final exam-bio 1520
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
interphase (ex)
G1; cell growth
S; synthesis (DNAR)
G2(continue to prepare for mitosis)
interphase
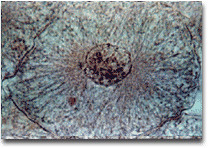
prophase (ex)
nuclear membrane breaks down
chromatin(protein+DNA) condenses
DNA condenses around protein (chromosomes)
spindle fibers form
prophase
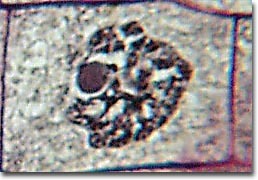
metaphase (ex)
chromosomes meet in the _____ plate
metaphase
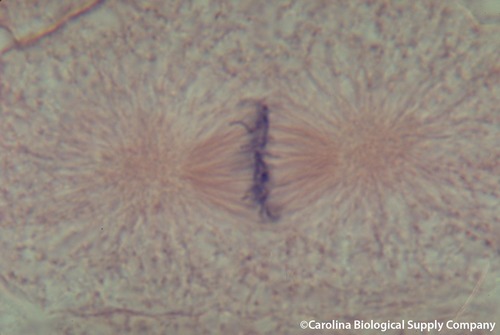
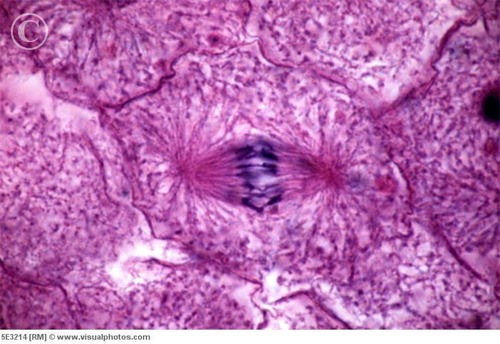
anaphase (ex)
kinetochore spilts
line gets shorter and chromosomes follow
use protein to connect to fibers
anaphase
telophase (ex)
spindles disappear
nuclear membrane forms around sets of chromosomes (2 nuclei) different spindles (actin) contract against nuclei
telophase
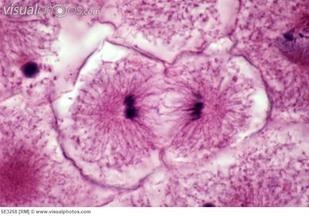
cytokinesis (ex)
division of cell membrane
cleavage furrow
cytokinesis
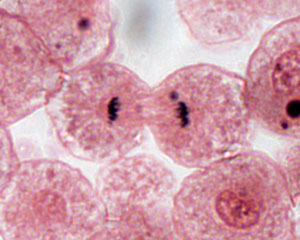
what are the general functions of mitosis
produce two identical daughter cells
growth ,repair ,maintenance
example of mitosis
skin cell replication
meiosis
occurs in reproductive organs
what does meiosis produce
haploid cells( sex cells )
what does mitosis produce
diploid cells ( somatic)
prophase 1
synapsis ; chromosomes from mom and dad pair up crossover; take different parts of chromosomes, combine with other genes
“why don’t we look alike”
metaphase 1
duplicate chromosomes line up in middle
mitosis number of divisions
1
meiosis number of divisions
2
mitosis number of cells produced
1 daughter cell
meiosis number of cells produced
4 daughter cells
mitosis genetic variation
no, exact copy of parent cell
meiosis genetic variation
yes, all four cells have genes form mom and dad crossover, combine in P1
mitosis reduction division
2N→2N
meiosis reduction division
2N-n
overall function mitosis
growth, repair , maintenance
overall function meiosis
haploid cell production ( sex cells ) egg/sperm
mitosis identical to
parents
meiosis identical to
nothing, each cell is different
chromosome number mitosis
23→23
46 pairs in all
chromsome number of meiosis
23-23-23-23
92 pairs in all
haploid
single set of chromosome (n) sex cells
diploid
having two complete sets of chromosomes (2N), somatic cells
homologous chromosome
diploid cell, one from mom (egg), other from dad (sperm) 23 pairs
homologous chromosome vs.sister chromatids
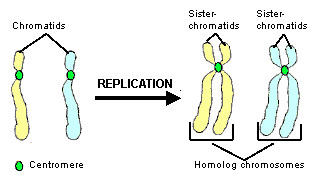
allele
alternate forms of gene
homozygous
same allele for a gene
two copies of same allele
(YY, yy)
heterozygous
different alleles for a gene (Yy)
dominant
allele expressed in homo dom and hetero
recessive
allele only express in homo rec
incomplete dominance
heterozygous phenotype, combination of two homozygous phenotypes
RR:red
Rr: pink
