(8) Linear Kinematics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Kinematic quantities
Linear Position
Linear Distance and Displacement
Linear speed and velocity
average vs instantaneous
Linear acceleration
Vector and Scalar
Tip to tail method (adding multiple vectors)
Vector Resolution and Composition (how to utilize vectors)
Component method
Linear Position
Linear location of object of interest at a given instant
Vector: Magnitude + Direction
Coordinates: r= [x, y] (r is the position vector)
Unit: m (meter)
![<ul><li><p>Linear location of object of interest at a given instant </p></li><li><p>Vector: Magnitude + Direction</p></li><li><p>Coordinates: <strong>r</strong>= [x, y] (r is the position vector)</p></li><li><p>Unit: m (meter)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/163cb788-5ddb-4392-822b-ed2b0702999e.png)
Linear Distance
length of the path
how long/far
Scalar: Magnitude only
Unit: M
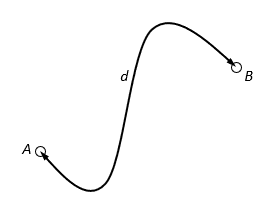
Linear Displacement
change in linear position
net effect of motion
Vector
Unit: m
d= delta r= r2 — r1 = [x2 - x1, y2 - y1]
![<ul><li><p>change in linear position </p><ul><li><p>net effect of motion</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Vector</p></li><li><p>Unit: m </p></li></ul><p><strong>d=</strong> delta <strong>r= r<sub>2 </sub>— r<sub>1 </sub> = [x<sub>2</sub> - x<sub>1</sub>, y<sub>2</sub> - y<sub>1</sub>] </strong></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b17fcf12-cf62-4e2d-a632-3f9e231cb0f1.png)
Tip to tail method- Purpose
used in vector ADDITION
to find the resultant(sum/net)
tip to tail- procedure
connect all vectors tip to tail
resultant(sum or net): the vector from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the last vector
connection sequence is not important
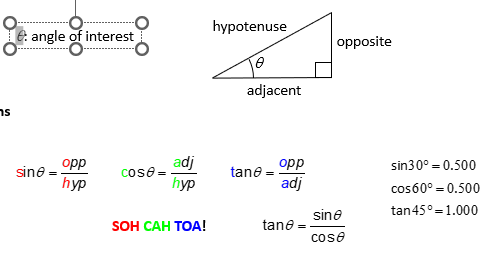
Basic Trigonometric functions
Right triangle- hypotenuse, opposite leg, adjacent leg, theta is the angle of interest
Basic trig functions
sine (theta)= opposite/hypotenuse
cosine(theta)= adjacent/hypotenuse
tangent(theta)= opposite/adjacent or sin/cos

Vector resolution (decomposition)
Breaking down a vector into components
v=vx+vy
use hypotenuse and angle to find length of opposite and adjacent legs
adj=hyp*cos(angle)
opp=hyp*sin(angle)

Vector Composition
composing a vector from components
v=vx+vy
use adj and opp to find hyp and angle
use Pythagorean theorem to find hyp
use arctan(opp/adj) to find theta
