Microbiology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What does the science of microbiology study?
Life forms too small to see with the unaided eye.
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, 1673
made first observations of bacteria and protozoa on microscopes, termed them “animalcules”
Nomenclature
naming of organisms
latin
started with Carlos Linnaeus
Genus species
G. species
EX: Escherichia coli or E.coli
if handwriting, underline not italicized
Types of microorganisms:
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Protozoa
Algae
Viruses (NOT living)
other multicellular animal parasites
Bacteria
prokaryote
unicellular
cell wall is peptidoglycan
asexual reproduction
obtains nutrition through organic molecules, photosynthesis, and inorganic substances
Archaea
prokaryote
unicellular
Yes/No cell wall (no peptidoglycan)
asexual reproduction
extreme halophiles, thermophiles, and methanogens
Fungi
eukaryotes
uni/multicellular
cell wall is chitin
sexual and asexual reproduction
obtain nutrition through absorption of organic compounds
Protozoa
eukaryote
unicellular
yes/no cell wall (varies)
sexual and asexual reproduction
absorbs or ingests organic compounds from environment, some are parasites and some are photosynthetic
Algae
eukaryote
uni/multicellular
cell wall is made of cellulose
sexual and asexual reproduction
nutrition through photosynthesis
Helminths
eukaryotes
multicellular
n/a cell wall
sexual reproduction
obtain nutrition through absorption, ingestion, and phagocytosis
viruses
n/a prokaryote or eukaryote
acellular
n/a cell wall
n/a nutrition
reproduction happens within the host
Robert Hooke, 1665
coined the term “cells”
smallest living structural units
Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells
All living things can arise only from preexisting living cells
Louis Pasteur, 1861
S-shape flask experiment
aseptic technique
People believed in spontaneous generation, but Pasteur believed spoilage or mold must have come from something
debunked spontaneous generation
showed the difference between fermentation, souring, and spoiling
contributed to Germ Theory of Disease
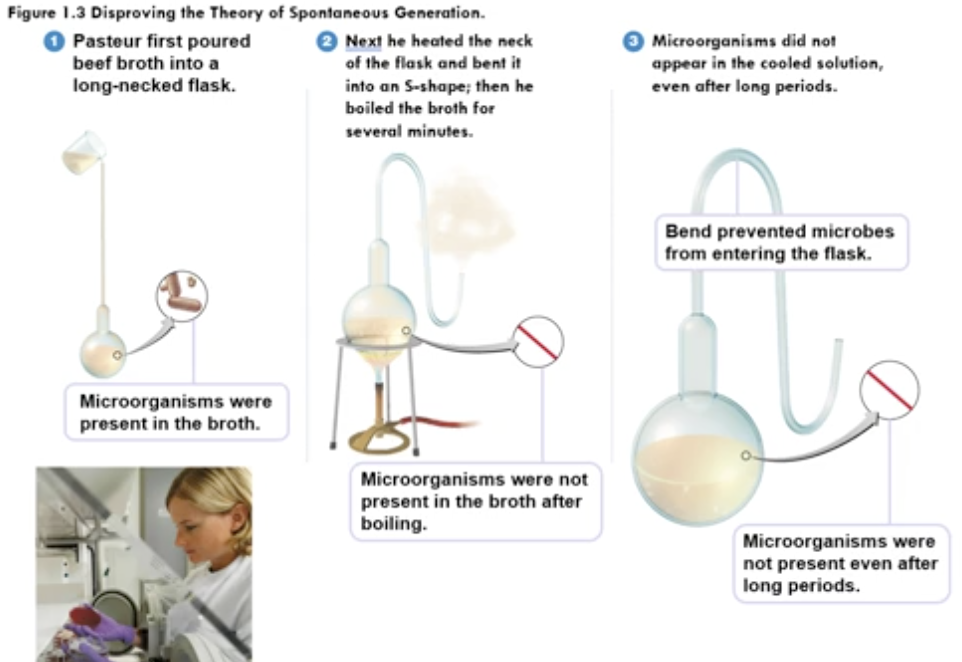
aseptic technique
prevent contamination by unwanted organisms
fermentation
process by which yeasts convert sugars into alcohol in the absence of air
souring and spoiling
process by which bacteria convert alcohol into acetic acid (vinegar) in the presence of air
pasteurization
process that utilizes just enough heat to kill most of the bacteria that cause spoilage (not sterile)
Joesph Lister
applied germ theory to medical procedures by disinfecting surgical wounds with phenol (carbonic acid)
Robert Koch
discovered cause of anthrax in cattle and sheep
he identified rod shaped bacteria, cultured in media, injected into healthy animals, which then got sick from same bacteria.
he took a blood sample from those then sick animals to re-isolate the bacteria and double check work
Koch’s postulates
Edward Jenner
inoculated a healthy volunteer with cowpox
volunteer then became immune to smallpox
similar to vaccinating
vaccine
cultures of avirulent microorganisms used for preventative inoculation
chemotherapy
treatment of a disease using chemical substances
antibiotics: chemicals produced naturally by bacteria and fungi to act against other microbes
synthetic drugs: chemotherapeutic agents prepared from chemicals in the lab
Alexandar Flemming
Penicillium mold contaminated plates inhibited bacterial growth
fungus produced a chemical - penicillin
resistance
genetic changes in microbes that enables them to tolerate a certain amount of an antibiotic that would normally inhibit them
What role do microorganisms play in the environment?
bioremediation and recycling
Which has a nucleus? - prokaryotes or eukaryotes
eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
lack nucleus
no histones
organelles: not membrane-enclosed
cell walls: peptidoglycan
cell division: binary fission
can read DNA and make protein
bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotes
have nucleus
DNA: nuclear membrane, multiple chromosomes
histones
organelles: membrane-enclosed
The cell wall won’t be peptidoglycan- if have one
cell division: mitosis
What are external structures of bacterial cells?
