Dental Anatomy Quizzes/FINAL EXAM
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
maxillary arch
the teeth in the upper jaw ( the upper jaw is the "maxilla")
occlusion
the contact of the maxillary and mandibular arch "the bite"
line angle
the junction of two tooth surfaces
curve of Spee
the curve formed the occlusion from anterior (front) to posterior (back)
mandibular arch
the teeth in the lower jaw ( the lower jaw is the "mandible")
primary dentition
the first set of 20 teeth (baby teeth)
permanent dentition
the secondary set of 32 teeth
embrasure
the triangle formed by the contact of two proximal teeth
Convex means
Curving (or bulging) outward
Choose below which groups of teeth are Anterior teeth:
molars
incisors
canines
premolars
Incisors and canines
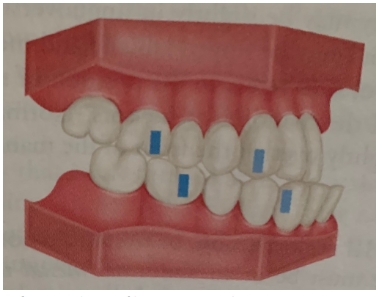
Above is a diagram of a:
class II occlusion
class I occlusion
class II division 2 occlusion
class III occlusion
class III occlusion
The first permanent molars usually erupt_______________.
At about age 6 (5-7)
Distal to the primary molars
All of the above
Before the second permanent molars
All of the above
The cervical third of the crown and the root refers to:
the middle 1/3 of the crown and root
the occlusal edge of the crown
the area where the crown and the root meet
the apex of the root
the area where the crown and the root meet
Choose from below the permanent teeth that are succedaneous:
central incisors
premolars
canines
molars
central incisors, premolars, and canines are succedaneous
There are _______ teeth in the primary dentition.
20
The primary teeth do not have premolars, and the permanent premolars are succedaneous to the primary molars. True or False?
True
The mouth can be divided into 4 sections called:
arches
dentitions
sextants
quadrants
quadrants
The mixed dentition period begins with the eruption of the first permanent tooth. True or False?
True
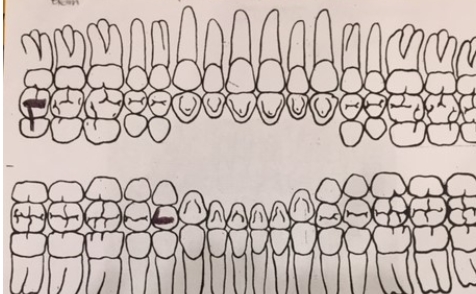
Using this anatomical chart, what is the correct indication?:
tooth #29 indicates a DO amalgam
tooth # 16 indicates a OB amalgam
tooth #1 indicates an OL amalgam
tooth #21 indicates a DO amalgam
tooth #1 indicates an OB amalgam.
In ideal centric occlusion the maxillary permanent dentition should slightly overjet the mandibular permanent teeth. True or False?
True
Buccal surfaces face the ___________; and lingual surfaces face the____________.
cheek; tongue
tongue; labial
lips; lingual
cheek; tongue
There are premolars in the primary dentition. True or False?
False

Using this geometric chart, determine the indication:
the primary left 1st molar indicates an occlusal amalgam
the permanent left 1st premolar indicates an occlusal amalgam
the primary right central incisor indicates a MIL filling
the primary left central incisor indicates a MI filling
the primary left 1st molar indicates an occlusal amalgam
cusp of Carabelli
a fifth cusp found lingual to the ML cusp of the permanent maxillary first molar
cingulum
raised, round area on the lingual surface, at the gingival third of anterior teeth
furcation
the area of the start of root divisions of teeth with 2 or more roots (mostly the molars-primary and permanent)
diastema
space between adjacent teeth (esp: the maxillary central incisors)
cusp
major elevation on the occlusal surfaces posterior teeth AND canines
mamelon
round enamel bumps on the incisal edge of newly erupted permanent incisors
morphology
the study of form and shape
fossa
wide, shallow depression on the lingual surface of anterior teeth (just incisal of the cingulum)
Choose from below the teeth that have a palatal root (three roots):
maxillary 2nd premolar
primary maxillary 2nd molars
permanent maxillary 1st molars
maxillary 2nd molars
primary mandibular 1st molars
mandibular 2nd molar
maxillary 1st premolar
permanent mandibular 1st molars
primary maxillary 2nd molars
permanent maxillary 1st molars
maxillary 2nd molars
Choose from below the teeth that have a cingulum:
maxillary incisors
maxillary canines
maxillary premolars
mandibular premolars
maxillary molars
mandibular molars
mandibular incisors
mandibular canines
maxillary incisors
maxillary canines
mandibular incisors
mandibular canines
fossa
shallow depression on the lingual surfaces on anterior teeth
bifurcation
area at which two roots divide
apex
tip of the root of a tooth
mamelon
rounded extension of enamel on the incisal edge of newly erupted incisors
cusp
the prominent enamel extensions of the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth (and canines)
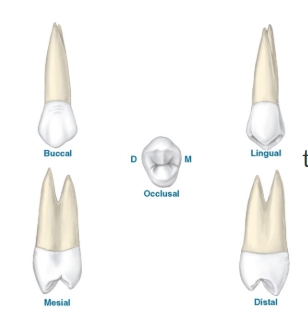
this is a drawing of:
a maxillary 1st premolar
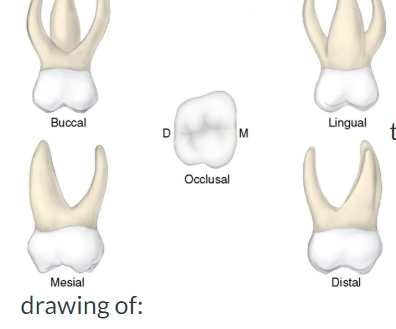
this is a drawing of:
a primary maxillary molar
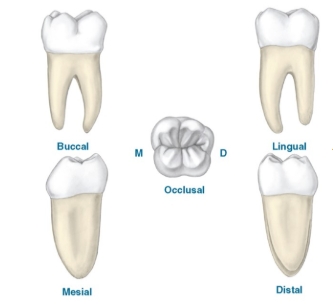
this is a drawing of:
a mandibular molar
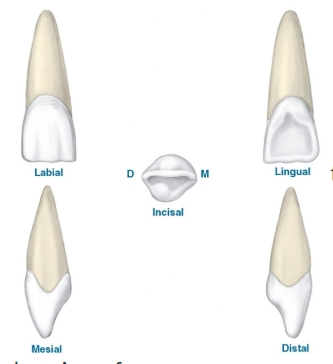
this is a drawing of:
a maxillary central incisor
The Cusp of Carabelli is a fifth cusp found on the mesial-lingual surface of:
mandibular 2nd molar
mandibular 1st molar
maxillary 2nd molar
maxillary 1st molar
maxillary 1st molar
hydroxyapatite (HAP)
material that forms the hard structure of bones and teeth
frenum
the tissue attachments that bind the oral mucosa to the dental arches
vermilion border
border of the lips to the facial skin (think 'lip liner')
histology
the study of human tissues at a microscopic level
mucogingival junction
the line between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa
periodontium
structures that surround, support, and are attached to the teeth
embryology
the study of prenatal development
vestibule
space between the teeth and the inside of the cheeks and lips
The dorsal of the tongue contains the lingual frenum. True or False?
False
The pear-shaped bump between the maxillary incisors on the hard palate is:
the lingual frenum
the incisive papilla
the labial frenum
the vermilion border
the incisive papilla
The filiform papillae are the bigger, redder papillae that cover the dorsal surface of the tongue and have the taste buds. True or False?
False (this describes fungiform papillae)
The large, raised papillae on the posterior of the tongue are and arranged like a V are:
filiform papilla
foliate papillae
vallate papillae
fungiform papillae
vallate papillae
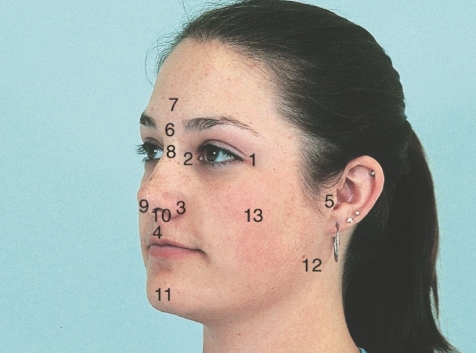
match the correct face feature to the appropriate numbers:
#5
#13
#12
#8
#1&2
#3
#5- tragus of the ear
#13- zygoma and zygomatic arch
#12- angle of the mandible
#8- the bridge of the nose
#1&2- outer and inner canthus of the eye
#3- ala of the nose
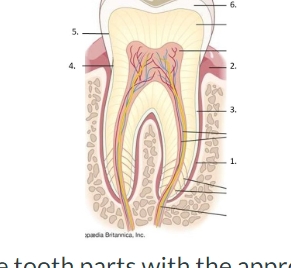
match the tooth parts with the appropriate corresponding numbers:
#2
#5
#3
#4
#6
#1
#2- unattached gingiva
#5- DEJ: dentinoenamel junction
#3- cementum
#4- CEJ: cementoenamel junction
#6- enamel
#1- PDL: periodontal ligament
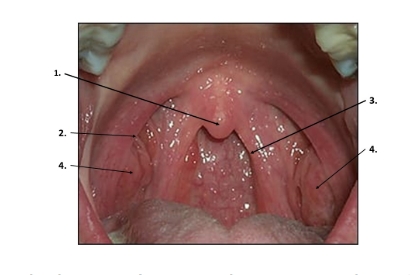
match the numbers to the correct description in the soft palate
#3
#4
#2
#1
#3- posterior faucial pillar
#4- tonsils
#2- anterior faucial pillar
#1- uvula
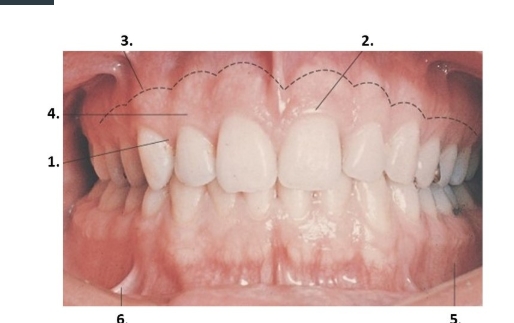
match each number to the description of the gingiva
#4
#3(dotted line)
#1
#5
#2
#6
#4- attached gingiva
#3(dotted line)- mucogingival junction
#1- interdental papilla
#5- alveolar mucosa in the mandibular vestibule
#2- marginal gingiva
#6- a buccal frenum
___________ is the study prenatal development before birth and ___________is the study of tissue structure and function at a microscopic level.
embryology / histology
Place in chronological order the embryonic development stages of a human.
1st- preimplantation stage (zygote)
2nd- embryonic stage (embryo)
3rd- fetal stage (fetus)
Select the three embryonic layers:
mesoderm
mucosalderm
epiderm
stomodeum
endoderm
ectoderm
mesoderm
endo derm
ectoderm
The three stages of formation of the palate are formation of the primary palate, formation of the secondary palate, and fusion of the palate. True or False?
True
The process of deposit of bone is called resorption and
the process of bone loss or removal is called deposition. True or False
False
match the name of the cell to its function
Odontoblasts
Osteoblasts
Ameloblasts
Osteoclasts
Cementoblasts
Fibroblasts
Odontoblasts- forms dentin
Osteoblasts- forms bone
Ameloblasts- forms enamel
Osteoclasts- breaks down bone
Cementoblasts- forms cementum
Fibroblasts- forms PDLs (periodontal ligaments)
State the three periods of odontogenesis, the process of tooth formation:
Growth, Calcification, and Eruption
The Anatomic crown is the portion of the tooth that is covered with enamel.
The Clinical crown is the portion of the tooth that is visible in the mouth. True or False?
True
What are enamel rods?
They are very small units of tooth enamel that makes acid etch work and also help to resist fractures.
A pit
is a deep hole in enamel from two developmental grooves cross each other.
A fissure
is a fault line along a developmental groove on the occlusal surface caused by incomplete joining of the lobes.
Match the dentin category to its description:
Secondary dentin
Primary dentin
Tertiary dentin
Secondary dentin- forms AFTER eruption
Primary dentin- forms BEFORE eruption
Tertiary dentin- forms as a response from irritation
Match the cementum category to its description:
Secondary cementum
Primary cementum
Secondary cementum- forms after the tooth has erupted and in occlusion
Primary cementum- forms as the root develops
match the oral mucosa type to its description
specialized mucosa
lining mucosa
masticatory mucosa
specialized mucosa- mucosa with papilla, dorsum side of the tongue
lining mucosa- buccal, vestibule, underside of tongue
masticatory mucosa- keritinized, attached gingiva, palatal mucosa
orbital region
area around the orbit or eyes
lacrimal bones
small facial bones that form the medial side of the orbit (surround the tear ducts)
alveolar process
a process of the maxilla and mandible that socket the teeth
a foramen
a hole in the bone that allows veins, arteries, and nerves to pass through
zygomatic process
the maxillary bone process that articulates with the zygoma
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
the joint between the mandible (condyle) and the skull (temporal bone)
mental region
area inferior to the lower lip and superior to the chin (pout)
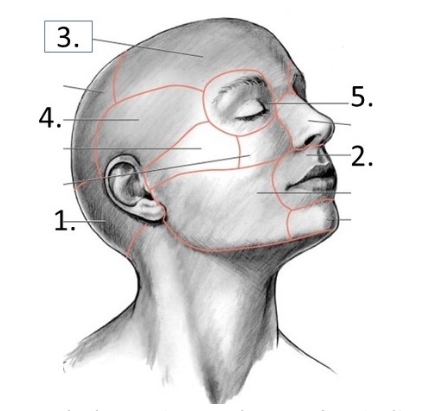
Match the region to the number indicated
#1
#2
#3
#4
#5
#1- Occipital region
#2- Oral region
#3- Frontal region
#4- Temporal region
#5- Orbital region
A hole in a bone is called a foramen. True or False?
True
A bony partition or a wall in a cavity is called a ridge.
False
The cranial bone that is the floor of the cranium is:
Ethmoid bone
The one bone that does not articulate with another is the:
hyoid bone
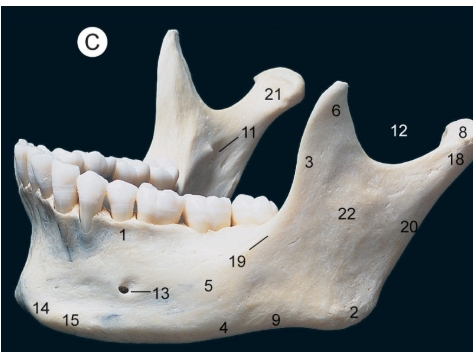
What are #s 11, 6, and 13?
#11- mandibular foramen
#6- coronoid process
#13- mental foramen
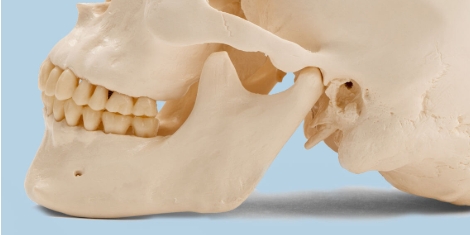
The scooped out part of the skull that articulates with the condyloid process is called:
the glenoid fossa
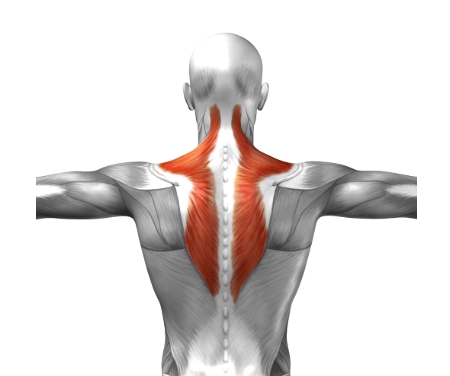
What muscle is shaded in red?
Trapezius
Choose the muscles of the tongue:
stylohyoid
palatoglossus
mylohyoid
palatopharyngeus
genioglossus
hyoglossus
palatoglossus
genioglossus
hyoglossus
The salivary gland that is in the cheek is the parotid gland and the saliva flows out of the Stenson duct. True or False?
True
The common artery brings blood to the external carotid artery to the maxillary and mandibular arteries. True or False?
True
The deep cervical lymph nodes run along the internal jugular vein and can be palpated along the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
True
Choose from below the cranial nerves that are motor nerves for the eye:
abducans
vestibulocochlear
oculomotor
hypoglossal
trochlear
abducans
oculomotor
trochlear
Name the Cranial nerve the has a sensory maxillary and mandibular division that is anesthetized with local anesthetic to make the teeth numb for dental work.
Trigeminal nerve (V)