Biol1406 lab exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:31 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Where is the chiasma position to produce this new allele combination? ABCD → ABCd abcd → abcD
between C & D
2
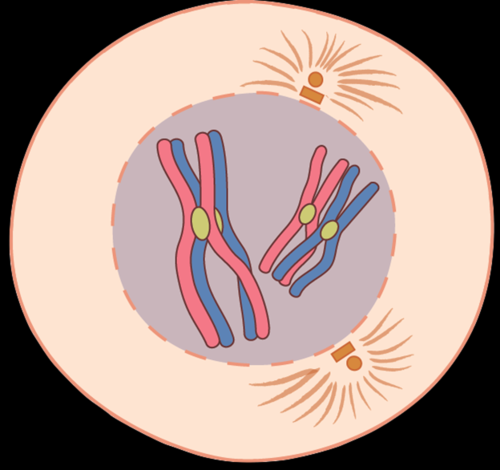
New cards
What stage of Meiosis is this?
Prophase 1
3
New cards
_____ always involves two successive divisions.
Meiosis
4
New cards
The diploid chromosome number in humans is _____.
46
5
New cards
Sister chromatids separate in ____.
Meiosis II
6
New cards
Which represents a haploid arrangement of chromosomes?
N
7
New cards
Crossing over occurs in ____
Prophase I of Meiosis I
8
New cards
_________ chromosomes are chromosomes having the same genes at the same loci but different alleles, and one comes from each parent.
Homologous
9
New cards
Allele Combination Before Crossing Over: A B C d e F a b c D E f
Chiasma position between C and D.
10
New cards
What is the new combination of alleles?
A B C D E f a b c d e F
11
New cards
______ is a type of division that produces genetic variation within the new cells produced.
Meiosis
12
New cards
Homologous chromosomes separate in ______.
Meiosis I
13
New cards
Different forms of a gene at a given locus on a chromosome are called _______.
Alleles
14
New cards
The two homologous chromosomes that come together in Prophase I in Meiosis I are called a(n) _______.
tetrad
15
New cards
About how many different combinations of chromosomes are expected to result from independent assortment in humans? (Mark all correct answers)
8 million and 223
16
New cards
What happens to the observed and expected outcomes as sample size increases?
They should get closer.
17
New cards
If we tested pea plants and observed purple flowers, white flowers, tall plants, and short plants, what is the Degree of Freedom?
3
18
New cards
The _________ is the the actual genes in an organism, and it normally is represented by two letters.
Genotype
19
New cards
If yellow peas are dominant to green peas, and one parent is heterozygous and one parent has green peas, what is the expected phenotypic ratio in F1?
25%
20
New cards
What is the expected phenotypic ratio when two heterozygous parents are crossed?
3:1
21
New cards
What kind of alleles are represented by capital letters?
Dominant alleles
22
New cards
When individuals are true breeding, they can be ______.
Homozygous, Heterozygous
23
New cards
The ___________ is the physical appearance of an organism, like red eyed fruit flies.
Phenotype
24
New cards
What are different versions of a gene called?
Alleles
25
New cards
What is the expected genotypic ratio if two heterozygous parents are crossed?
1:2:1
26
New cards
MALE Bee
27
New cards
What is the probability of being born on 1st October?
1/365
28
New cards
Probability
the number of specific events/ total number of possible events. EX: 1 event (heads) / 2 events (heads or tails) = ½=50%
29
New cards
If we tested pea plants and observed purple flowers, white flowers, tall plants, and short plants, what is the degree of freedom?
3
30
New cards
What kind of alleles are represented by capital letters?
Dominant Alleles
31
New cards
What happens to the observed frequency as sample gets larger?
It gets closer
32
New cards
what happens to the observed frequency as sample size gets large?
As sample size increases the closer your observed outcome should be to the expected outcome.
33
New cards
Gene
a stretch of nucleotides along the length of a chromosome that code for a protein or sometimes an RNA molecule (proteins in some way determine phenotype).
34
New cards
Alleles
different forms of a gene (the various alleles have different sequences of nucleotides and may code for different versions of the protein that can affect phenotype in various ways).
35
New cards
Dominant Allele
any allele which when present with its recessive counterpart produces the same phenotype as when present in two copies. Tt and TT look the same-tall. Represented by a capital.
36
New cards
Recessive Allele
any allele which must be present in two copies to produce the characteristic phenotype, represented by a lower case.
