Ch. 12 Central Nervous System
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Sulci
shallow grooves that separate gyri of the brain
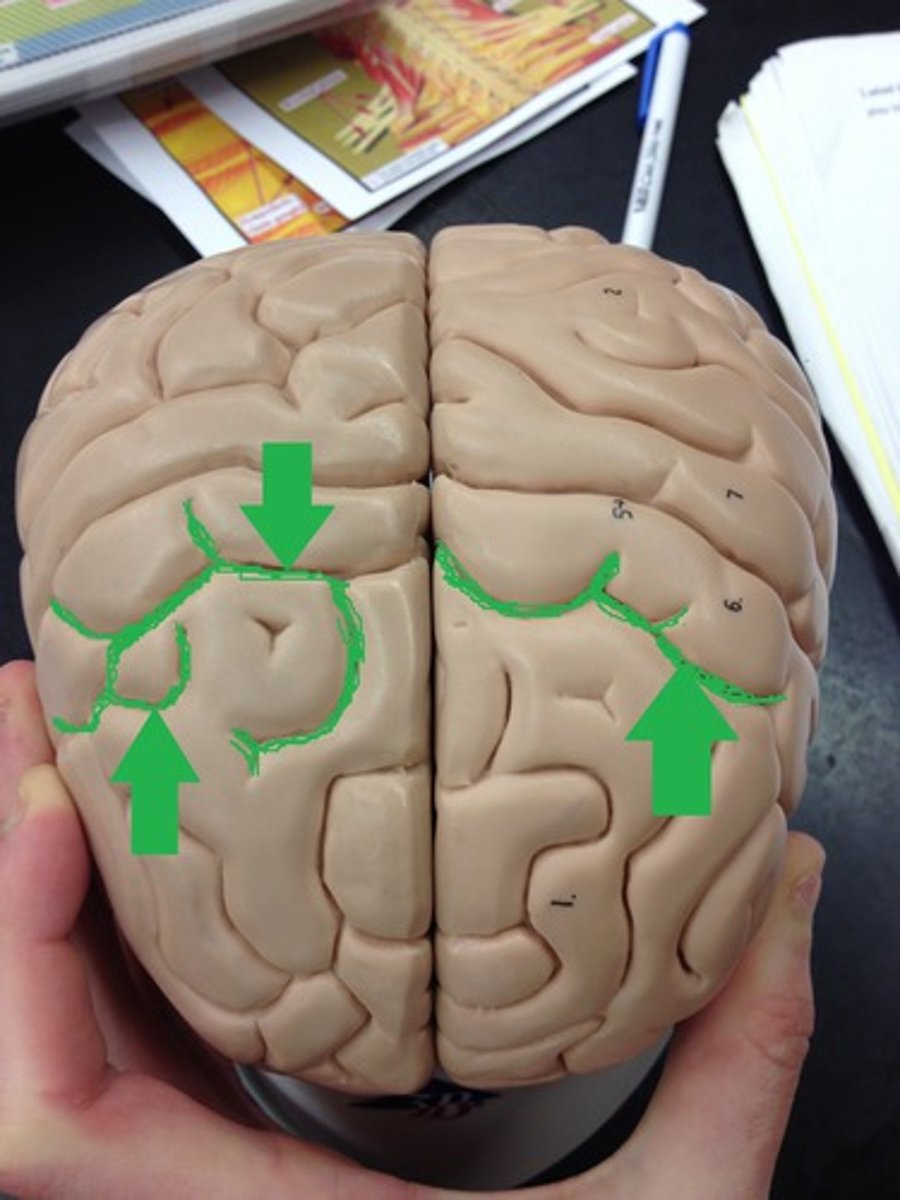
Gyri
elevated ridges of the brain
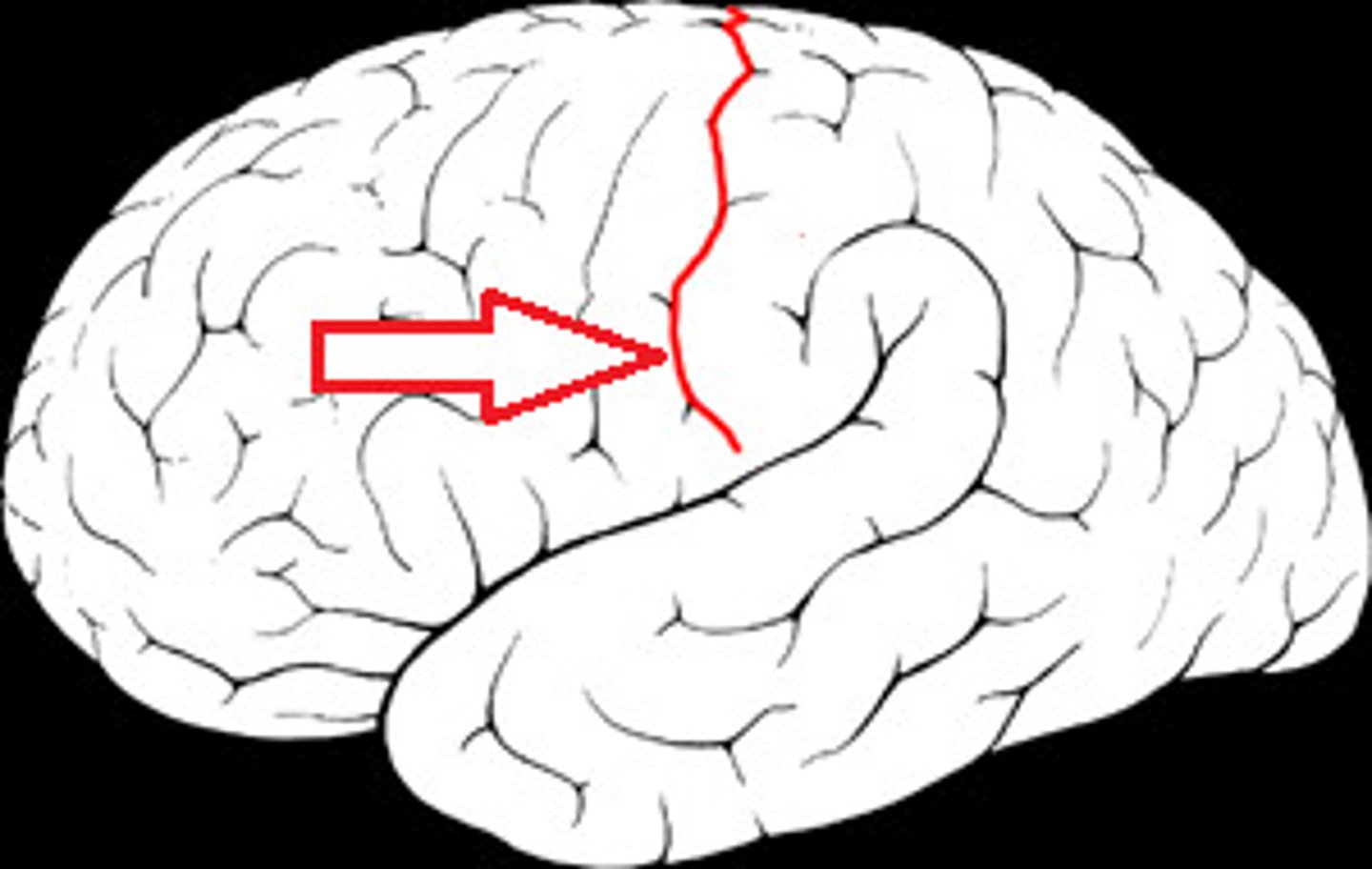
The central sulcus separates which lobes?
frontal and parietal
The parieto-occipital sulcus separates which lobes?
parietal and occipital
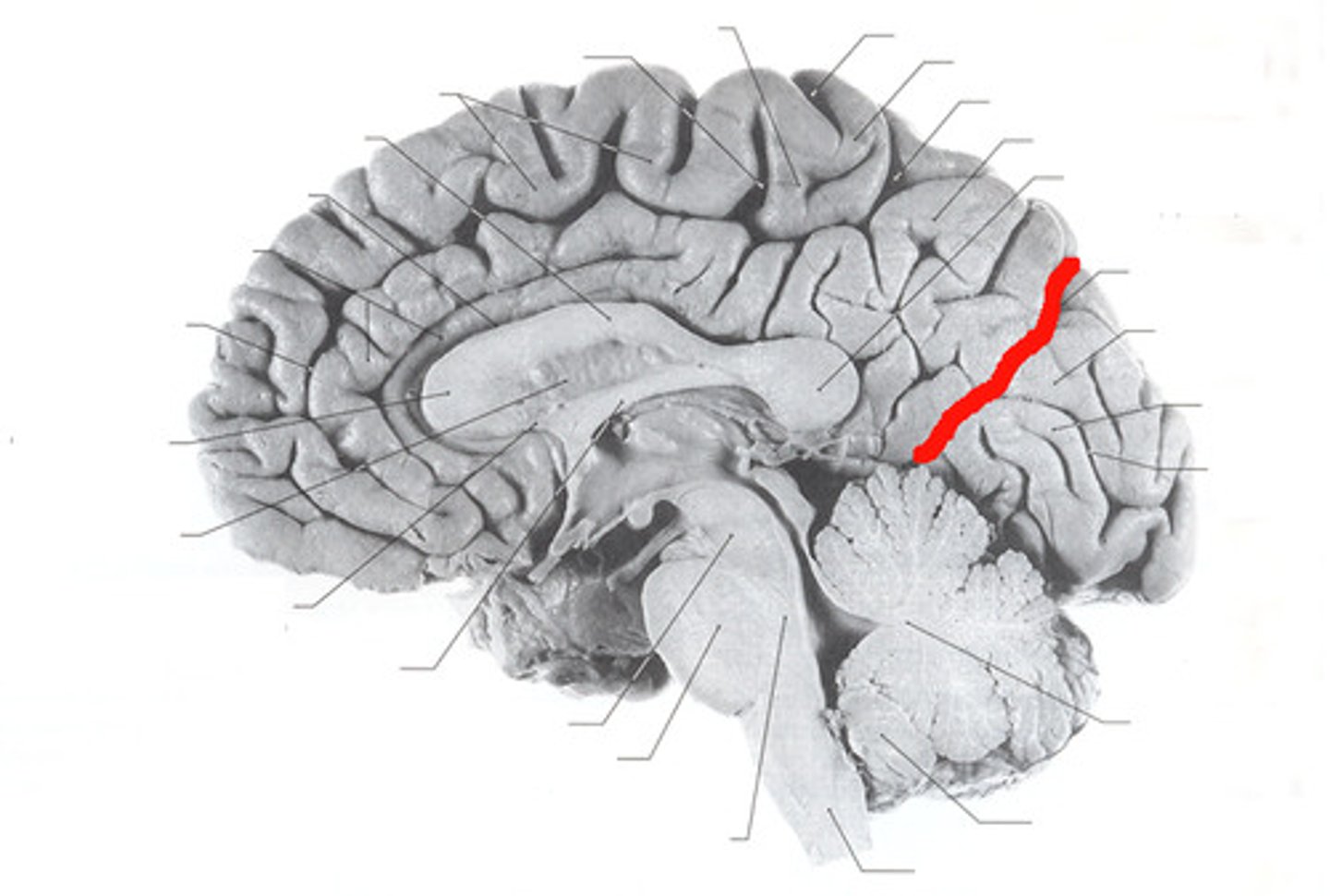
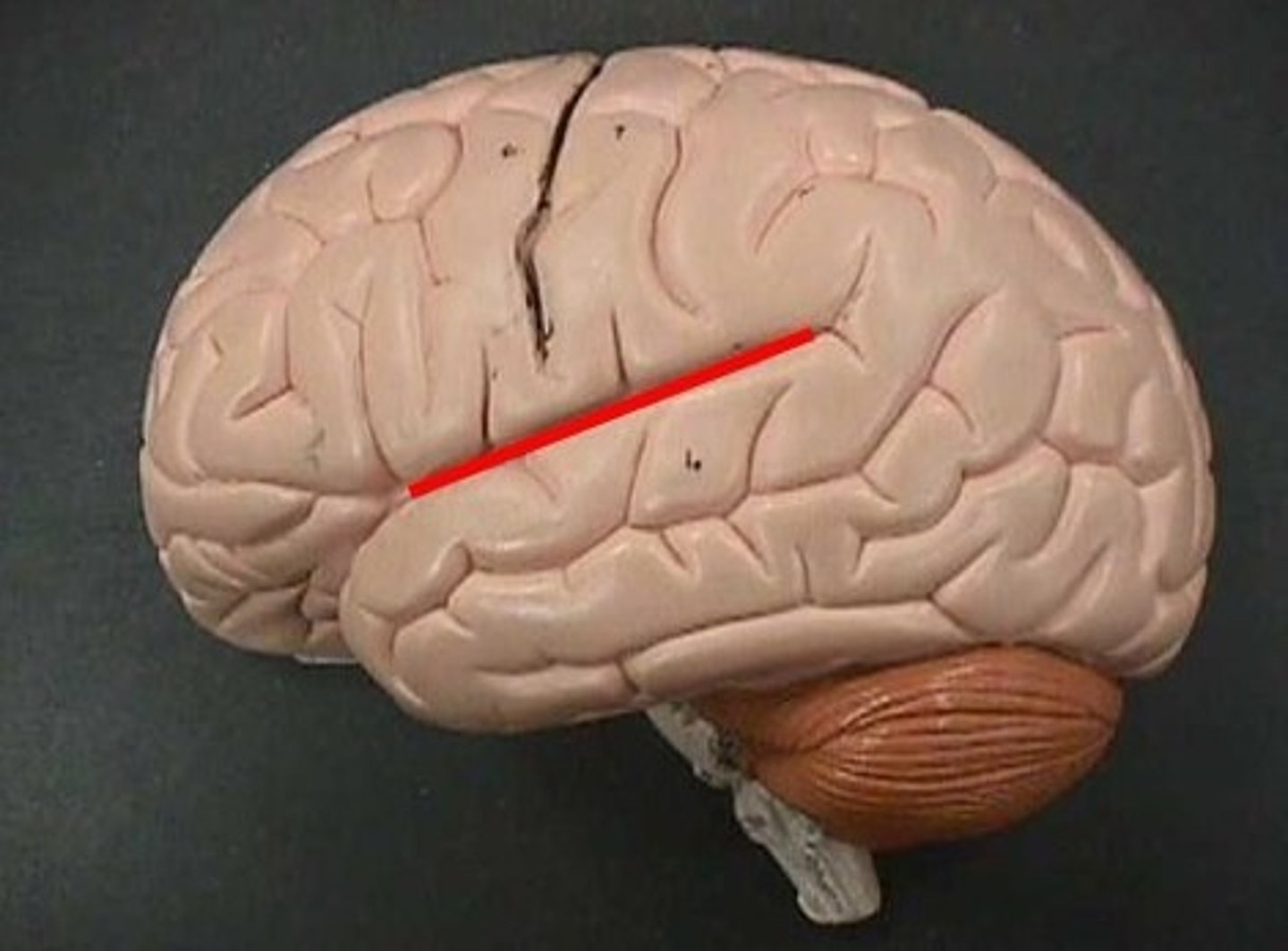
The lateral sulcus separates which lobes?
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Fluid produced in the ventricles of the brain that flows in the subarachnoid space and bathes the meninges. Is used to carry dissolved gases, nutrients, and wastes
cerebrospinal fluid is produced where
choroid plexus
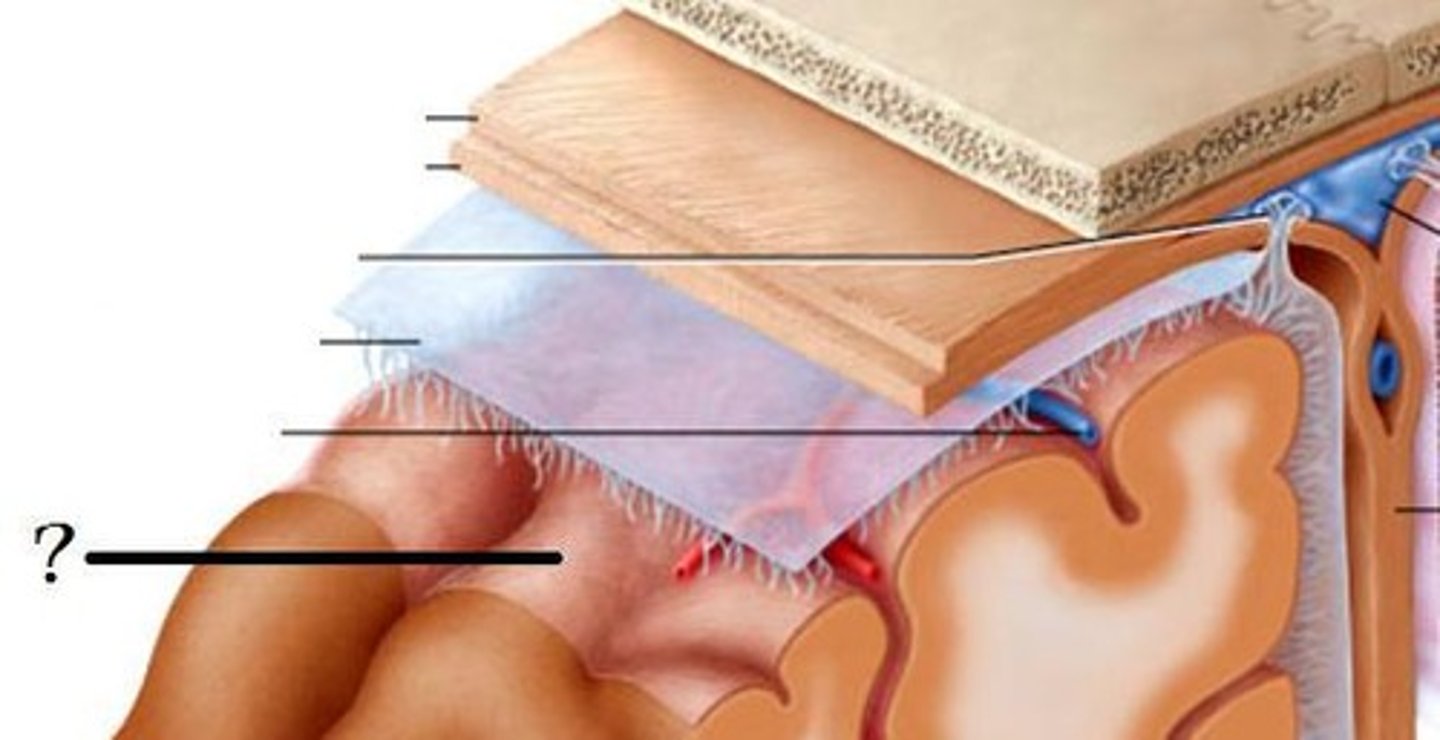
Three membranes that protect the brain, superficial to deep
Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Pia Mater
Dura mater
thickest, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
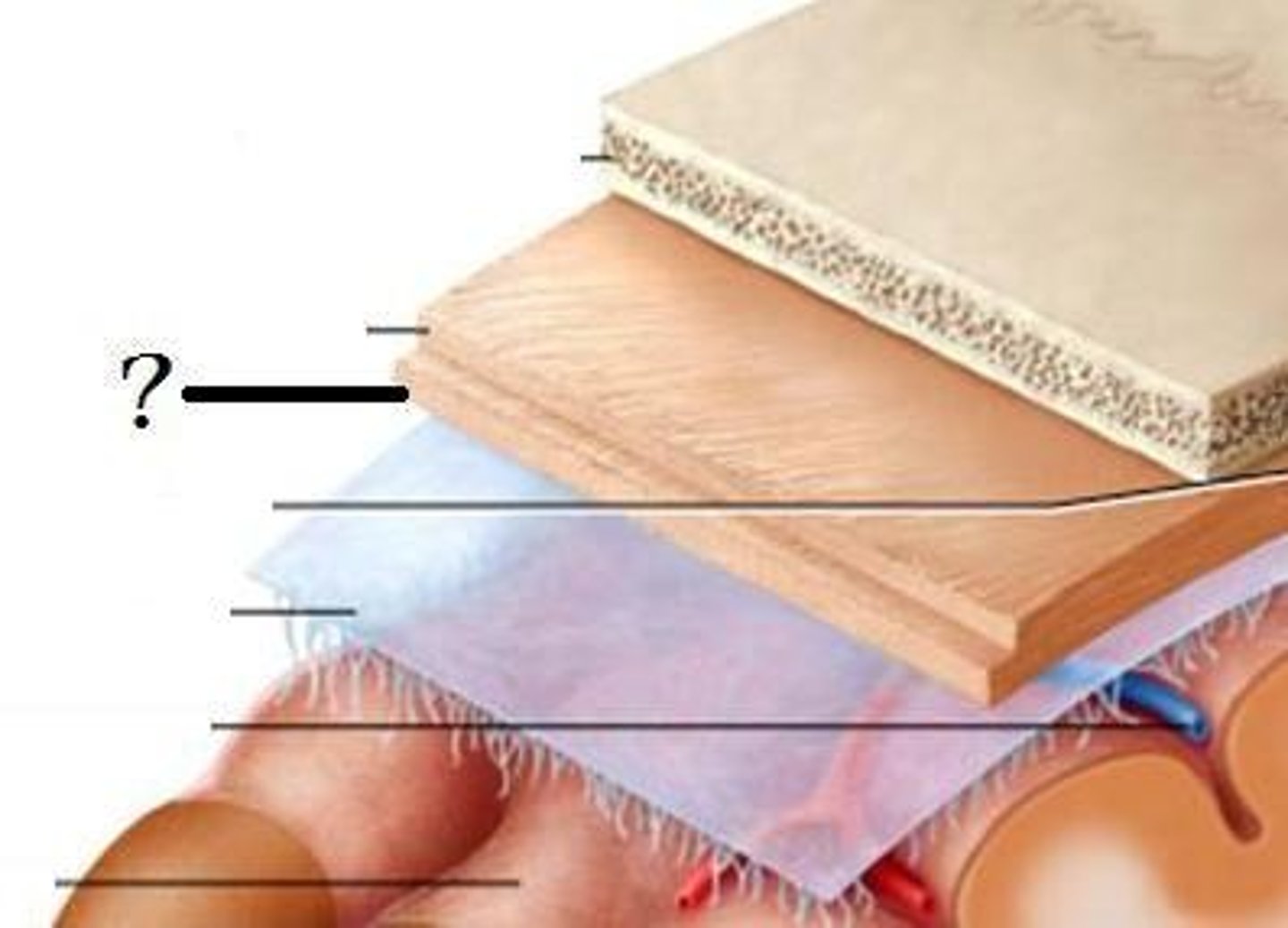
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
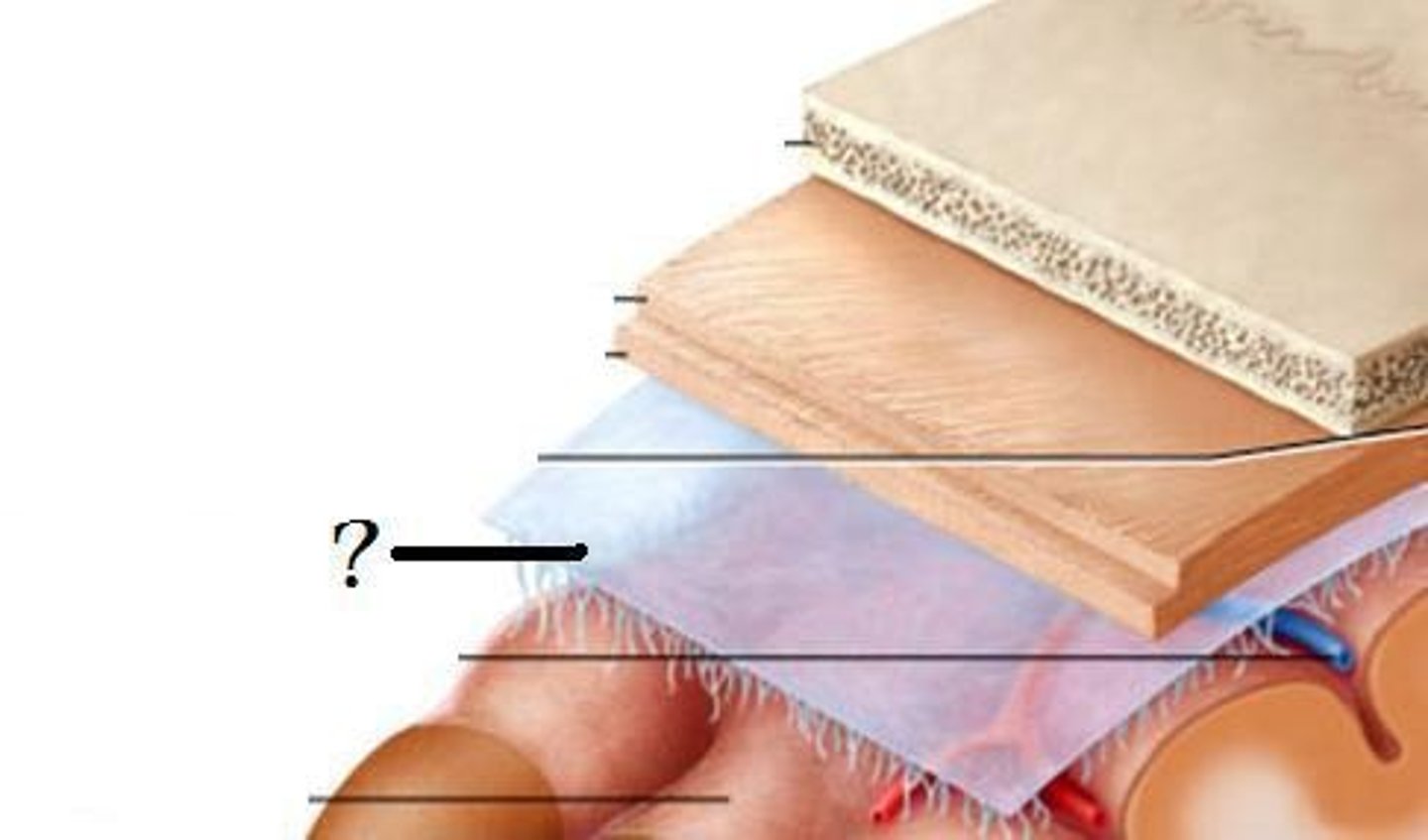
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
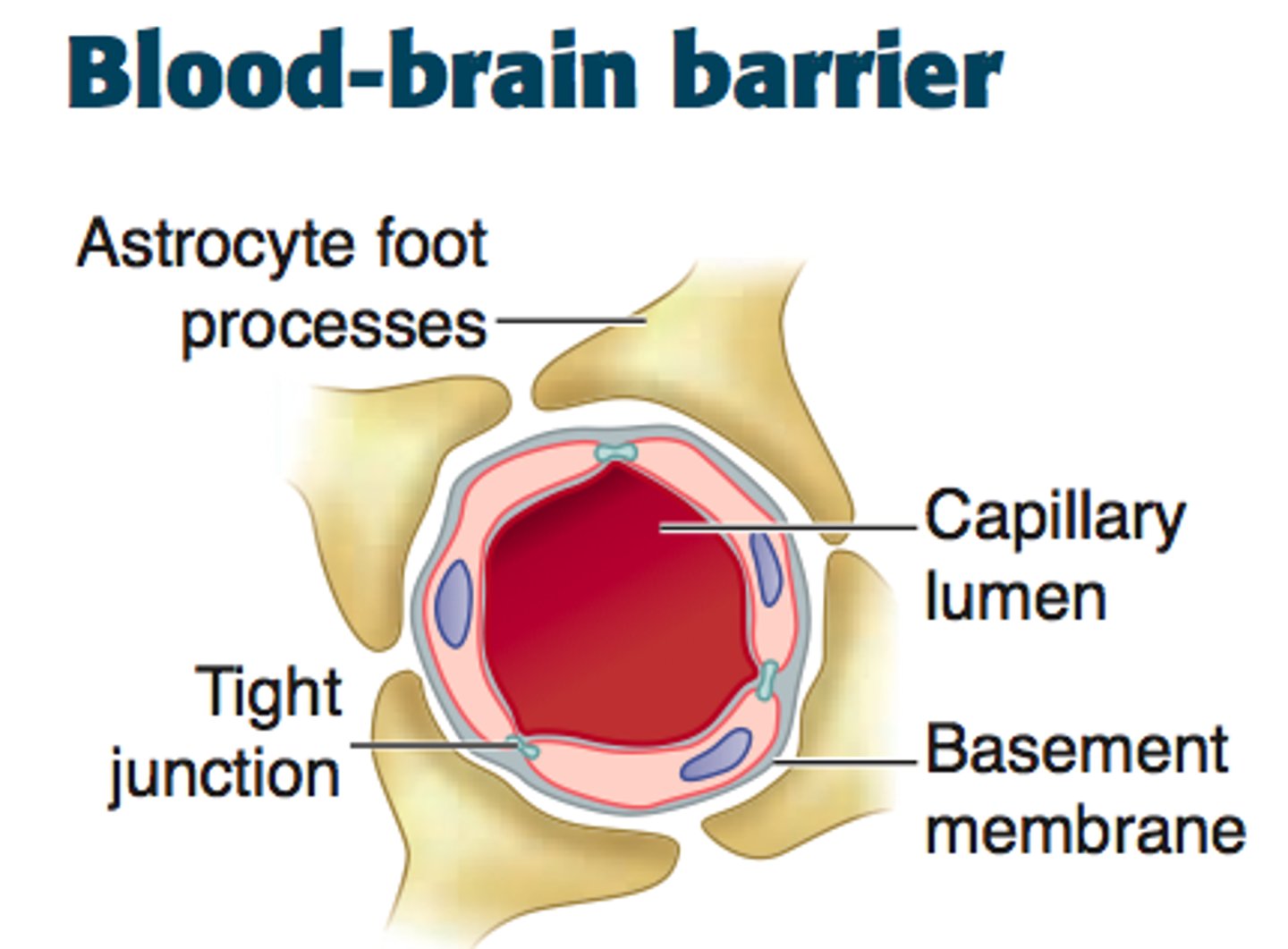
Blood Brain Barrier
a filtering mechanism of the capillaries that carry blood to the brain and spinal cord tissue, blocking the passage of certain substances.