glycocalyx
flagella
axial filaments
fimbriae
pili
Glycocalyx
“sugar coat”
viscous, gelatinous polymer surrounding cell wall
would be termed a “capsule” or “slime layer”
Capsule: organized and firmly attached to cell, virulence factor that resists phagocytosis
Slime layer: unorganized and loosely attached, biofilm formation
source of energy and dehydration process
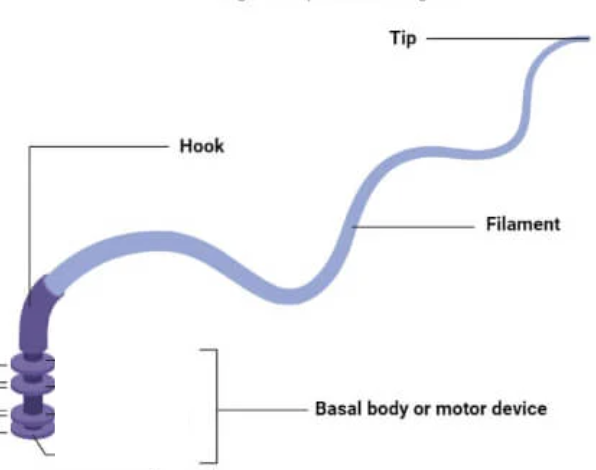
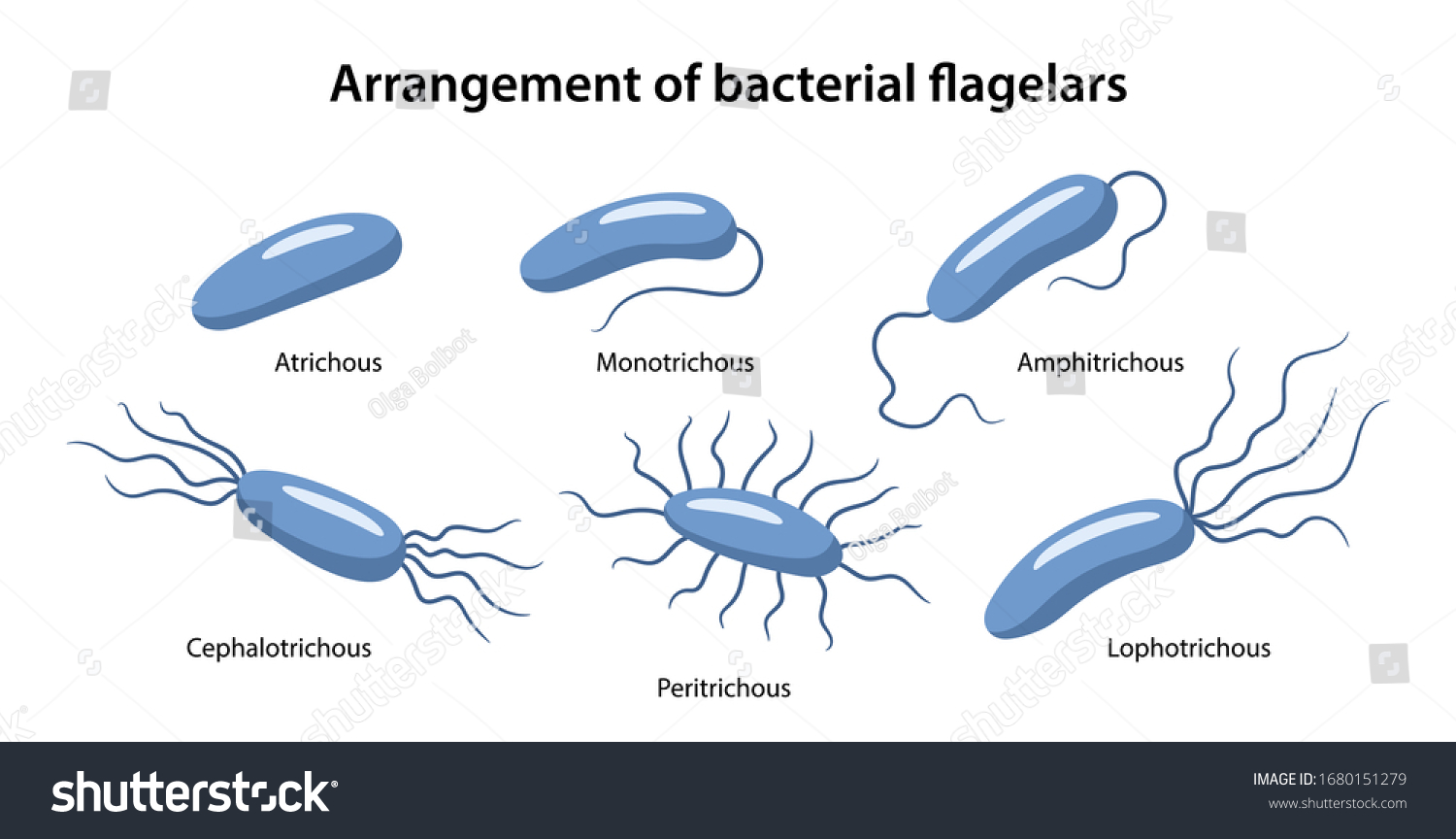
Flagella
Arrangements:
atrichous
peritrichous
polar:
monotrichous
lophotrichous
amphitrichous
Basic parts:
filament
hook
basal body
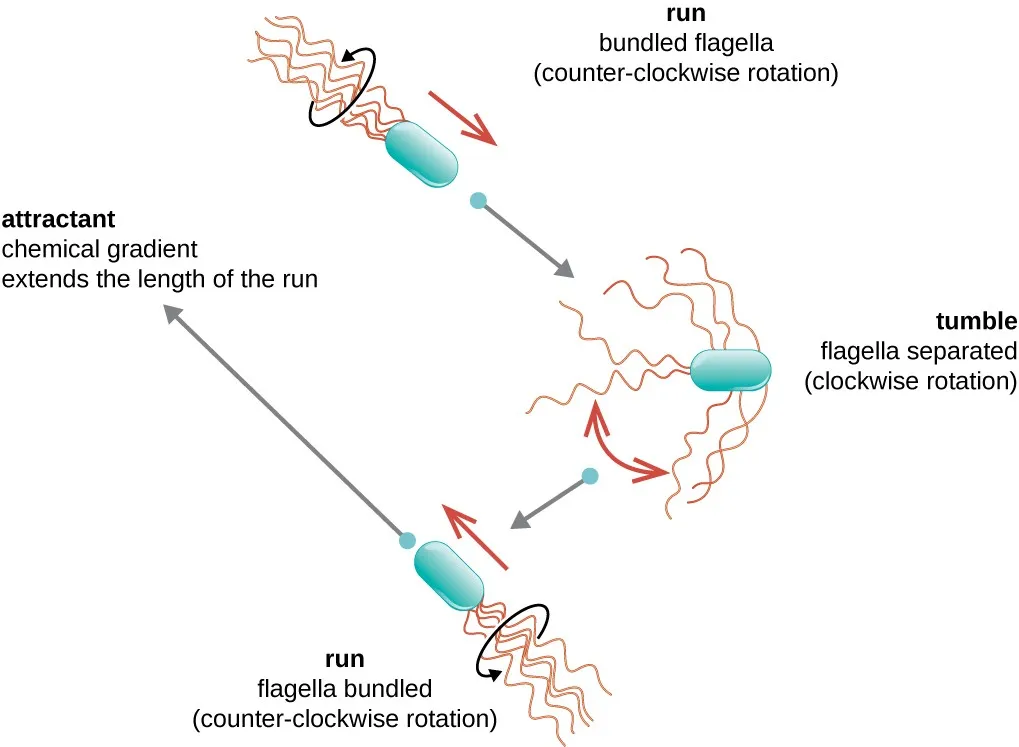
Flagella- movement
Motility: ability of an organism to move by itself
runs and tumbles
swarming
Taxis: ability to move toward or away from a stimulus
chemotaxis
phototaxis
H antigen: flagellar protein useful for serotyping
ex: E. coli O157:H7
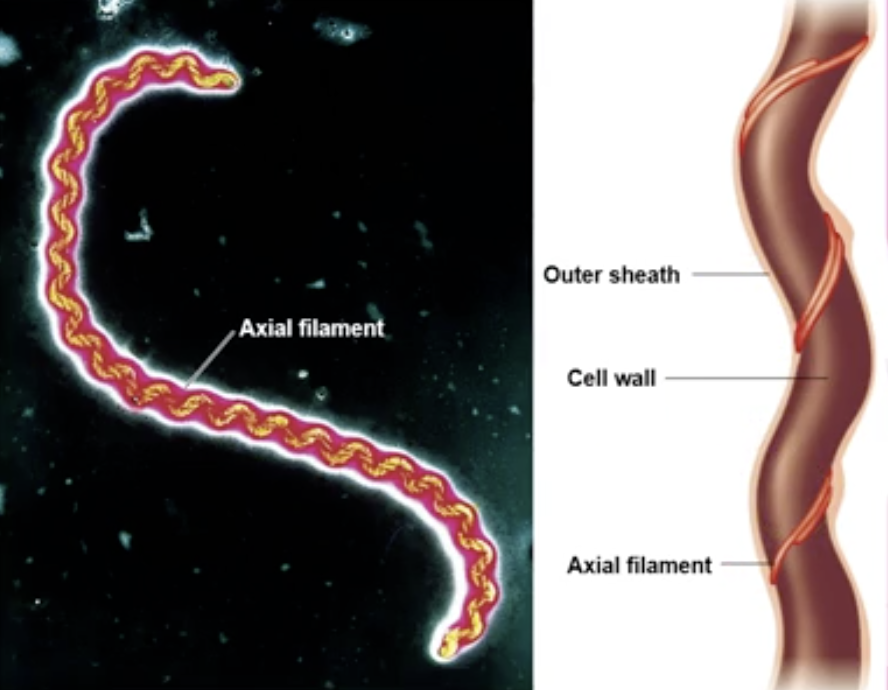
Axial filament
utilized by spirochetes for movement
bundles of fibrils at the ends of the cell beneath an outer sheath
