Ch 6: Thermochemistry
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
thermodynamics
study of energy and its transformations
thermochemistry
branch of thermodynamics that deals with the heat involved in chemical and physical changes
when energy is transferred from one object to another, it appears as ______ and/or ______
work, heat
a meaningful study of any transfer of energy requires that we first clearly define both the __________ and its _________________.
system, surroundings (system + surroundings = universe)
internal energy E
system is the sun of the potential and kinetic energies of all the particles present
the total energy of the universe remains __________
constant
a change in the energy of the system must be accompanied by an ______ and ___________ change in the energy of the surroundings
equal, opposite
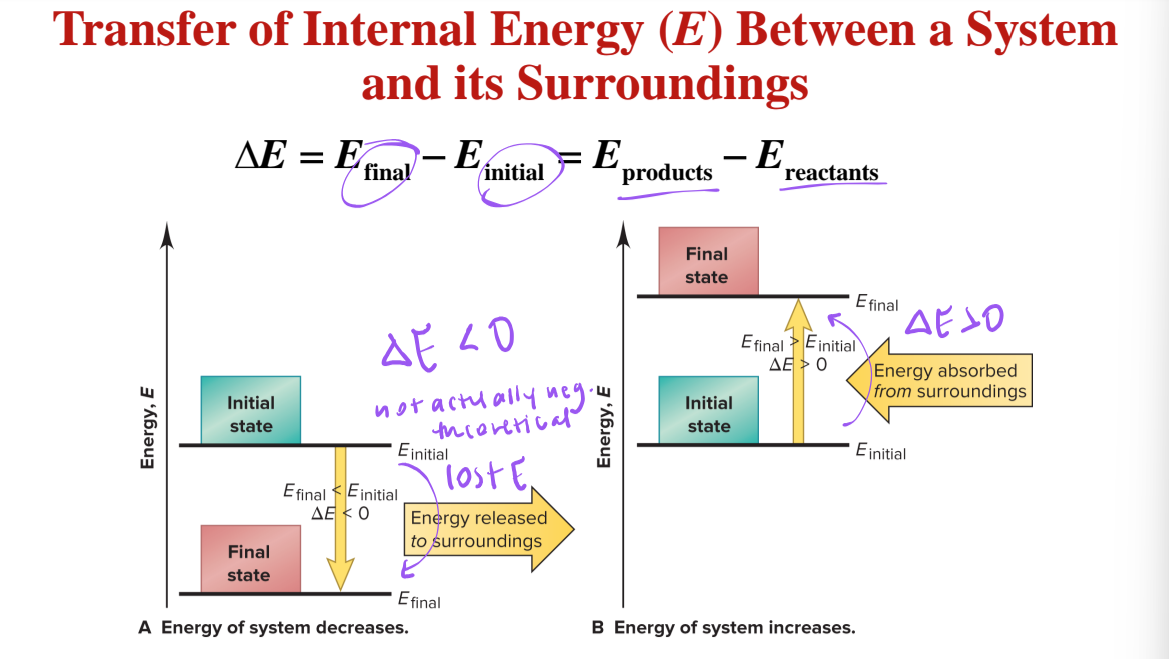
transfer of internal energy (E) between a system and its surroundings
ΔE = Efinal - Einitial = Eproducts - Ereactants
two forms of energy transfer
heat and work
heat (q)
is the energy transferred as a result of the difference in temperature between the system and surroundings
heat (w)
the energy transferred when an object is moved by a force
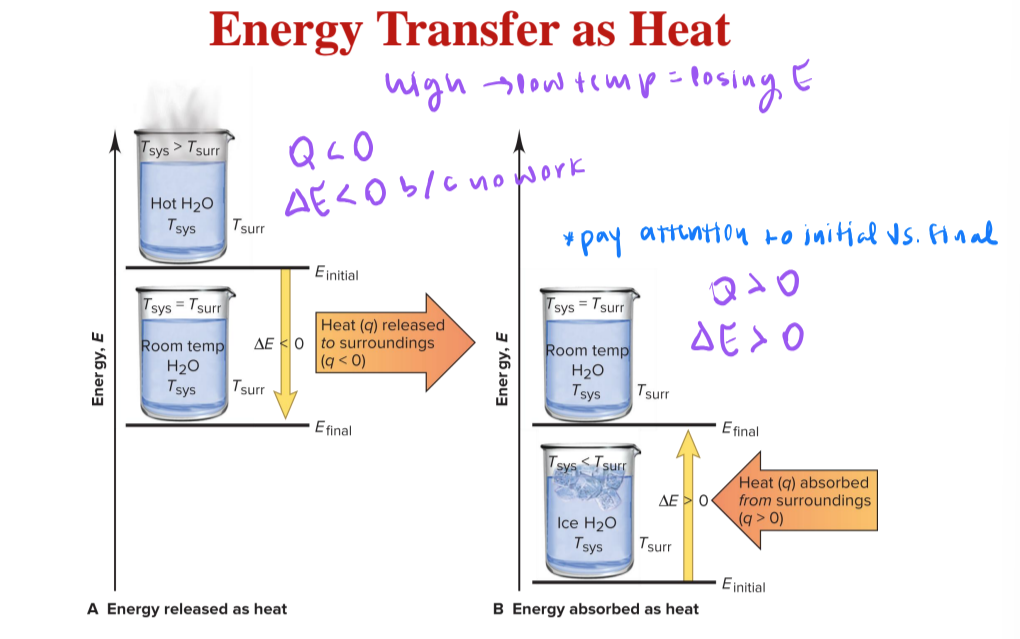
equation for the total change in a system’s internal energy is the sum of the energy transferred as heat and/or work
ΔE = q + w
q + (heat absorbed) + (+ (work done on))
ΔE + (energy absorbed)