Cerebrum
Largest part of brain
Controls higher mental functions
Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
lateralization of brain function
the unequal representation of various functions in the two hemispheres of the brain
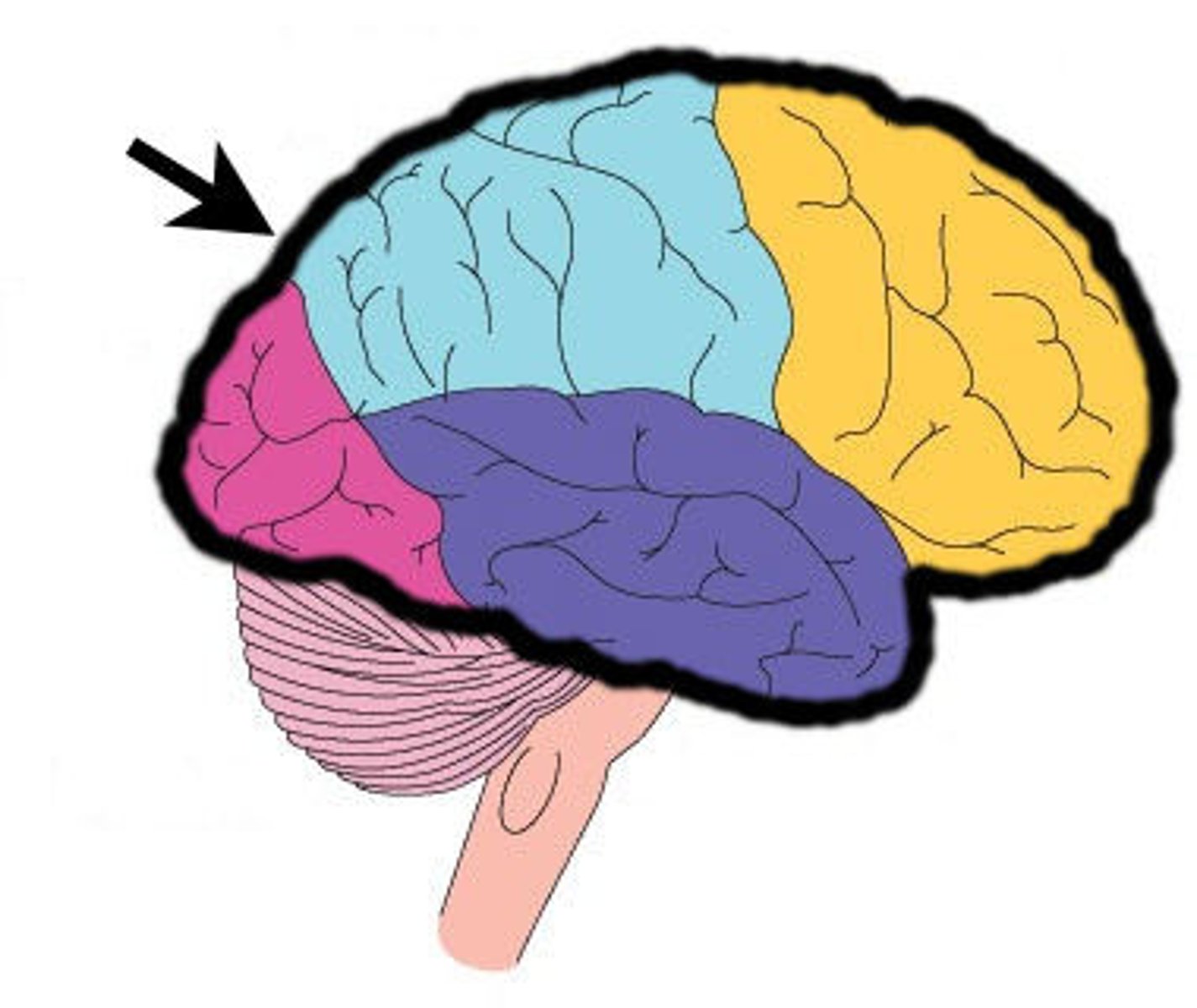
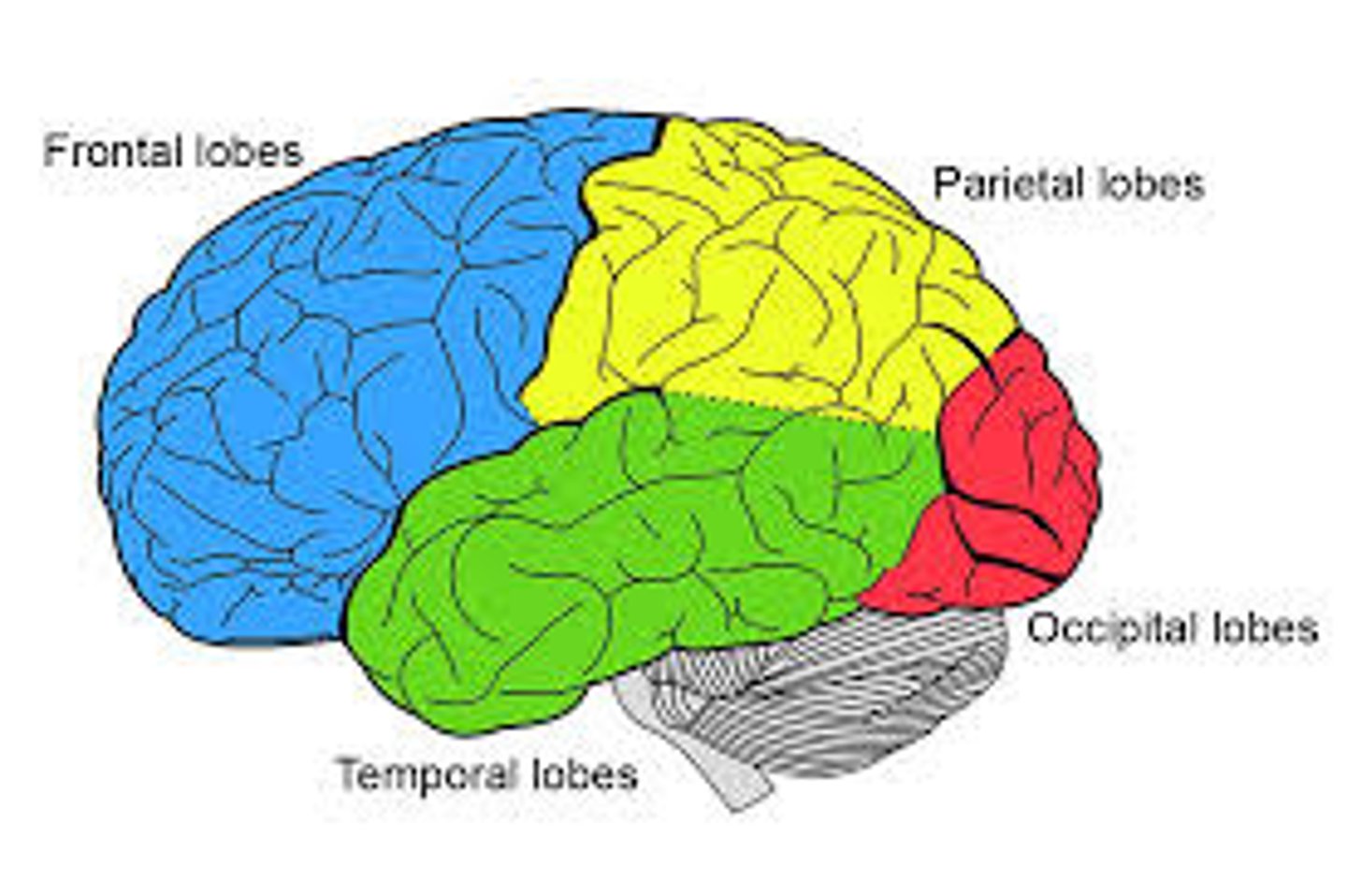
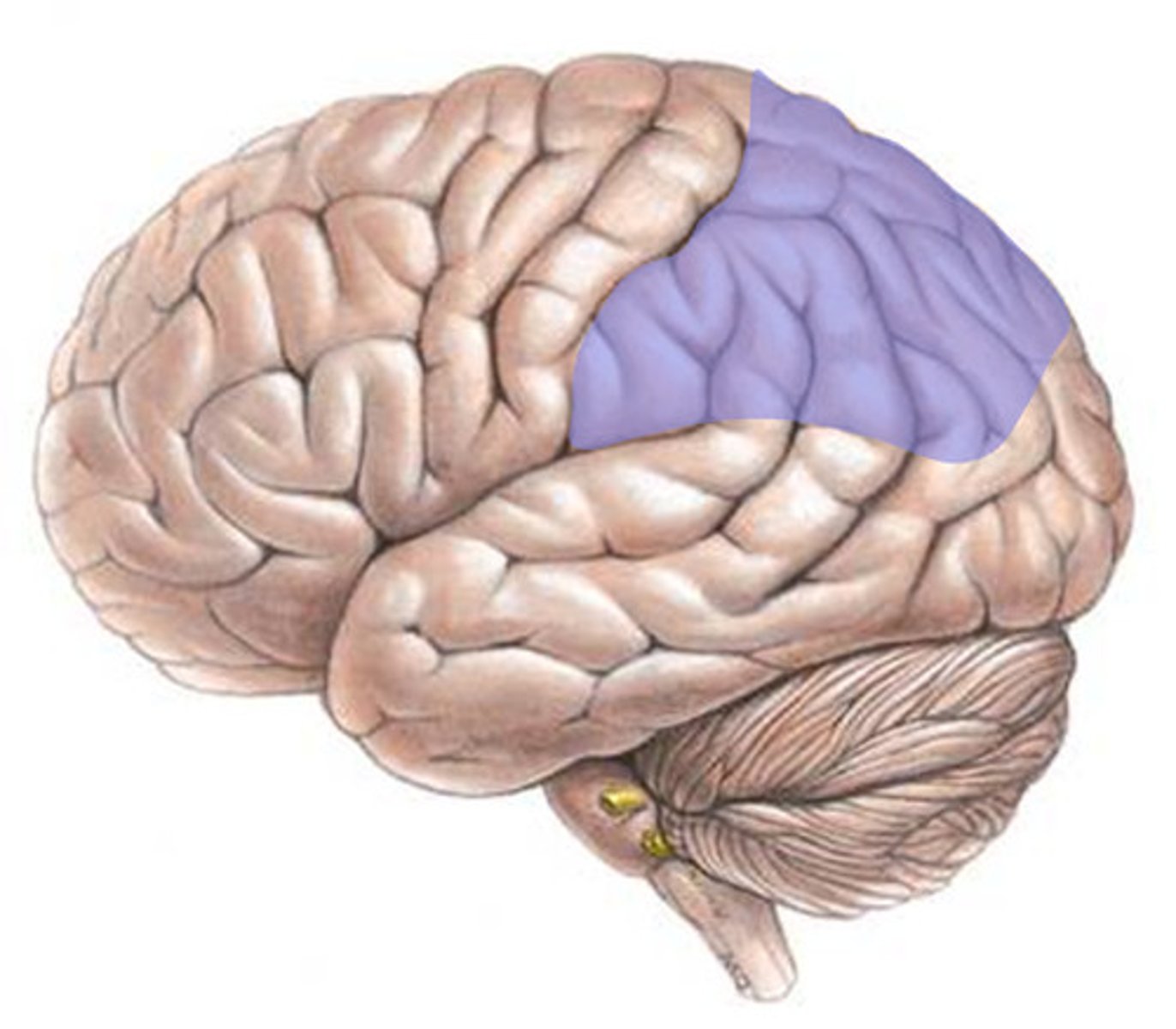
5 lobes of the cerebrum
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula (deep)
frontal lobe function
involved in motor function: problem solving, memory, judgment, impulse control
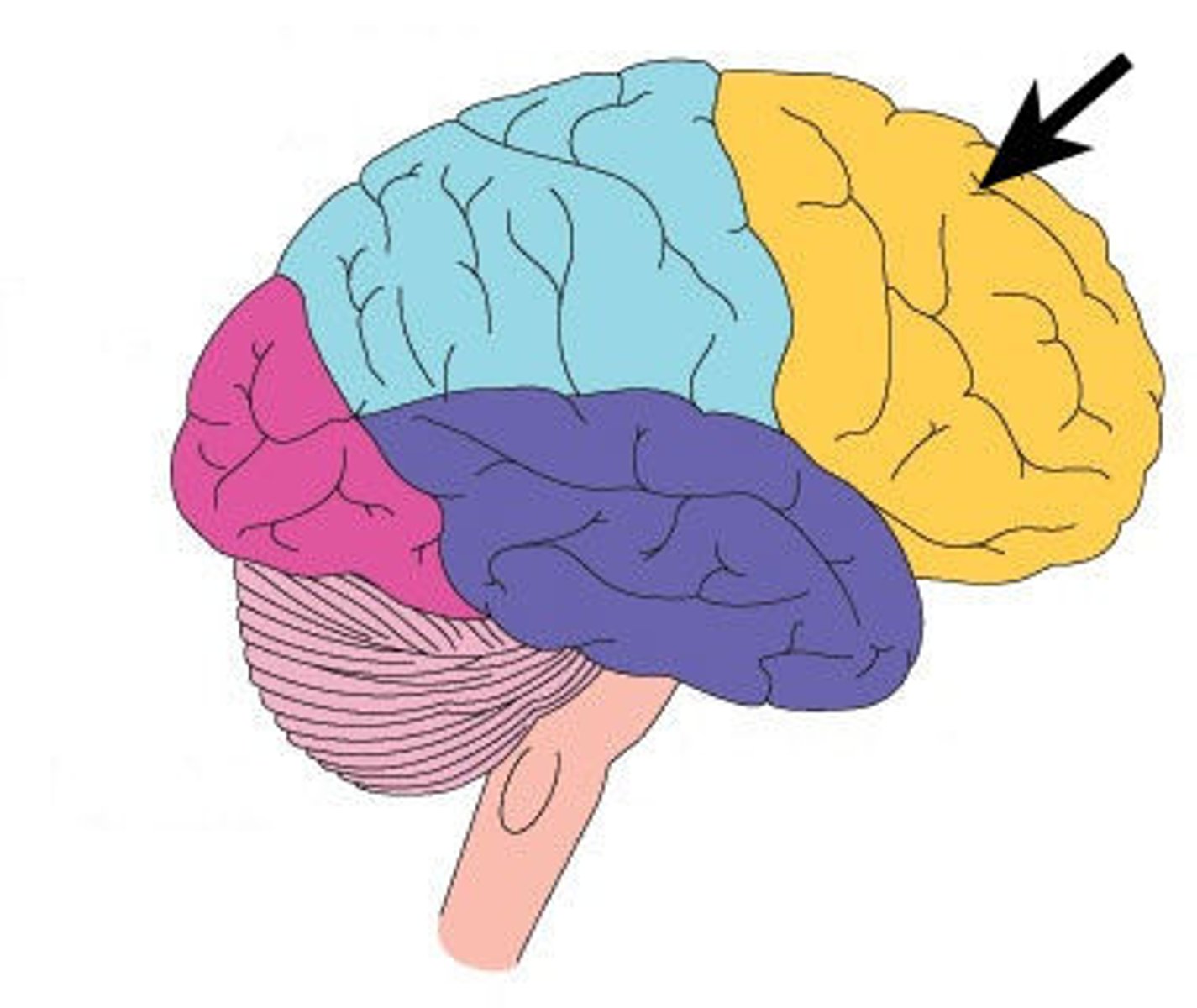
parietal lobe function
somatic sensory processing
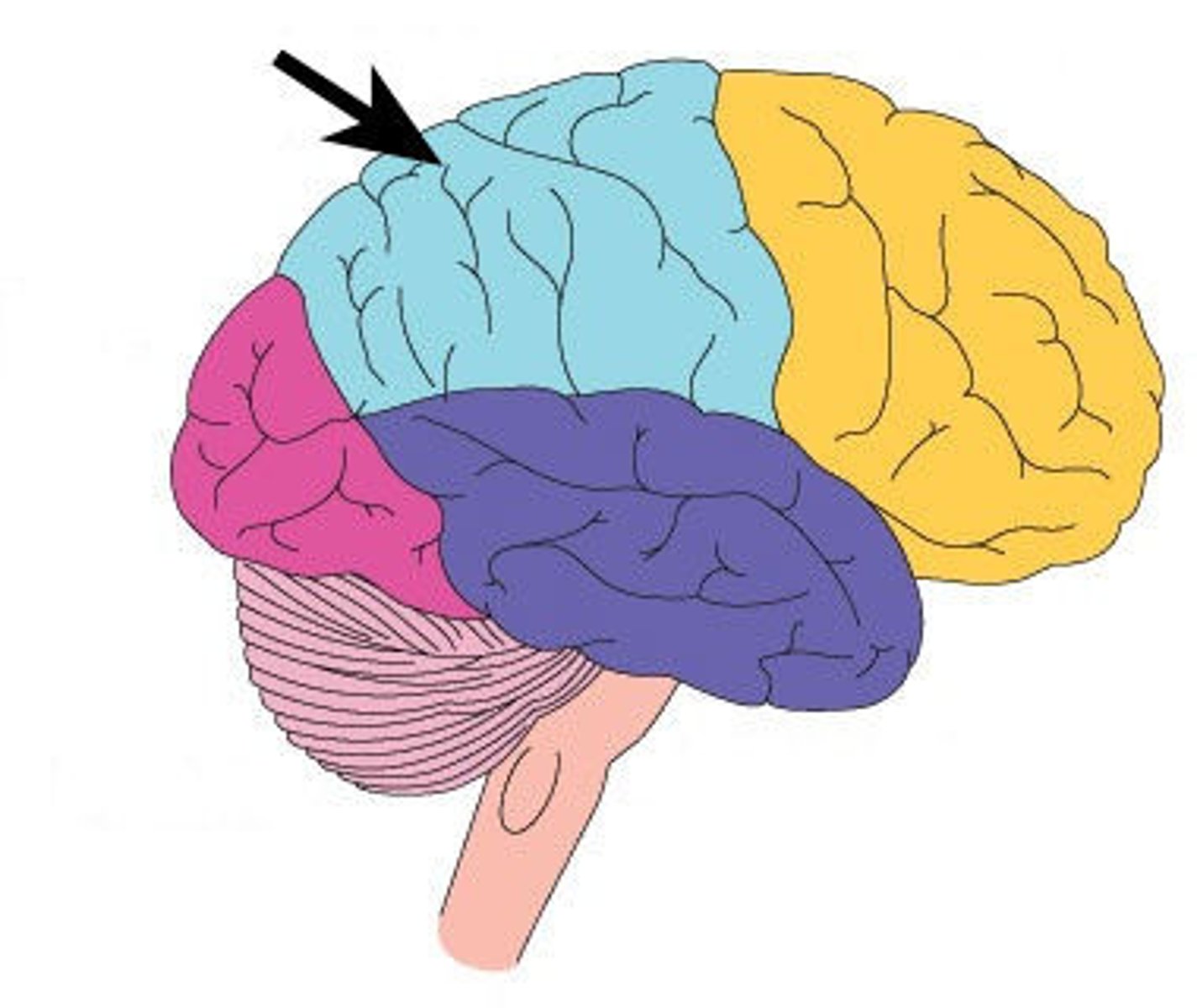
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
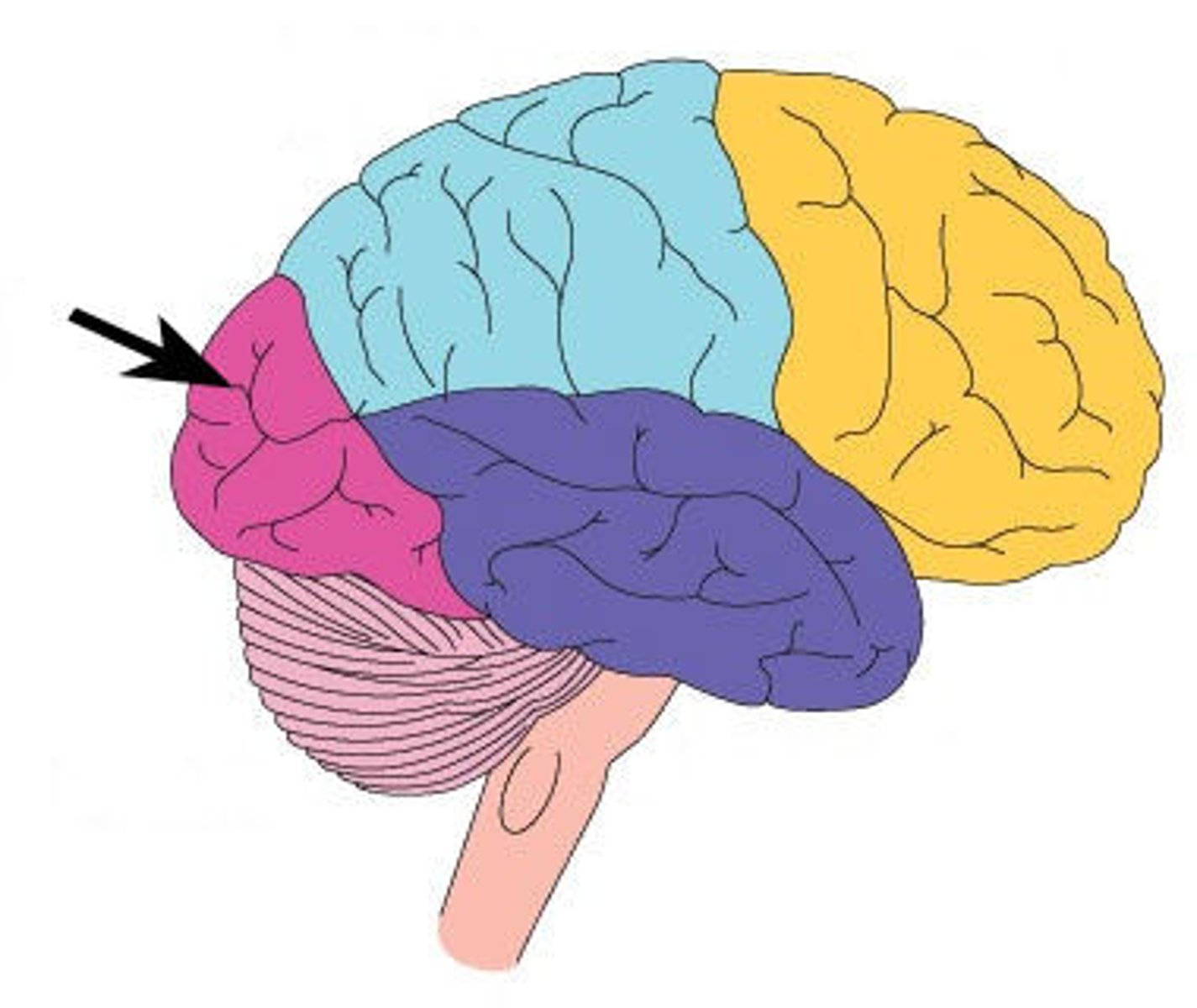
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
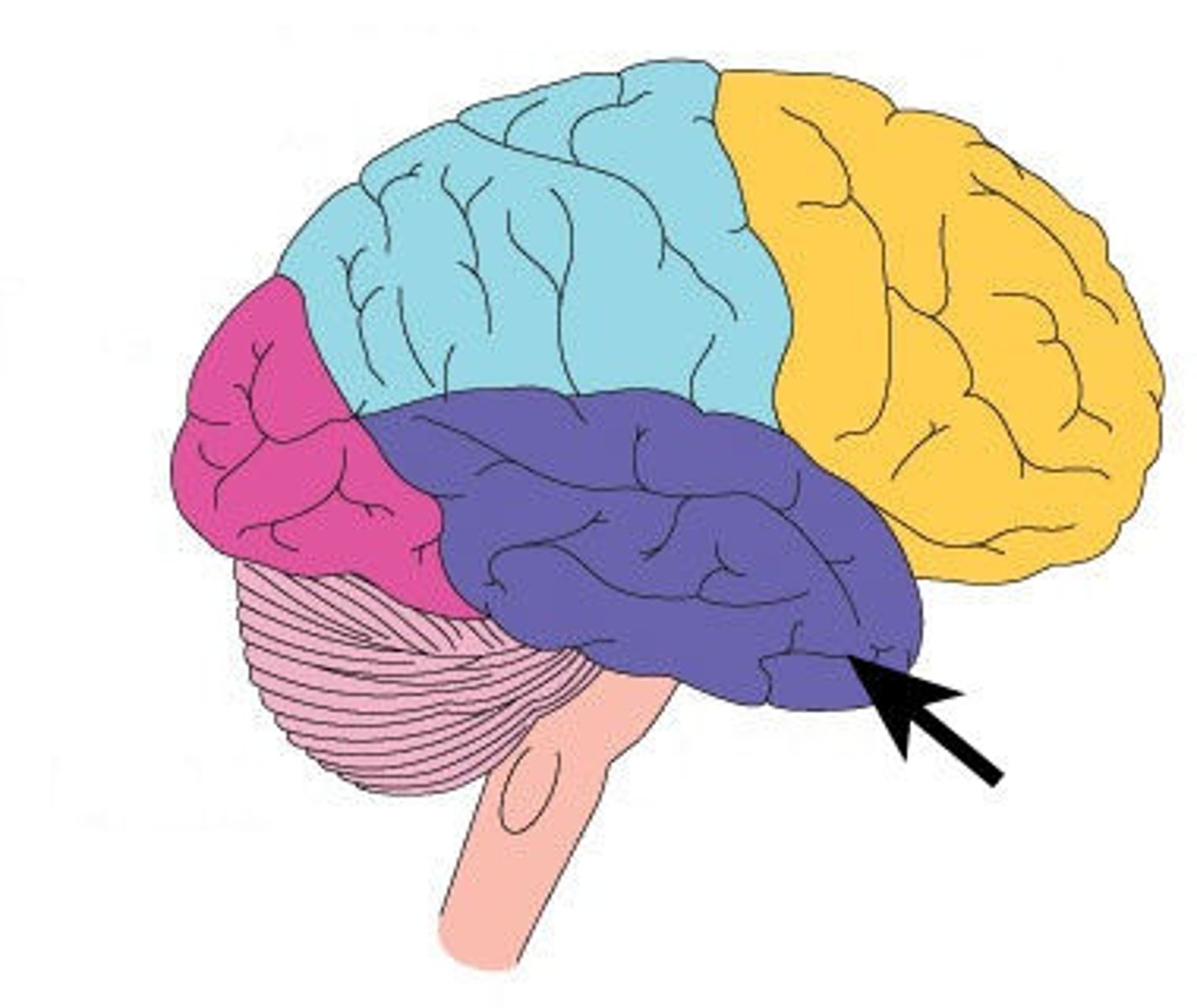
prefrontal cortex (PFC)
Large frontal-lobe area anterior to the motor and premotor cortex, plays a key role in controlling executive functions such as planning and coordinating
Diencephalon
contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
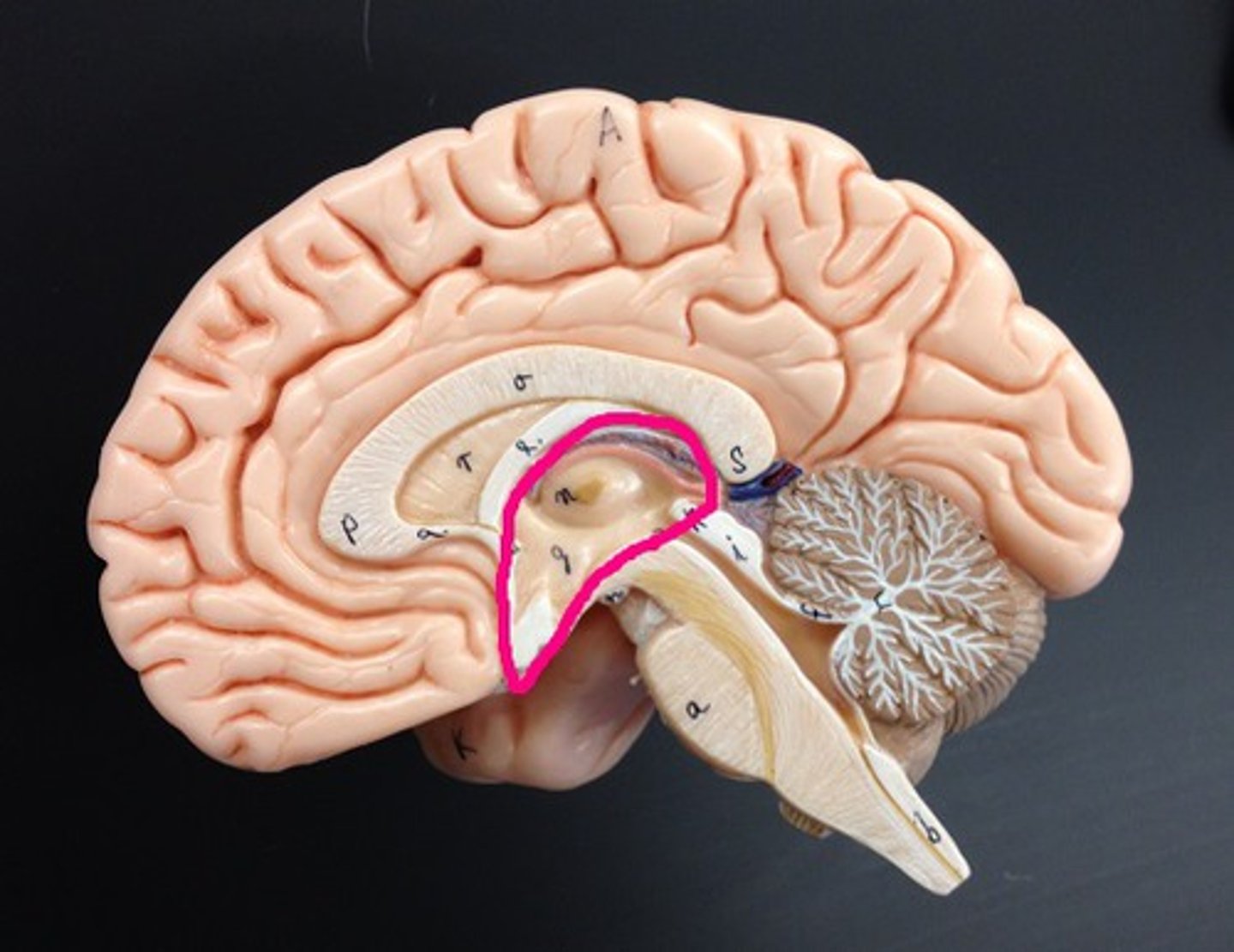
thalamus
The brain's relay station (Gateway to the cerebral cortex) for information coming into the cerebral cortex. Afferent information from all senses converges and is sorted and edited. Crude pleasant/unpleasant determination.
