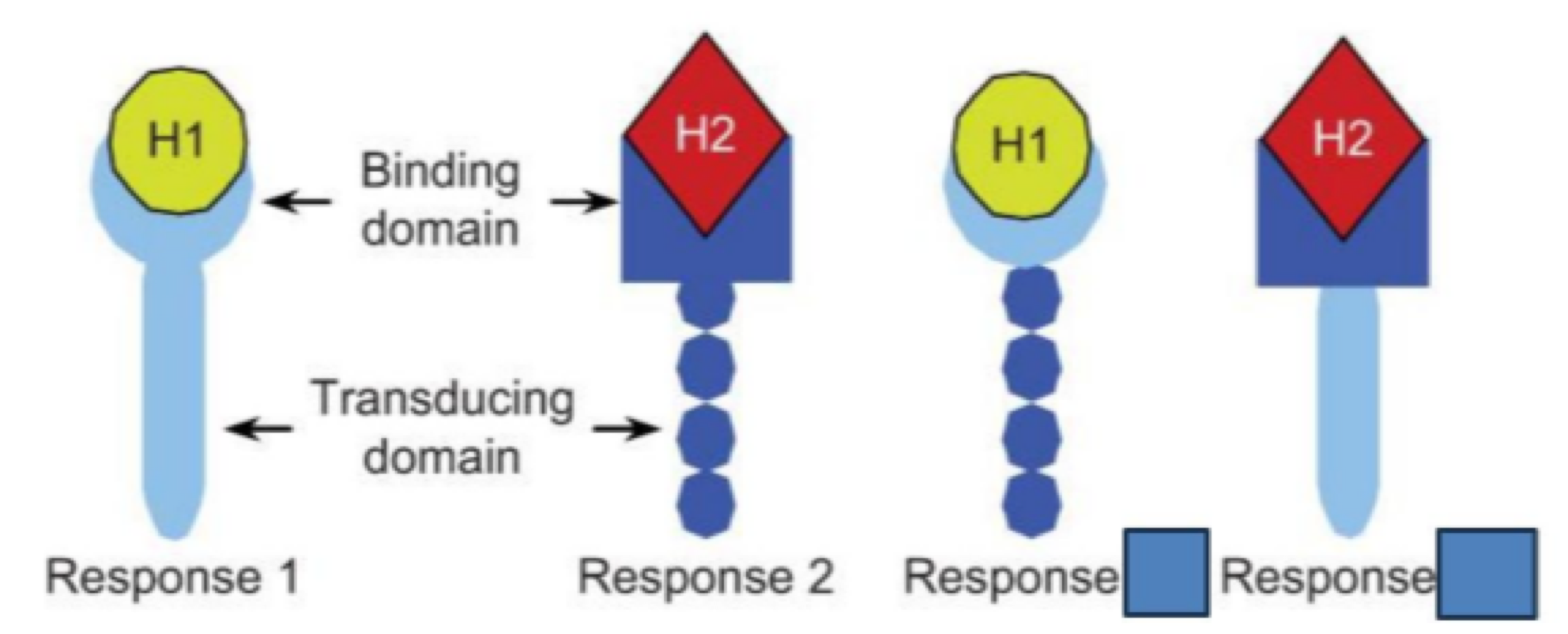
the _______ is where the response is created on a receptor
transducing domain
true or false: fat soluble steroids binding to intracellular receptors results in enzyme production/changes in enzyme production rate
false. fat soluble steroids binding to intracellular receptors results in protein