37
New cards
The Physical appearance in an organism
Phenotype
38
New cards
The genes present in an organism
Genotype
39
New cards
What is the probability of being born on a Wednesday?
1/7
40
New cards
When individuals are true breeding, they can be
Homozygous, Heterozygous
41
New cards
If yellow peas are dominant to green peas and one parent is heterozygous and one parent has green peas how many of the offspring are true breeding for pea color?
1/2
42
New cards
What is the expected phenotypic ratio when two heterozygous parents are crossed?
3.1
43
New cards
What probability or alpha value do we use in science when using the test or Chi Square Table?
.05%
44
New cards
Know how to setup and solve a monohybrid cross and what the expected phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratios are (page 66 and 67) Expected phenotypic ratio- 3:1 Expected genotypic ratio- 1:2:1
45
New cards
What proportion is expected to breed true (homozygous) for flower color?
2/4=½=50%
46
New cards
What proportion is expected to segregate (heterozygous) for flower color?
2/4=½=50%
47
New cards
What proportion of the purple flower is expected to breed true?
⅓
48
New cards
What proportion pf the purple flower is expected to segregate for flower color?
2/3
49
New cards
The 5 reasons why we use fruit flies for genetic experiments
They are easily cultured. 2. They have short generation times, with the life cycle being completed in as little as 10 days. 3. A single cross can produce a large number of progeny, which increase the sample size and reduces sampling error. 4. A large number of mutations are well known. 5. True-breeding lines are available for contrasting characters under simple genetic control.
50
New cards
Be able to identify male and female fruit flies
Males are smaller and have sex combs. Females have more stripes.
51
New cards
Is the template strand or the coding strand complementary to mRNA?
The coding, or non-template, strand is the DNA strand complementary to the template strand; it has the same sequence (except for T & U substituitions) as the mRNA. It is also the lower strand.
52
New cards
_____ is a mutation that changes a base pair in DNA and codes for another amino acid.
A missense mutation
53
New cards
_____ is a mutation the changes a base pair in DNA but codes for the same amino acid.
A silent mutation
54
New cards
What is the final product of translation?
RNA,
55
New cards
Stop codon in the mRNA
UAA, UAG, or UGA
56
New cards
Does mRNA copy the coding strand or the template strand of DNA?
Template strand of DNA
57
New cards
Where does transcription take place in the cell? (Assume eukaryotes.)
nucleus
58
New cards
Where does translation take place in the cell?
Ribosome
59
New cards
Know what transcription is and how it occurs and where in the cell it occurs
Creates mRNA .... Nucleus of Eukaryotes
60
New cards
Know what translation is and how it occurs and where in the cell it occurs
Creates polypeptide chain/proteins.... ribosomes
61
New cards
What is the start codon?
AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine.
62
New cards
What nitrogen base is found in RNA but not DNA?
Uracil
63
New cards
Give the standard notation for a strand of DNA that is complementary to: 5' - CGGTA - 3'
3' - GCCAT - 5' -> 5' - TACCG - 3'
64
New cards
Describe the orientation of the two DNA strands with respect to one another in a double-stranded DNA molecule.
Antiparallel
65
New cards
______is the process where mRNA makes a copy of DNA, normally copying a gene.
Transcription
66
New cards
If an organism's DNA contains 35% adenine, how much guanine does it contain?
15% We know that the sample is 35% adenine, which tells us that it is also 35% thymine. We know that cytosine and guanine pair together and will be present in equal amounts, so we can divide this final total by 2 to find our answer. The sample is 35% adenine, 35% thymine, 15% guanine, and 15% cytosine.
67
New cards
The 5' end of DNA has a ____.
Phosphate
68
New cards
Are the two ends of a strand the same, or are they different?
Different
69
New cards
AAG
lysine silent mutation
70
New cards
AAC->ASN
asparagine different amino acid missense mutation
71
New cards
AUG-GUA-UAA
stop codon nonsense mutation
72
New cards
Missing letter
frameshift
73
New cards
DNA
double-stranded, thymine, deoxyribose sugar
74
New cards
RNA
single-stranded, uracil, ribose sugar
75
New cards
Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection
high reproductive capacities (superfecundity)->competition->heritable variation in populations of organisms->differential survival and reproduction
76
New cards
Mutation
is spontaneous and random
77
New cards
Does natural selection work on the individual or the population?