Not all spiral-shaped bacteria are spirochetes, but all spirochetes are spiral-shaped bacteria
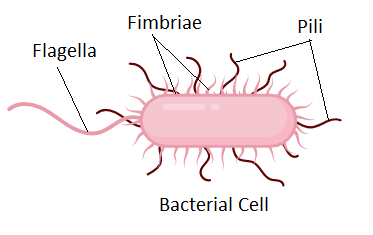
Fimbriae
short, straight, thin projections
used for attachment
very numerous
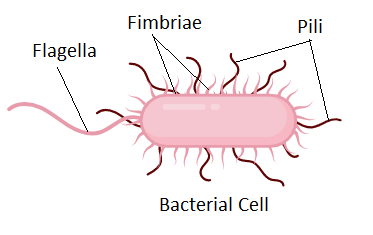
Pili
longer than fimbriae
used for DNA transfer
1-2 per cell
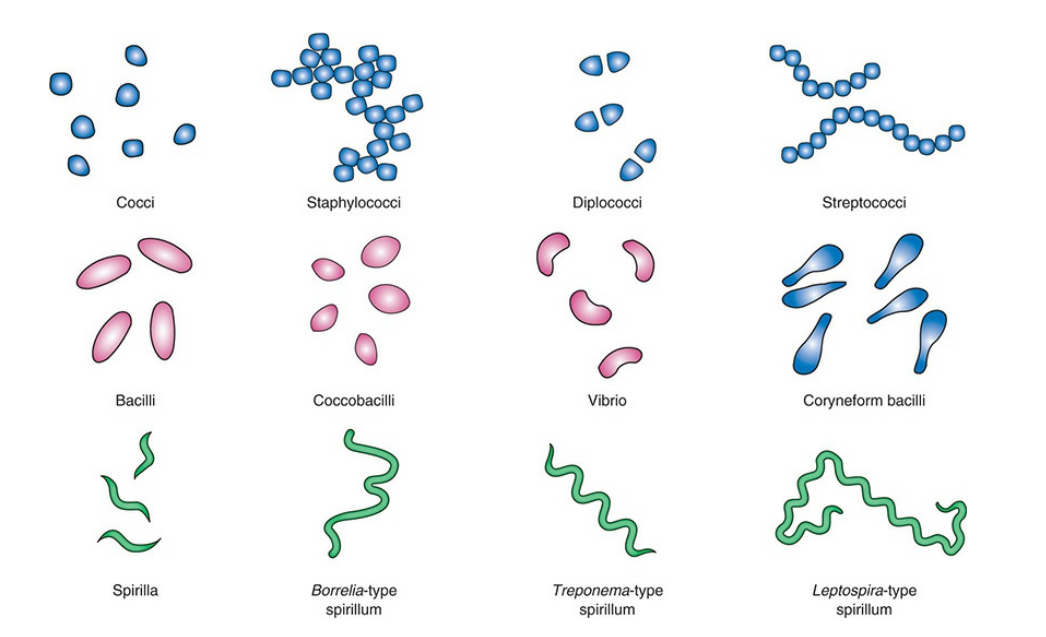
Shapes and Size of Bacteria:
Size: from .2-2.0 um diameter x 2-8 um length
Shape:
coccus/cocci
bacillus/bacilli
spiral
Vibrio: curved rods
Spirilla: helical shape, rigid body
Spirochetes: helical shape, flexible
monomorphic: maintain shape
pleomorphic: environmental conditions or genetics can alter shape
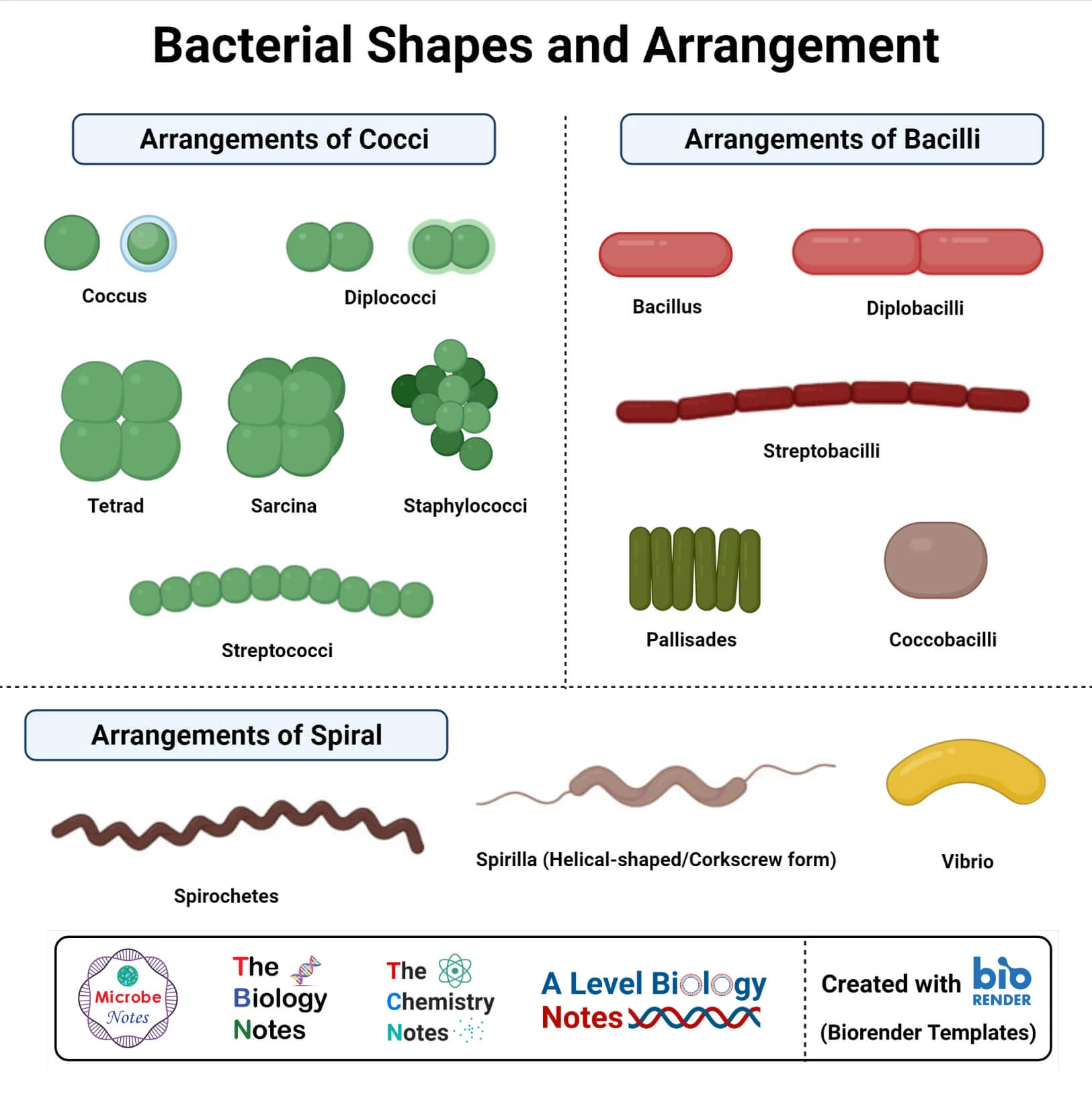
Bacterial Arrangement:
Arrangement:
Singles
Diplococci or Diplobacilli
Streptococci or Streptobacilli
Tetrads
Sarcinae
Staphylococci (clusters)
Coccobacilli
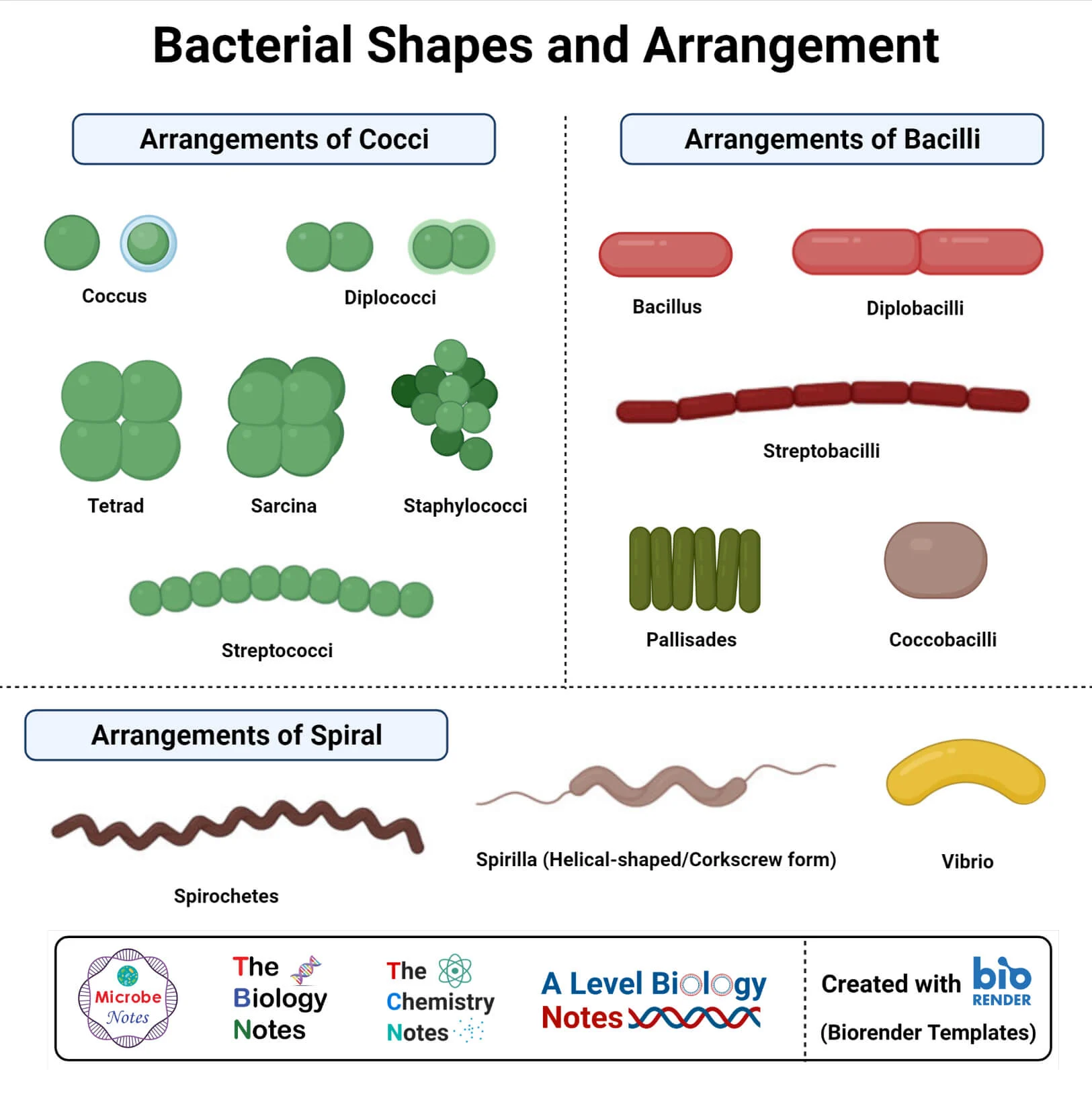
Cell wall
peptidoglycan: repeating disaccharide attached with polypeptides
made of sugars and proteins (NAM+NAG mono’s)
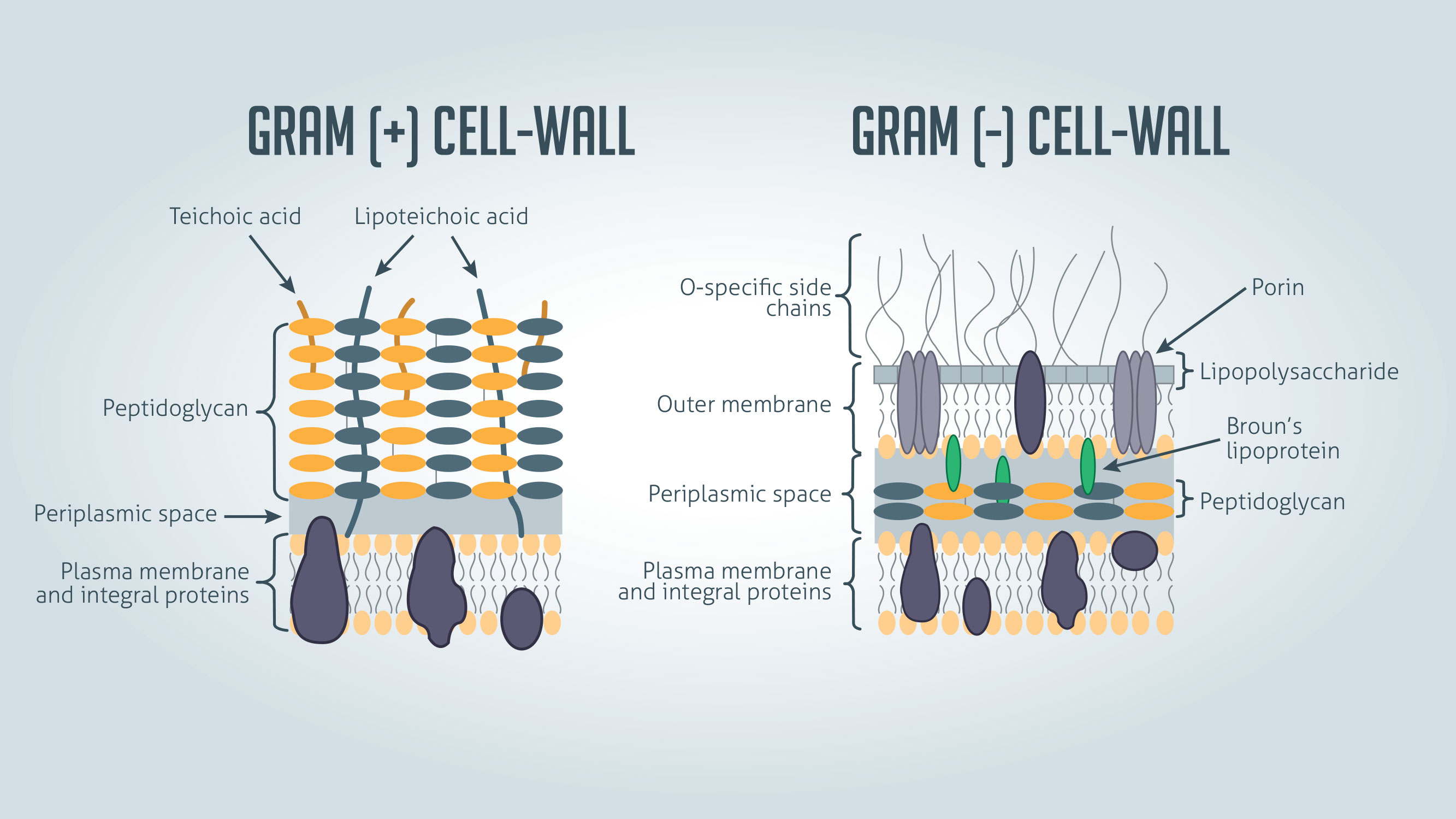
