Faraday's Law
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
Faraday's Law
In his experiment in 1831, he noticed that when he moved a permanent magnet in and out of a coil or loop of wire, it induced an electromotive force or emf, in other words a voltage, and therefore a current was produced.
2
New cards
Michael Faraday
He discovered the faraday's law
3
New cards
law of electromagnetic induction
Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux relative to the coil, an electromotive force is induced.
4
New cards
law of electromagnetic induction
The magnitude of the induced electromotiveforce is directly proportional to the rate ofchange of the magnetic flux linked with thecoil.
5
New cards
magnetic flux
the amount of magnetic field lines through a given conductor
6
New cards
changing magnetic flux
The change in magnetic field in the coil can be quantified as
7
New cards
Strength the magnet
Increasing the strength of the magnet will increase change in magnetic flux and also the magnitude of the induced emf and induced current.
8
New cards
Increasing the motion of the magnet
As the speed of the magnet increases as it moves through the coil, the magnitude of the induced emf and induced current also increases.
9
New cards
The number of turns of the coil
Increasing the number of turns of the coil will also increase the magnitude of the induced emf and induced current.
10
New cards
decreases
When the speed of the magnet decreases as it moves towards a coil, the magnitude of the induced current also \___________.
11
New cards
increases; increases
If the strength of a magnet \_________,the magnitude of induced current \_______.
12
New cards
D
Electromotive force can be induced by\____.
A. Moving a magnet near a wire
B. Moving the wire near the magnet
C. Changing magnetic field in a near by wire
D. All of these
A. Moving a magnet near a wire
B. Moving the wire near the magnet
C. Changing magnetic field in a near by wire
D. All of these
13
New cards
C
Which of the statements is true when there is change in magnetic field in a closed loop of wire.
A. There is no current induced in the wire
B. The induced current is free to move in any direction of the wire
C. Electromotive force is induced in the wire
D. All of these
A. There is no current induced in the wire
B. The induced current is free to move in any direction of the wire
C. Electromotive force is induced in the wire
D. All of these
14
New cards
D
Which of the following is NOT a way that a magnetic field can be varied to induce a current in a wire?
A. Rotate the coil inside the magnetic field
B. Move the coil in and out the magnetic field
C. Change the strength of the magnetic field
D. Move the coil out of the magnetic field
A. Rotate the coil inside the magnetic field
B. Move the coil in and out the magnetic field
C. Change the strength of the magnetic field
D. Move the coil out of the magnetic field
15
New cards
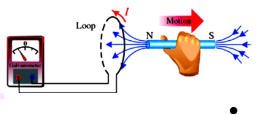
When the north pole of the magnet is moved towards the loop or coil, the pointer of the galvanometer deflects towards the right. The direction of the induced current is opposite the movement of the magnet.
16
New cards
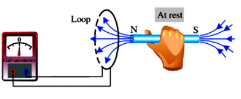
When the magnet is at rest, the galvanometer shows zero reading. There is no current induced at this time. This proves that as long as the magnet keeps moving, current flows in the coil.
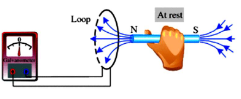
17
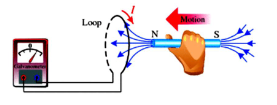
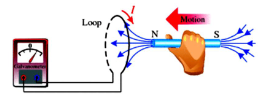
New cards
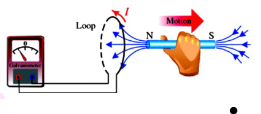
If the magnet is moved away from the coil, the induced current flows to the direction opposite the movement of the magnet. Thus, the galvanometer deflects towards the left