Echinoderms and Hemichordates
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Echinodermata
"Echinodermata" means "prickly skin" (due to external spines or projections)
Calcareous endoskeleton: plates or scattered ossicles
Evolved from bilateral ancestors (larvae show bilateral symmetry)
Adults have pentaradial symmetry with ambulacral (radial) grooves
Unique water vascular system for movement and feeding
No brain
Usually a complete digestive system
Cannot osmoregulate → avoid brackish water
Mostly benthic (bottom-dwelling) species
No known parasitic echinoderms (few are commensal)
Feeding varies: some are particle feeders, others predators

Features found only In Echinoderm
include pentaradial symmetry, a water vascular system, and calcareous endoskeletons unique to this phylum.
Echinodermata Symmetry
free-living larval stages exhibit bilateral symmetry
Pedicellariae
small pincer-like structures that help to keep the body surface clean and defend against predators.
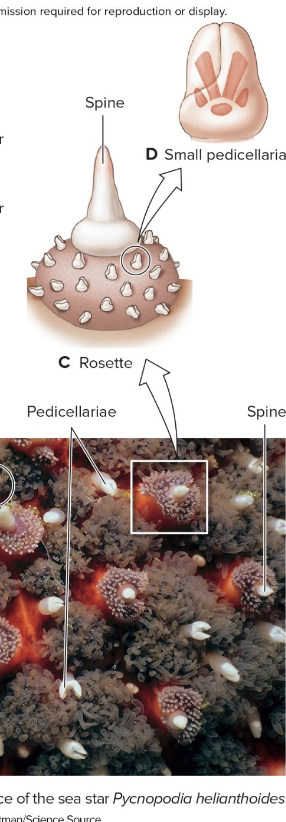
Dermal Branchiae
projections of the coelomic cavity covered with epidermis and lined with peritoneum
Ciliary action moves fluids in the opposite direction (countercurrent)
Class Asteroidea
A class of echinoderms, commonly known as sea stars, characterized by their star-shaped body and ability to regenerate lost arms.
mouth underside
Water- Vascular system
A unique hydraulic system found in echinoderms, responsible for locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange through the use of tube feet.
Madreporite
A perforated structure in echinoderms that regulates water entry into the water vascular system, aiding in locomotion and feeding.
Stone Canel
Reinforced canal connecting madreporite to ring canel
Polian Vesicles
storage fluid structures- regulate internal pressure
Radial Canal
Symmetrically from ring canal and run the length of arm toward the tips of the arms.
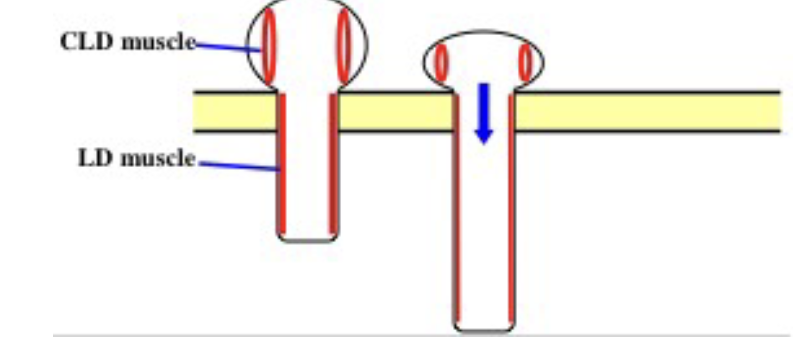
Tube foot extension
Circumlongitudinal (CLD) muscles contract and podial longitudinal LD muscles relax
fluid forced into podial region extending by hydraulic pressure
End of podium gains traction by suction of duo-adhesive glands
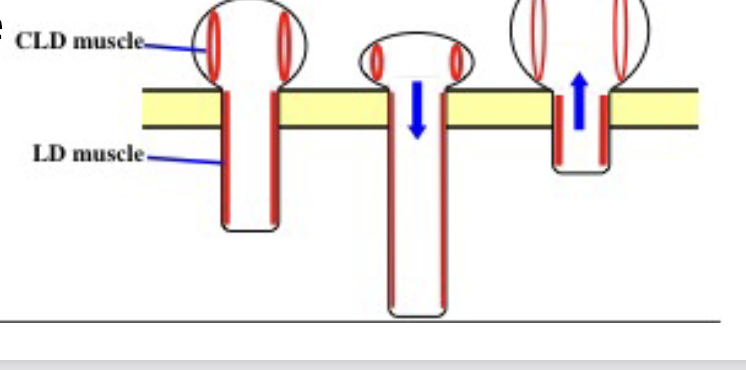
Tube feet Retraction
Circumlongitudinal (CLD) muscles relax and podial longitudinal (LD) muscles contract, pulling the tube foot back. This process allows the tube foot to retract and gain stability for movement or attachment.