Gram Positive Cell Wall
thick, multilayers of peptidoglycan
teichoic acids
linkers
bind/regulate cationic movement across cell
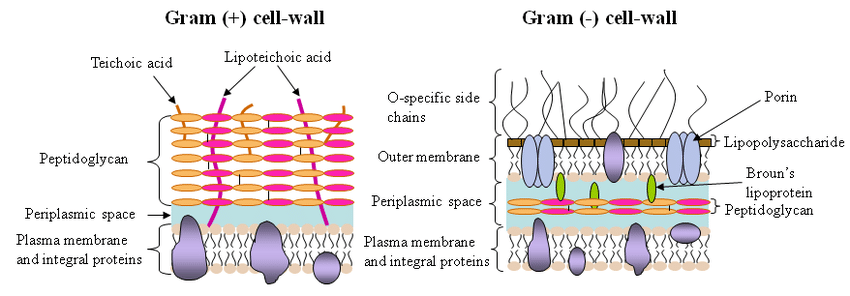
Gram Negative Cell Wall
thin, single layer of peptidoglycan
outer membrane:
lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins, phospholipids
Lipid A portion of LPS can cause fever, vasodilation, inflammation, shock, and blood clotting
may impede treatment of disease
Bacteria w/o cell walls
often mistaken for viruses due to small size and lack cell wall (Mycoplasma)
have other features of prokaryotic cells such as ribosomes
Atypical Cell Walls
Mycobacterium: Acid-fast cell wall, Mycolic acid
Mycolic Acid: hydrophobic waxy lipid, prevents uptake of dyes (gram stain), slow transmission of nutrients/wastes across cell, meaning they grow slowly
Archaea: Prokaryotes that are NOT bacteria, either lack cell walls or have cell walls w/o peptidoglycan
Structures Internal to the Cell Wall:
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleoid
ribosomes