production/changes in protein production rate
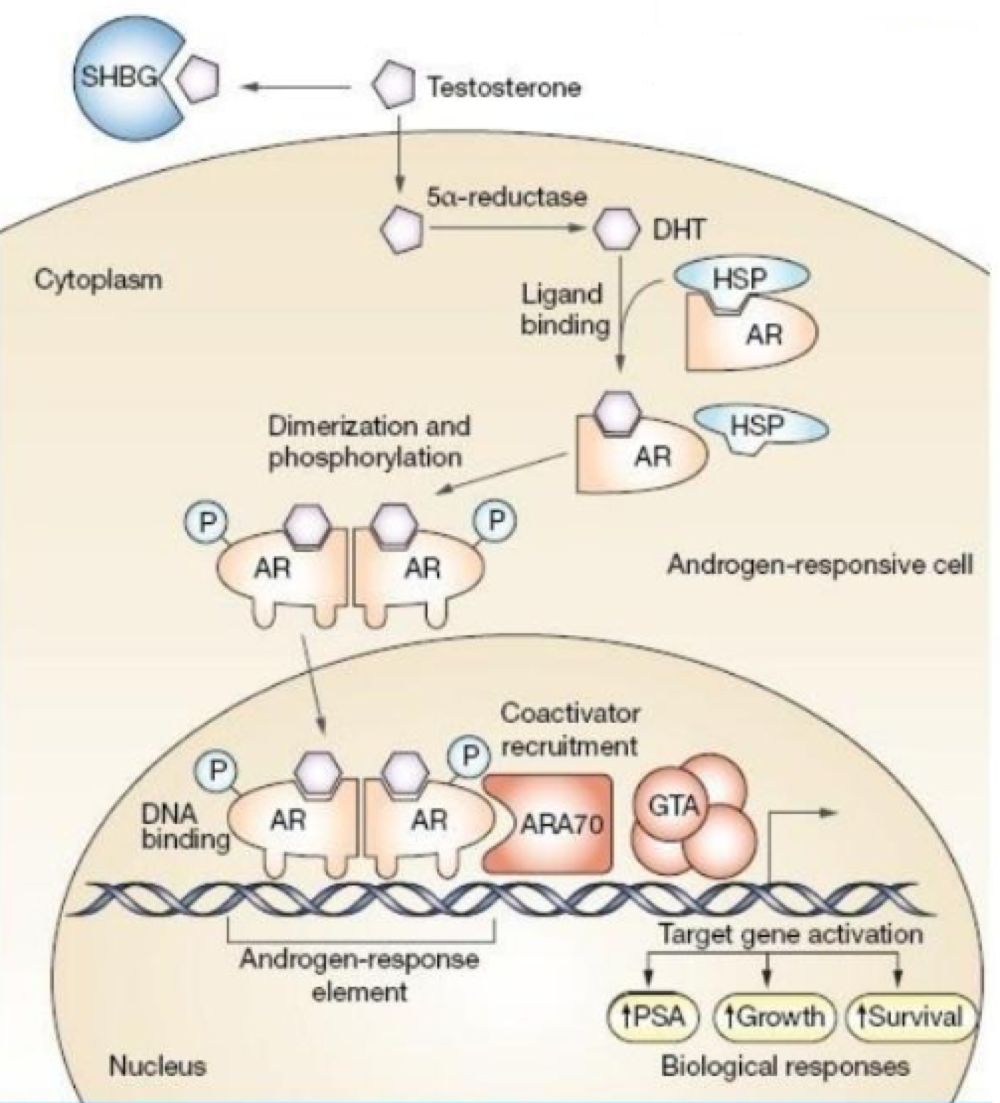
true or false: adding a phosphate to a steroid hormone activates it
true
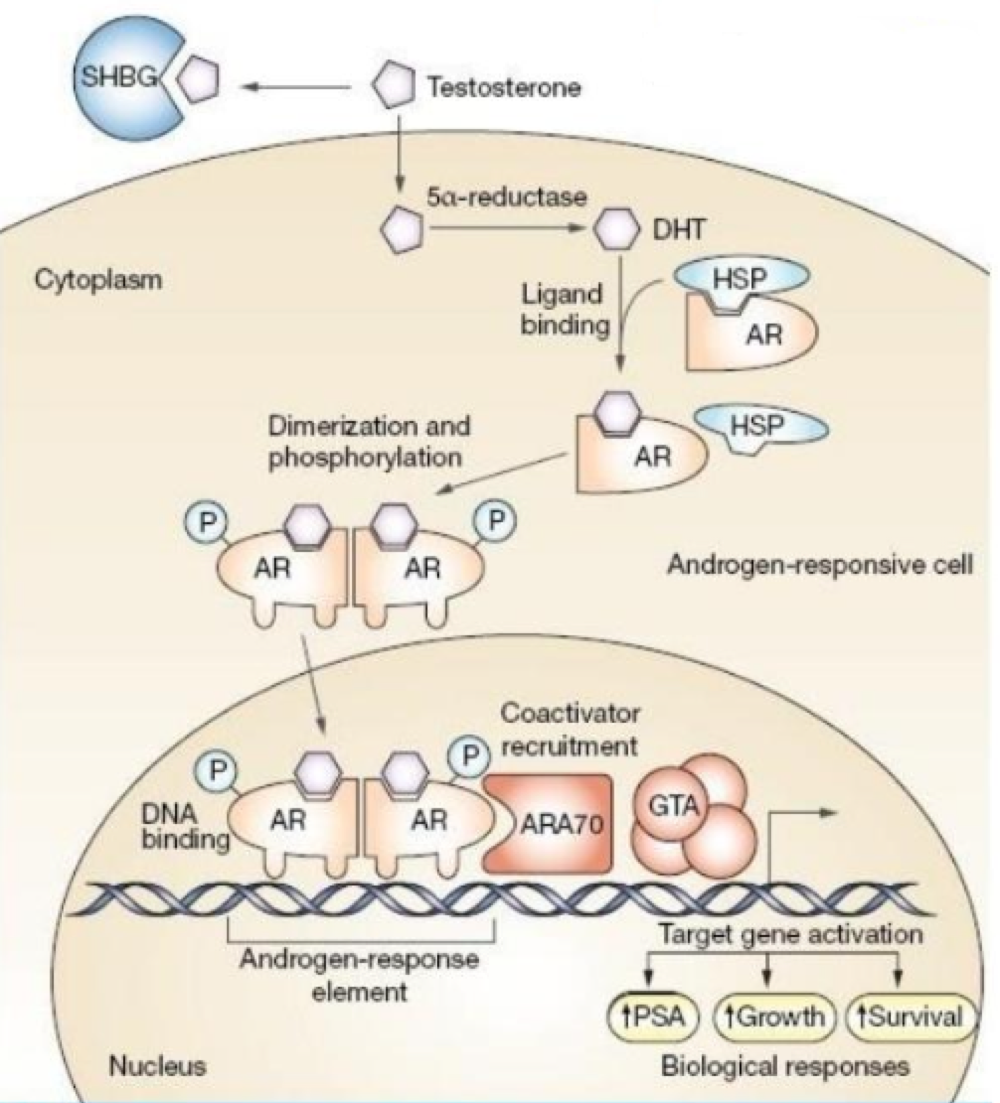
intracellular receptors are _______. if they’re separated, they don’t work
dimers