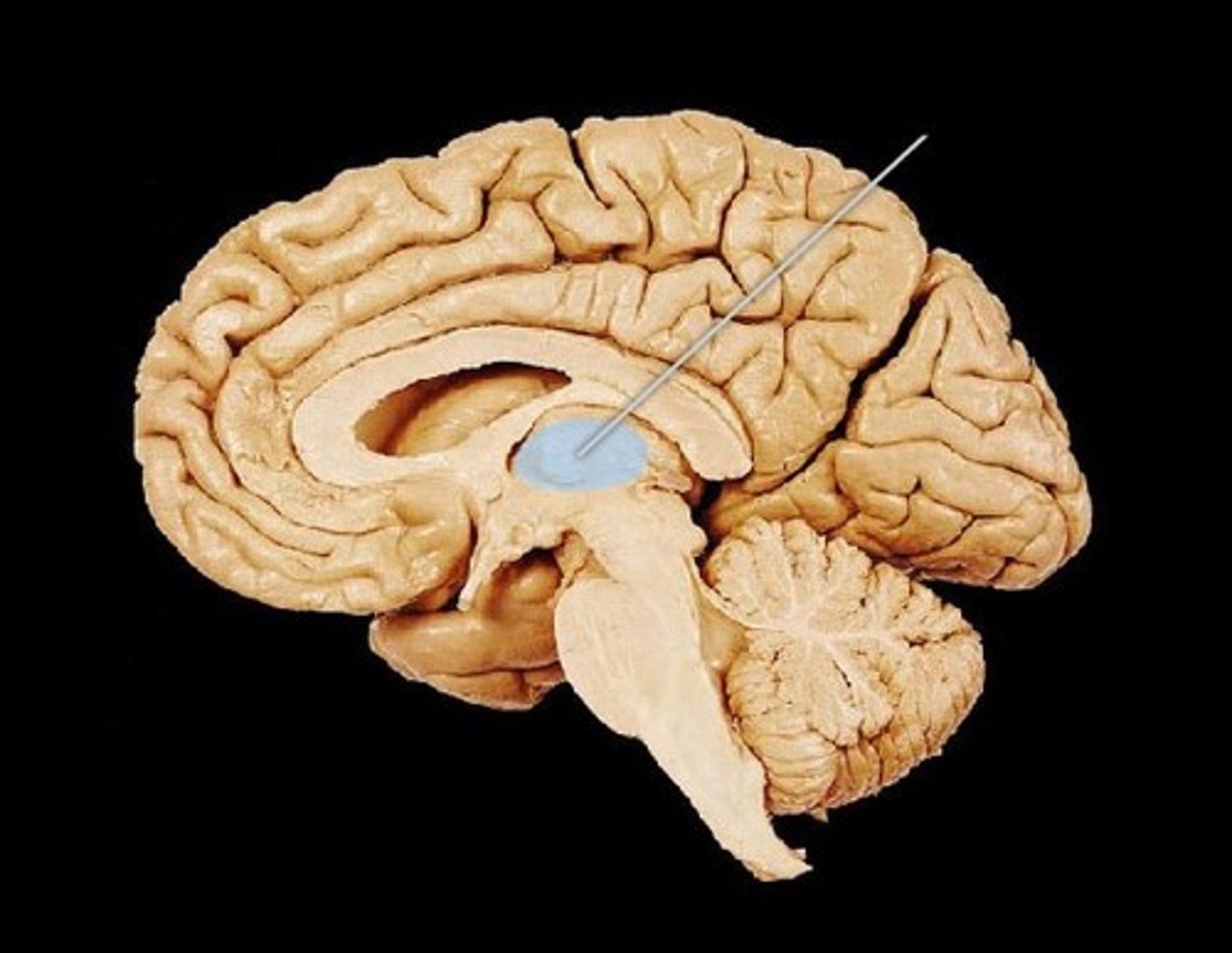
hypothalamus
Main visceral control and homeostasis. Autonomic control center that directs blood pressure, rate and force of heart beat, digestive motility and pupil size by controlling smooth and cardiac muscle and glands. It is the center for emotional response, determines pleasure, fear and rage, as well as sex drive. Maintains homeostasis of body temperature, nutrients by controlling appetite and food intake, salt and water balance through control of ADH as well as the sleep wake cycle by directing melatonin release
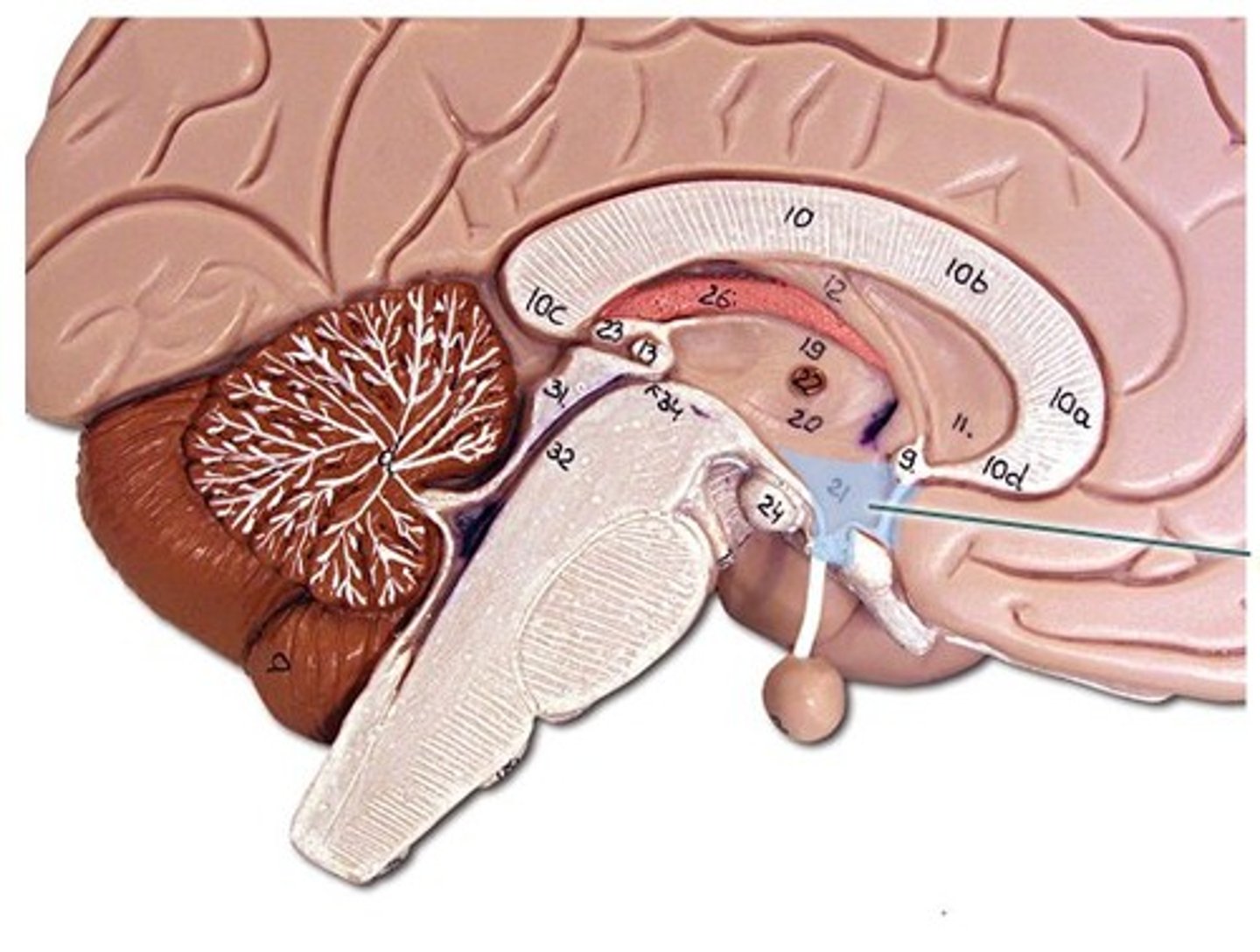
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands. Acts as the major interface between the endocrine and nervous systems.
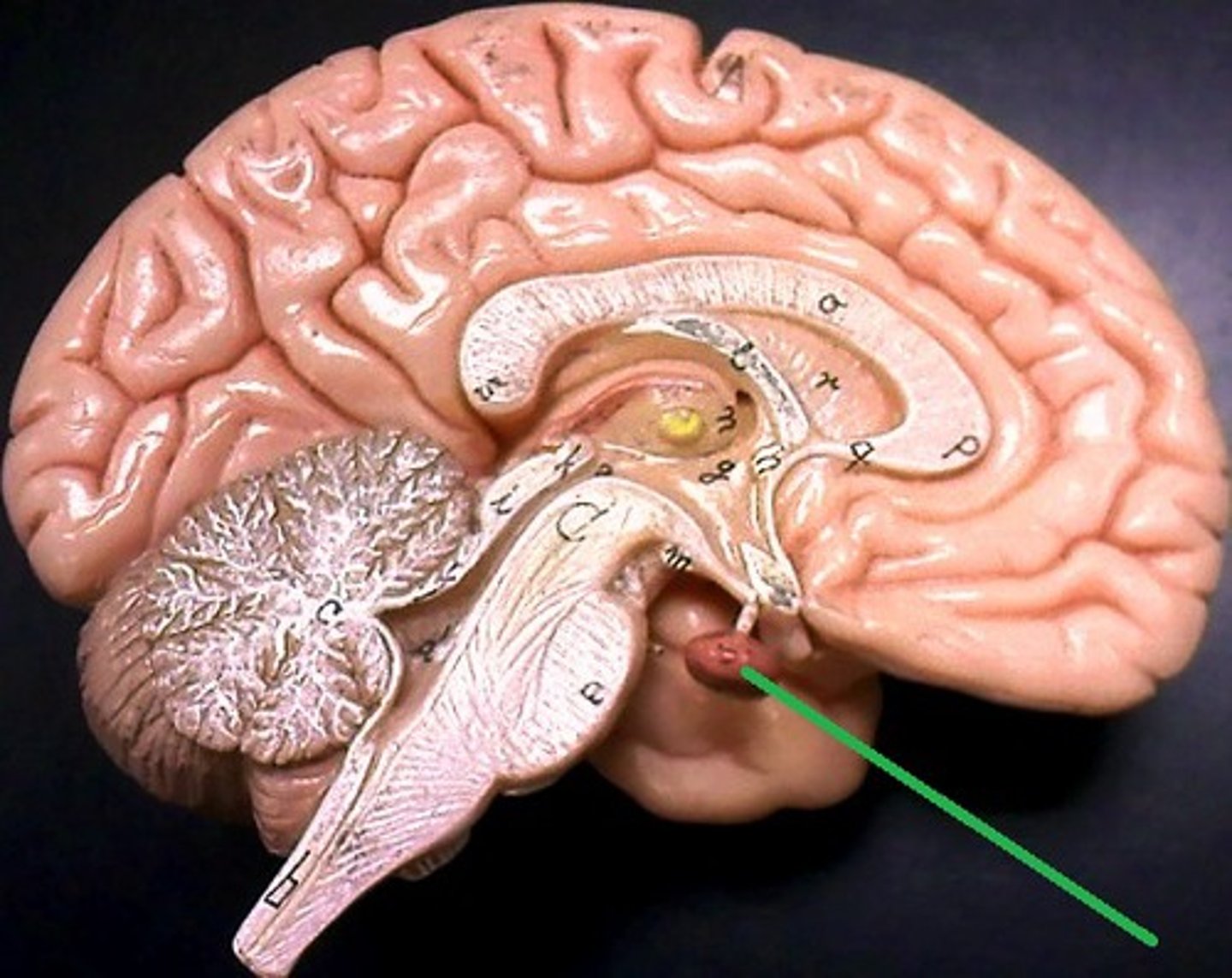
The brain stem
Connects the brain to spinal cord. Filters information flow between the peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
Regions of the brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Midbrain
Superior to the pons: integrates sensory information and relays it upward. Also known as the mesencephalon.
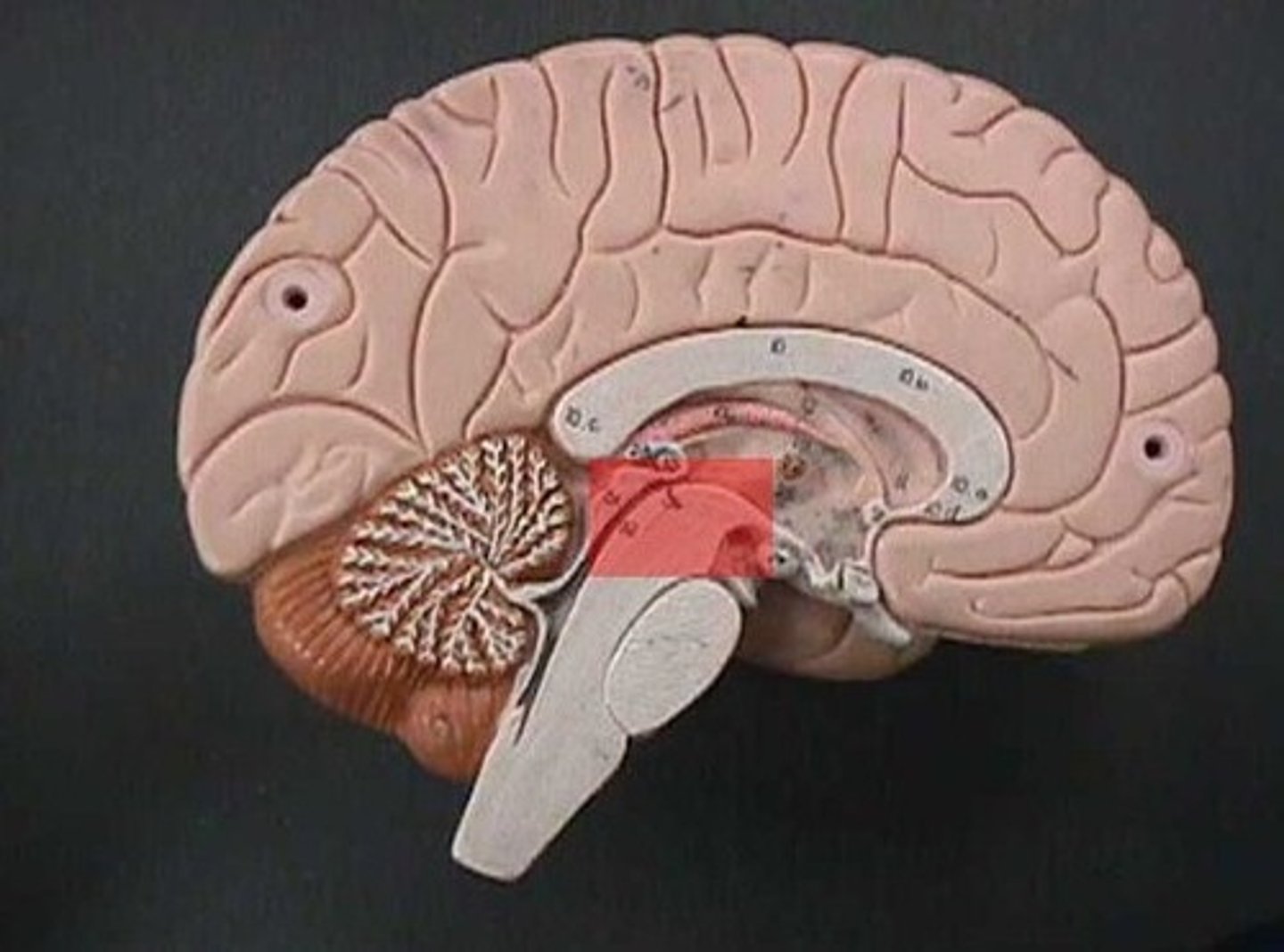
Pons
Acts as a relay for conversations between the motor cortex and cerebellum. Helps the medulla maintain breathing rhythm by governing the rate and depth of respirations.
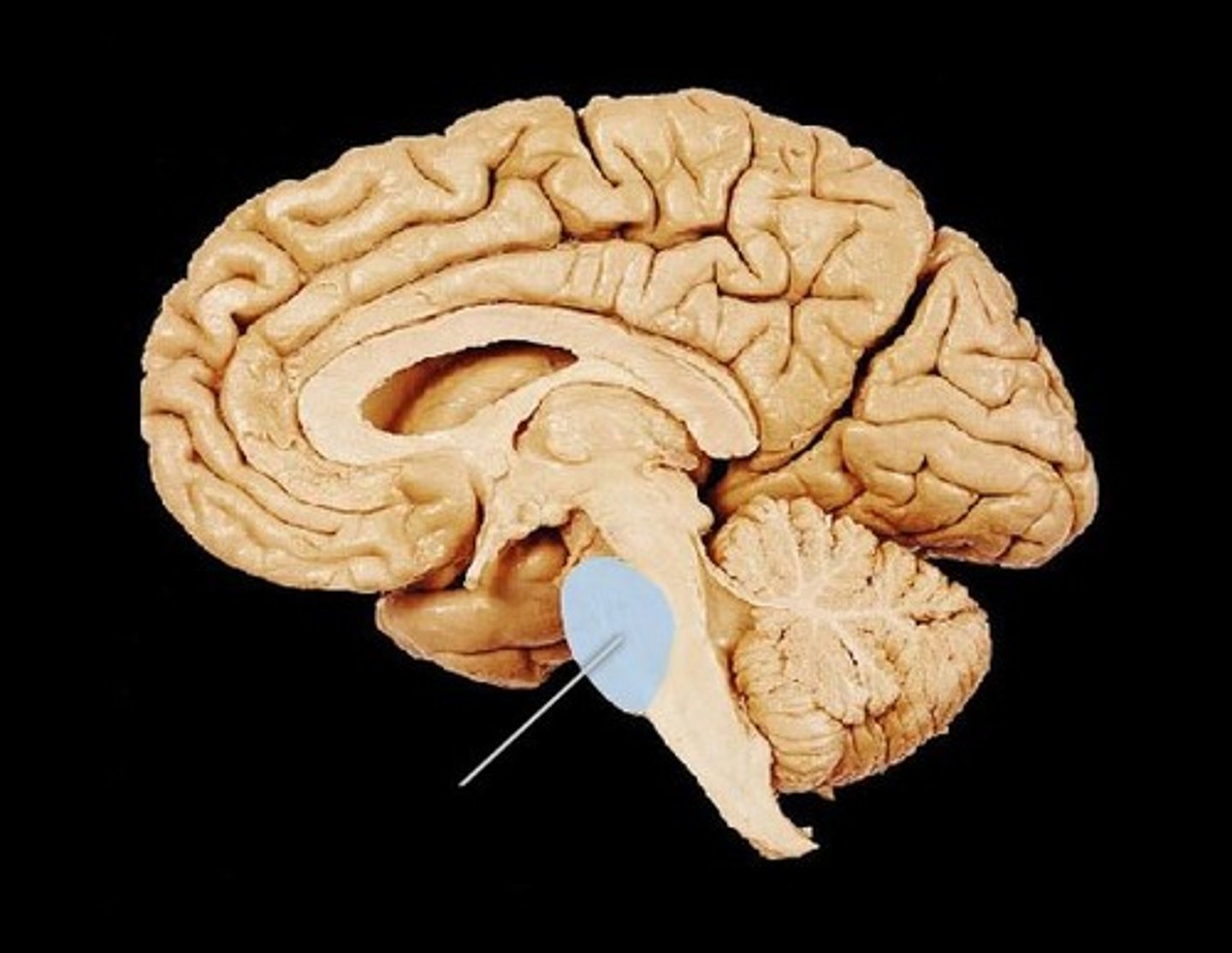
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion. Relays proprioception information (state of stretch of muscles and joints) to the cerebellum. Controls the cardiovascular and respiratory centers and controls various reflexes such as coughing, vomiting, hiccups, swallowing