rr: white
codominance
both homozygous phenotypes expressed completely in heterozygous ex: type AB blood
genotype
allele present for single trait
example : hetero, homo, dom, homo rec
phenotype
physical expression of trait
ex: pink, round, yellow, gray
polygenic trait
trit encoded by multiple pairs of genes, range of phenotypes
ex: hair color, skin color, height, foot size
law of segregation (ex)
every trait has 2 alleles, they separate and combine during inheritance
meiosis law of segregation
separates alleles of a single individual, fertilization randomly combines alleles from both parents
each offspring has equal chance of receiving one of two genes, but not both expressed at the same time
law of segregation
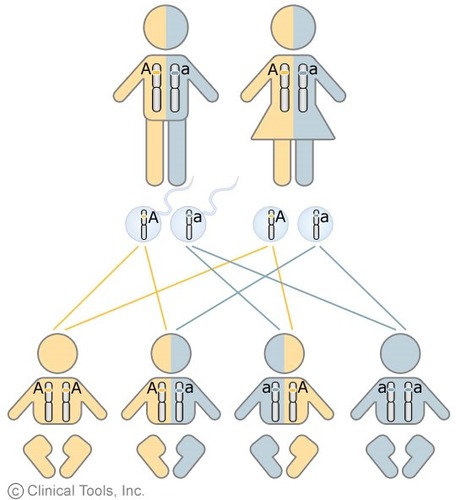
law of independent assortment (ex)
alleles of gene for one trait separate from alleles of another gene for a trait
law of independent assortment
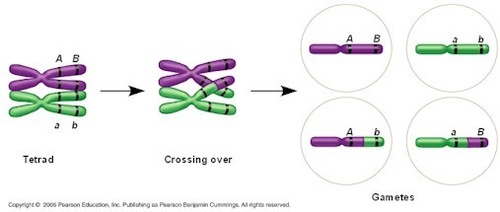
mendelian trait examples
widows peak, earlobe, freckles, eyebrows, eyelashes, eye space , eye size, dimples
non medalian trait examples
polygenic: hair color, eye color, height, foot size
incomplete dominance: mixed skin color
co-dominance: AB blood
a yellow flower (pp) was crossed with purple flower (Pp). what is the chance of obtaining yellow offspring
1/2
what is the genotype for this parent? heterozygous purple, homozygous dominant round corn. P-Purple,p-yellow, and R-round ,r-wrinkled
PpRR
in dogs long hair (L) is dominant over short hair (l) and wavy hair(W) is dominant over straight hair (w). what are the chances of obtaining puppies that have short straight hair if you breed two dogs that are heterozygous for both traits
1/16
in dogs, long hair (L) is dominate over short hair (l) and wavy hair(W) is dominate over straight hair (w). what are possible sex cells for this dog.Llww
Lw,Lw,lw,lw
STE buffer kept the ____ stable during our DNA isolation
pH
the SDS detergent _____ during our DNA isolation
dissolved the nuclear membrane
the proteinase K____during our DNA isolation
digested chromosomal proteins
DNA will not stay dissolved (in solution) in the presence of
salt and alcohol
a nucleotide consists of
5C sugar, phosphate group, N- base
how long is DNA
approx. 6ft
____ are the monomers (building blocks) of DNA
nucleotides
____ are given credit for publishing the first accepted model of DNA that we still use today
Watson and crick
DNA will migrate towards the ____ pole during electrophoresis
positive
base pair rules
A=T
G=C
basic DNA structure
double stranded
complementary
anti-parellel
double H bonds
chromosomes made from
DNA wrapped around protein and condensed
electrophoresis
analyzes DNA size
what does electrophoresis do
measures DNA by size of n-base pairs
bigger pieces are slower, don’t go as far in gel