Directions relative to the cardinal directions
Reminder- the direction after Due is the side it starts on
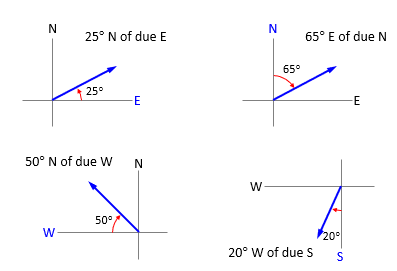
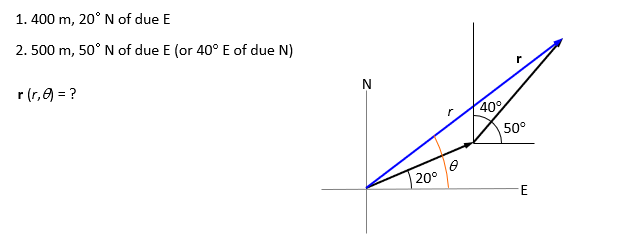
Example of directions
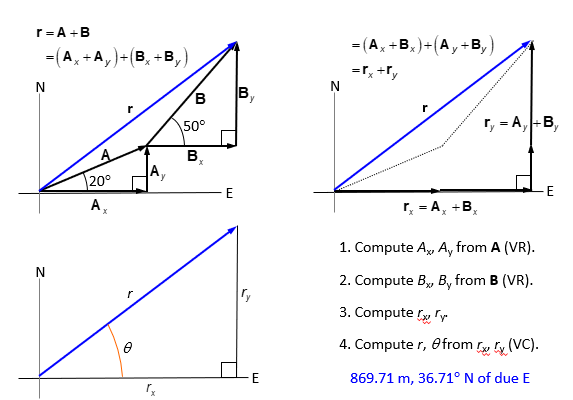

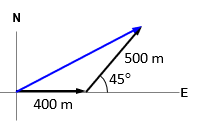
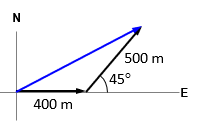
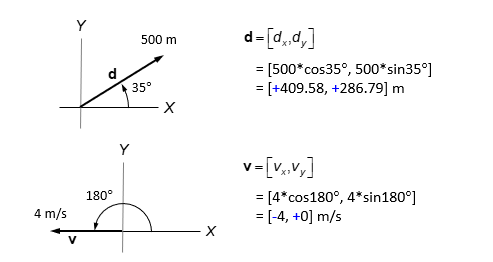
The component method
vectors can be described in components
v=[vx, vy] = [vcosΘ, vsinΘ]
Θ is the direction angle (measured from the X-axis)
Components
vx,vy = + or - number
sign= direction
numeric value: magnitude
v= vx+vy
Component method example
Vector addition
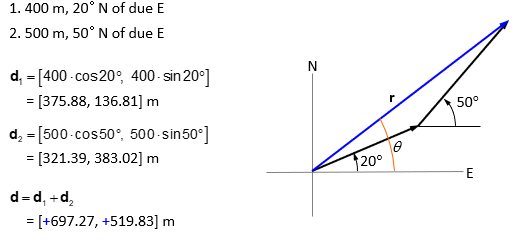
A= [Ax, Ay]
B=[Bx, By]
A+B= [Ax, Ay] + [Bx, By] = [Ax + Bx, Ay + By]
Example of vector addition
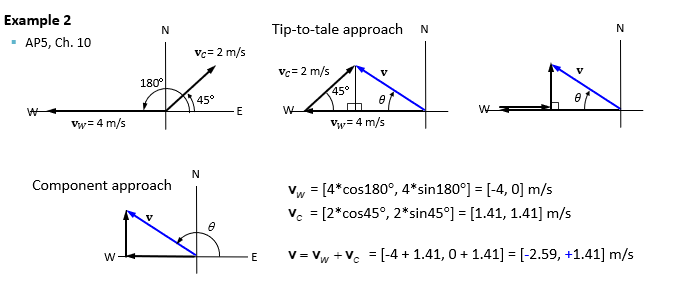
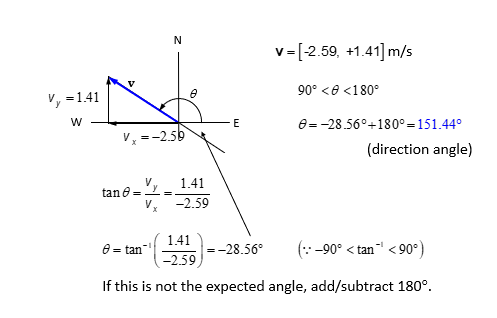
Example 2 of vector addition
Linear speed
how fast an object moves
linear distance/elapsed time v(bar)= d/𐤃t or v=d/dt
v (bar)= average speed
v= instantaneous speed
dt= infinitesimal duration
scalar quantities
unit: m/s
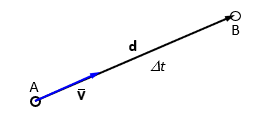
Linear velocity
rate of change in linear position
rate of linear displacement
how fast an object moves in which direction
linear displacement/elapsed time
v(bar)=𐤃r/𐤃t= d/𐤃t v=dr/dt=d/dt
dr: displacement during dt
vector
unit: m/s
CONT. Linear velocity
direction of velocity=direction of displacement
components
v=[vx , vy] = [ dx/dt , dy/dt]
direction of the component velocity
positive: rightward/upward motion
negative: Leftward/downward motion
![<ul><li><p>direction of velocity=direction of displacement </p></li><li><p>components </p><ul><li><p>v=[v<sub>x</sub> , v<sub>y</sub>] = [ d<sub>x</sub>/dt , d<sub>y</sub>/dt]</p></li></ul></li><li><p>direction of the component velocity </p><ul><li><p>positive: rightward/upward motion </p></li><li><p>negative: Leftward/downward motion</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b971fa67-46ab-4b0d-a0ed-a195f34b06a7.png)
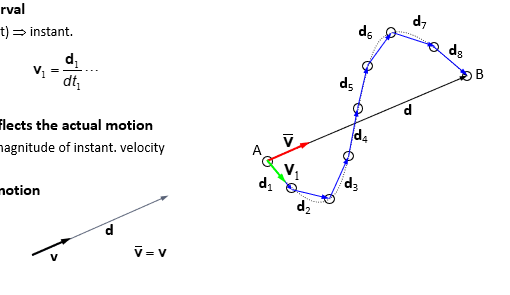
Average vs. Instantaneous
Length of time interval
dt (infinitesimal 𐤃t) —→ instant
v(bar)= d//𐤃t v1= d1/dt1
Instantaneous v reflects the actual motion
instant. speed = magnitude of instant velocity
constant velocity motion
v (bar)=v
Zero velocity
Average v=0
no displacement=no net motion
instantaneous v=0
zero instant speed= not moving
constant position
basically average v can move around but it then goes back to the original point and shows there was no displacement. instantaneous does not have enough time to move so you stay in the same spot
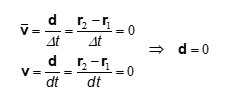
EX a swimmer
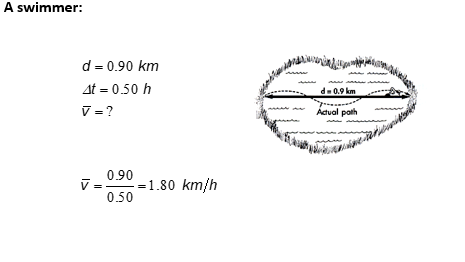
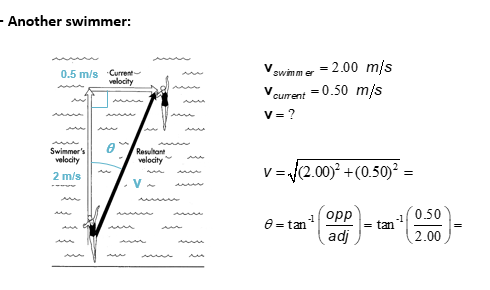
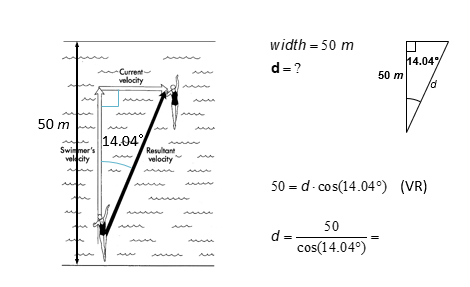
EX another swimmer
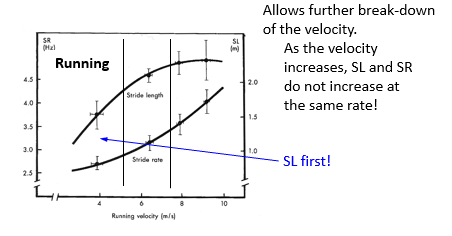
Velocity in cyclic movement
v= Cycle Length * Cycle Frequency(rate)
running: Stride Length (m/stride) * Stride Freq (stride/s)
Swimming: Stroke length (m/stroke) * Stroke F (stroke/s)
Linear Acceleration
Acceleration
rate of change in linear speed or velocity
Scalar acceleration
change in speed/ elapsed time
a(bar)= 𐤃v/𐤃t= v2-v1/t2-t1
a= dv/dt = v2-v1/t2-t1
positive acceleration= speeding up
negative acceleration= slowing down
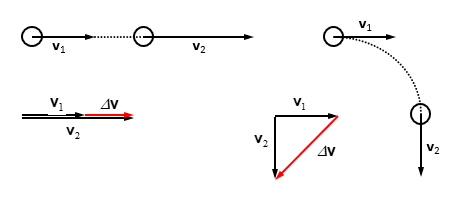
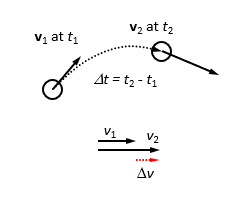
Vector acceleration
change in velocity/elapsed time
a(bar)= 𐤃v/ 𐤃t= v2-v1/ 𐤃t a= dv/dt=v2-v1/ dt
Components
a=[ax , ay]= [dvx/dt , dvy/dt]
![<ul><li><p>change in velocity/elapsed time </p><ul><li><p>a(bar)= 𐤃v/ 𐤃t= v<sub>2</sub>-v<sub>1</sub>/ 𐤃t a= dv/dt=v<sub>2</sub>-v<sub>1</sub>/ dt </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Components </p><ul><li><p>a=[a<sub>x</sub> , a<sub>y</sub>]= [dv<sub>x</sub>/dt , dv<sub>y</sub>/dt]</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0bd4a3c4-476f-471a-9693-b5032ef9217a.png)
Vector acceleration continued
Positive component acceleration
speed up of positive velocity
slow down of negative velocity
ax>0 ay>0
Negative component acceleration
slow down of positive velocity
speed up of negative velocity
ax<0 ay<0

projectile motion
a=[ax , ay]
units in m/s2
horizontal velocity stays the same while vy slows down and speeds up
![<p>a=[a<sub>x</sub> , a<sub>y</sub>] </p><p>units in m/s<sup>2</sup></p><p>horizontal velocity stays the same while v<sub>y </sub>slows down and speeds up</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a46cdb64-2b96-4e0f-9953-8bfd643c962c.png)
zero acceleration
zero average a= no net change in velocity (initial v=final v)
zero instantaneous a= constant velocity
a(bar)= 𐤃v/𐤃t=v2-v1/ 𐤃t= 0 a= dv/dt=v2-v1/ dt= 0
𐤃v=0 and dv=0
causes of acceleration
changes in magnitude of velocity( speed)
change in direction of velocity
(tangential acceleration is the straight lines and radial acceleration is the other one)