q + (heat absorbed) + (- (work done on))
ΔE depends on the sizes of q and w
q - (heat absorbed) + (+(work done on))
ΔE depends on the sizes of q and w
q - (heat absorbed) + (-(work done on))
ΔE - (energy absorbed)
first law of thermodynamics
total energy of the universe is constant
unit of energy is the joule (J)
1 J = 1 Kg/m2/s2
1 cal
4.184 J
1 Cal = 1000 cal
1 kcal = 4184 J
British thermal unit (Btu)
1 Btu = 1055 J
If the expanding gases do 451 J of work on the pistons and the systems releases 325 J to the surroundings as heat, calculate the change in energy (ΔE) in J, kJ, and kcal
-451 - 325 = -776 J
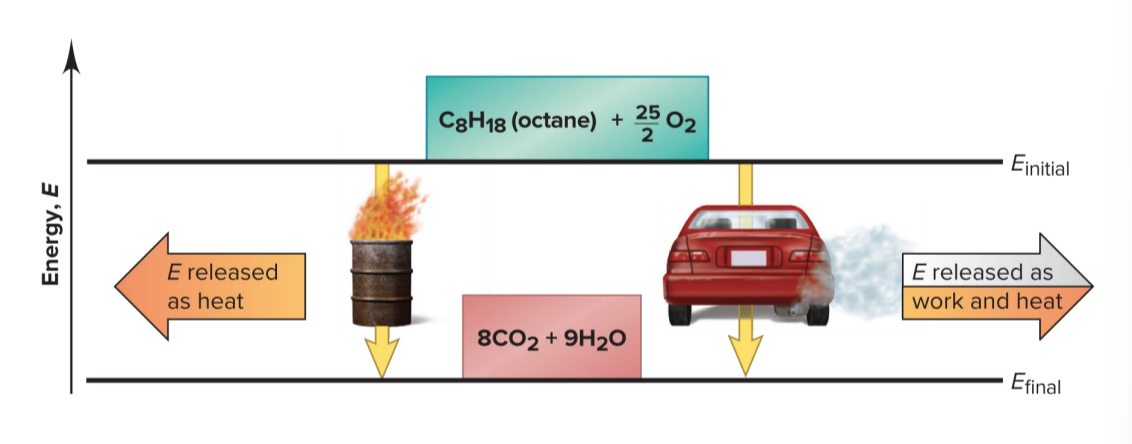
Two Different Paths for the Energy Change of a System
even though q and w for the two paths are different, the total ΔE is the same for both
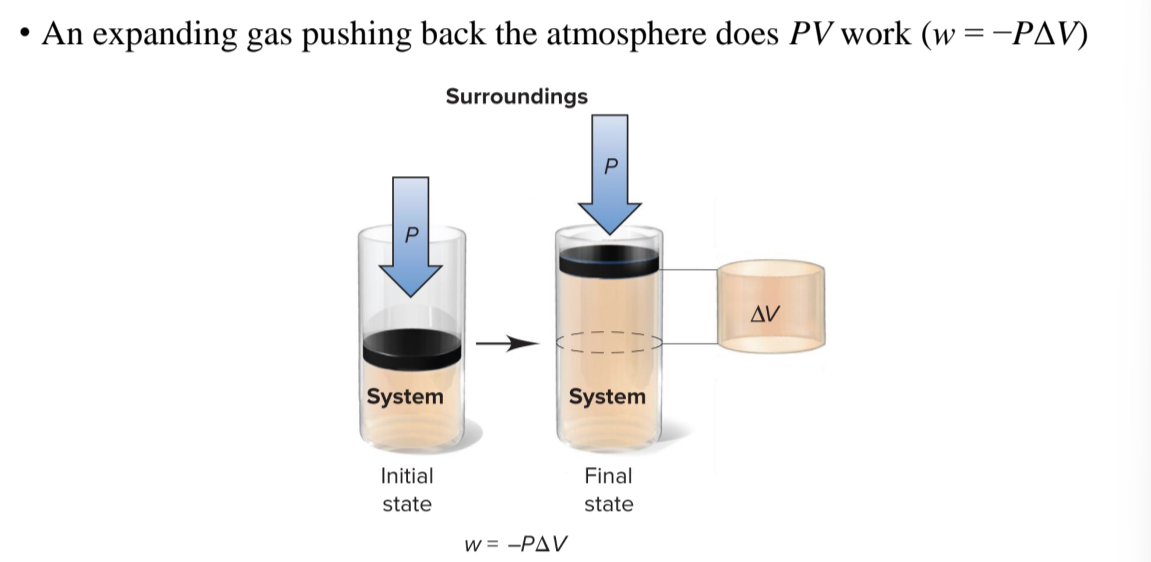
pressure-volume work
done when the volume of the system changes in the presence of an external pressure P
w = -PΔV
work of expansion
the volume of the systems increases if the temperature is raised or if a chemical reaction results in a net increase in the number of moles of gas. the system expands and does work on the system, losing energy
work of contraction
the volume of the system decreases if the temperature is lowered if a chemical reaction results in a net decrease in the number of moles of gas. the system contracts and has work done on it by the surroundings, gaining energy as work
