Psychiatric Disorders
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is neurology?
Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of nervous system disorders.
what are neurological disorders?
Ranging from multiple sclerosis to aphasia.
Help illustrate the role of physiological processes in normal brain function
what is psychiatry?
Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders that affect the mind or psyche.
what are examples of psychiatric disorders?
Anxiety disorders
Affective disorders
Schizophrenia
what are antipsychotics?
Haloperidol, fluphenazine, loxapine and thioridazine
First generation “typical” antipsychotics.
Clinical efficacy correlates to dopamine D2 receptor binding and dampening
what are the functions of classification?
Denomination→ Assigning a common name to a group of phenomena.
- Qualification→ Enriching the information content of a category by adding relevant descriptive features.
- Prediction→ A statement about the expected course and outcome as well as the response to the treatment.
what is categorial classification?
Fundamental diagnostic element→ syndrome (group or pattern of symptoms).
• Diagnostic criteria for each disorder.
- Represents the clinical presentation either meets or doesn’t meet the requirement for a particular disorder.
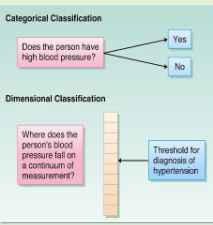
what is dimensional classification?
Fundamental diagnostic element→ symptoms.
• Dimensions:
- Extent the psychiatric symptomatology across a number of dimensions.
- Avoids setting of a particular threshold for distinguish between pathology and normality.
what is the DSM-5?
Manual used to diagnose mental health disorders
what are neurodevelopmental disorders?
Impairments of the growth and development of the brain and/or central nervous system.
- Specific vs global.
- Non-pharmacological treatment.
what are examples of neurodevelopmental disorders?
1. Intellectual Disabilities
2. Communication Disorders
3. Autism Spectrum Disorder
4. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
5. Specific Learning Disorder
6. Motor Disorders
7. Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders
8. Schizophrenia
what are positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
Delusions, hallucinations.
- Disorganized speech.
- Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior.
what are negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
- Reduced expression of emotion, poverty of speech.
- Difficulty initiating goal-directed behaviour.
- Memory impairment.
what is GWAS?
A genome-wide association study is a research method that compares the DNA of many people to find genetic variants linked to a disease or trait
100s of genetic risk factors identified
interact with environmental risk factors
what is gene x environment interaction?
- “Faulty” genes → vulnerability to environmental factor
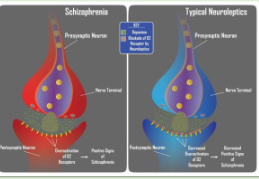
what do neuroleptic drugs do?
Neuroleptic drugs—potent blockers of dopamine receptors
what is the glutamate hypothesis?
Observed behavioural effects of phencyclidine (PCP) and ketamine.
- Neither affects dopaminergic transmission.
- Both affect synapses that use glutamate as a neurotransmitter.
- Inhibit NMDA receptors.
Hypothesis: schizophrenia reflects diminished activation of NMDA receptors in the brain
what are the treatments for schizophrenia?
Drug therapy combined with psychosocial support.
Conventional neuroleptics, such as chlorpromazine and haloperidol, act at D2 receptors.
- Reduce the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
- Numerous side effects.
what are affective disorders?
Mood disorders.
• Recurrent depression.
- Major depression (MDD).
- Dysthymia (‘mild’ depression).
what is type I and Type II bipolar disorders?
Recurrent, repeated episodes:
1. Type I: mania (e.g. increased goal-directed activity, grandiosity, diminished need for sleep).
2. Type II: hypomania (periods of current or past major depressive episodes interspersed with current or past hypomania)
what is the monoamine hypothesis?
Depletion of monoaminergic neurotransmitters in CNS.
- Deficit in central diffuse modulatory systems.
- Studied by effects of drugs.
1. Reserpine.
2. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
3. Imipramine.
- Pharmacological compounds elevate levels in CNS.
what is the monoamine hypothesis of mood disorders?
Treatment focus on central serotonergic and/or noradrenergic synapses.
what is the diathesis-stress hypothesis?
- Genetic predisposition (diathesis) influences stress responses
- Role of HPA axis.
- Impact of CRH.
- HPA function becomes hyperactive.
- Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene expression regulated by early experience.
what is electroconvulsive therapy; localised electrical sitmulation?
Unknown mechanism in relieving depression.
- Affects temporal lobe.
- Advantage: quick relief of depression, mania.
- Adverse effect: loss of prior memories, impaired storage of new information.
what is deep brain stimulation?
When severe depression fails to respond to other treatment.
- Electrode implanted deep in the brain
what is the stress response?
Humoral response: corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) → adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) → cortisol
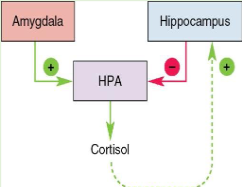
what is the regulation of the HPA axis by the amygdala and hippocampus?
Both regulate CRH neurons.
Amygdala projects to bed nucleus of stria terminalis, which activates the HPA axis.
- Hippocampus deactivates the HPA axis.
- Glucocorticoid receptors
- Feedback loop
• Push–pull regulation.
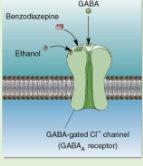
how is anxiety treated?
Psychotherapy.
• Anxiolytic medications.
- Role of GABA.
- Benzodiazepines
- Serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Target for new drugs: CRH receptors
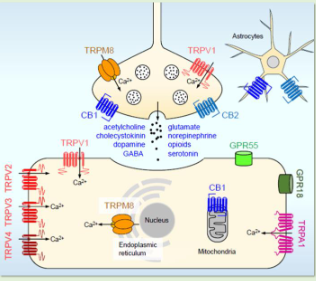
what is the endocannabinoid system?
endogenous cannabinoid system.
• GPCRs expressed:
- CB1 and CB2.
- Retrograde inhibition of neuronal signalling.
- Postsynaptic effects on presynaptic membranes.
- Unknown safety and efficacy.
- Developmental effects.