receptor conformation changes stimulates the complex to bind to _______ on DNA, which are specific sequences that stimulate/repress activity of transcription factors
hormone receptor elements (HREs)
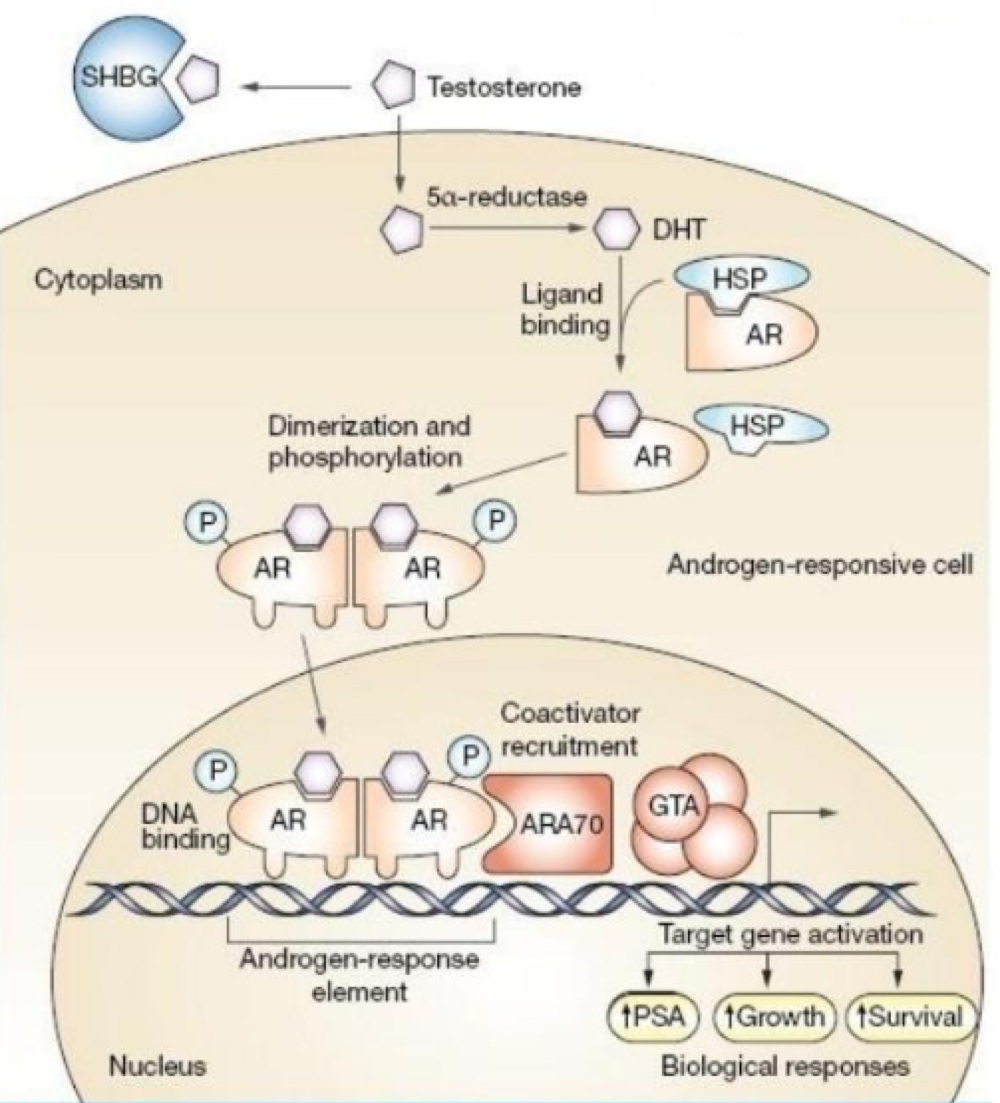
true or false: thyroid/vitamin D hormones are permanently attached to HREs on DNA, regardless if the hormone is present.
true