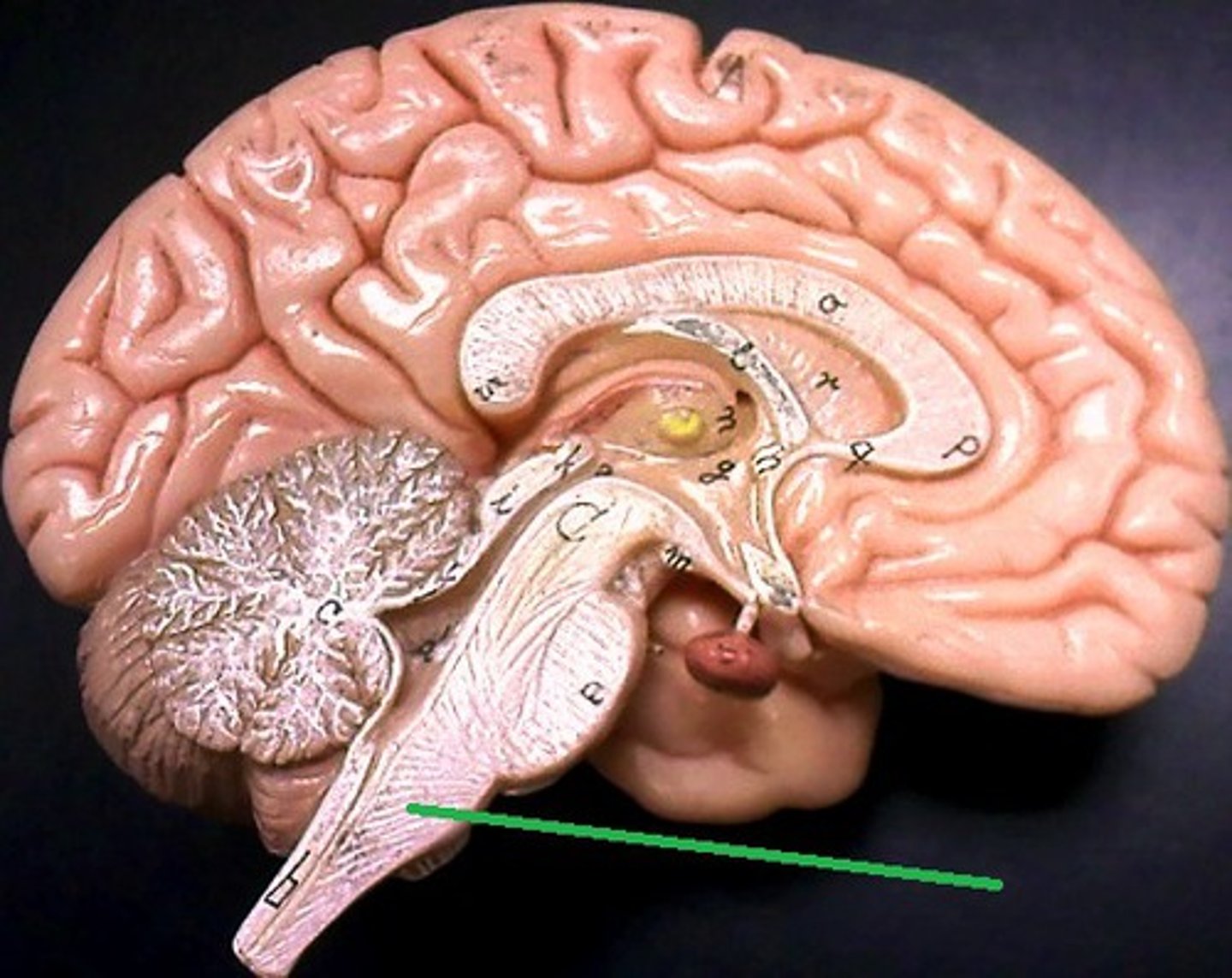
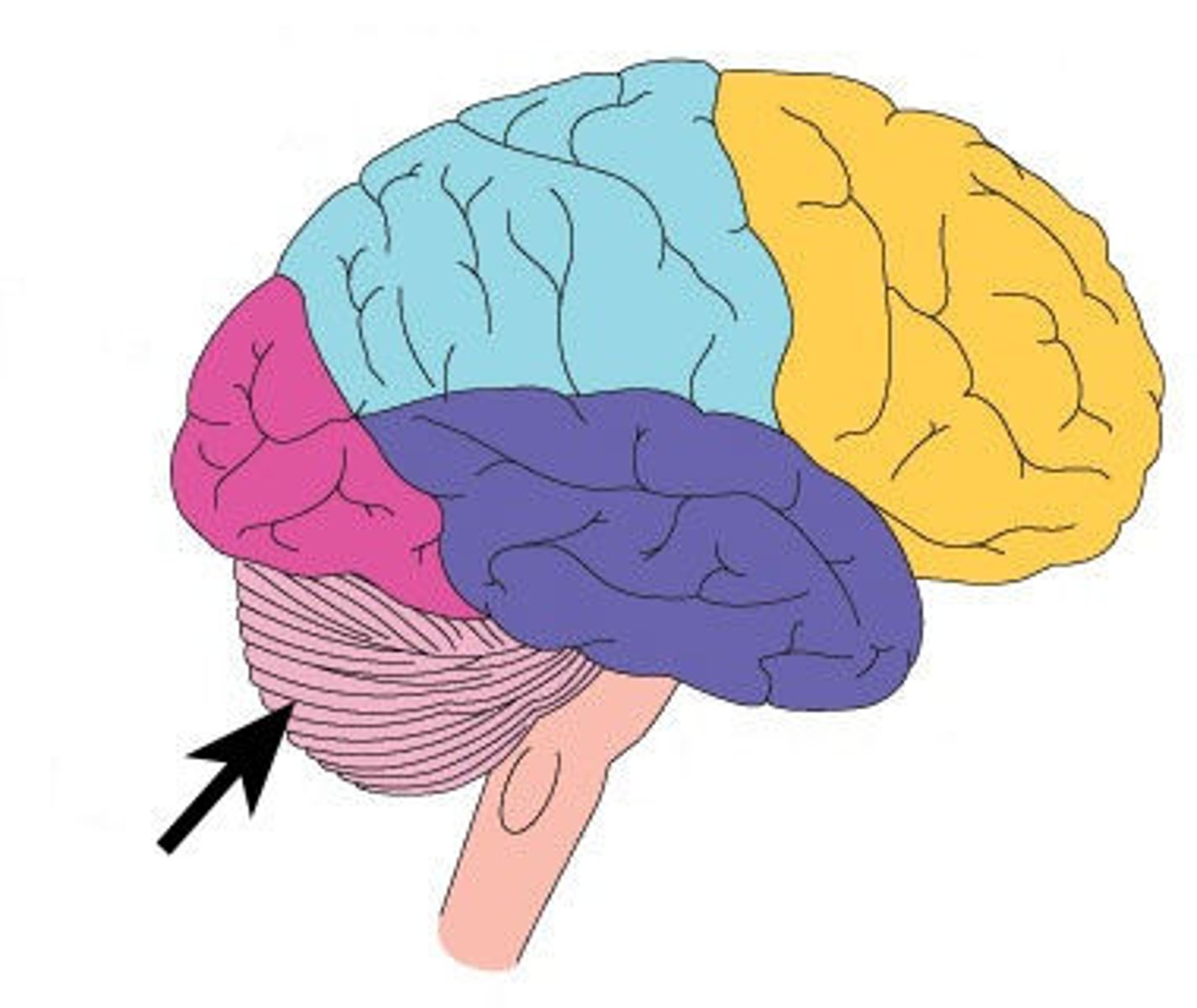
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance (smoothes out movements)
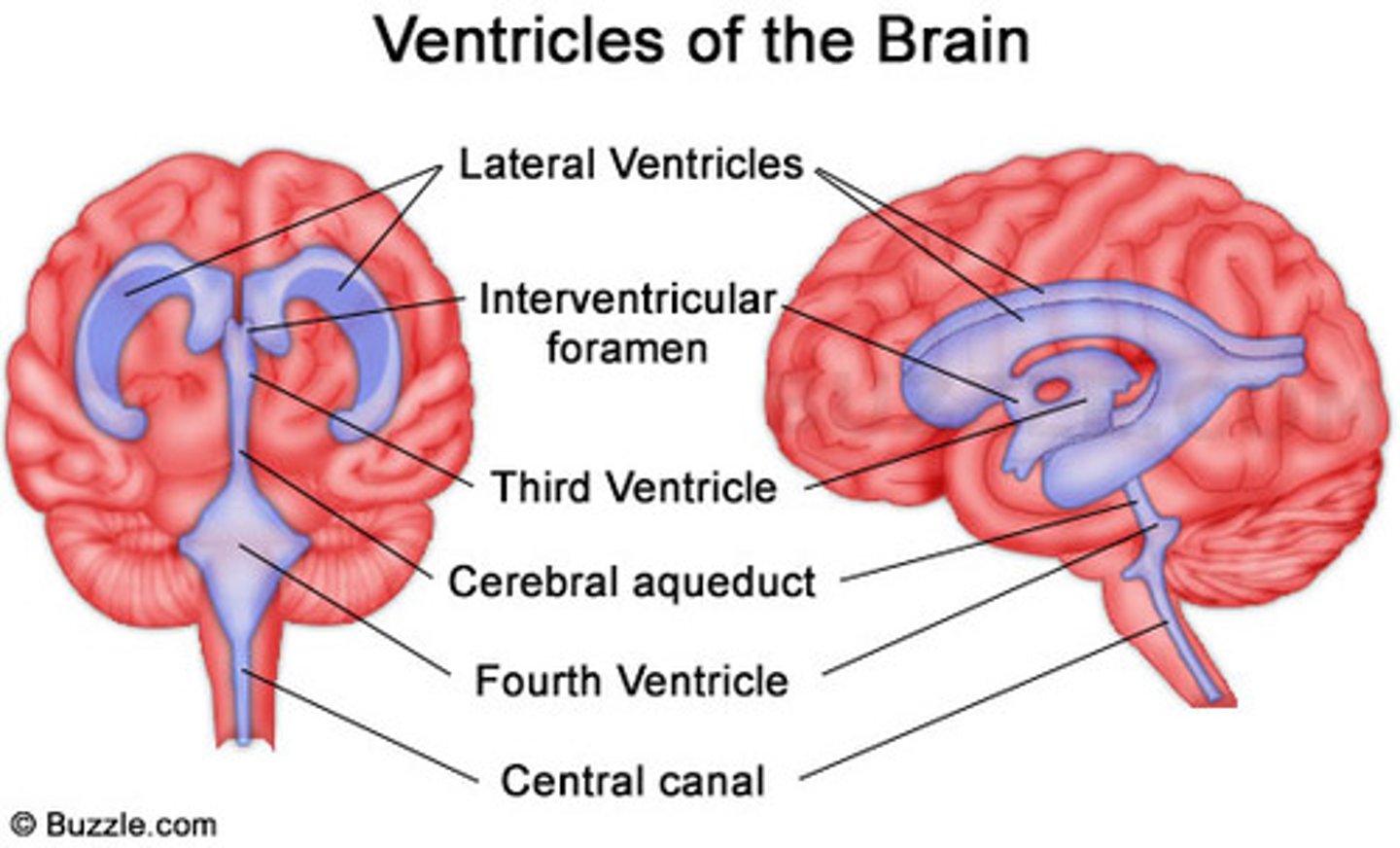
ventricles of the brain
Spaces/Canals in the brain that contain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
number of ventricles in the brain
4
1st and 2nd ventricles (lateral)
one located in each hemisphere of the cerebrum
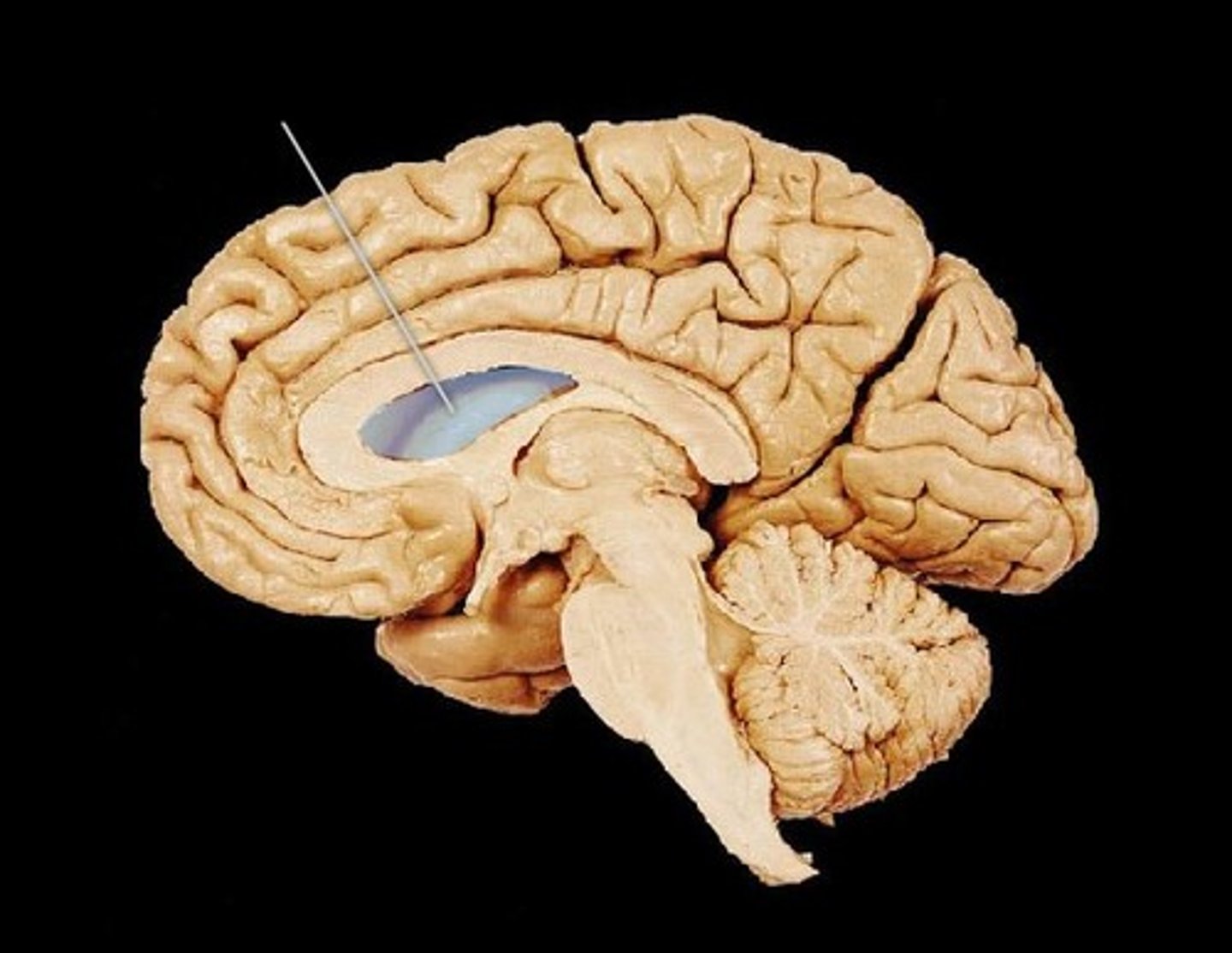
3rd ventricle of brain
Ventricle of the diencephalon
4th ventricle of brain
Extends into medulla oblongata
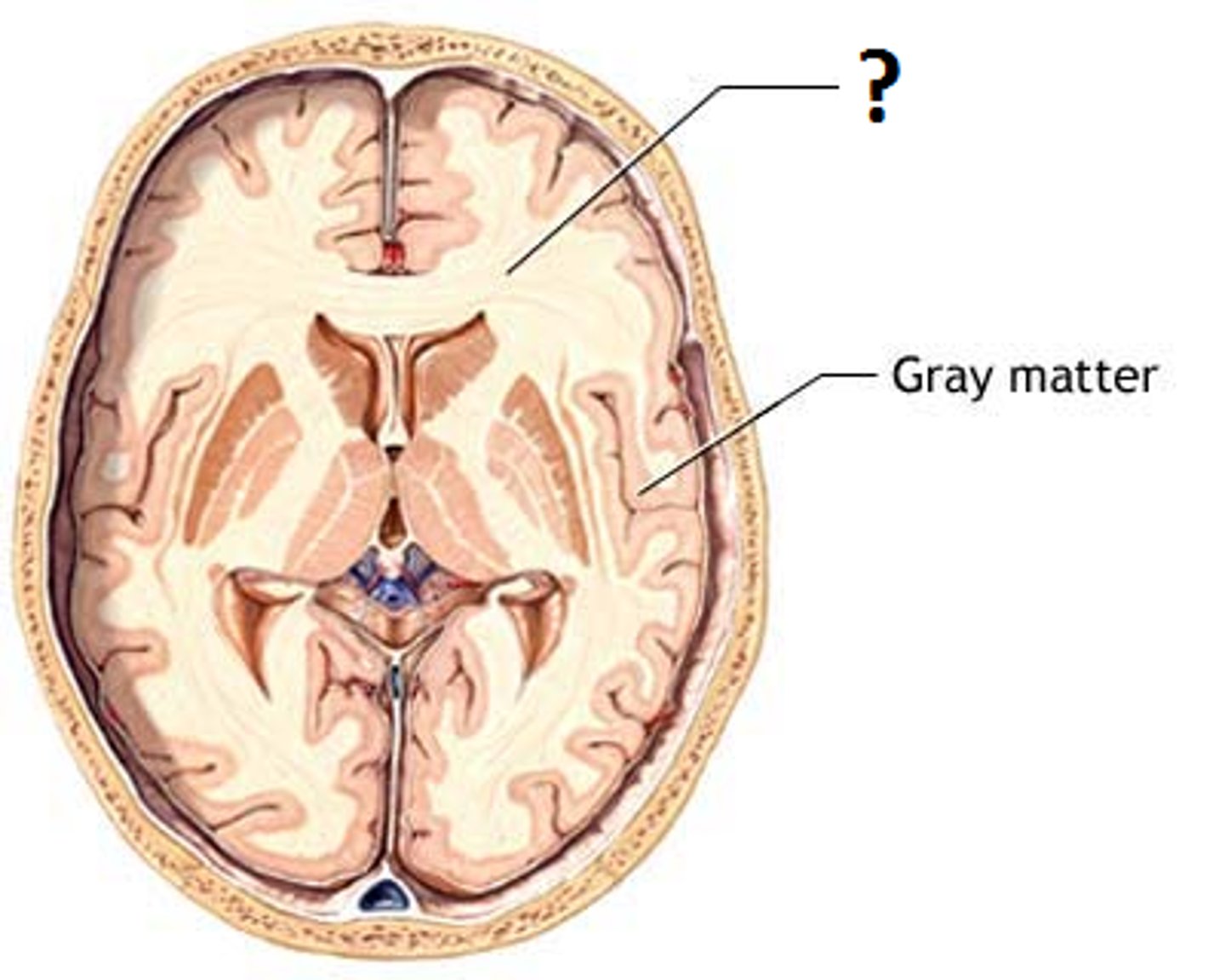
grey matter (makes up cerebral cortex)
Gray matter, named for its pinkish-gray color, is home to neural cell bodies, axon terminals, and dendrites, as well as all nerve synapses. This brain tissue is abundant in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also forms a butterfly-shaped portion of the central spinal cord.
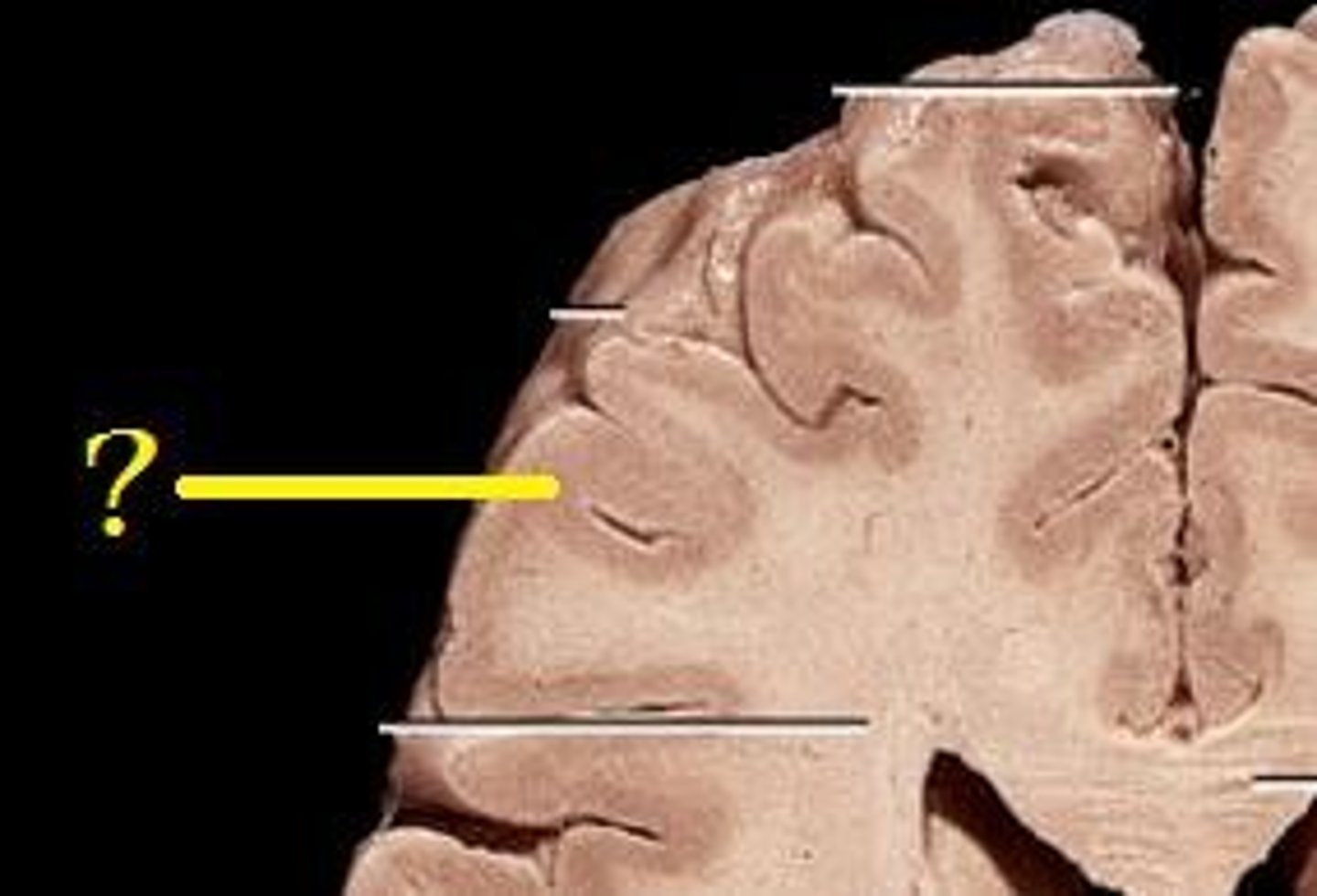
white matter
The white matter of your brain and spinal cord is composed of bundles of axons. These axons are coated with myelin, which helps conduct nerve signals and protect the axons.
number of spinal nerves
31 pairs
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
regions of the spinal cord
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
cervical enlargement of spinal cord