Individual
78
New cards
In areas where coral snakes were present, artificial brown snakes were attacked much more frequently than artificial kingsnakes.
True
79
New cards
________________ ______________ is when an edible animal is protected by resembling a poisonous or noxious one that is avoided by predators.
Batesian mimicry
80
New cards
Aposematic coloring is a type of coloring where an organism is camouflaged in their environment.
False
81
New cards
When you simulated evolution in the Grabber game on the computer, what happened to the phenotype over 250 generations when there were no mutations?
There was no change in phenotype
82
New cards
What kind of mimicry do bees and wasps exhibit?
mullerian mimicry
83
New cards
When two different species live in different geographic areas, what is this called?
Allopatry
84
New cards
Kingsnakes should be protected in areas of ____ with coral snakes.
Sympatry
85
New cards
The coral snake was the ______ species in the article you read.
Model
86
New cards
Who wrote the Theory of Evolution by Natural selection?
Darwin & Wallace
87
New cards
Are sharks and dolphin examples of convergent evolution or divergent evolution?
Convergent
88
New cards
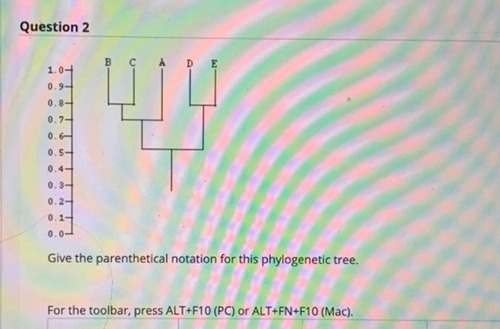
Give the parenthetical notation for this phylogenetic tree.
(((B,C)A) (D,E))
89
New cards
List one characteristic of Tikaalik that is tetrapod-like.
tetrapod rib bones, neck, ribs, fin skeleton, flat skull, eyes on top of skull.
90
New cards
List one characteristic of Tikaalik that is fish-like.
Fins, scales, gills and lungs
91
New cards
What is the significance of Tiktaalik?- Tiktaalik is one of the most important fish fossils for unravelling the evolutionary transition from fish living in water to tetrapods living on land.
Does this have fins? Yes Scales? yes Shape of head? flat skull Position of the eyes? eyes on top of skull Neck? yes Bones in fins? yes Which of these characters go with fish?- Fins, scales, gills and lungs Which of the characters go with tetrapods?- neck, ribs, fin skeleton, flat skull, eyes on top of skull.
92
New cards
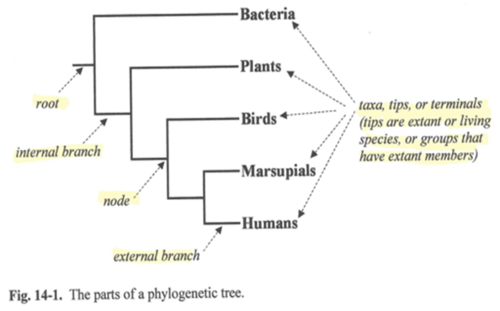
What is 1 called? Root What is 2 Called? Internal branch What is 3 called?Node What is 4 called? External branch What is 5 called? Taxa
phylogenic tree
93
New cards
Which letter corresponds to the first appearance of fur
Y

94
New cards
Species that are alive today are called what? It is the opposite of extinct.
Extant
95
New cards
What is Archaeopteryx?
Oldest known fossil bird; transitions between dinosaurs(reptiles) and modern birds. Give two reptilian characteristics?- Large skull, solid bones, claws on forelimbs Give two bird characteristics?- strong legs, feathers, rounded wings for gliding
96
New cards
Give a bird characteristic of Archaeopteryx.
feathers, wings, furcula and reduced fingers
97
New cards
Are crocodiles more closely related to birds or lizards?
Birds
98
New cards
Parsimony
calls for the simplest tree, with the least number of character changes
99
New cards
What is polytomy
Polytomy is a term for an internal node of a cladogram that has more than two immediate descendents (i.e, sister taxa). In contrast, any node that has only two immediate descendents is said to be resolved.
100
New cards
What is convergent evolution?
the process when organisms that are not closely related, independently evolve to have similar traits as a result of adapting to similar ecological niches/environments. Give an example.- Sharks and dolphins (same body shape due to aquatic environment) Bats and Butterflies (gain of wings for good adaption), Bats and whales (echolocation to find food).