inclusions
endospores
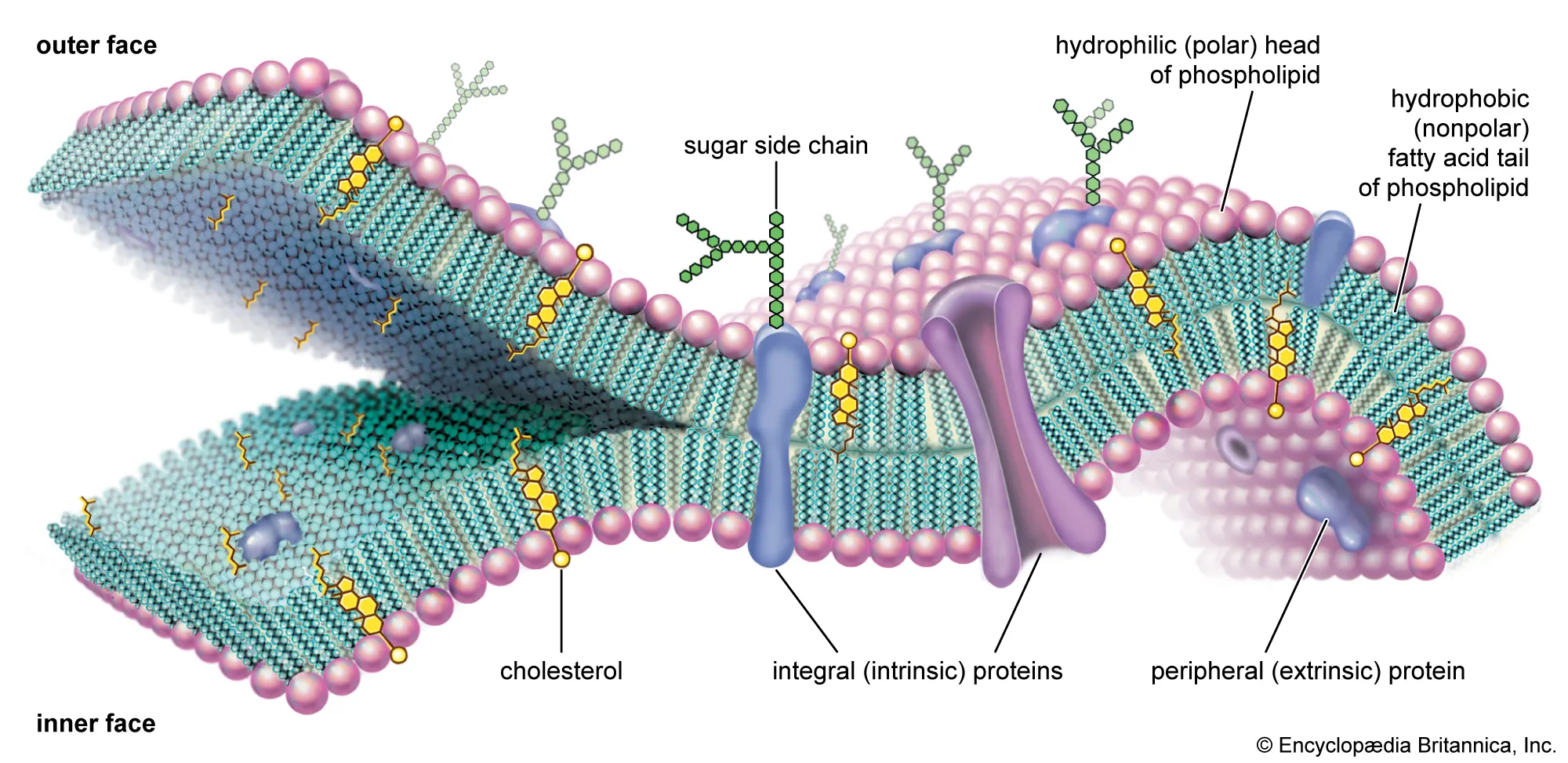
Plasma Membrane
phospholipid bilayer
composed of lipids and associated proteins (integral and peripheral proteins)
Fluid Mosaic Model: dynamic arrangement of phospholipids and proteins
Functions:
energy storage
selectively permeable
passive and active process
Cytoplasm
cytosol
liquid portion of cytoplasm
mostly water
contains cell’s DNA in region called nucleoid
Nucleoid
region of cell containing chromosome
chromosome: long, circular, double-stranded DNA containing genetic info
Plasmid:
small circular, dsDNA
extrachromosomal genetic elements
may be gained/lost w/o harm to cell
replicated independently of chromosome
Inclusions
Act as storage centers
reserve deposits
metachromatic granules
polysaccharide granules
lipid inclusions
etc
EXTRA stuff in a cell
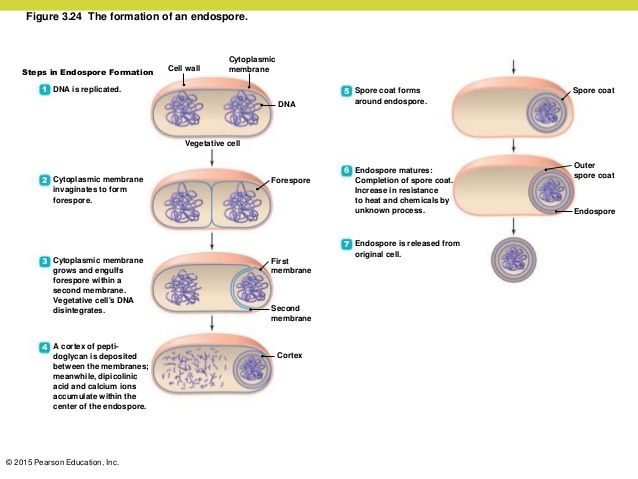
Endospores
resting state that forms when nutrients are depleted
durable, dehydrated, thick wall
can survive extreme conditions (heat, radiation, chemicals)
sporulation and germination
terminally, subterminally, or centrally located
Ribosomes
sites of protein synthesis
composed of polypeptides and ribosomal RNA
small 30S subunit and Large 50S subunit = 70S
Cytoskeleton
composed of three or four types of protein fibers
functions:
cell division
cell shape
segregate DNA molecules
move through environment
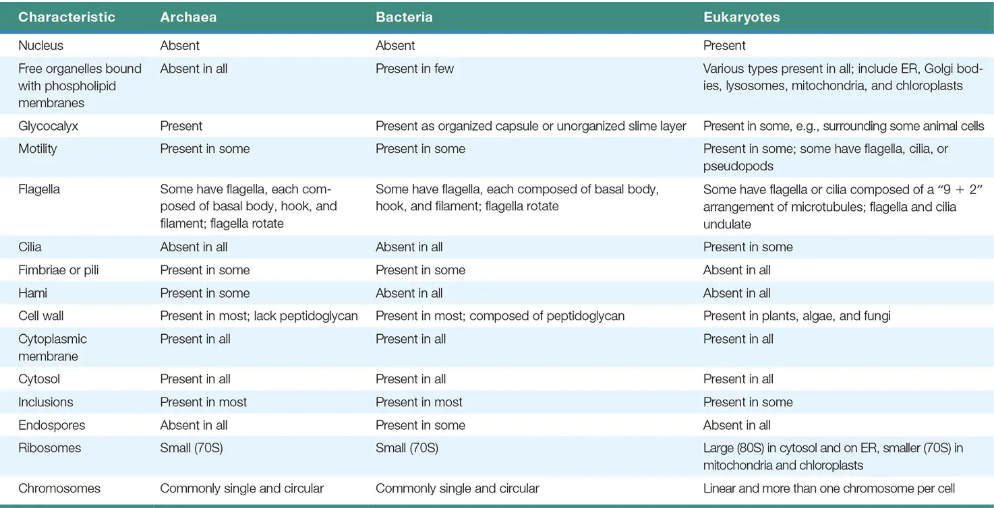
Archaea vs Bacteria
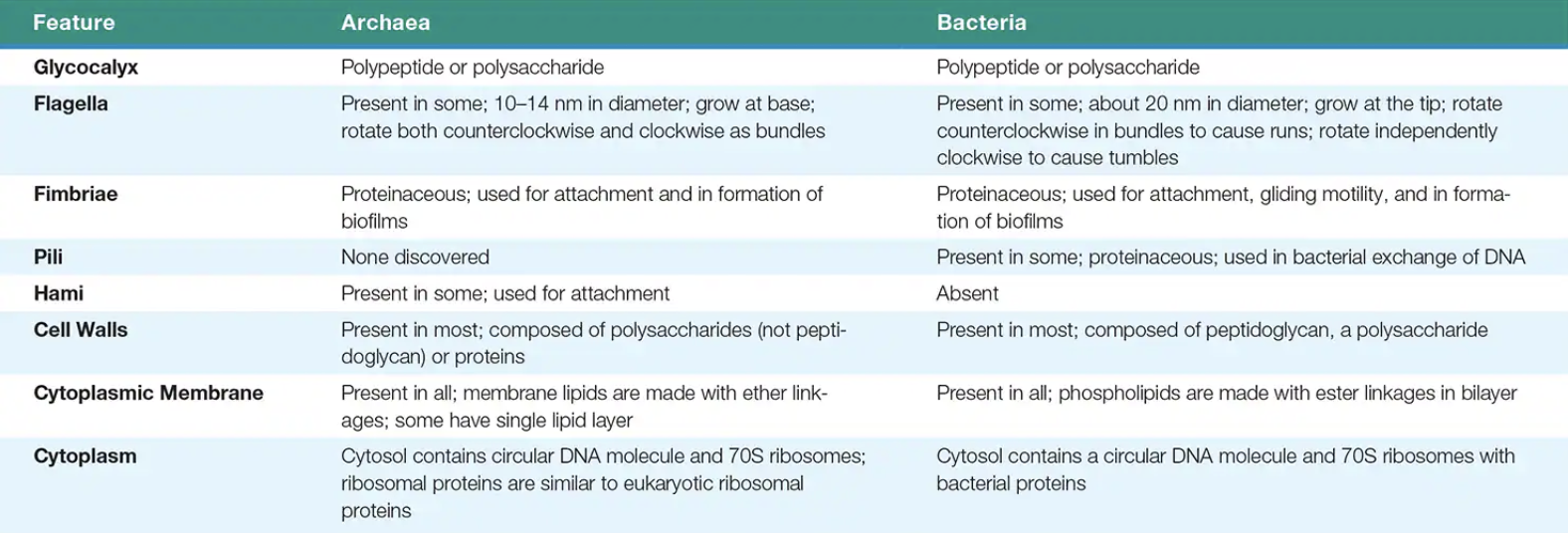
Bacteria vs Archaea vs Eukaryotes
In ___ reactions, the energy released in downhill reactions drives energy-dependent uphill reactions
Coupled
Bacteria live the lives of scavengers, fluctuating between periods of nutrients readily available and meager periods when they are scarce. Which structure minimizes the negative effects of the periods of starvation?
Inclusions
What is the name of the process used by cells to make protein from mRNA template?
Translation
What allows for the passage of polar molecules and ions across the plasma membrane?
Integral proteins
Which phase is the rate of cell death equivalent to the rate of the new cell formation?
Exponential phase
Lag phase
Stationary phase
Stationary phase
What structure contributes to the spread of antibiotic resistance through the transfer of genetic information from one bacterial cell to another?
Conjugation pili
What is the role of pyruvate in fermentation?
It removes electrons directly from NADH to regenerate NAD+
Which molecules possesses the energy liberated after completion of glycolysis and Krebs cycle?
NADH, FADH2, and ATP
What is the benefit of using an mRNA intermediate in the flow of genetic info in a eukaryotic cell?
Connection of distant compartments, amplification of info, and genome protection
Which molecule contribute most to the selectivity of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
What is the function of oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation?
It acts as the final electron acceptor in the ETC
Which molecules are considered part of the cells savings account, because of their role in storing energy for the cell?