Responsible for supplying nerves to the upper limb
C4-T1
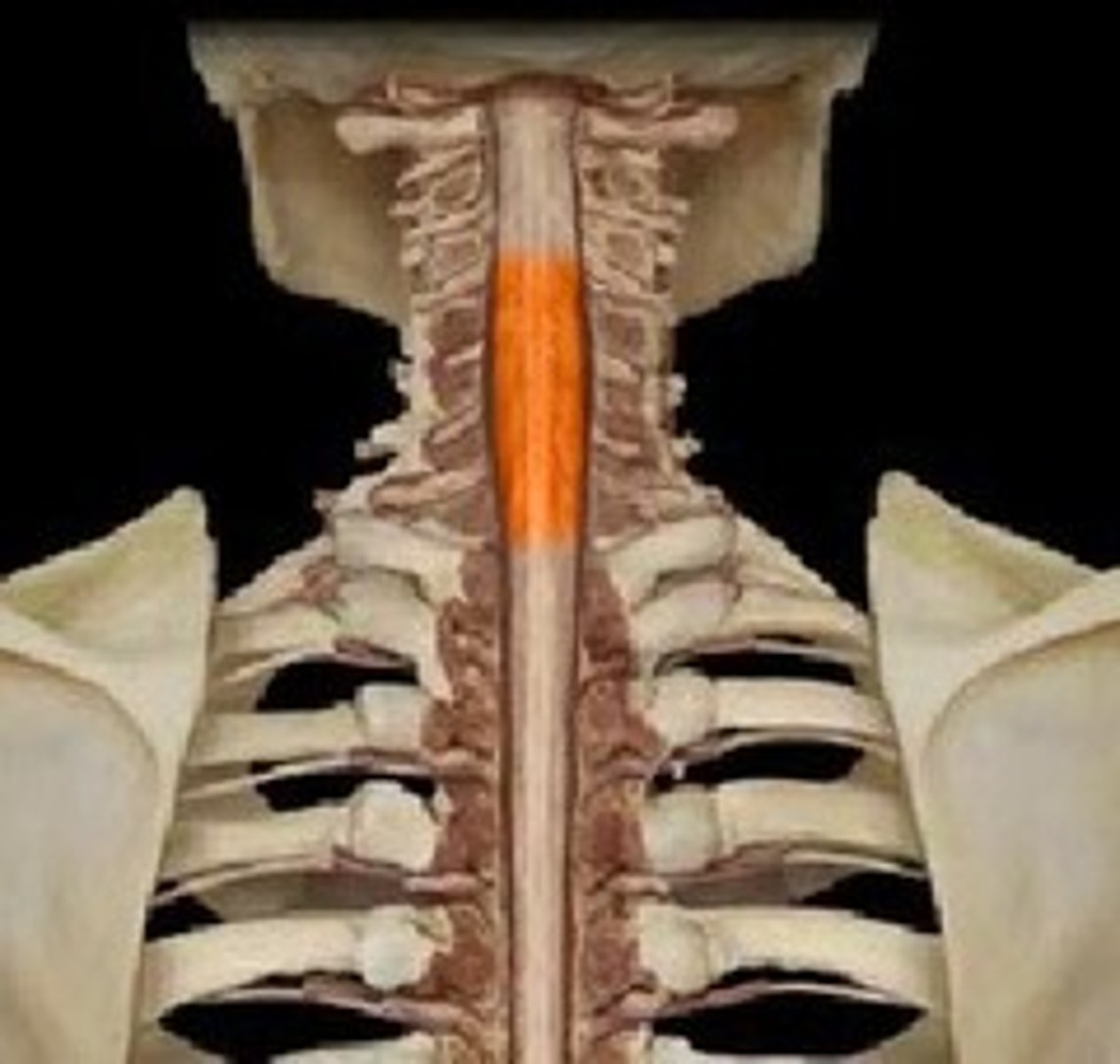
Lumbar enlargement of spinal cord
Responsible for supplying nerves to the lower limb
T9-T12
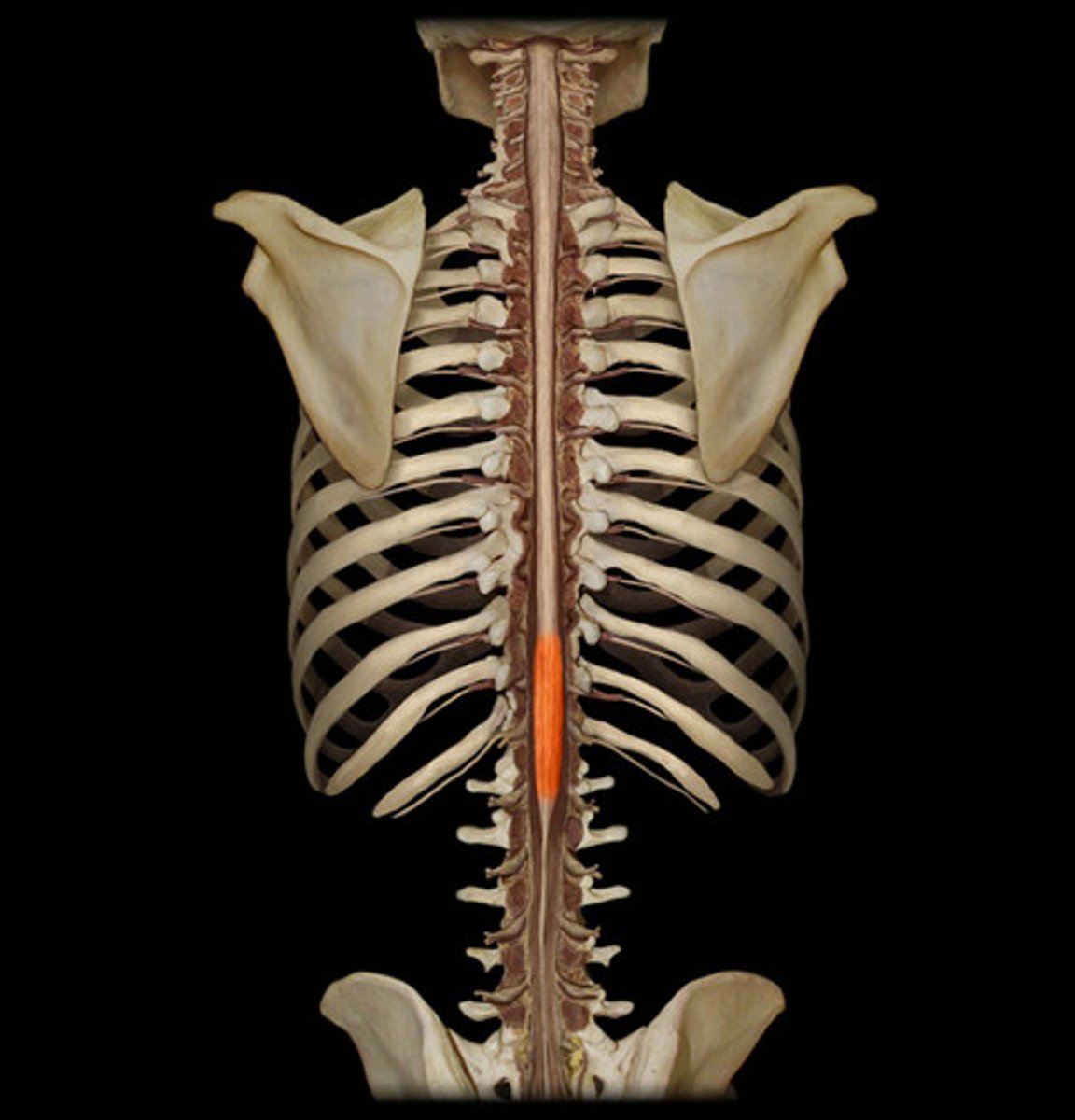
conus medullaris
tapered end of the spinal cord (L1-L2)
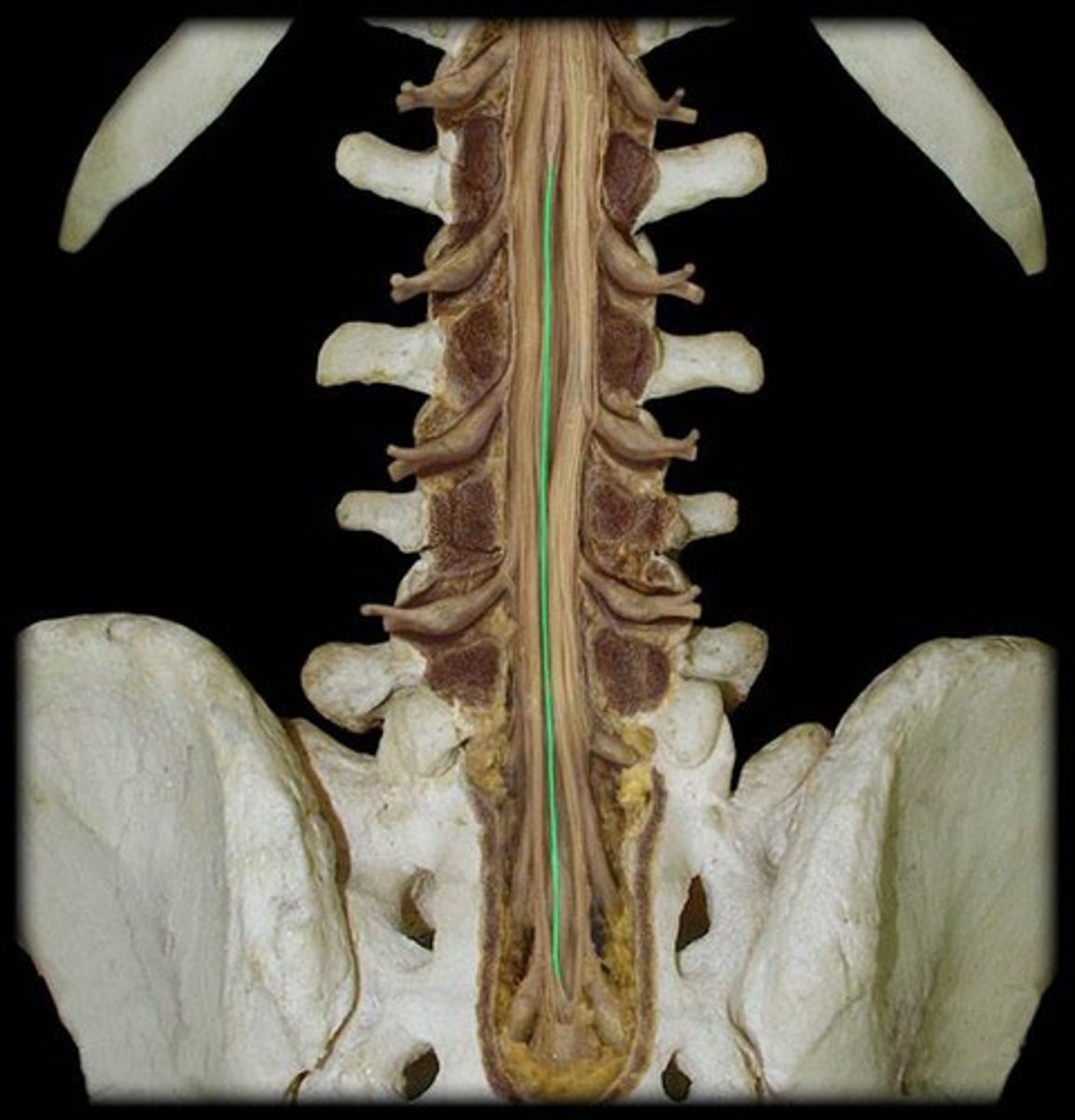
filum terminale
fibrous extension of the pia mater; anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
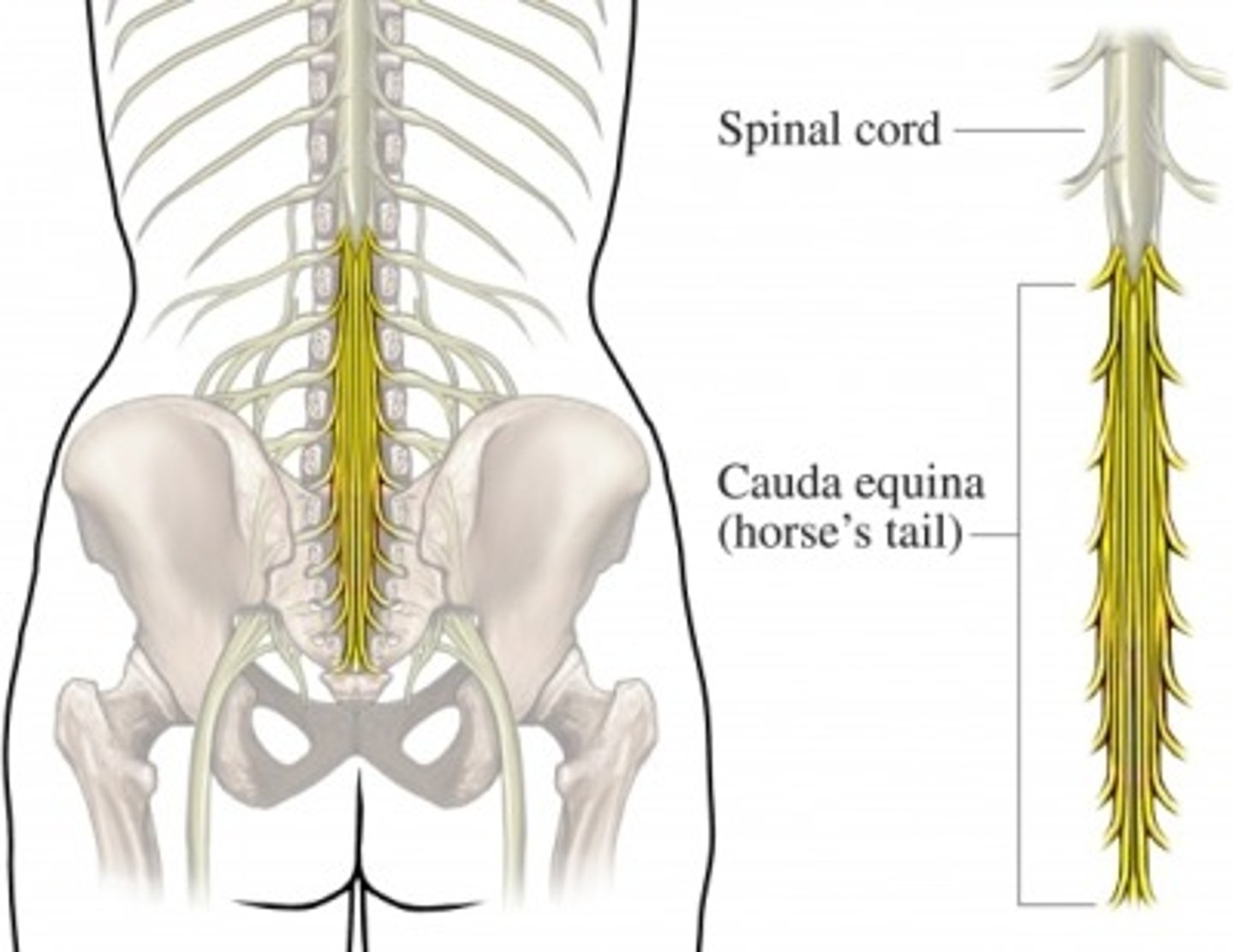
cauda equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
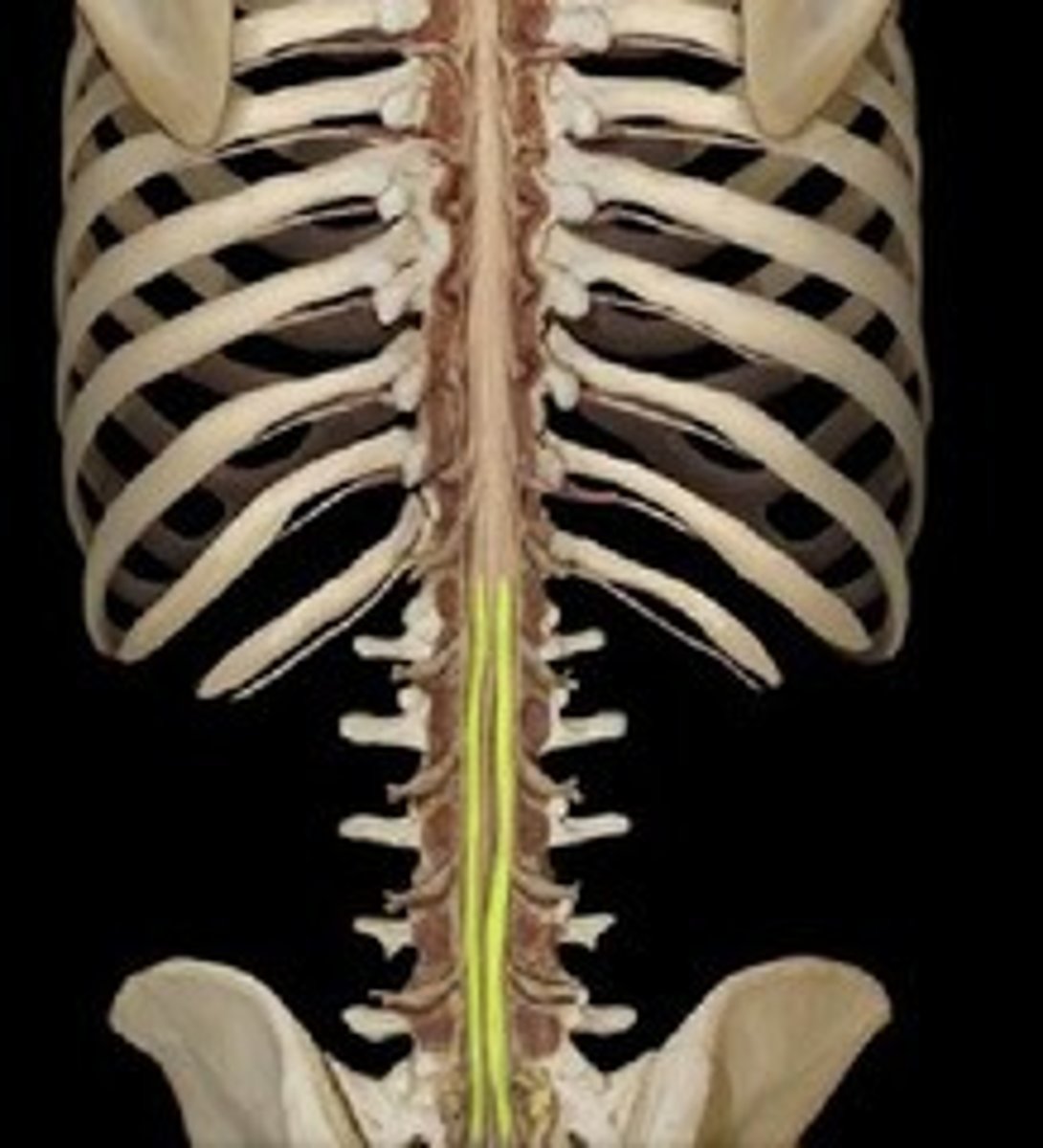
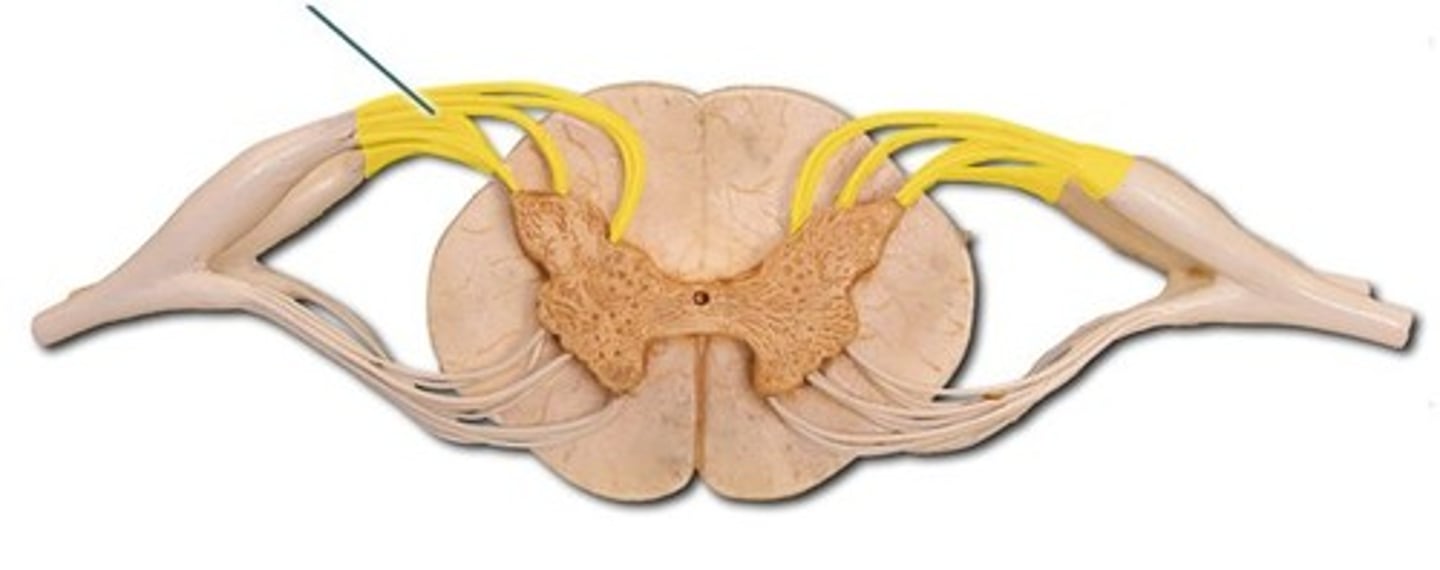
dorsal root
the sensory branch of each spinal nerve, contains axons of sensory neurons
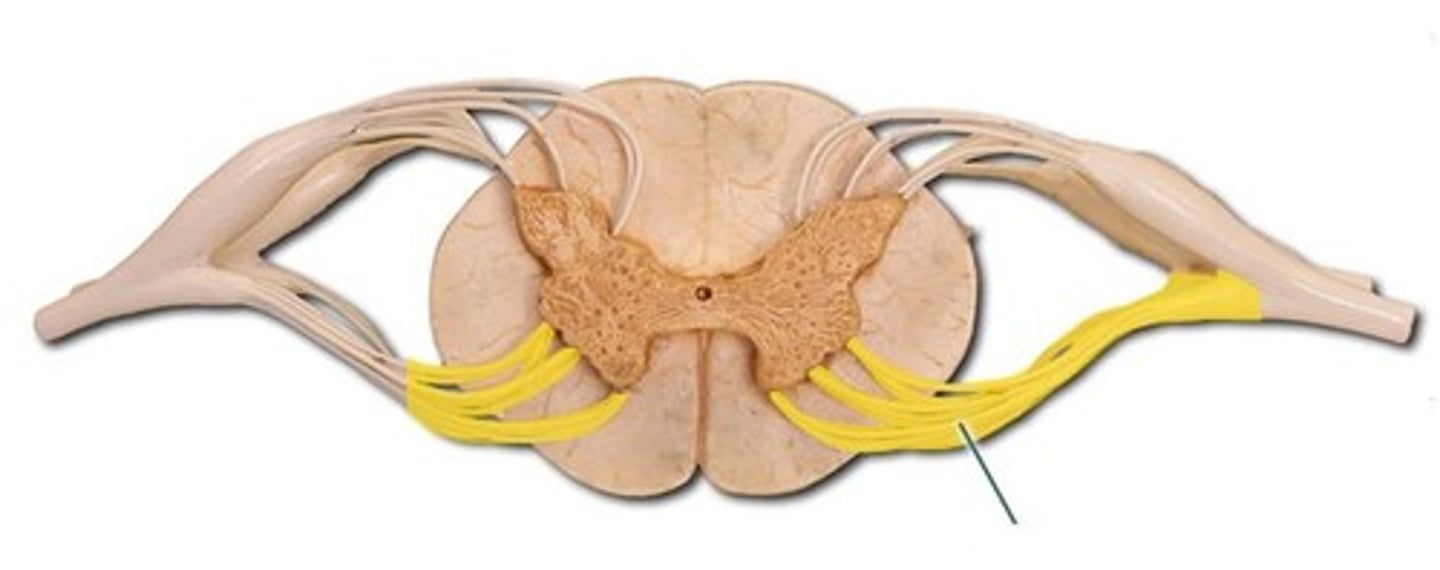
ventral root
the motor branch of each spinal nerve, contains axons of motor neurons
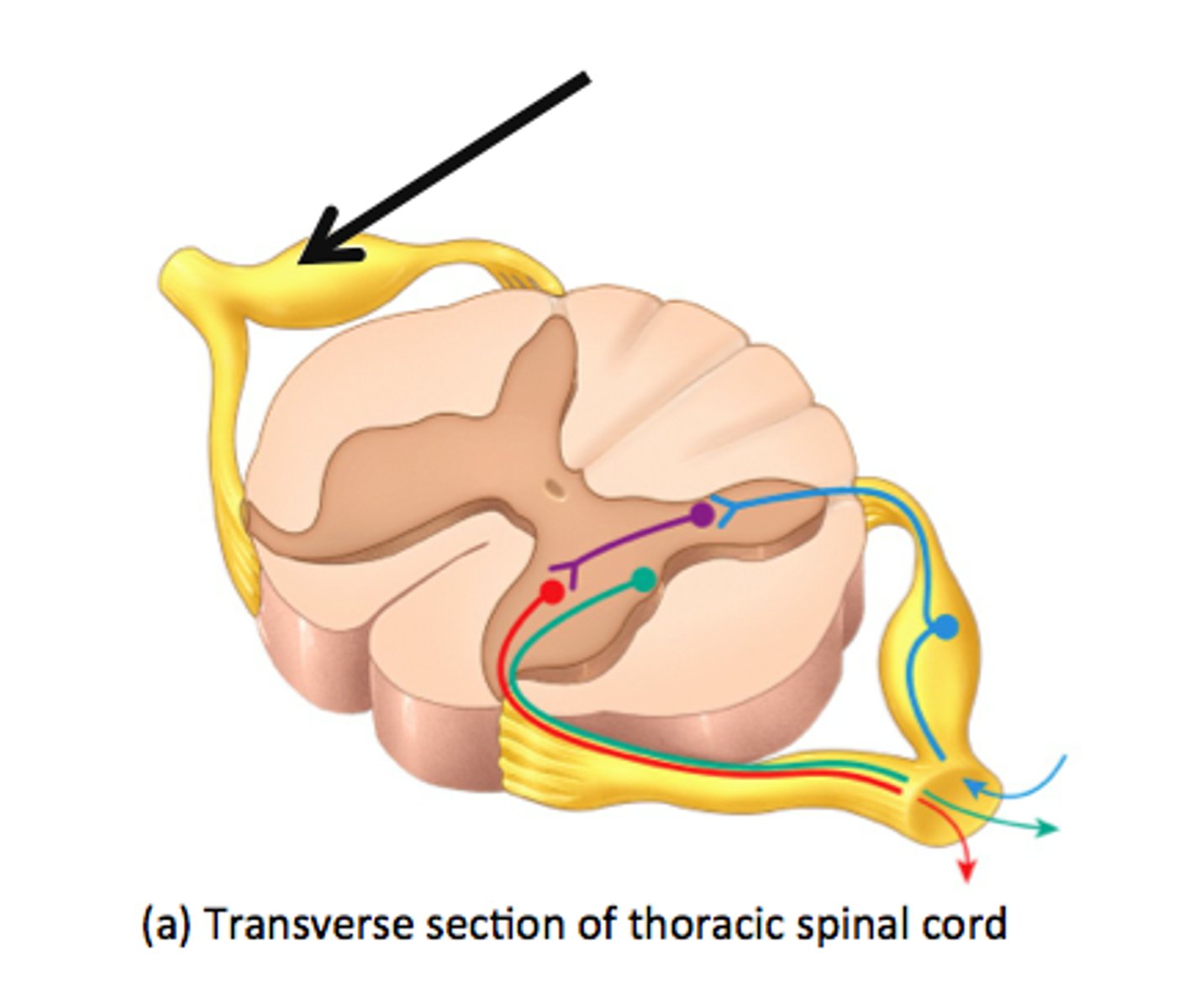
dorsal root ganglia
contain cell bodies of sensory neurons in the spinal cord
corpus callosum
A thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.

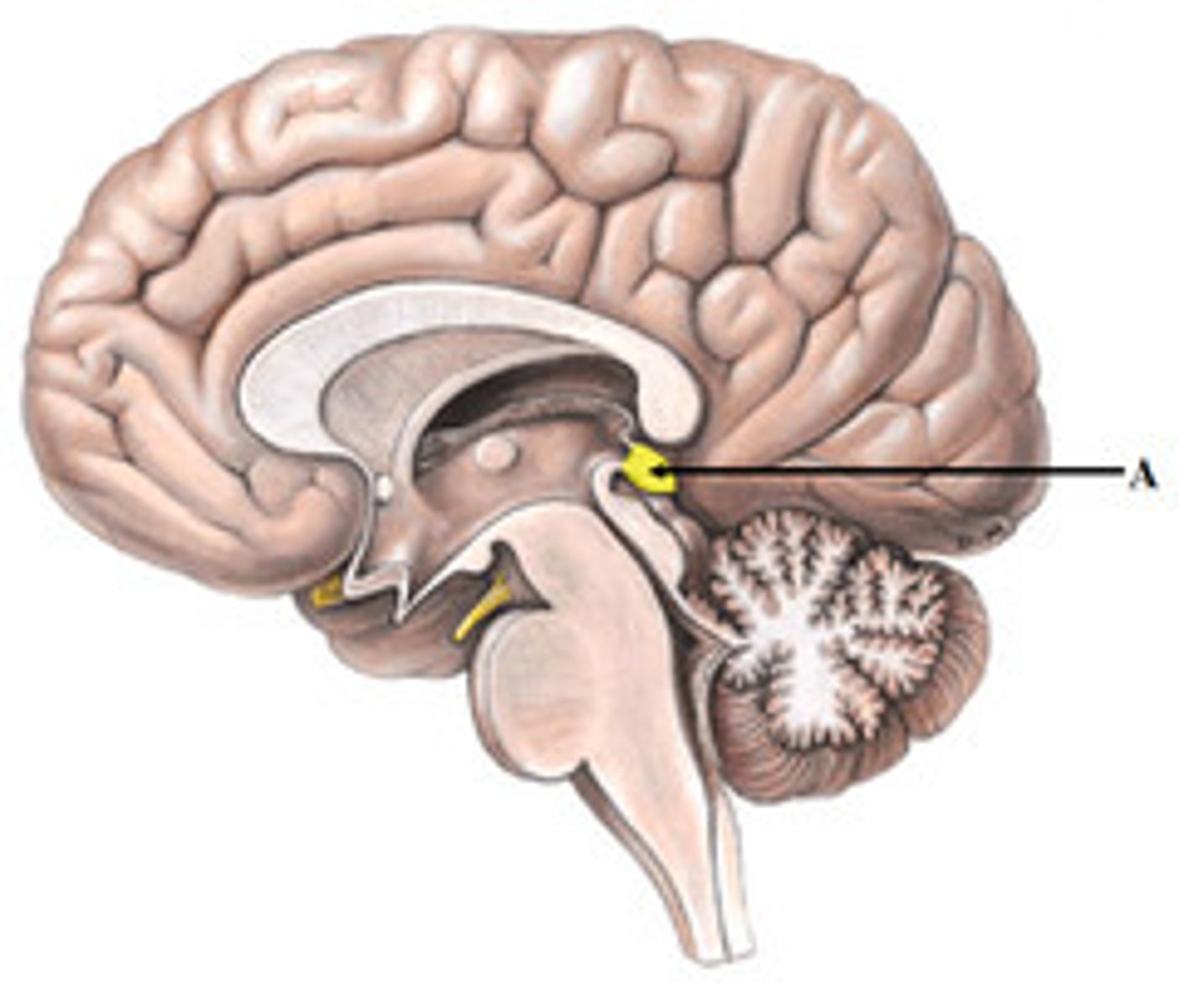
pineal gland (epithalamus)
secretes melatonin and is important for circadian rhythm
choroid plexus
A structure found within each of the brain ventricles. The location where CSF is produced by ependymal cells
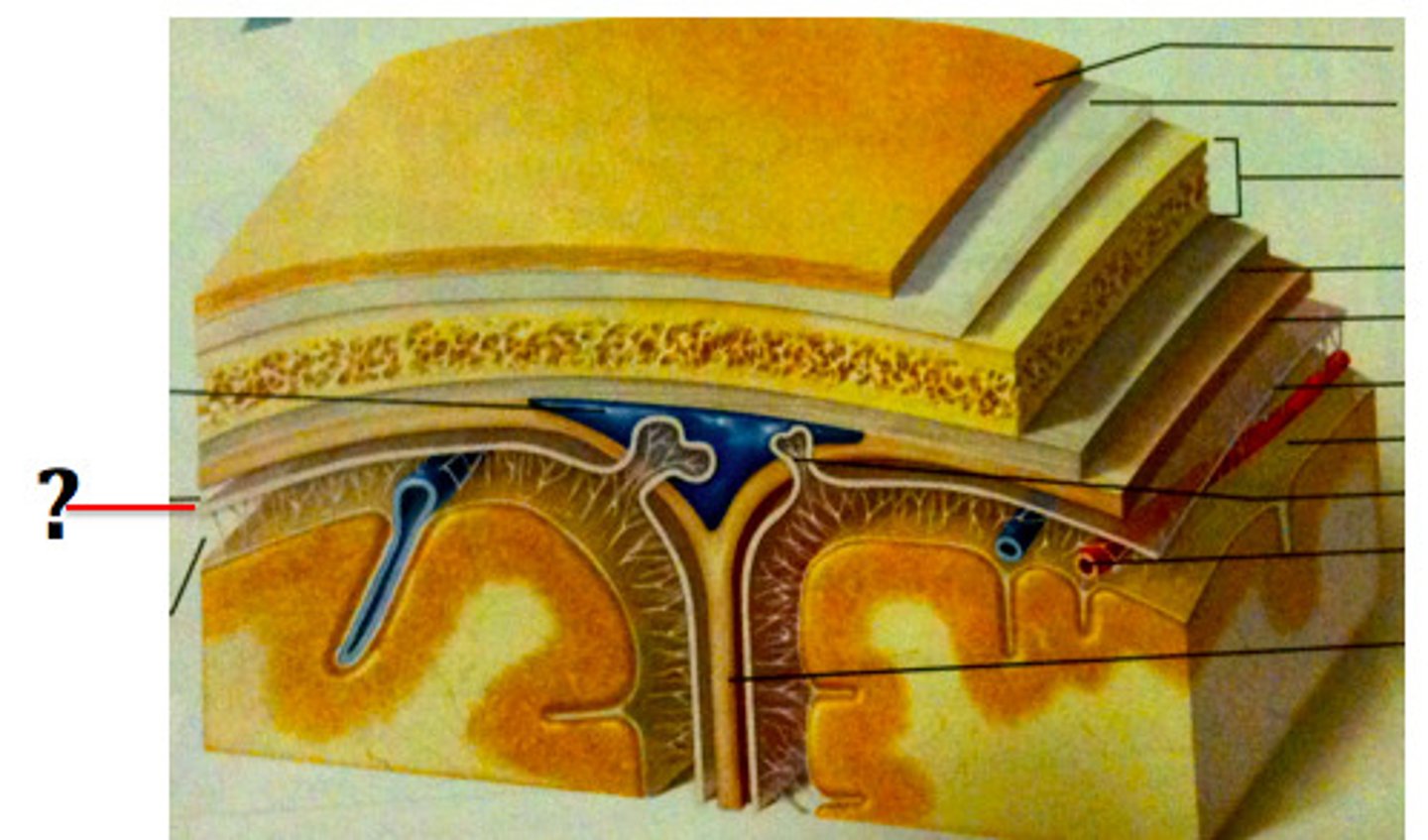
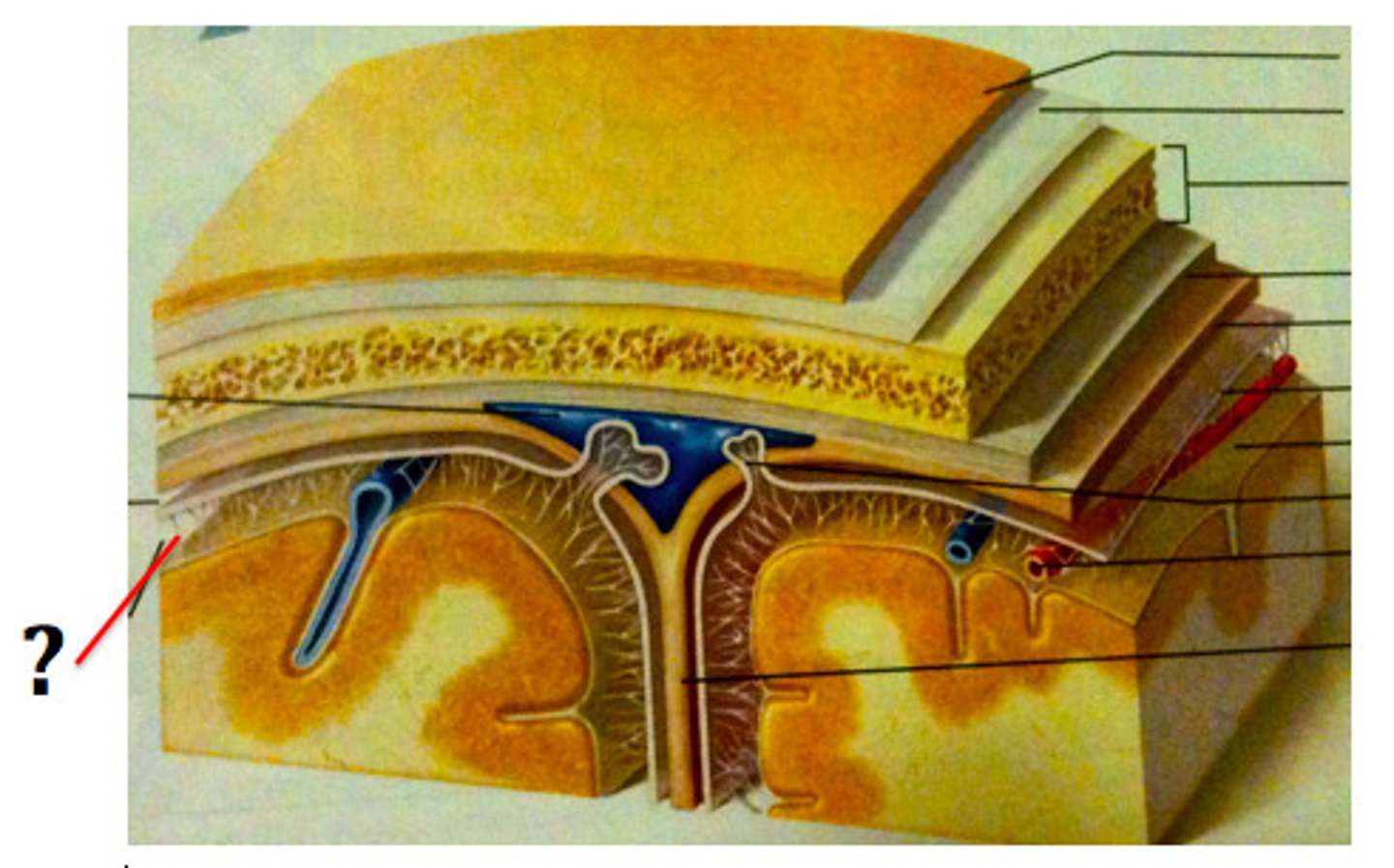
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater

subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
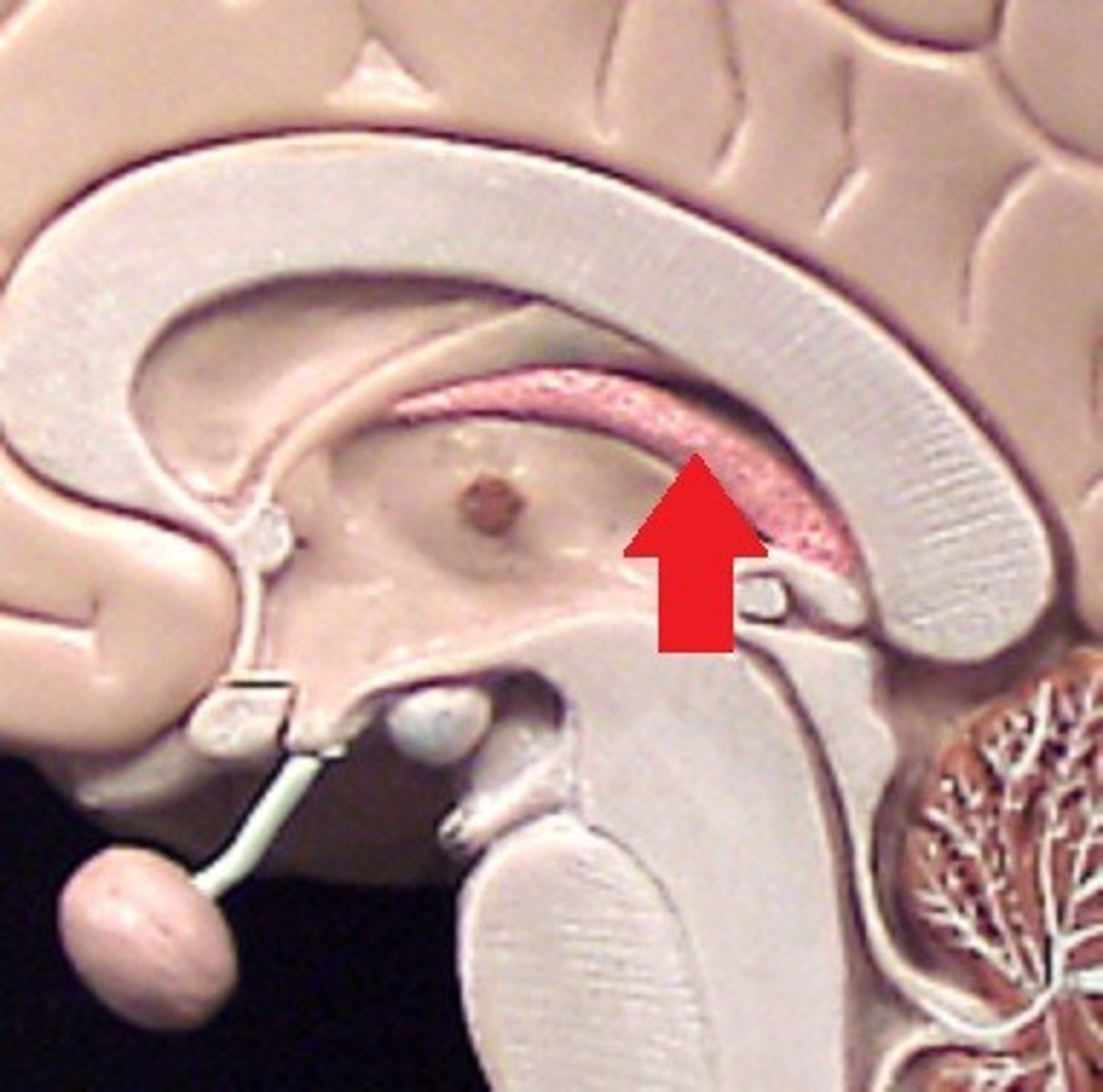