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, nuclear proteins attach to receptors to prevent DNA damage because _______
ligands are absent
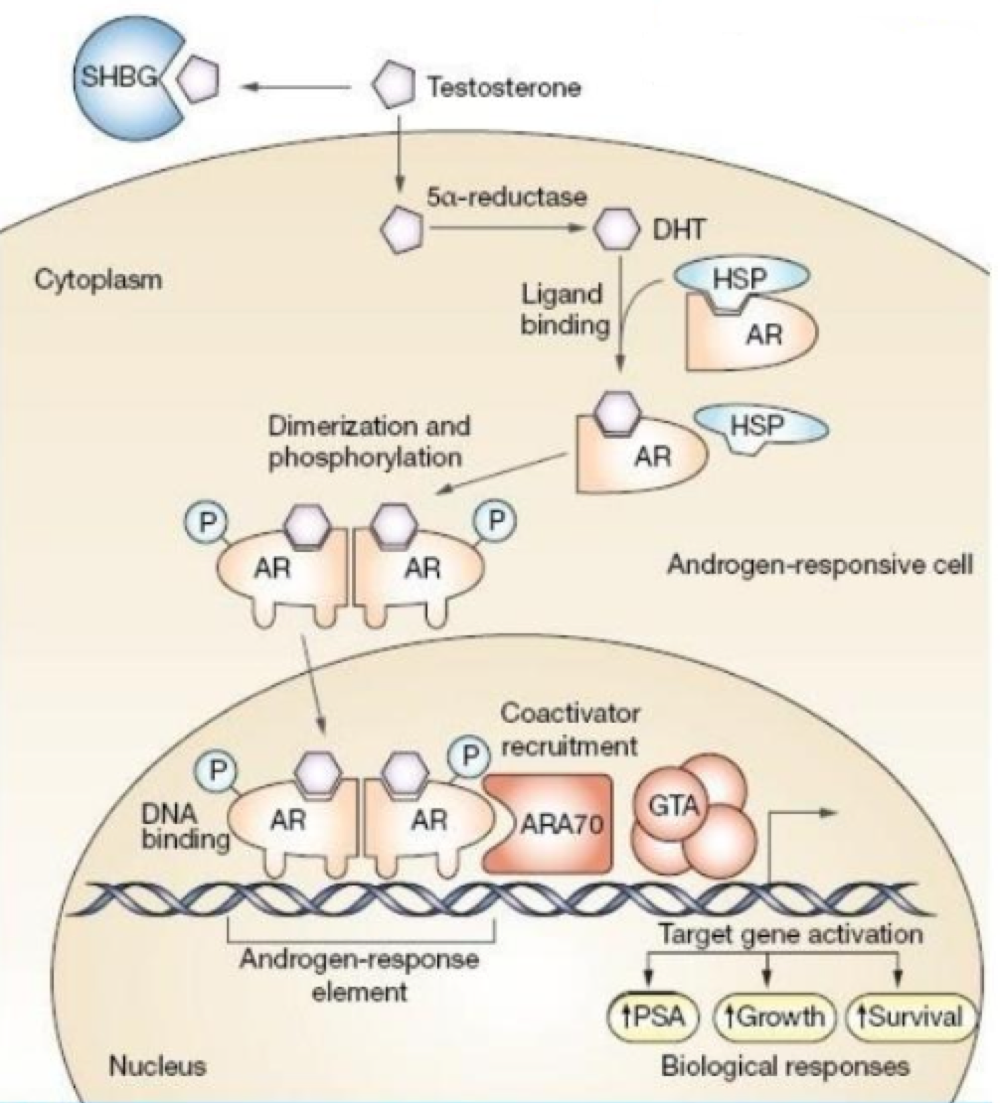
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, nuclear proteins which with other proteins so silent genes are expressed because _______