a reaction taking place in a container with a piston-cylinder assembly at constant temperature produces a gas, and the volume increased from 125 mL to 652 mL against an external pressure of 988 torr. calculate the work value in this process ( 1 atm L = 101.3 J)
-69.4 J
enthapy (H)
ΔH = ΔE + PΔV, if a system remains at constant pressure and its volume does not change much then ΔH = ΔE
ΔH is the change in heat for a system at constant pressure
qp = ΔE + PΔv = ΔH, ΔH = ΔE
for reactions that do not in involve gases, for reactions in which the total amount (mol) of gas does not change, for reactions in which qp is much larger than PΔV, even if the total mol of gas does change
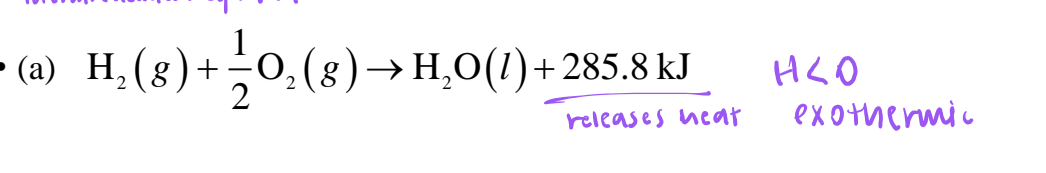
exothermic
releases heat, ΔH < 0
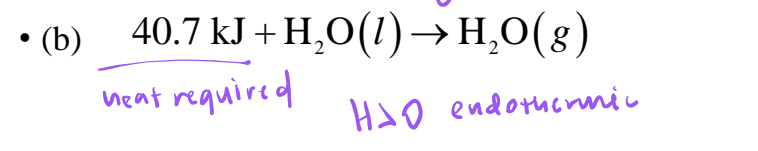
endothermic
absorbs heat, ΔH > 0
calorimetry
q = c x m x ΔT
specific heat capacity ©
the quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 K
You heat 22.05 g of a solid in a test tube to 100.00C and then add the solid to 50.00g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter. The water temperature changes from 25.10C to 28.49C. Find the specific heat capacity of the solid.
qH = -qC → qc = mcccΔTc = 0.449 J/g.K
constant-volume calorimetry
constant-volume calorimetry is carried out in a bomb calorimeter
used to measure heat of combustion
the heat capacity, C, of the entire calorimeter is known
qcalorimeter = Ccalorimeter x ΔTcalorimeter