cerebral aquaduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
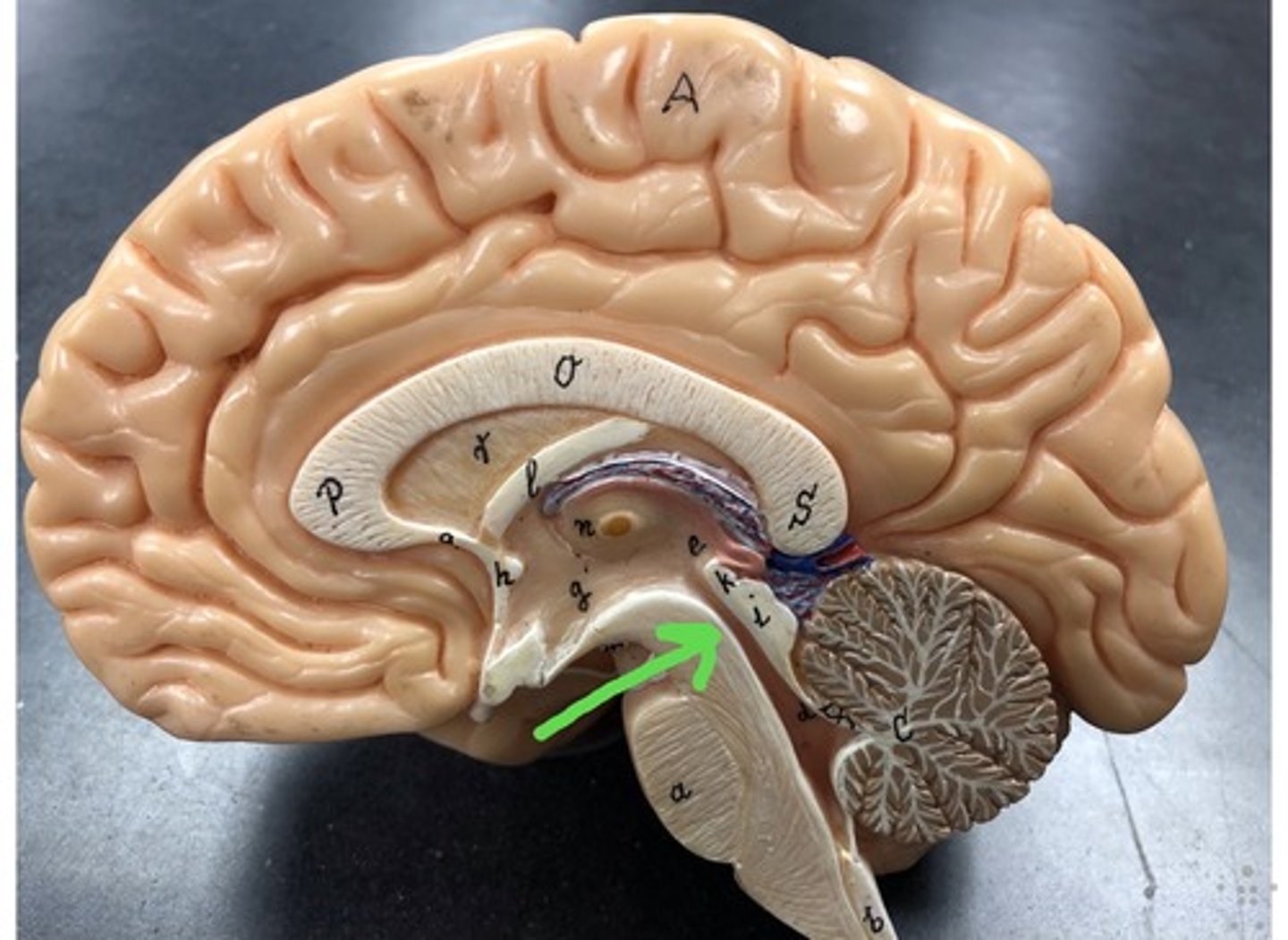
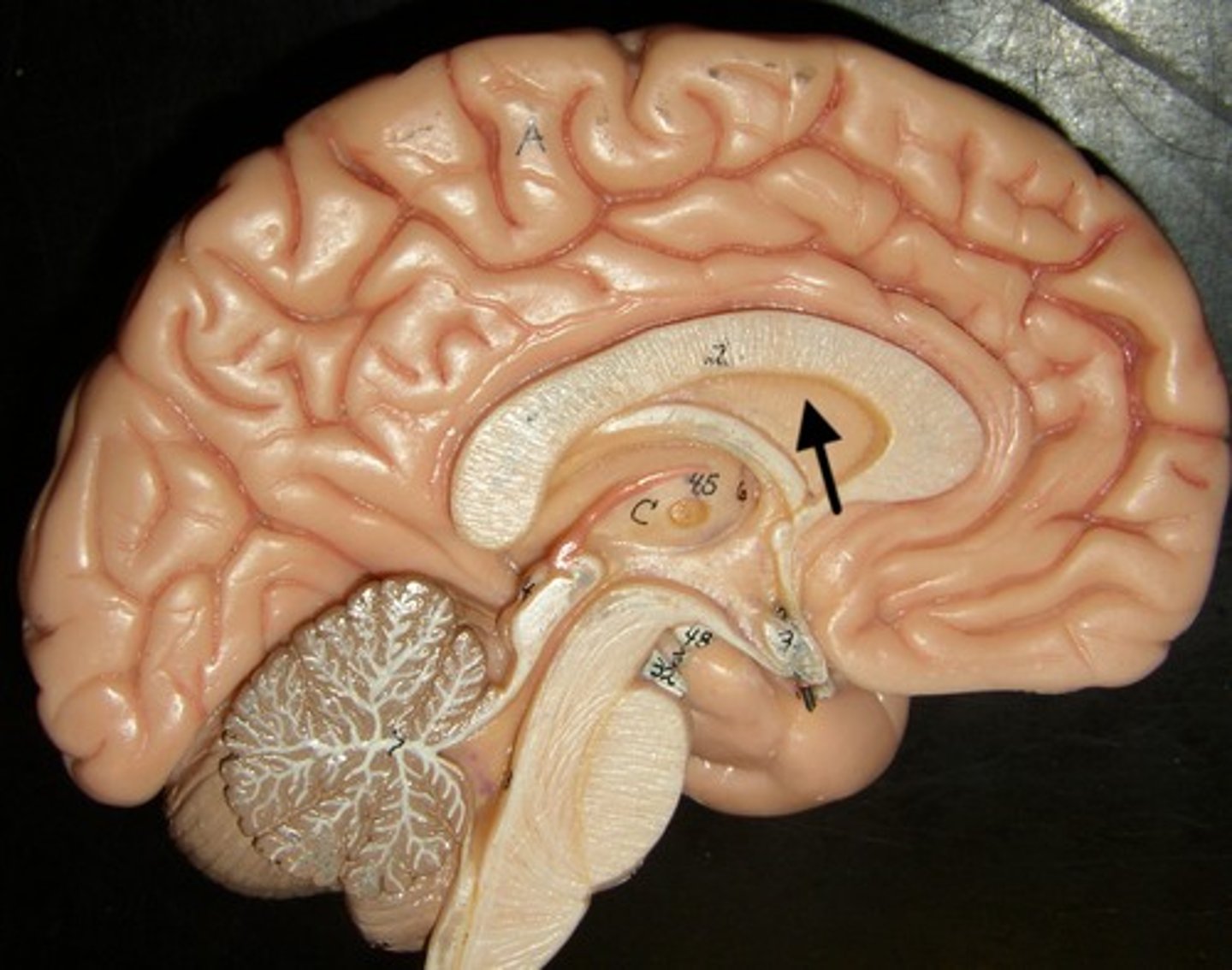
septum pellucidum
separates the lateral ventricles of the cerebral hemispheres
Pathway of CSF through the ventricles
lateral ventricle, inter ventricular foramen, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, fourth ventricle, central canal
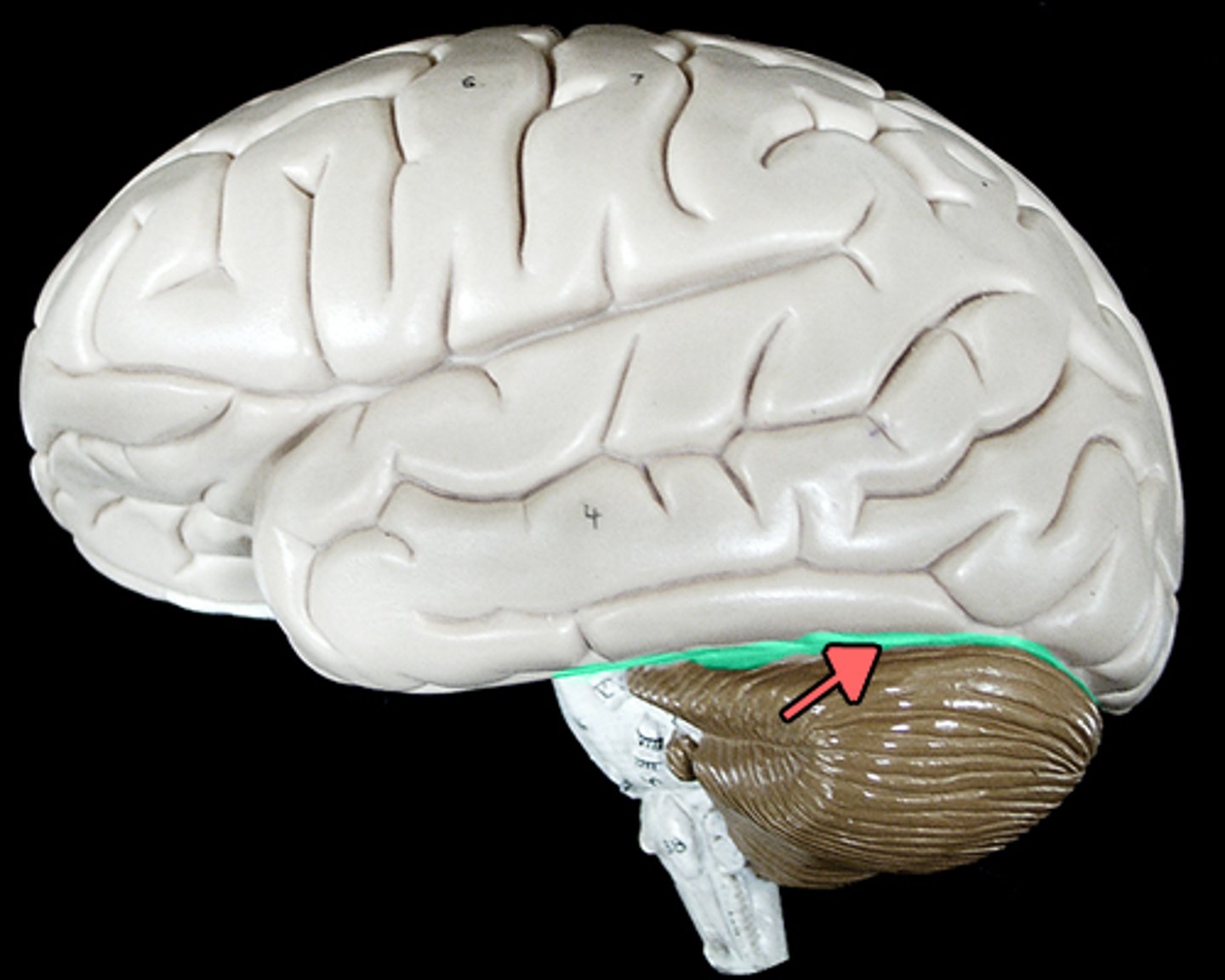
transverse cerebral fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
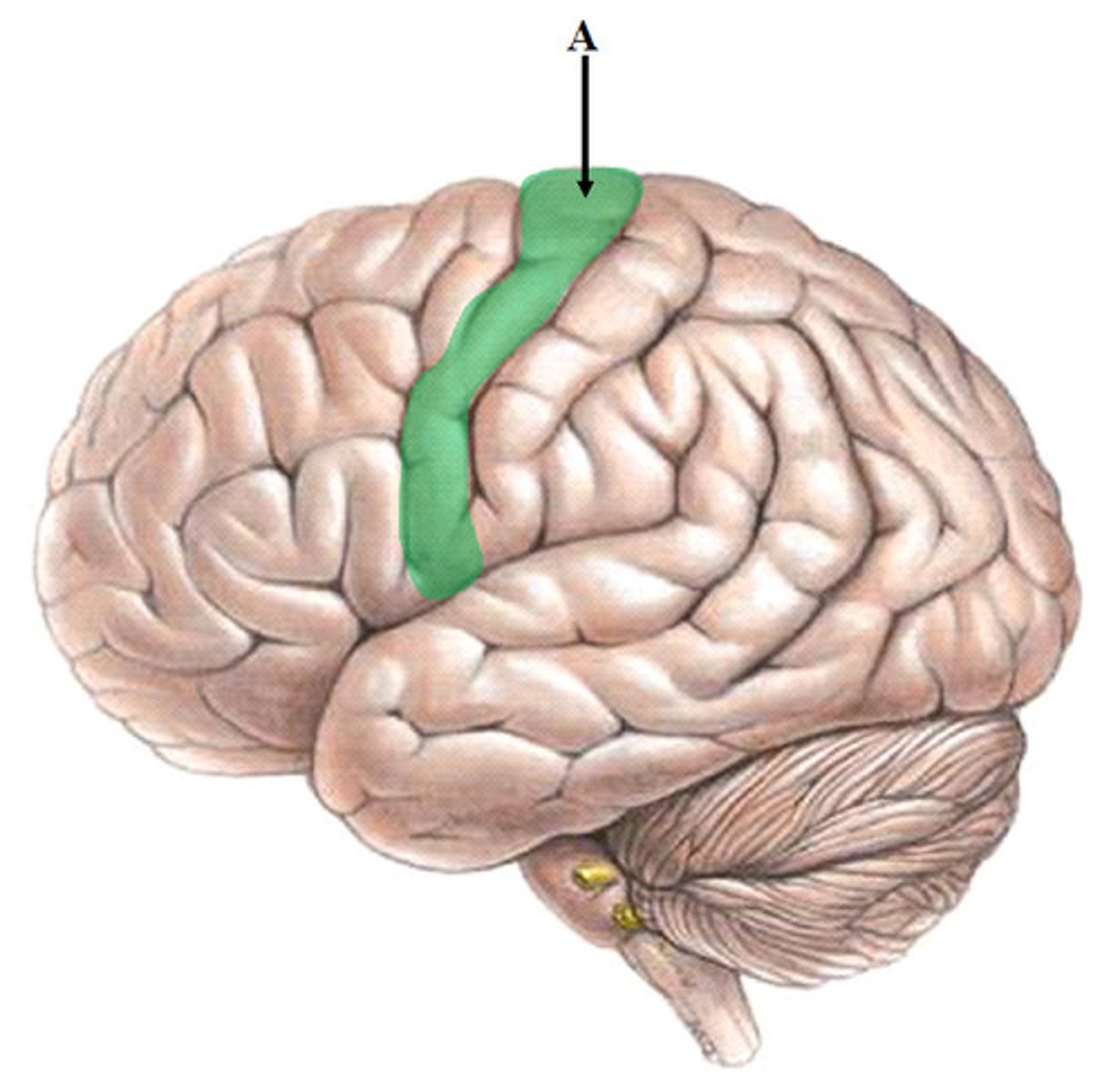
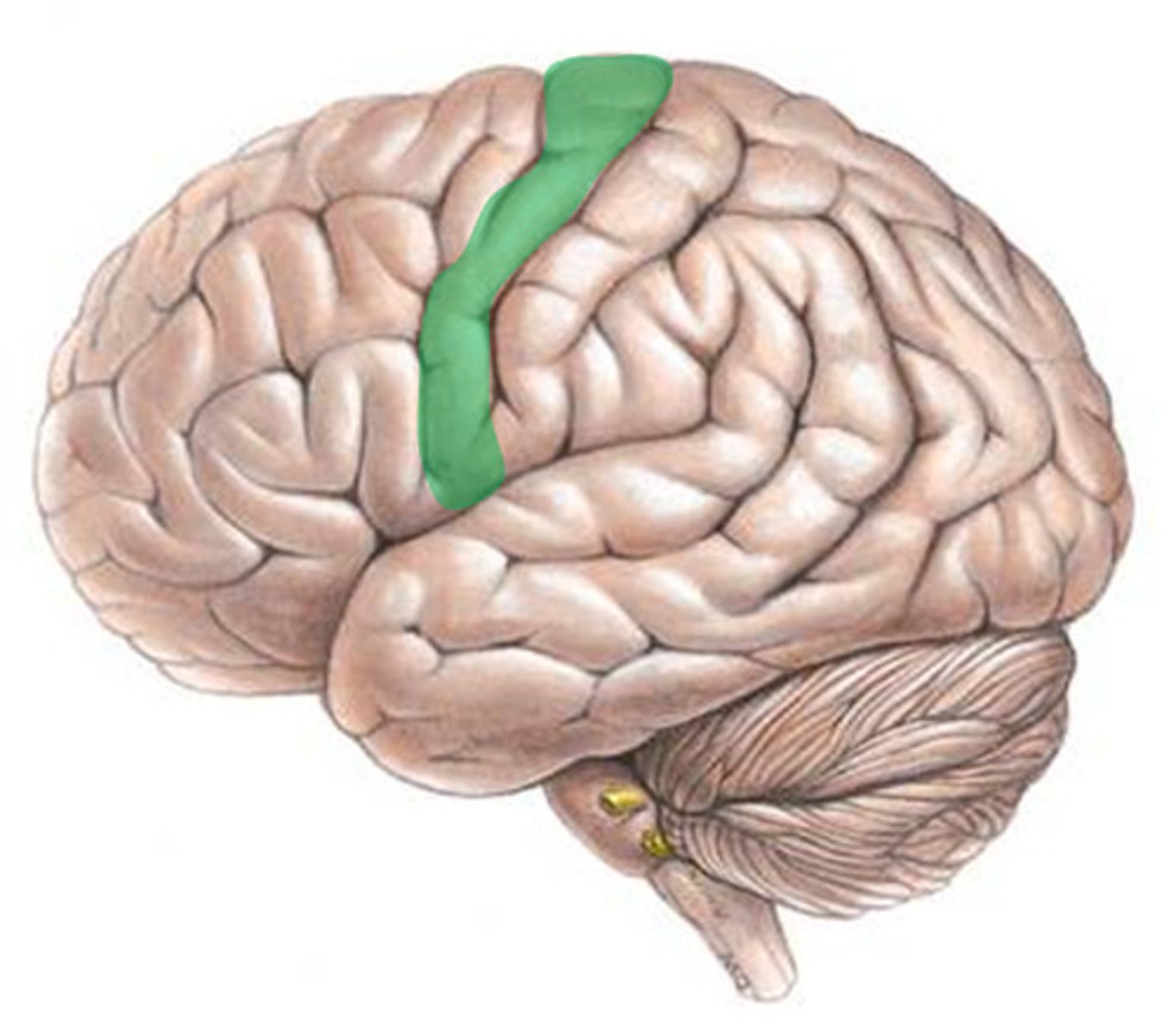
precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex)
the strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that is crucial for motor control
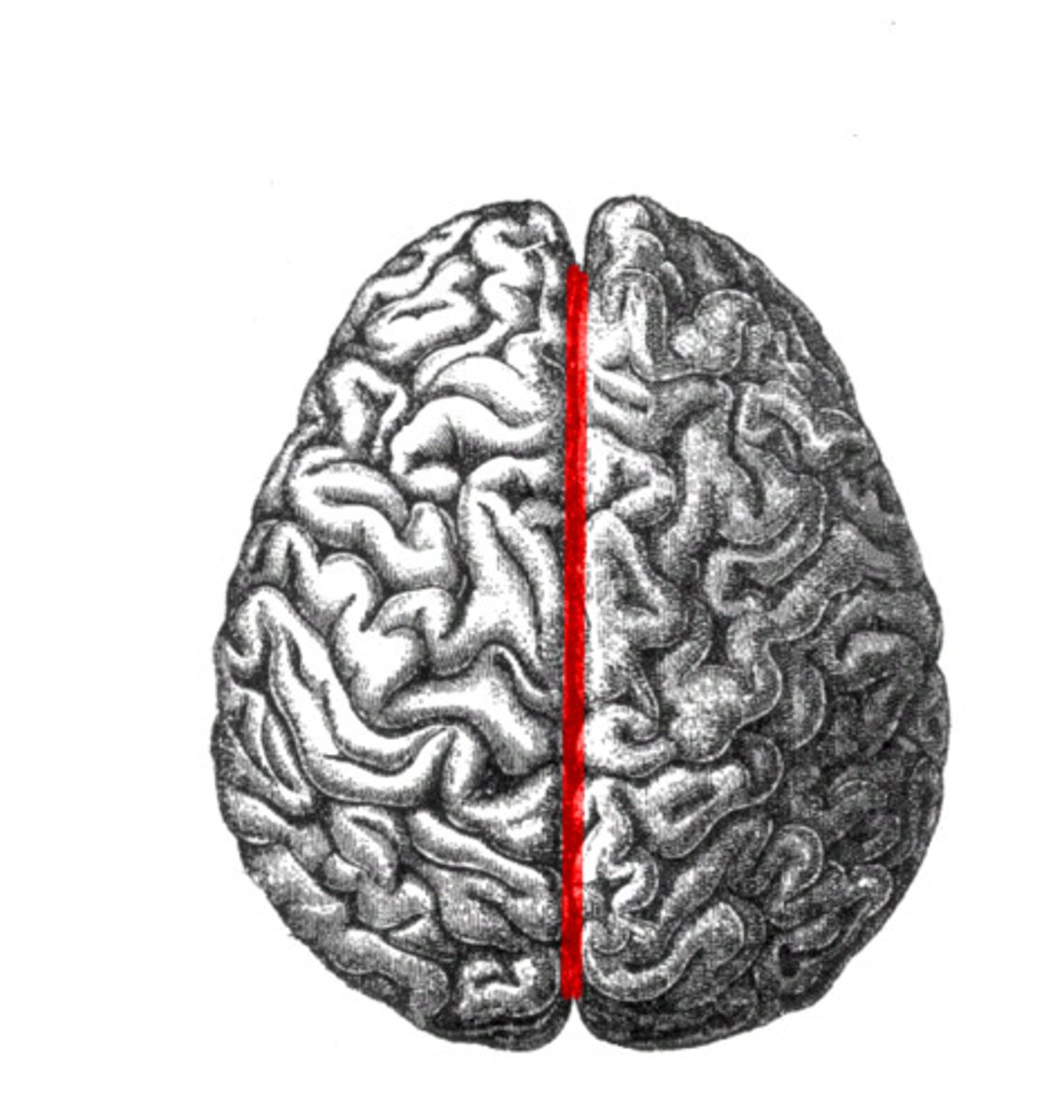
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
Structural divisions of the cerebrum
5 lobes separated by gyri, 2 hemispheres separated by longitudinal fissure
Functional Divisions of the Brain
Motor, Sensory, and Association
Primary Motor Cortex
Several adjacent and highly interconnected areas in the frontal lobe together mediate the planning and initiation of complex temporal sequences of voluntary movements.
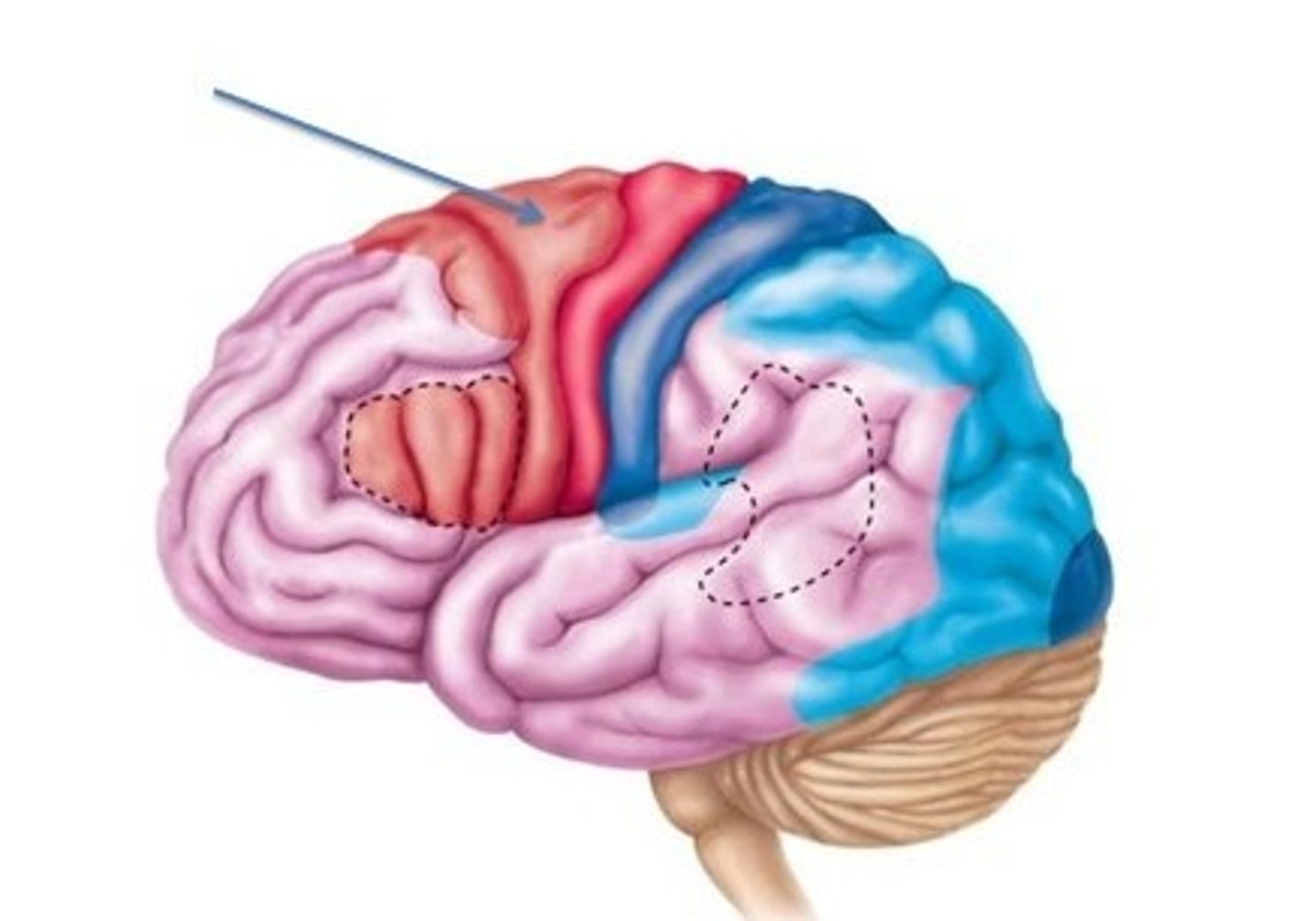
premotor cortex
Involved in planning and organizing movements and actions. It precedes the activation of the primary motor cortex and is part of the brain region responsible for coordinating complex movement sequences. The region controls learned and repeated motor skills.
