M5: Industrial PLC
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
It is a small computer that gets data from inputs and controls outputs like motors or lights.
What is Programmable Logic Controllers?

PLCs are strong and can survive shaking and heat, which makes them useful in factories with tough environments.
(because they can automatically control machines, processes, and equipment reliably and quickly)
Why PLC useful in factories?

Some Physical Tolerances of leading PLC brands
MEMORIZE IT!!
Because they are very reliable and can run continuously without stopping for long periods
(because they can automatically control machines, processes, and equipment reliably and quickly)
Why in 30 yrs, the PLC is the main choice in factory?
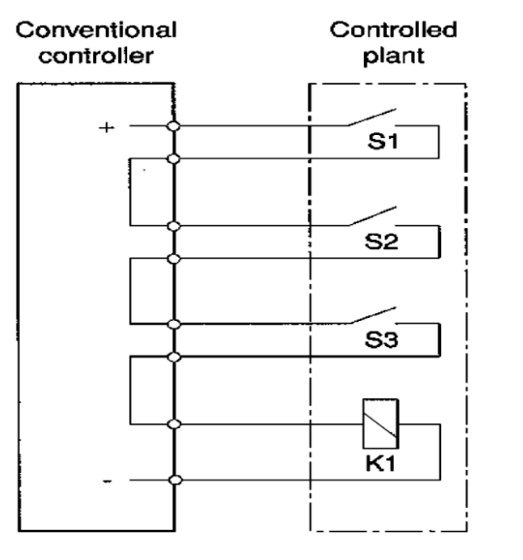
the switches S1, S2 and S3 must close for K1 to be turned on - the wiring makes the rule
Illustrate Traditional Control System
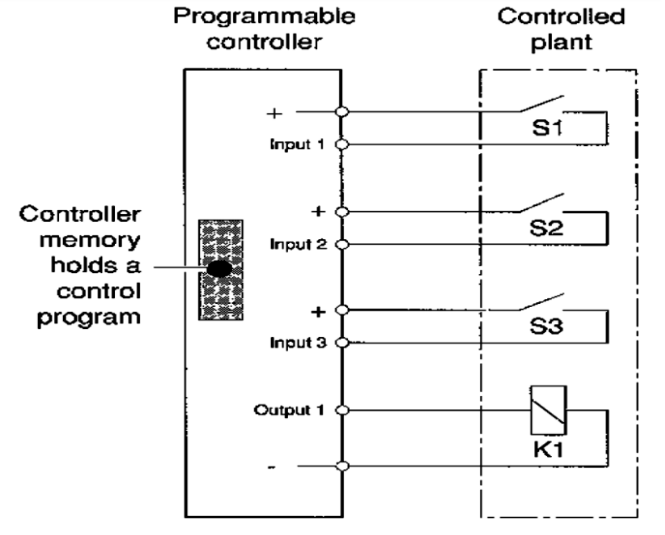
the program is written to perform the logic “when S1 is closed AND S2 is closed AND S3 is closed, THEN turn on K1” - the program makes the rule
Illustrate Programmable Control System
Its behavior depends mainly on the wiring arrangements.
Its behavior depends mainly on the instructions stored in the memory
Comparison between Traditional and Programmable Control System
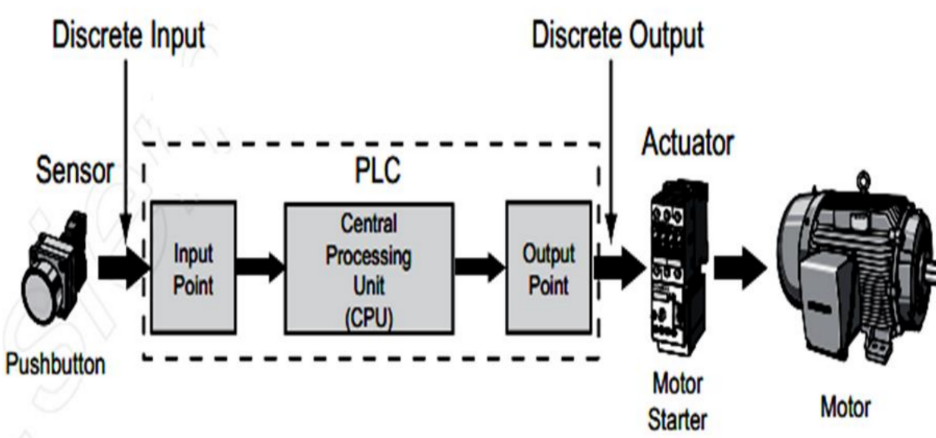
Illustrate Sample Industrial PLC
Interlocking
Sequencing
Timing, and
Counting
What task do PLCs perform?
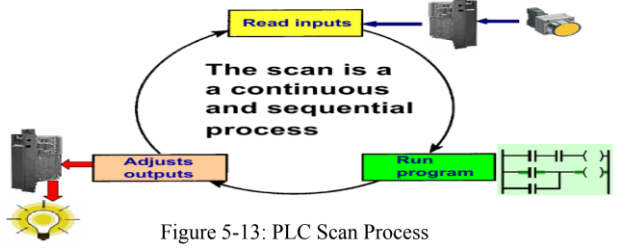
Read Inputs
– PLC checks inputs.Run Program
– PLC processes the logic and decides what to do.Adjust Outputs
– PLC turns ON/OFF motors, lights, valves based on the program.
It repeats continuously and very fast.
Illustrate PLC Scan Process
It indicates how fast the controller can react to changes in inputs.
It shows how fast the PLC can react. Too slow, and fast input changes may be missed.
What is scan time? Why is it essential?
The scan process is the cycle a PLC follows to control machines.
It is useful because it allows the PLC to continuously check inputs, run the program, and update outputs, keeping machines running automatically.
What is scan process? Why is it essential?
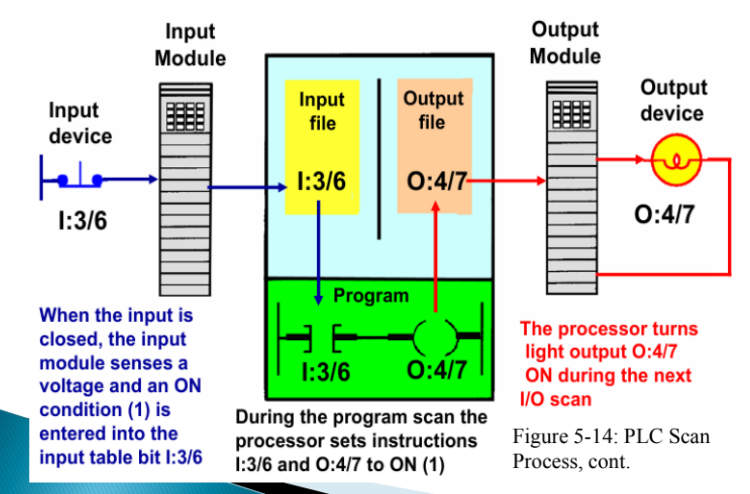
When the input (like a switch) is closed, the input module senses voltage.
So the PLC stores the input as ON (1) in memory at I:3/6.The PLC reads the input table and runs the program logic.
The PLC updates the output table and sends the signal to the output device.
The output device (like a light) turns ON.
This scan process repeats continuously, checking inputs and updating outputs every cycle.
Illustrate Scan Process