Feeding
Echinoderms typically utilize tube feet and a water vascular system to facilitate feeding. They often exhibit various feeding strategies, including predation and filter feeding.
Reproduction
Sexes seperate
Pairs of gonads
Fertilization is external
occurring in the water, often leading to larval stages that develop into adults.
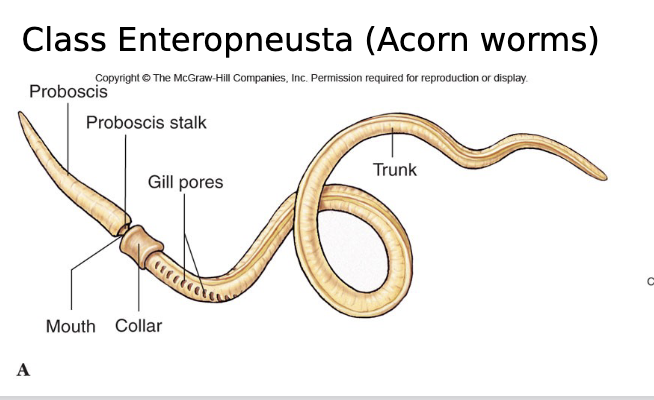
Hemichordata
A phylum of marine deuterostome animals that includes acorn worms and pterobranchs, characterized by a body divided into three parts: proboscis, collar, and trunk. They share features with both echinoderms (larvae) and chordates (gill slits).
Characteristics Hemichordata
Bilaterally symmetrical, soft bodied; triploblastic; free
living.Digestive system complete
Longitudinal and Circular muscles
A single glomerulus connected to blood vessels may have
excretory function (metanephridium)Respiratory system of gill slits connecting the pharynx
with outsideCirculatory system of dorsal and ventral vessels and
dorsal heart
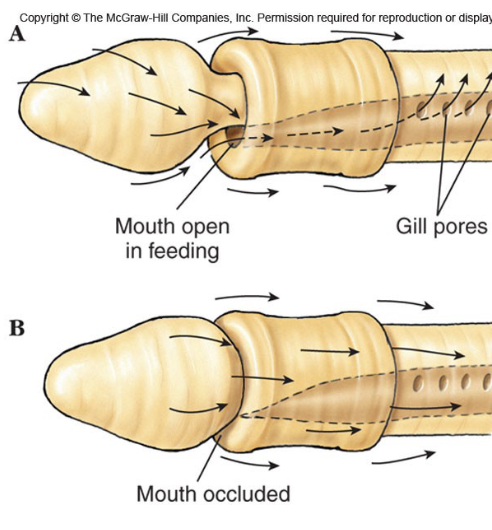
Enteropneusta
Wormlike acorn worms
cilla carry particles to mouth
Contraction of body musculature forces excess water out through gill slits
Pterobranchia
Small, colonial hemichordates that live in secreted tubes. - They possess a distinctive body plan with a proboscis and a collar that contains gill structures for feeding and respiration.
Both dioecious and monoecious
asexual reproduction