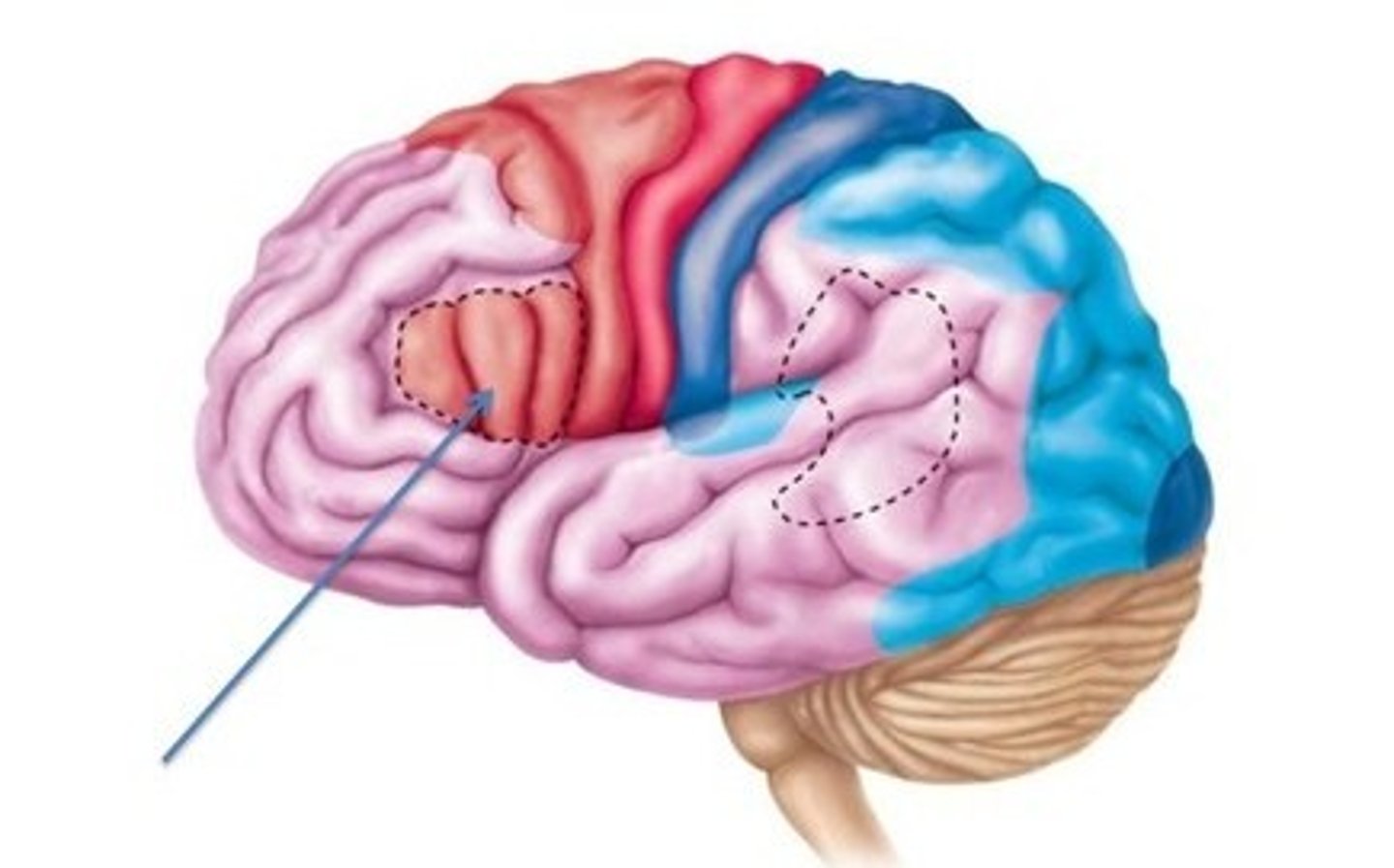
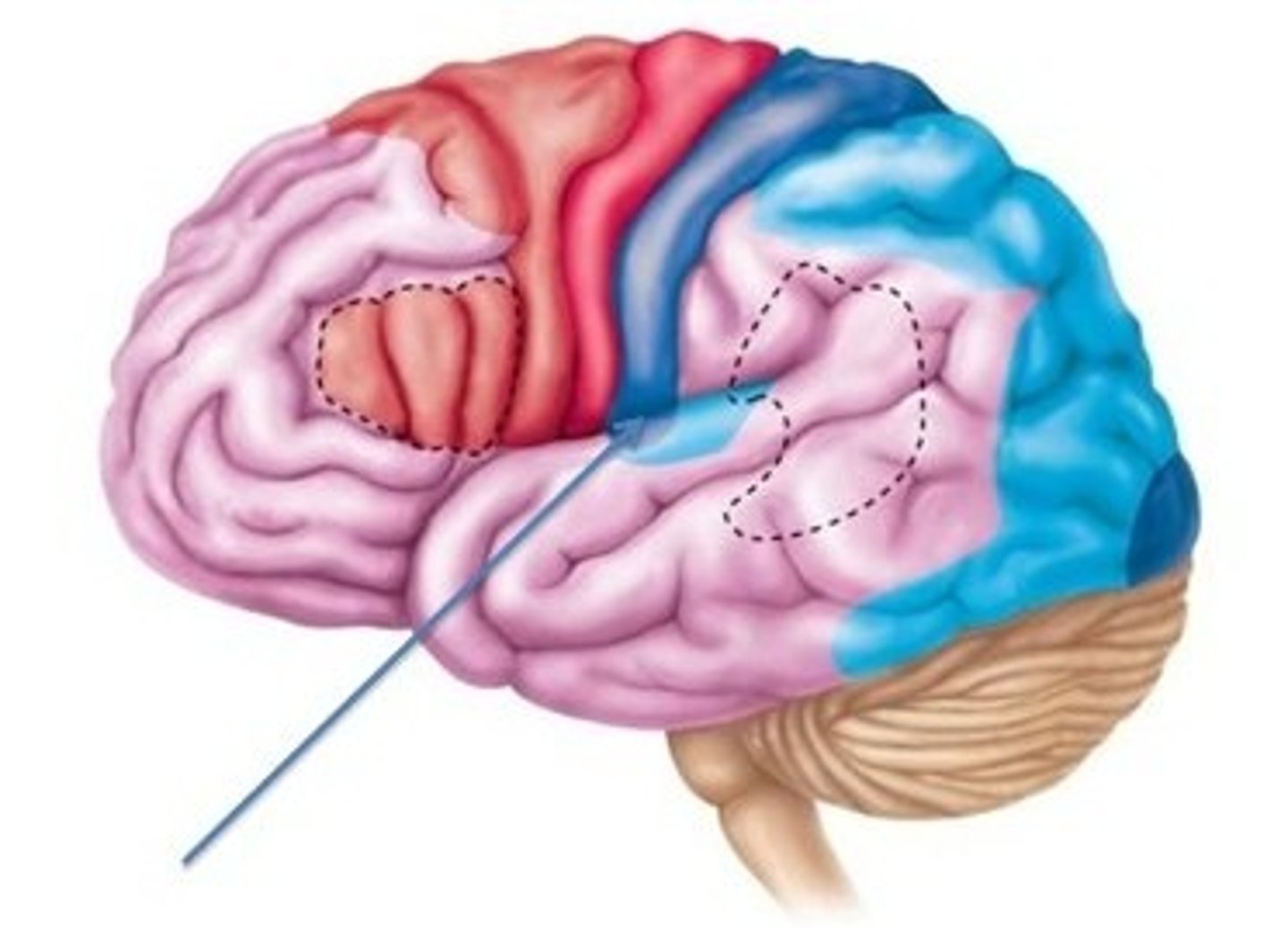
Broca's area
muscles of speech production
Regions of the cerebral motor cortex
primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, brocas area, frontal eye field
regions of sensory cortex
primary somatosensory cortex, somatosensory association cortex, visual cortex, auditory cortex, vestibular cortex, visceral sensory cortex, vestibular cortex, gustatory cortex, olefactory cortex
primary somatosensory cortex
general sensations in skin, proprioception of skeletal muscles joints and tendons, identification of region(s) of stimulation
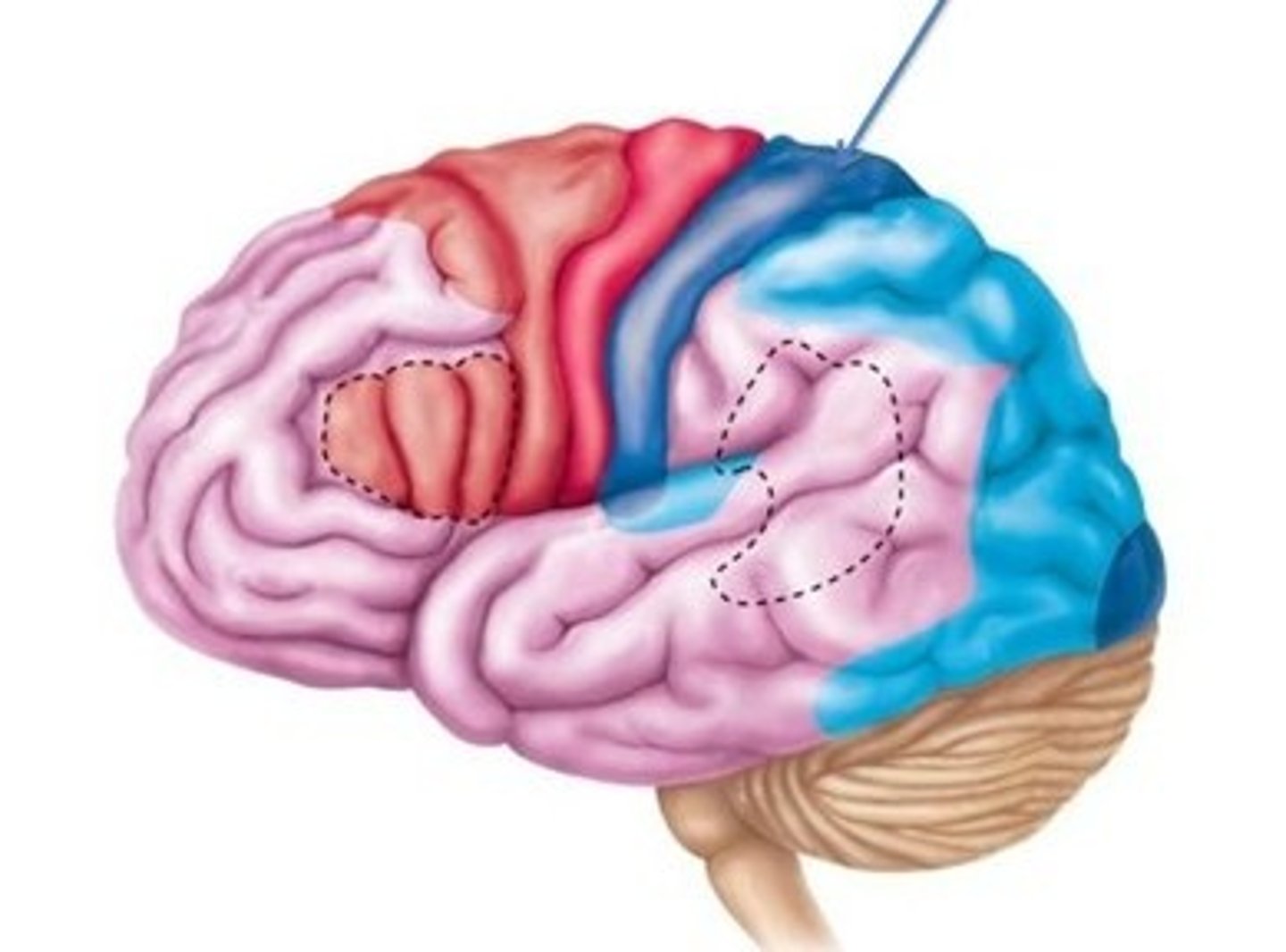
Somatosensory association
Integrate sensory information input to produce understanding of what is felt such as size, texture etc.
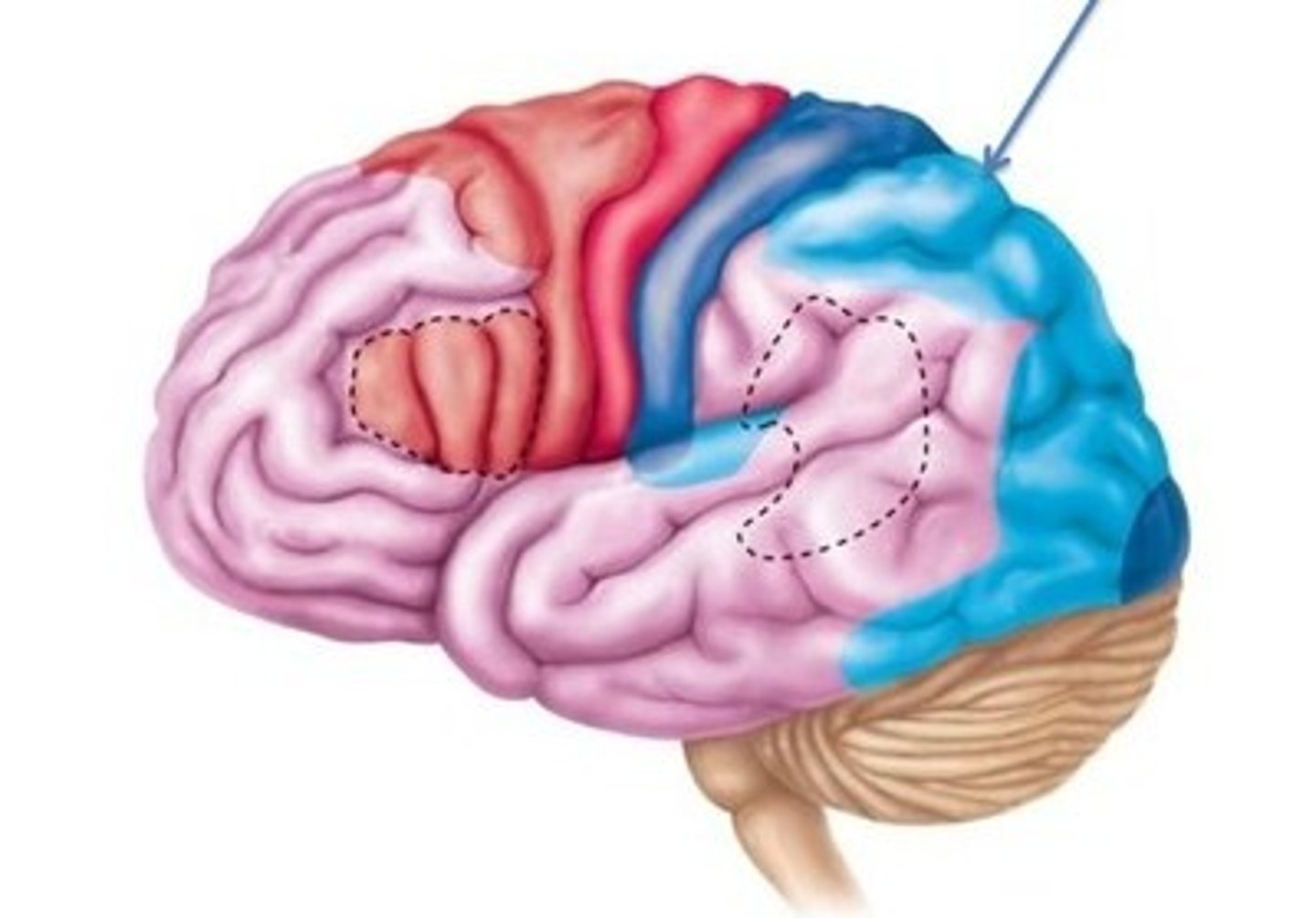
visual cortex
visual information
auditory cortex
use vibration to interpret pitch, loudness, location etc.
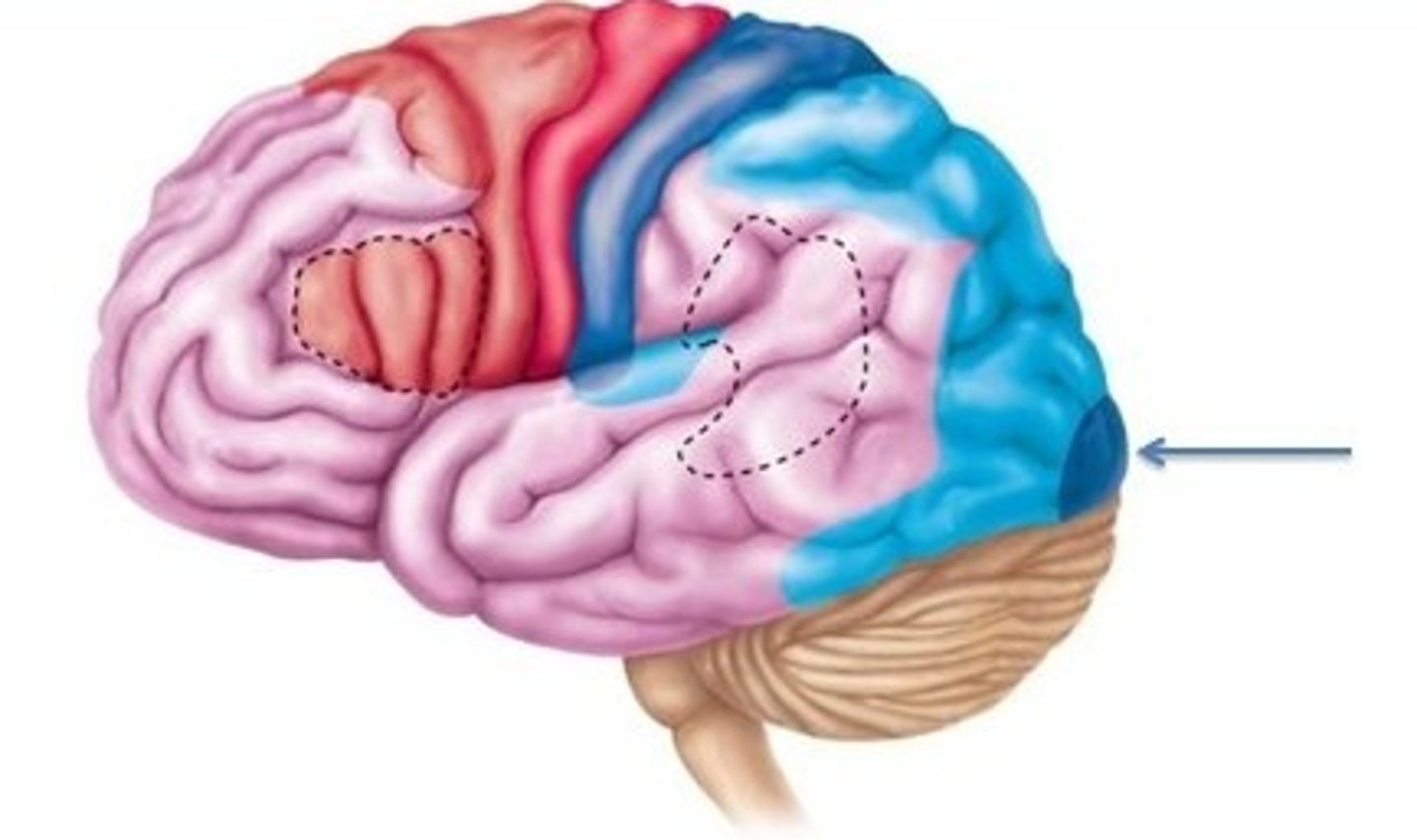
olfactory cortex
involved in conscious awareness of odors
gustatory cortex
area of the brain that receives and interprets tastes from the tongue found in the insula
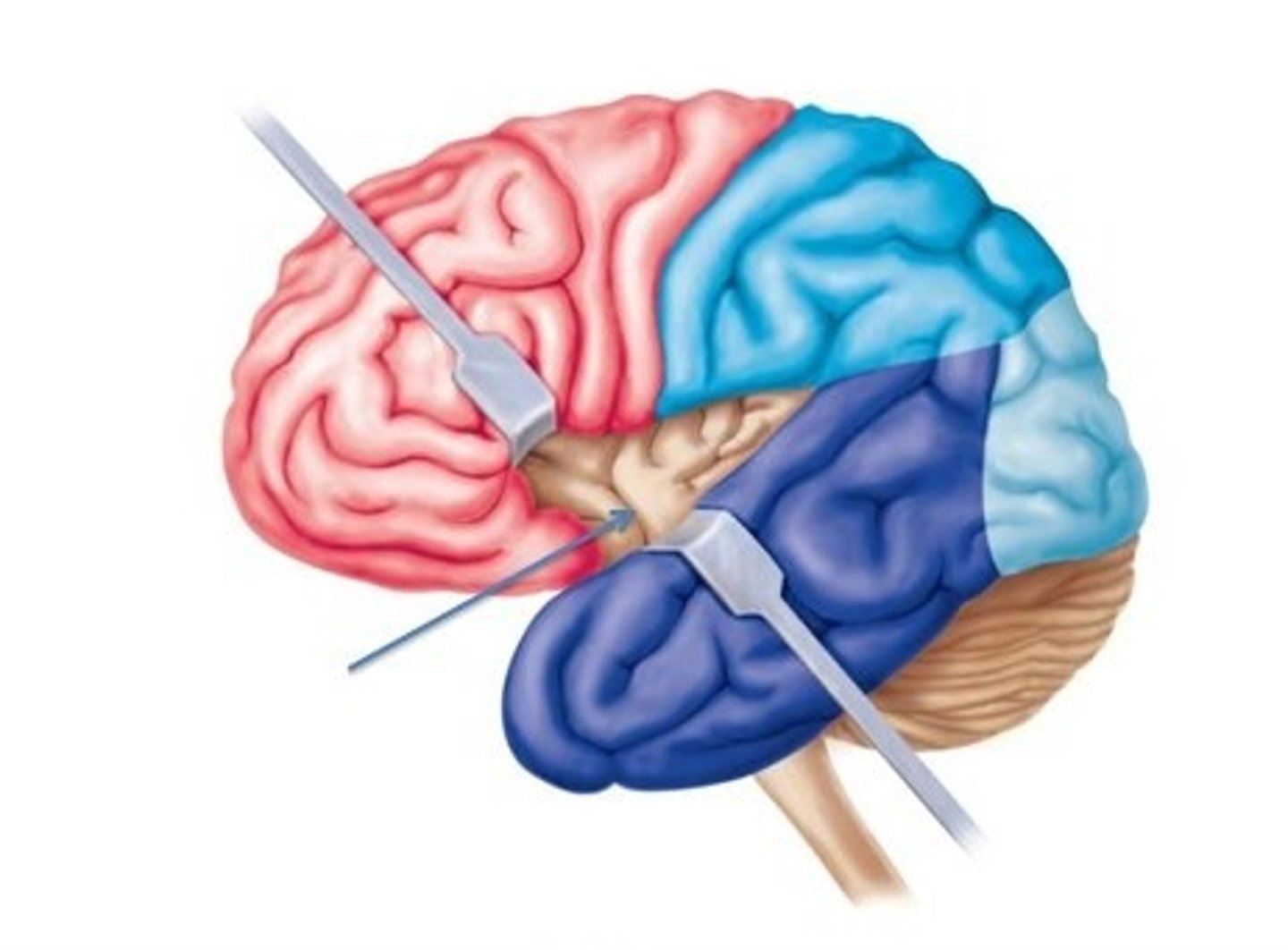
visceral sensory cortex
located in the insula and is involved in the conscious perception of visceral sensations (upset stomach, full bladder, urge to defecate, etc.)
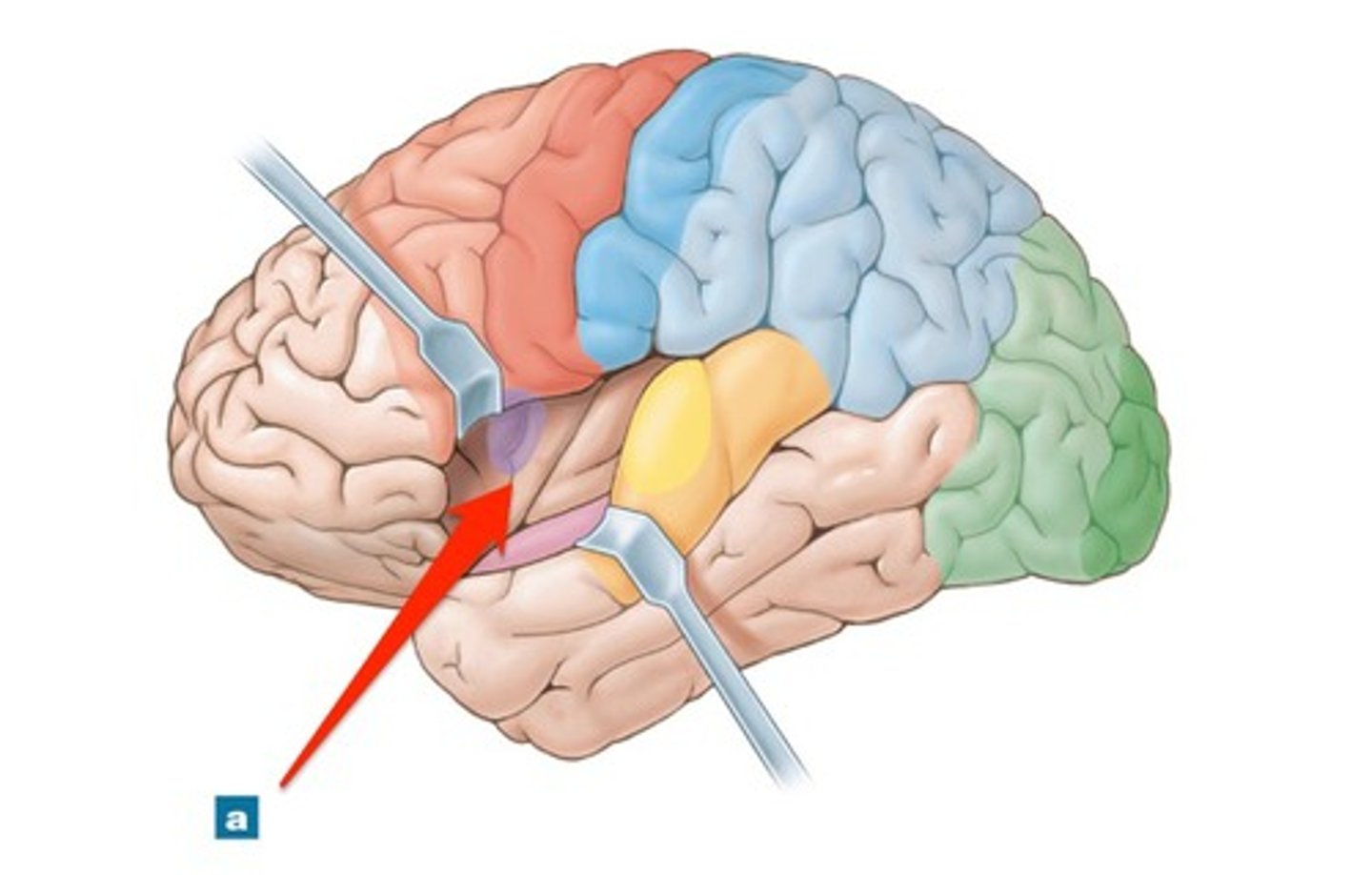
vestibular cortex
responsible for conscious awareness of balance
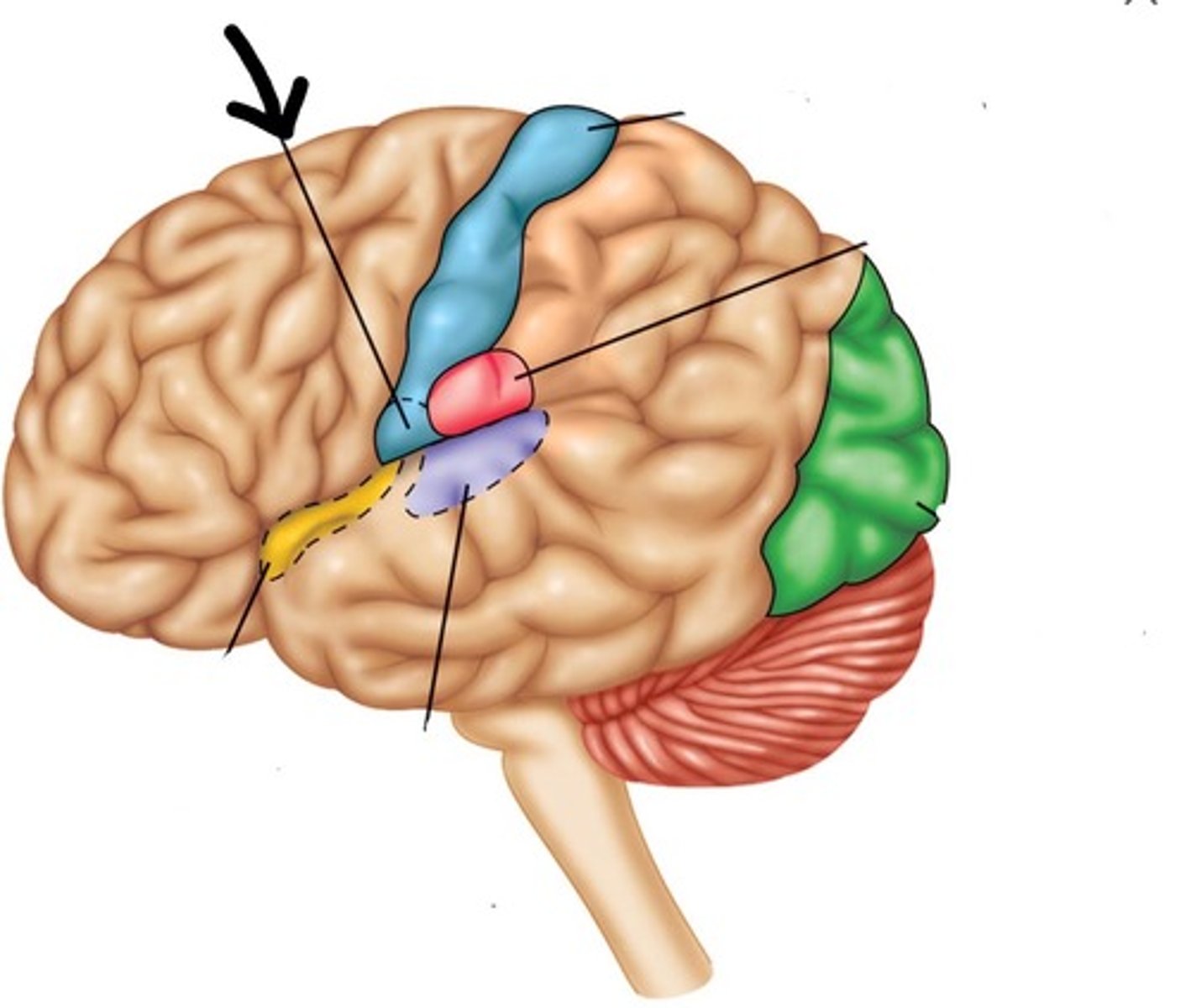
Association cortex
regions of the cerebral cortex that integrate simpler functions to perform more complex functions includes the anterior association cortex, posterior association cortex, and limbic association cortex
anterior association cortex
Prefrontal cortex