Lipids and carbohydrates
A cell that contains a nucleus us called _____ cell.
Eukaryotic
A microorganism has the following characteristics: its cells have a nucleus and cell walls, it is multicellular, and it grows in long filaments. What is its general classification?
parasitic worm
bacterium
fungus
protozoan
fungus
Which of the following individuals pioneered the use of chemicals to reduce the incidence of infections during surgery?
Lister
What is the correct order for the application of Koch’s postulates?
Inoculated suspect agent into test subject and observe that subject develops disease of interest.
Isolate and culture suspect agent in the lab.
Find suspect agent is every case of disease of interest but not in healthy host.
Recover and isolate suspect agent from test subject.
3, 2, 1, 4
How are the bacteria and archaea different from all the other cellular microbes?
they have no nucleus
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek was the first person in history to ___
view microorganisms and record these observations
Work by ___ laid the foundations of immunology with the development of vaccines
Jenner and Pasteur
Louis Pasteur demonstrated that fermentation of sugar to produce alcohol is caused by
facultative anaerobes
Microbiologists study parasitic worms because
they cause diseases that are diagnosed by finding microscopic eggs in clinical specimens
The term for the use of microorganisms to restore damaged environments is
bioremediation
Which of the following are paired incorrectly?
Gram : cholera
Jenner: smallpox
Enrlich: syphilis
Koch: anthrax
Gram: cholera
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of viruses?
they are visible with a light microscope
they are composed of genetic material and protein
they are obligatory parasites
they are acellular
they are typically smaller than prokaryotic cells
they are visible with a light microscope
which of the following techniques could be used to produce yeast capable of making viral proteins?
genome sequencing
bioremediation
gene therapy
recombinant DNA technology
recombinant DNA technology
Which of the following is an incorrect pairing?
algae: aquatic and marine habitats
viruses: acellular parasites
protozoa: multicellular
prokaryotes: no nuclei
fungi: cell walls
Protozoa: multicellular
Which of the following is not a characteristic of protozoa?
most exhibit asexual reproduction
they are eukaryotic organisms
they are all photosynthetic
they frequently posses cilia or flagella
they are single celled organisms
they are all photosynthetic
Bacterial protein synthesis can begin before the reading of the gene is complete.
T/F
T
Which of the following bacterial cell structures plays an important role in the creation of biofilms?
glycocalyces
flagella
pili
fimbriae
fimbriae and glycocalyces
fimbriae and glycocalyces
Which of the following are FALSE about pili?
not all bacteria have pili
pili are longer than fimbriae and flagella
pili are a special type of fimbriae
pili facilitate the transfer of DNA among bacterial cells
pili are longer than fimbriae and flagella
which of the following chemical substances contributes to the unique characteristics of acid-fast bacteria?
mycolic acid
lipoteichoic acid
endtoxin
peptidoglycan
mycolic acid
Peptidoglycans are composed of sugars and ____
amino acids
One chain of alternating NAGs and NAMs is connected to another via____
tetrapeptides
Within the peptidoglycan layer, the cross bridges that connect the chains of alternating sugar molecules extend between ____
two N-acetylmuramic acid molecules
What role do the teichoic acids play within the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria?
they serve to stabilize the cell wall and hold it in place
bacterial ___ are sites of metabolic storage
inclusions
a bacterial cell stains with the acid fast stain, which of the following is FALSE?
it may be a member of the genus Mycobacterium
it has a cell wall that contains waxy lipids
it will be difficult to stain this cell with the Gram stain
it has a cell wall that contains endotoxins
it has a cell wall that contains endotoxins
which of the following would NOT be found in the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell?
ribosomes
nucleoid
endospores
porins
porins
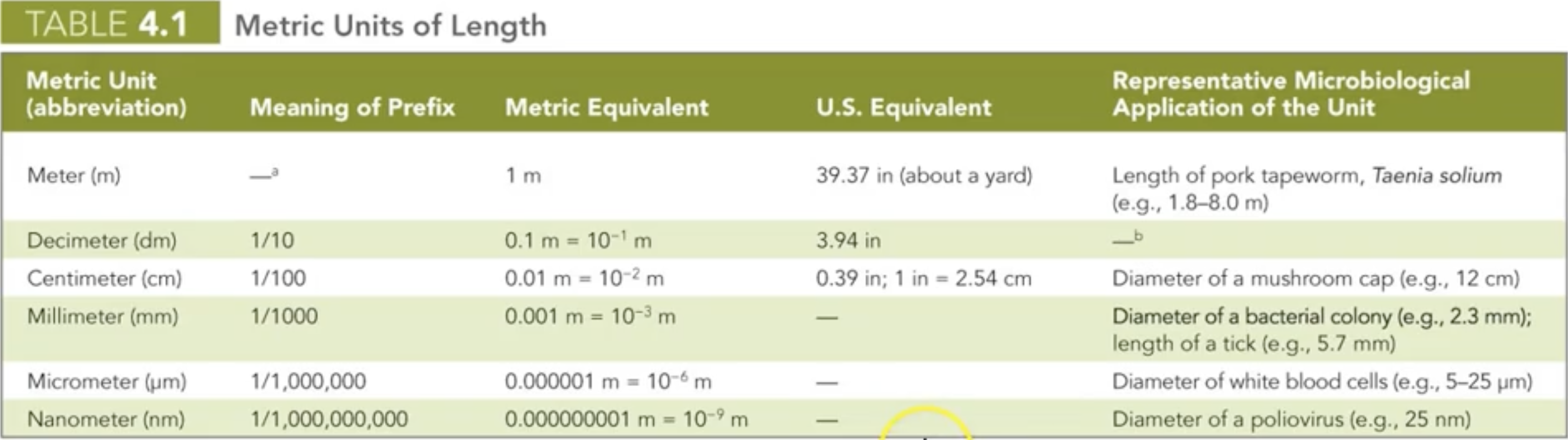
Metric system of measurement- micro
Examples:
2.3 m = 2300000 um
6.4 um = 0.0064 mm
Ocular lens
remagnifies the image formed by the objective lens
Body
transmits the image from the objective lens to the ocular lens using prisms
Objective lenses
primary lenses that magnify the specimens
Stage
holds the microscope slide in position
condenser
focuses light through specimens
illuminator
light source
coarse focusing knob
moves the stage up and down to focus the image
fine focusing knob
slightly moves the stage up and down for focusing
total magnification
objective lens x ocular lens
EX: 40x x 10 = 400x