ligands are present
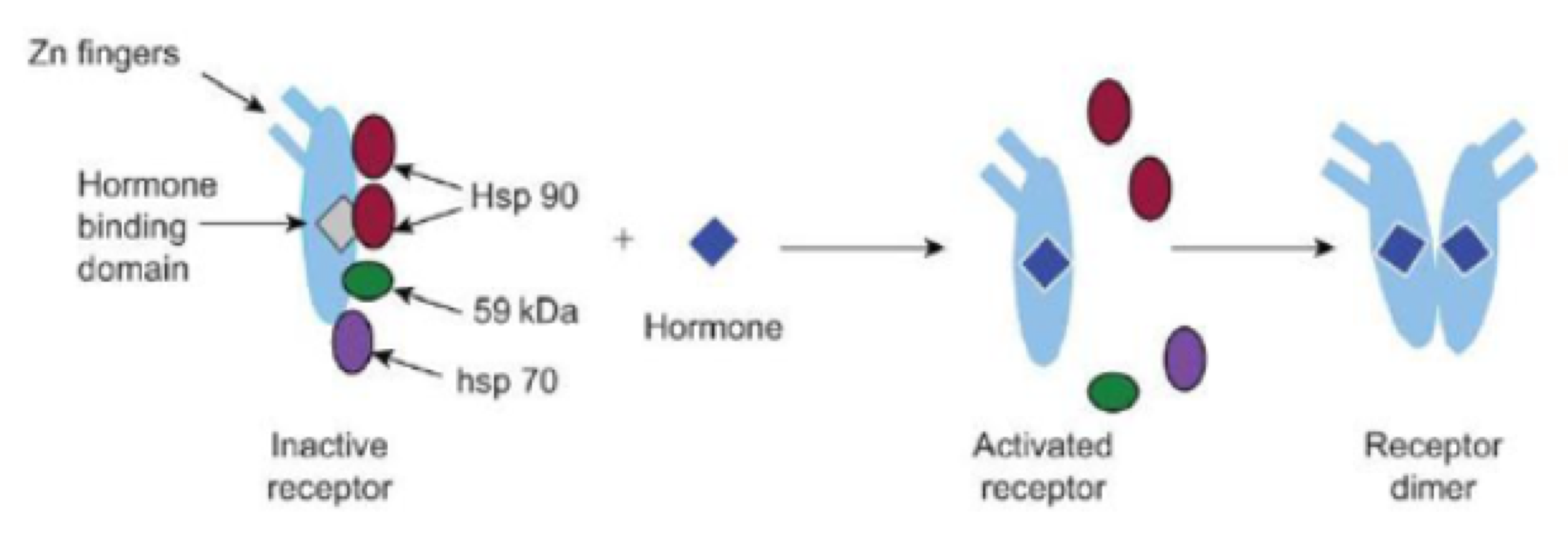
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, hormones dissociate from the receptor, are inactivated, then diffuse into ECF because_______
hormone levels declined
_______ initiate signaling pathways that changes gene expression or cell bio chemistry
secondary messengers
_______ receptors have single proteins strands and seven stretches of 25 amino acids
G-protein
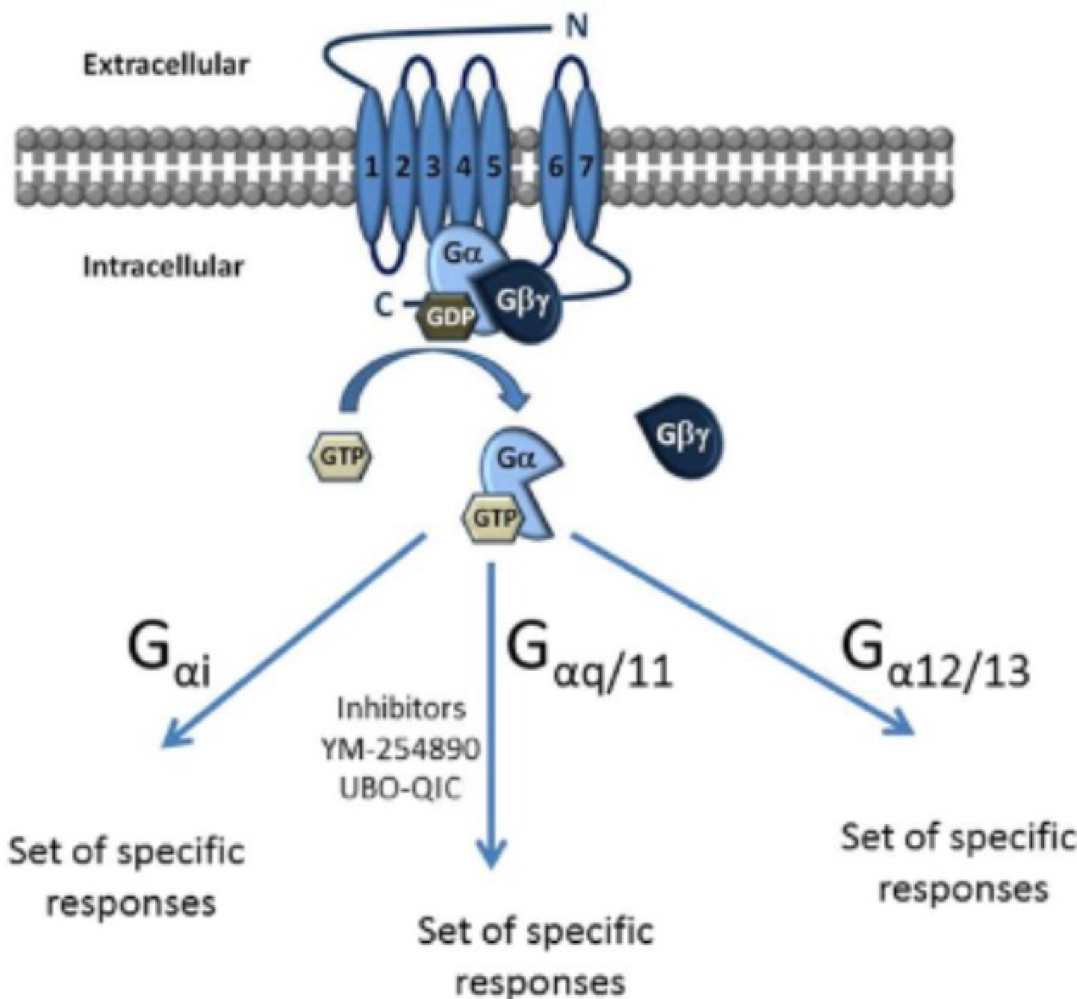
G-protein subunits are _______, _______, and _______; all bind to and activate ion channels
alpha, beta, and gamma
Gas proteins stimulate _______ to catalyze ATP → cAMP
adenylyl cyclase
Gai proteins _______ adenylyl cyclase
inhibit
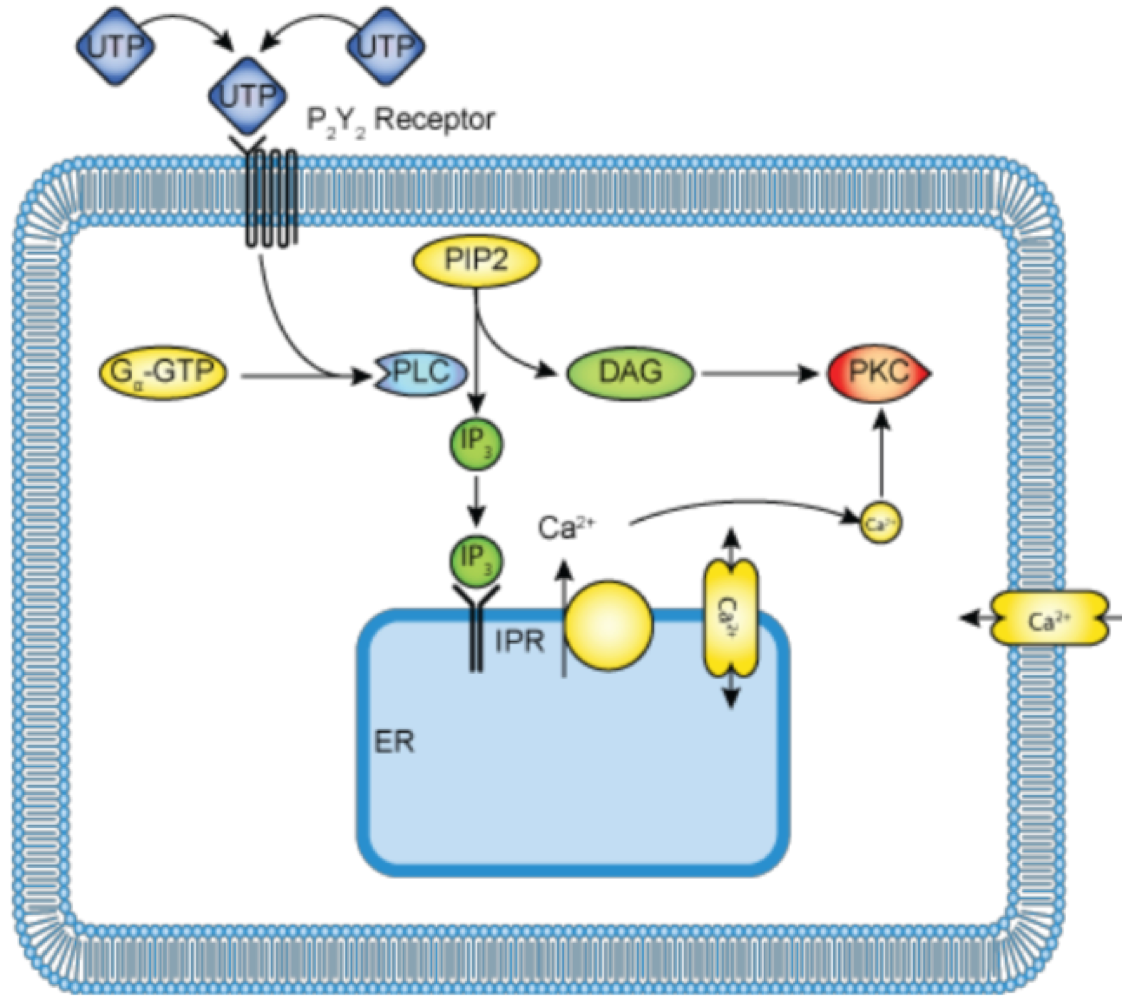
Gaq stimulates _______
phospholipase C
Ga12 binds to _______ nucleotide exchange factors
guanine
G-protein alpha subunit is GTPase, and catalyzes _______ to _______
guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to guanosine triphosphase (GTP)