Most complicated cortical area
Intellect, cognition
Logic, reasoning
Decision making
Behavior control
Working memory
Persistence
Planning
Development depends on social environment
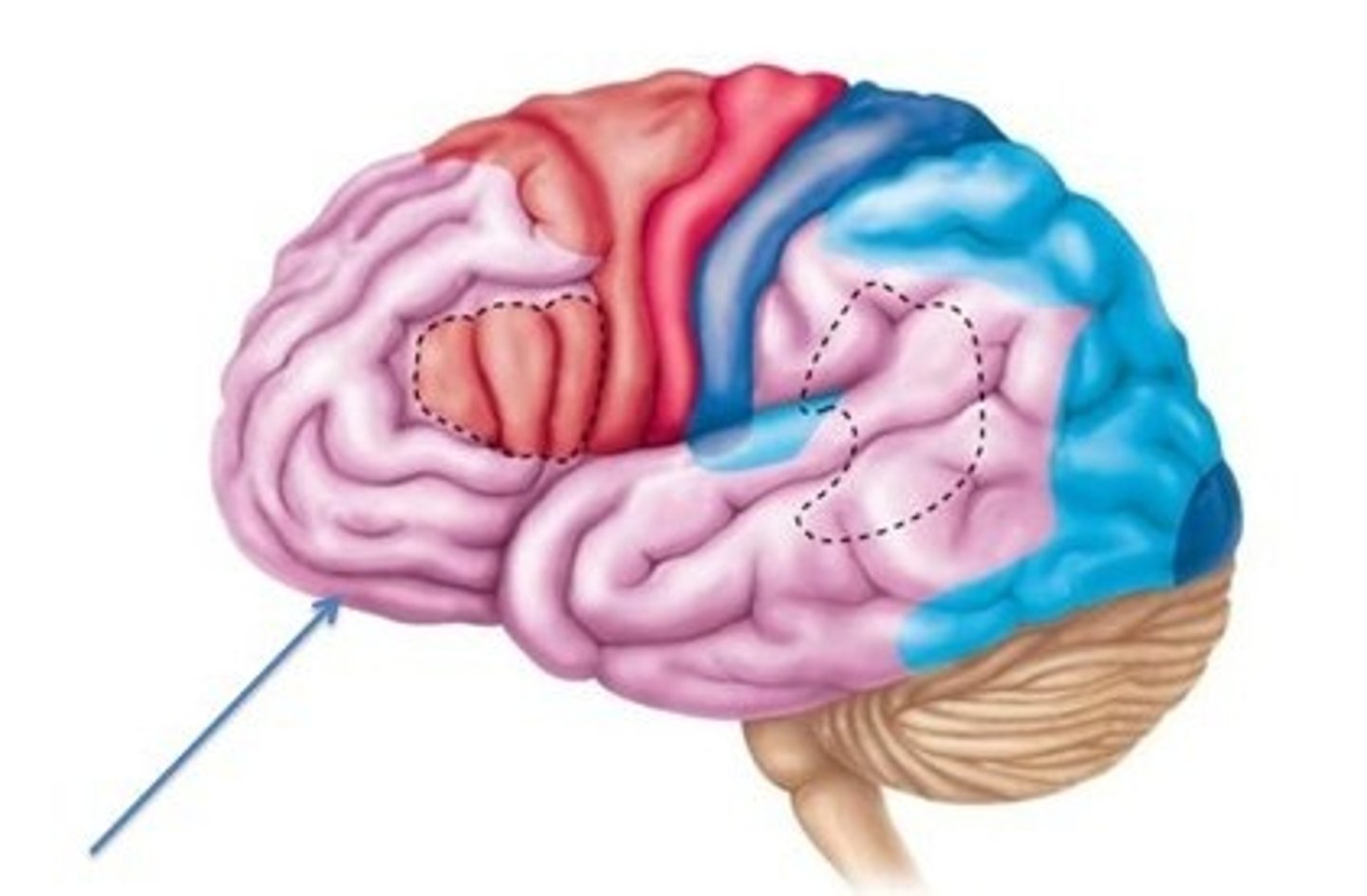
posterior association cortex
Pattern and facial recognition
Position in space
Understanding written and spoken language
Binding sensory input into coherent whole
amygdala
recognizes angry and fearful facial expressions, assesses danger. Elicit fear response
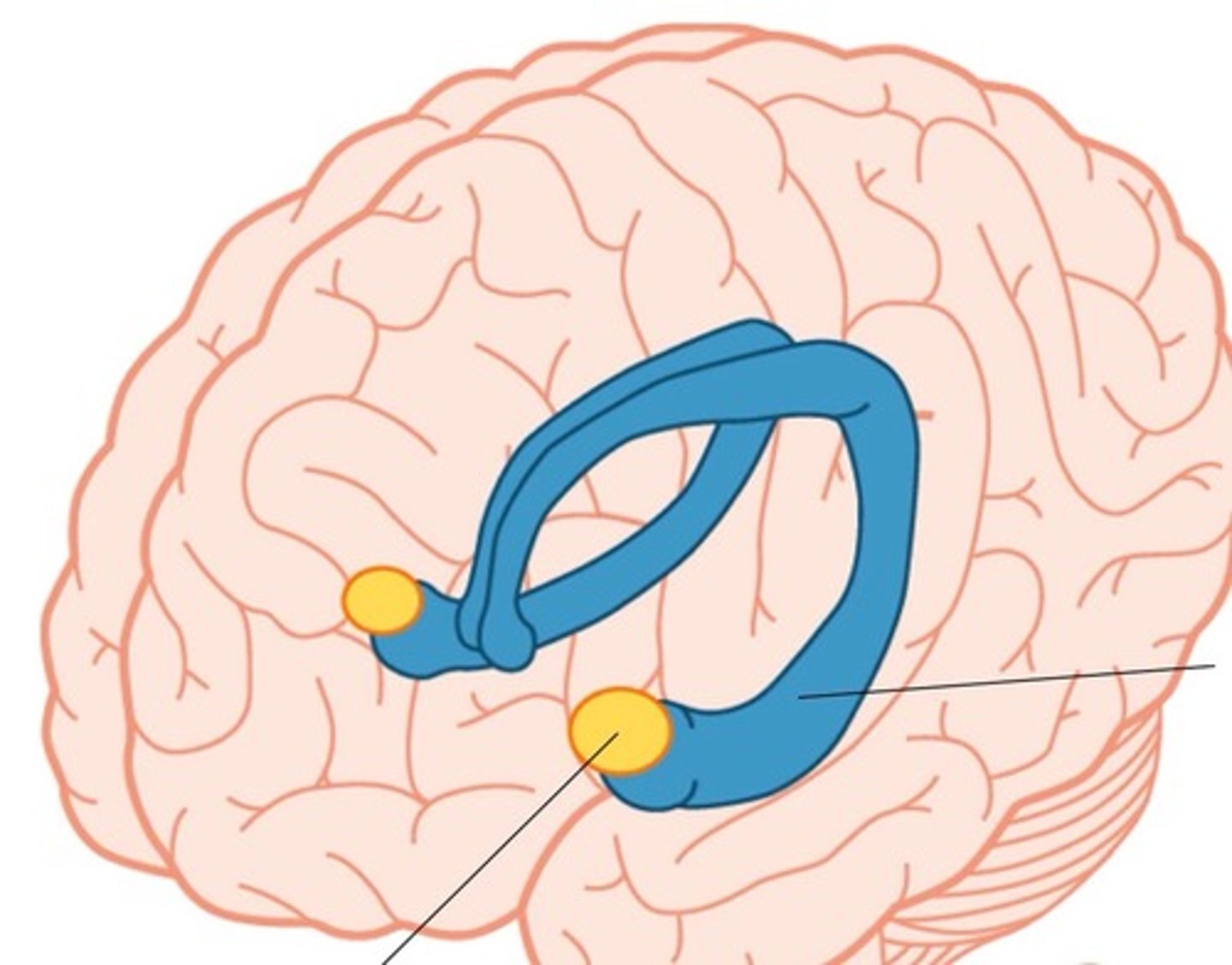
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
functions of the spinal cord
Provides two-way communication to and from brain, contains spinal reflex centers
spinal cord protection
Bone, meninges, and CSF
length of spinal cord
approx. 18 inches
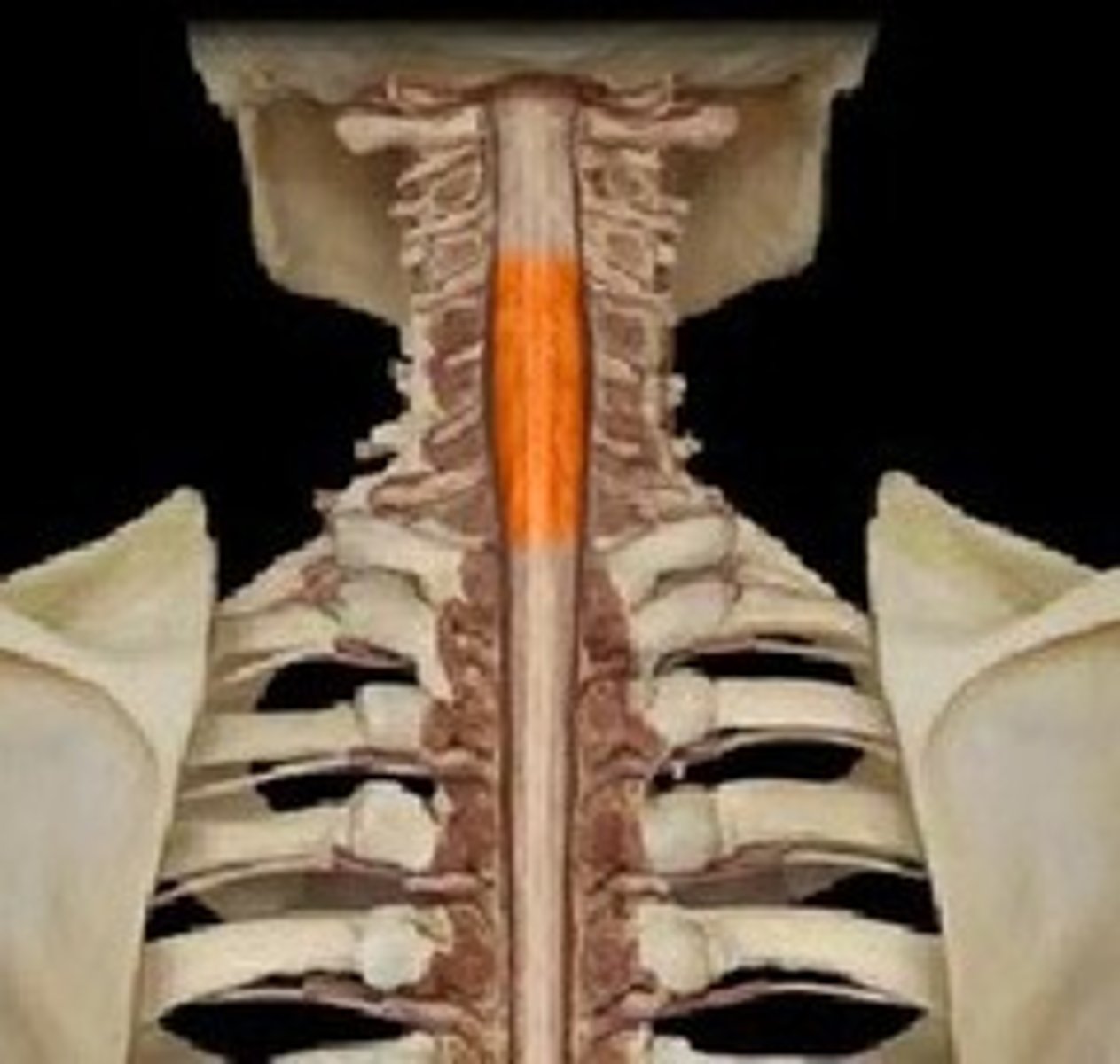
cervical enlargement of spinal cord
supplies nerves to the shoulder and upper limbs
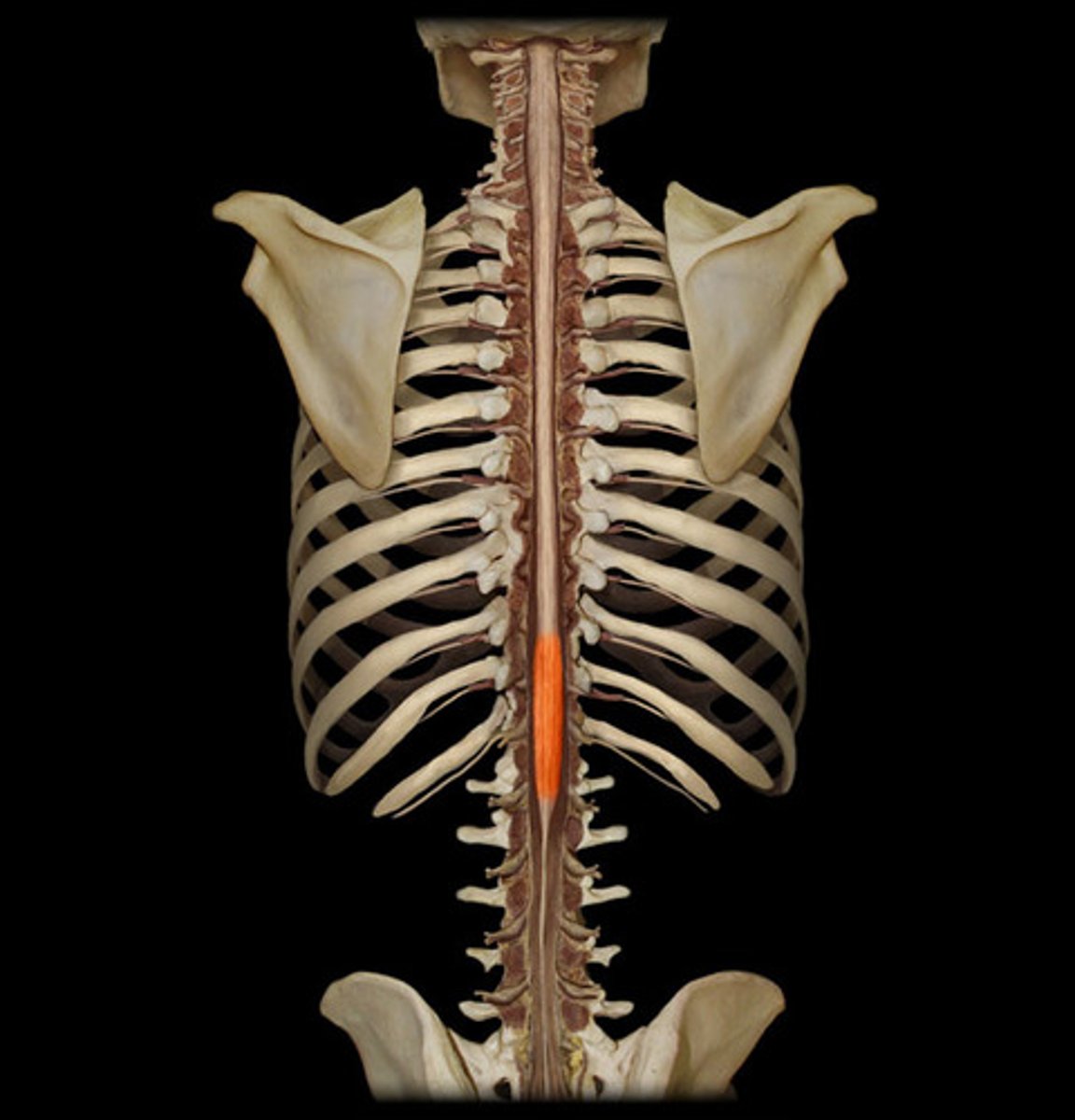
lumbar enlargement of spinal cord
nerves to pelvic region and lower limbs
ventral root of spinal cord
contains axons of motor neurons
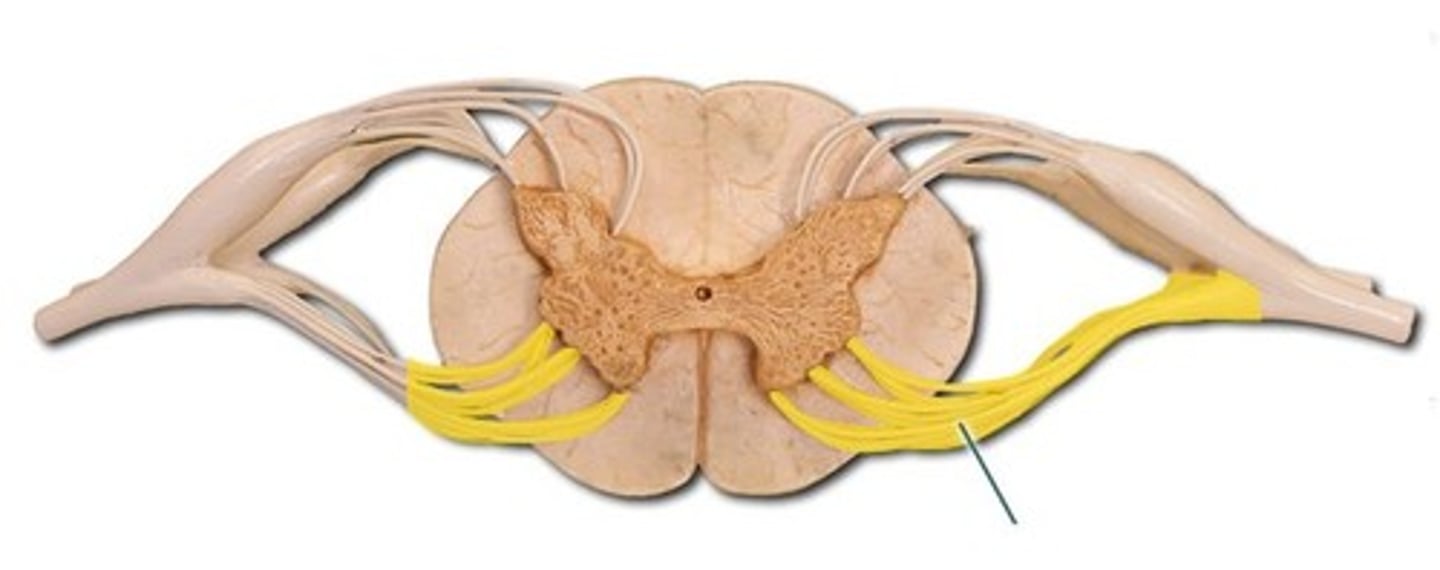
dorsal root of spinal cord
contains axons of sensory neurons
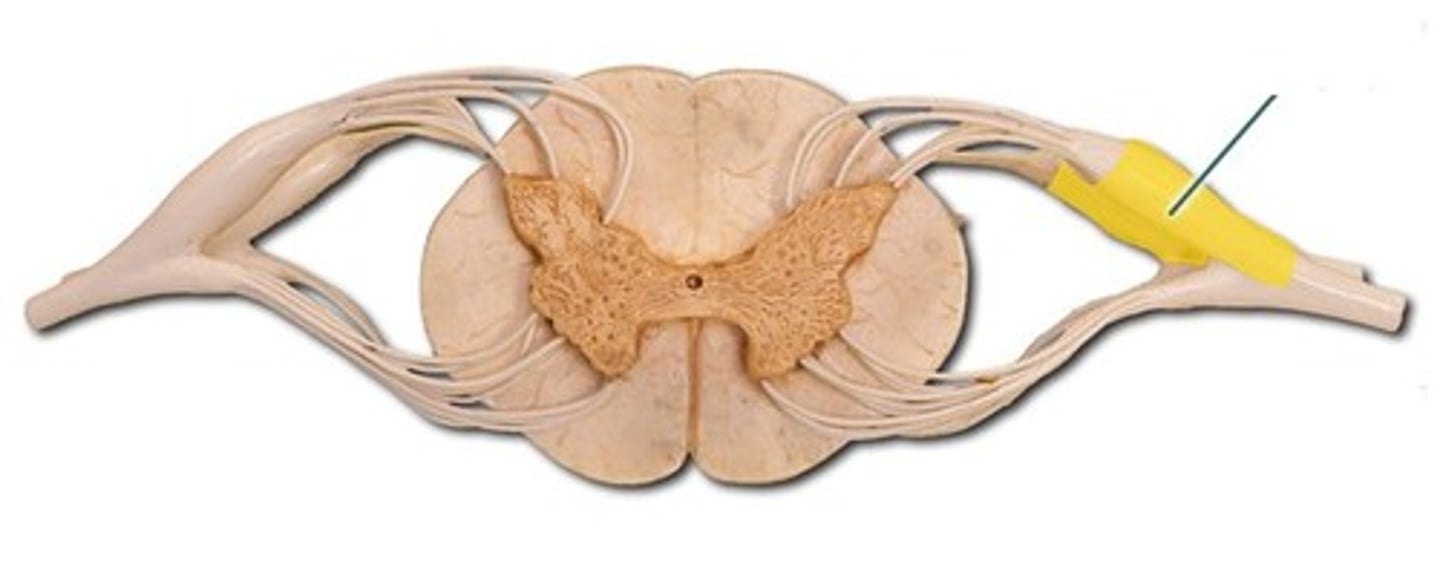
dorsal root ganglia
contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
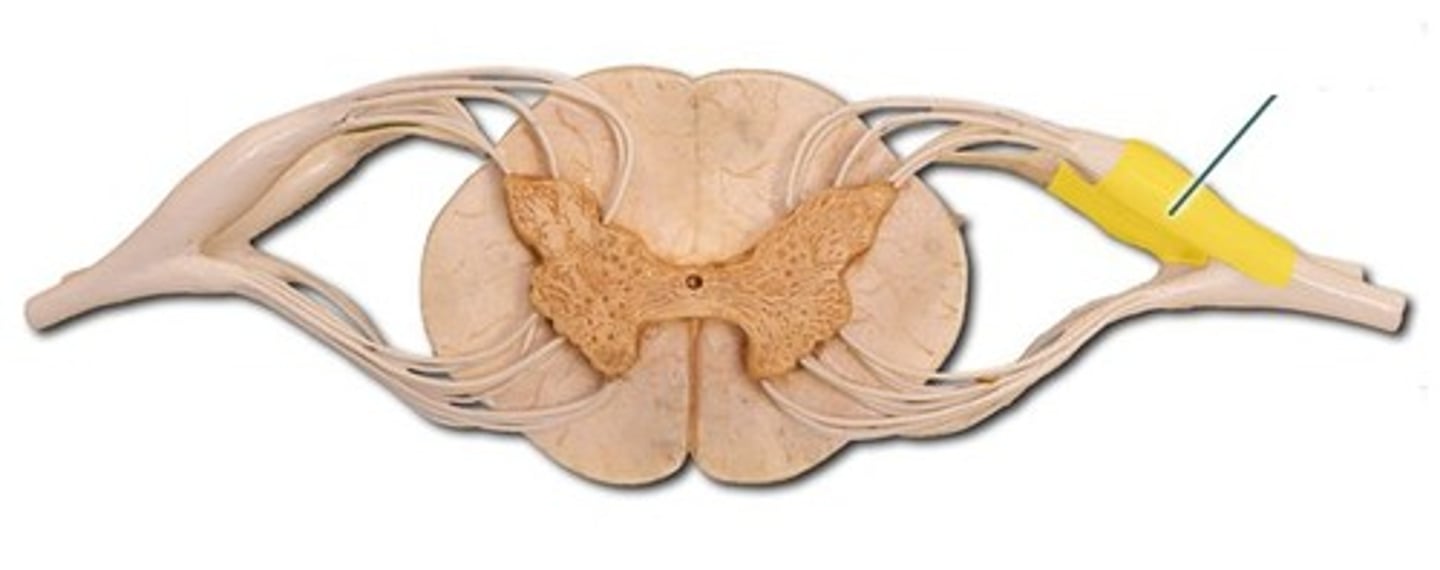
spinal nerve
A dorsal and ventral root of each spinal segment unite to form a.... there are 31 pairs
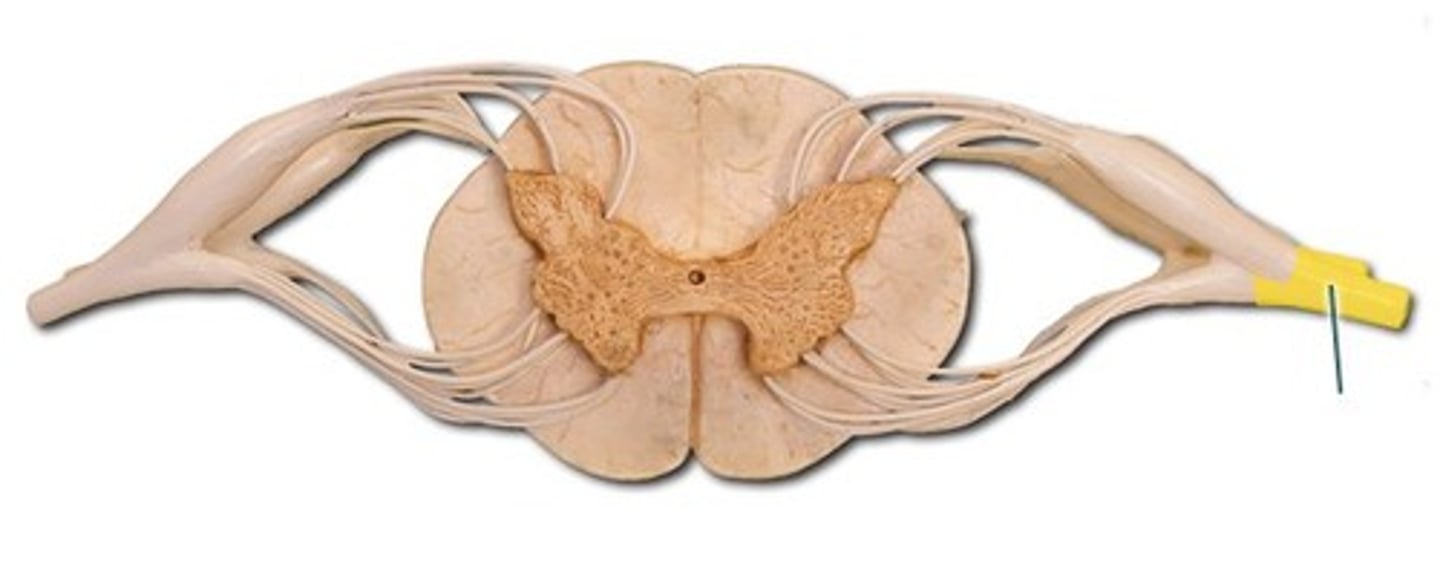
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord
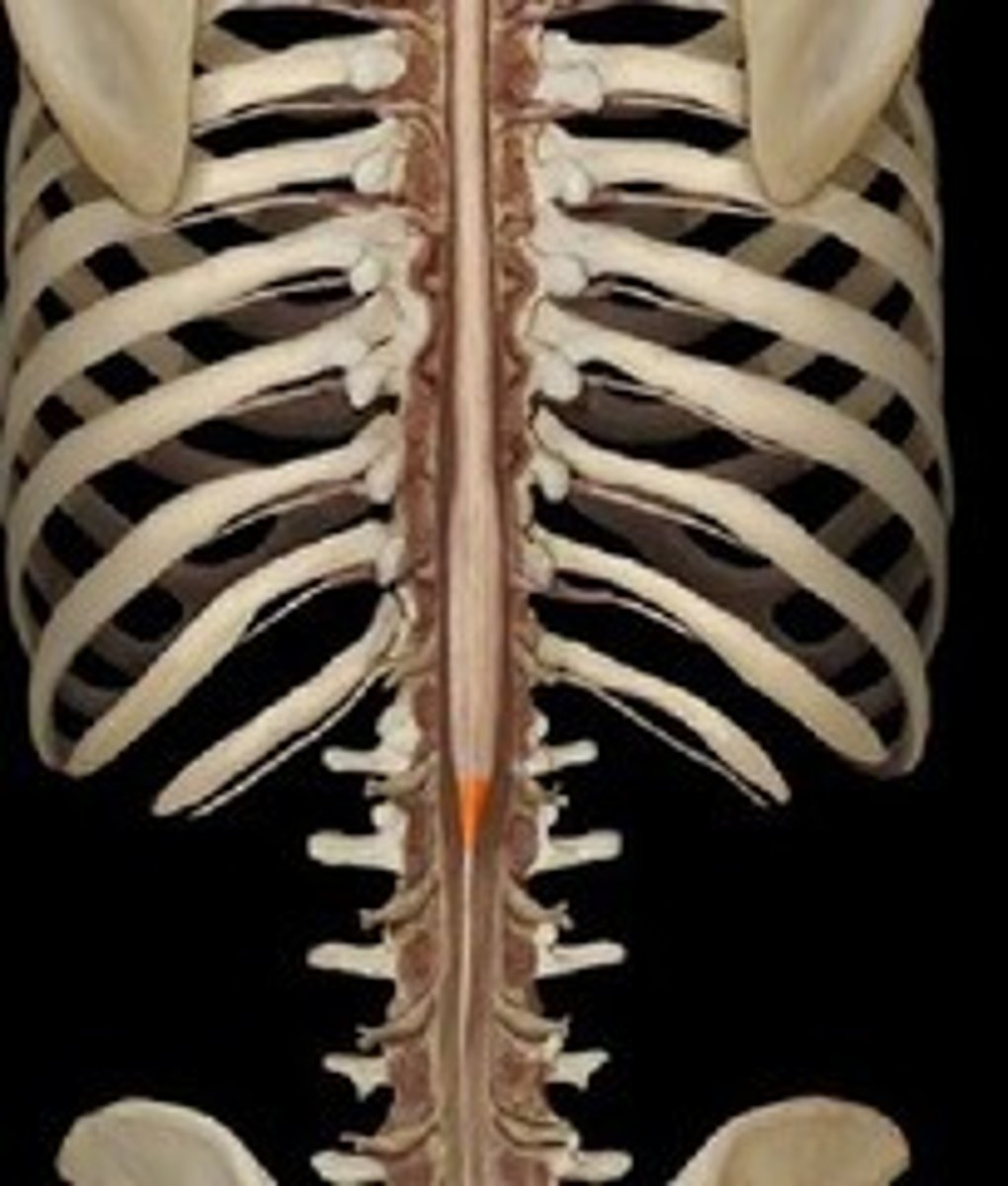
fillum terminale
thin thread of fibrous tissue at end of conus medullaris, attaches to coccygeal ligament
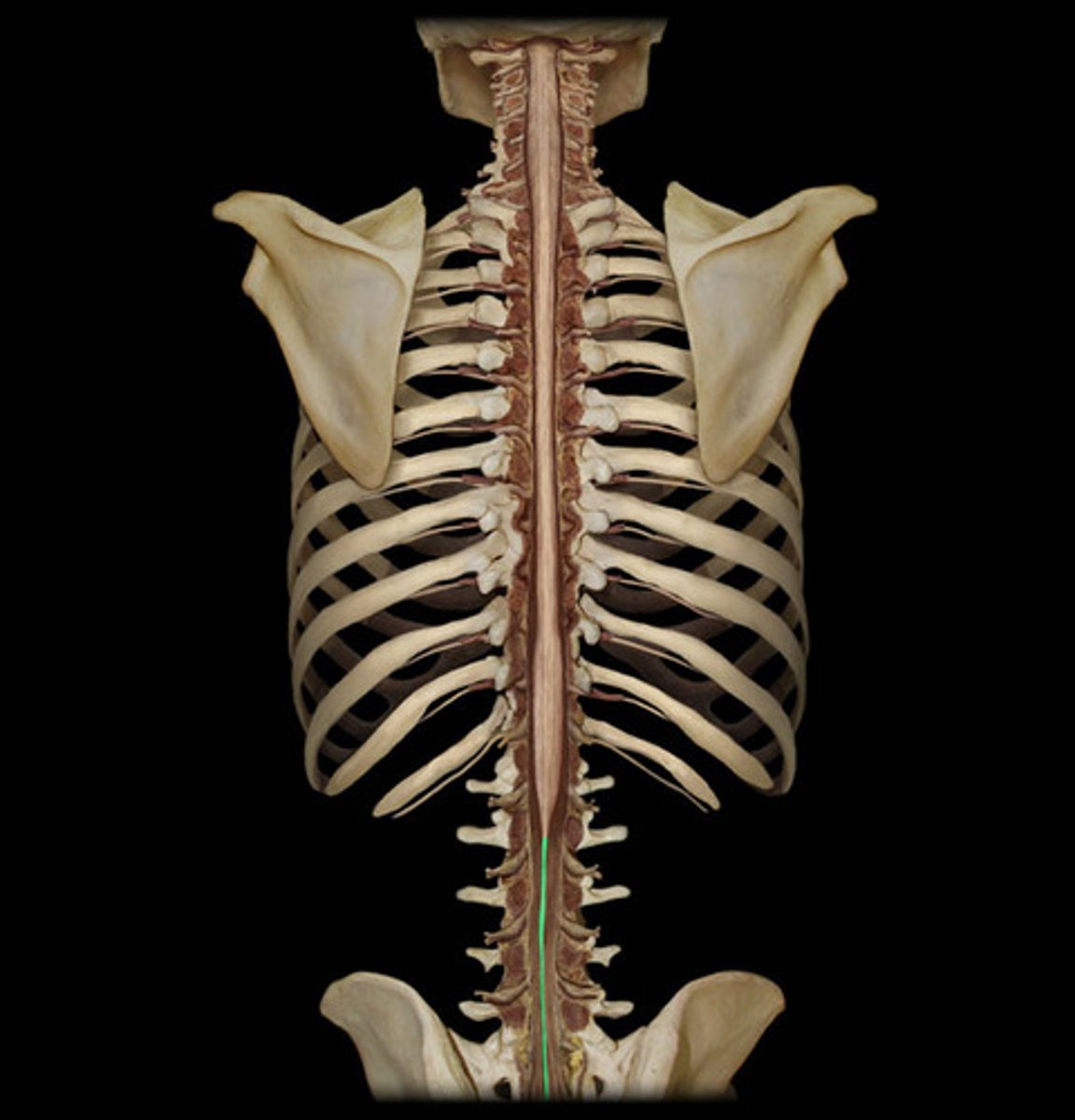
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord