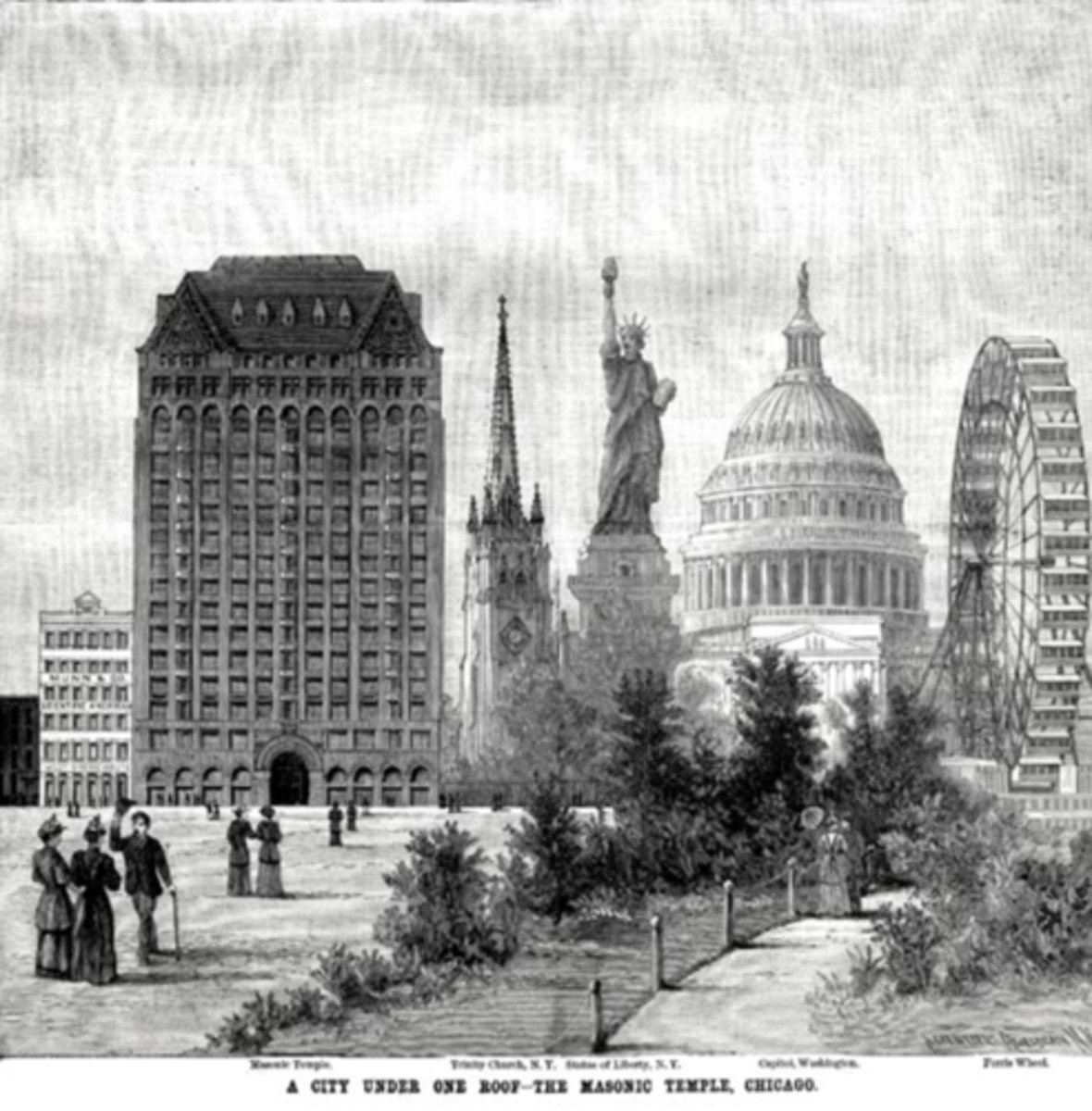
Exam 3 ARCH-4173-62517 History and Theory of Skyscraper Design
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
First Leiter Building
William Le Baron Jenney
Chicago
1879

When was the First Leiter Bldg demolished?
1972
How many stories did the First Leiter Bldg have?
7 stories, originally 5
How did the First Leiter Building by Irving K. Pond reflect the aesthetic principles of the Chicago School?
It featured simple architectural articulation and a straightforward design typical of the Chicago School style
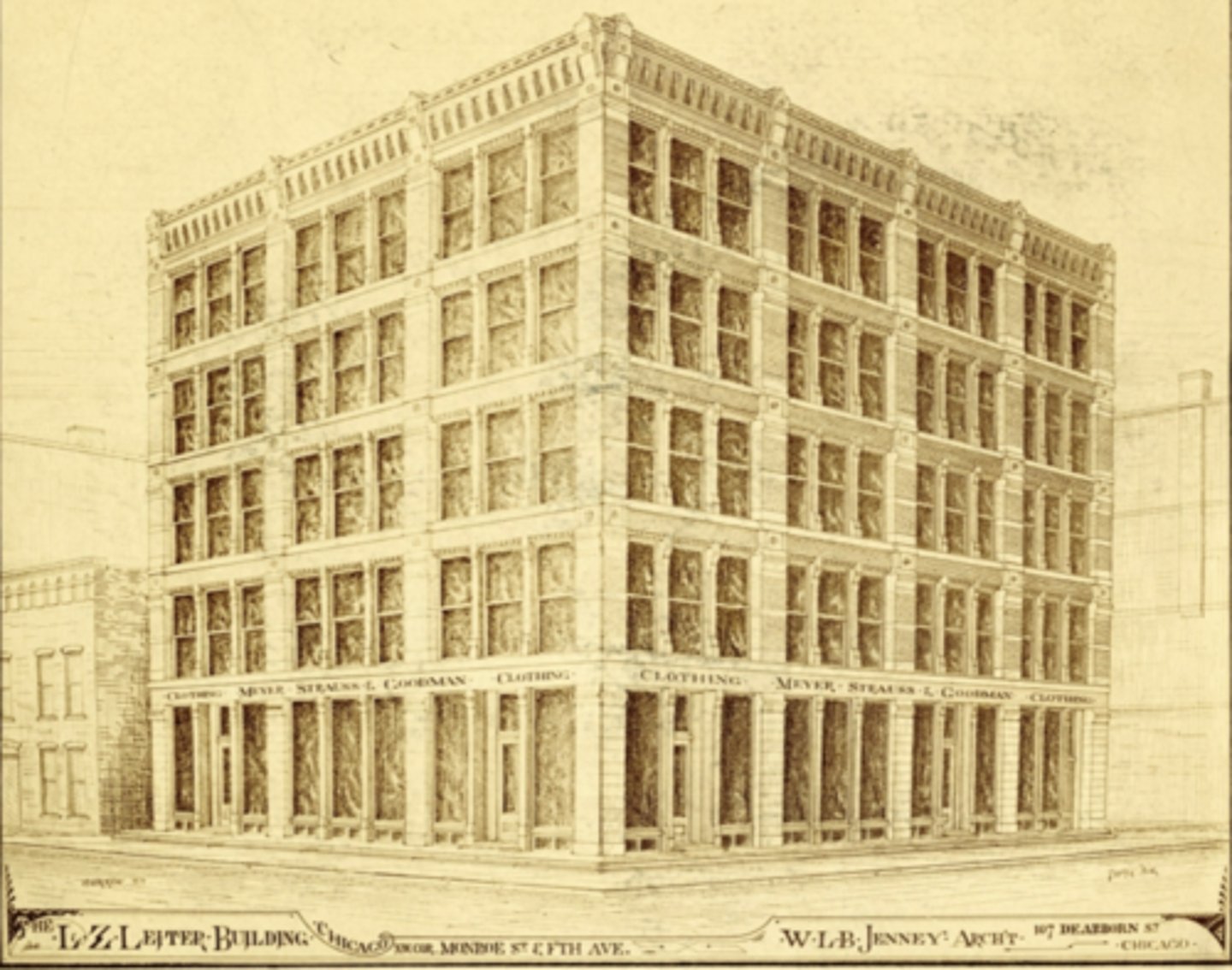

What material is there very little of in the First Leiter bldg?
iron
What elements were brick and which were iron in the First Leiter? What was made from limestone?
Birck piers, brick spandrels, iron mullions, limestone medallions
What material was used for the framing of the First Leiter Bldg?
Combination of iron and wood for framing
Who were the clients for the First Leiter Bldg?
Levi Leiter and he developed retail in Chicago
How can you tell the top 2 stories on the First Leiter Bldg were added later? Why is this important?
their floor to ceiling height and the lack of stone detailing; it anticipates the aesthetic of Chicago school, simplified bare bone structure
Field Building
Graham, Anderson, Probst& White (GAPW)
Chicago

Why was the Field Bldg the last skyscraper in Chicago?
There wasn't enough funding because of the Great Depression
What architectural style does the Field Bldg have?
Art Deco
What does the plaque say on the outside of the Field Bldg?
talks about skeleton framing
How was the Field Bldg built?
in two sections
Whats unique about the Field Bldg site?
on the same site of the Home Insurance Bldg
Home Insurance Building
William Le Baron Jenney
Chicago
1884-1885
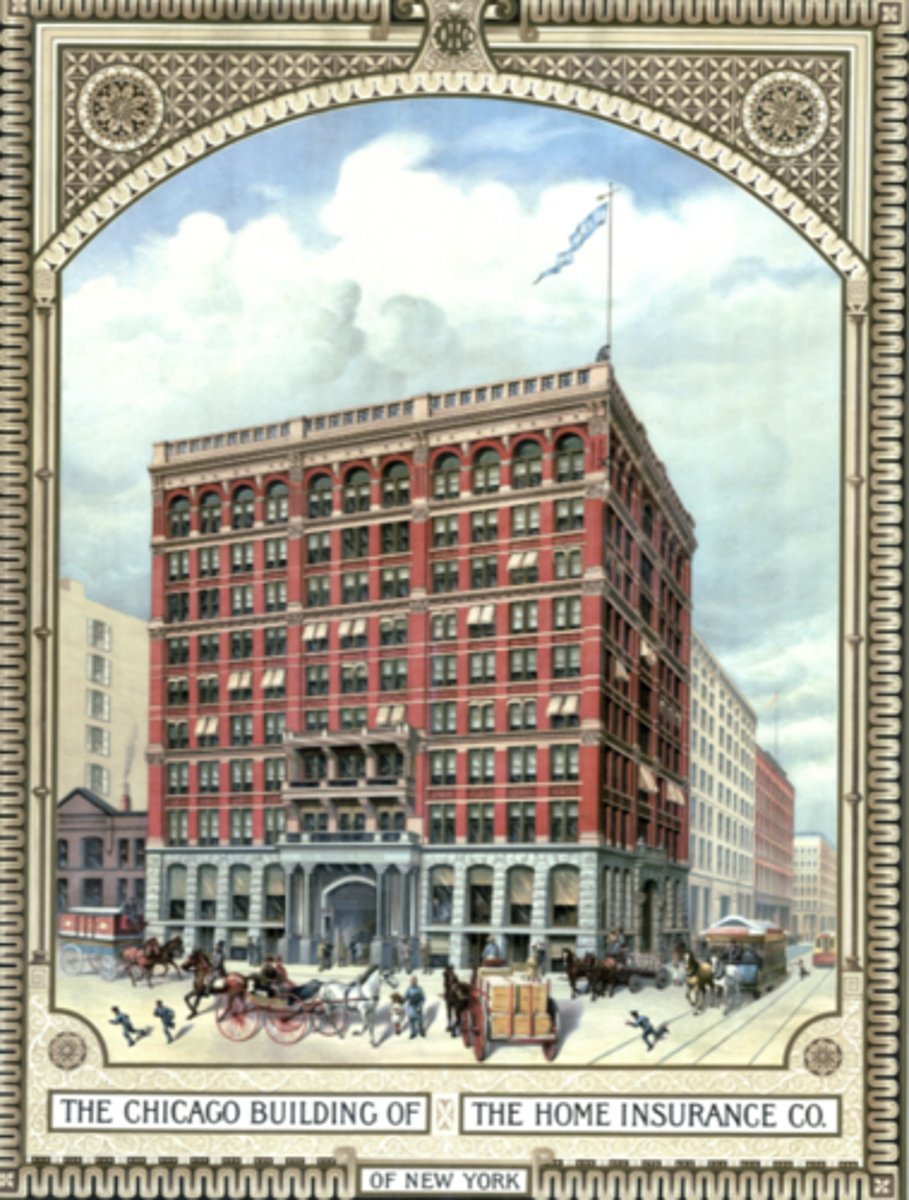

was the Home Insurance Bldg demolished? If so, when?
yes in 1931
which bldg do a lot of people consider to be the first skyscraper?
Home Insurance Bldg
what types of beams are used in the Home Insurance Bldg and why is it significant?
first bldg built with steel beams
how many stories does the Home Insurance Bldg have?
9 stories, 10 including the half basement
what was added to the Home Insurance Bldg and where?
2 floors were added to the original row of banded arches
What is the Home Insurance Bldg shaped like and why?
Floor plan looks like the map of Oklahoma and it has that shape because they could not get the land next to it
how is the Home Insurance Bldg heated?
Chimney
explain Efficiency in terms of renting out space in bldgs?
how much of the building you can rent out of what is built
what does the demolition photos of the Home Insurance Bldg show?
how much iron was in the framing of the building
is there iron in the bottom facade of the Home Insurance Bldg? why or why not?
No, load-bearing masonry (brick) walls because iron or steal wasn't strong enough
what did William L.B. Jenney want to have in the structure for the Home Insurance Bldg and why?
add more windows to make the space appealing to more clients, creating more rental opportunities and higher revenue
Monadnock Block (North Half)
Chicago
Burnham and Root
1889-1891
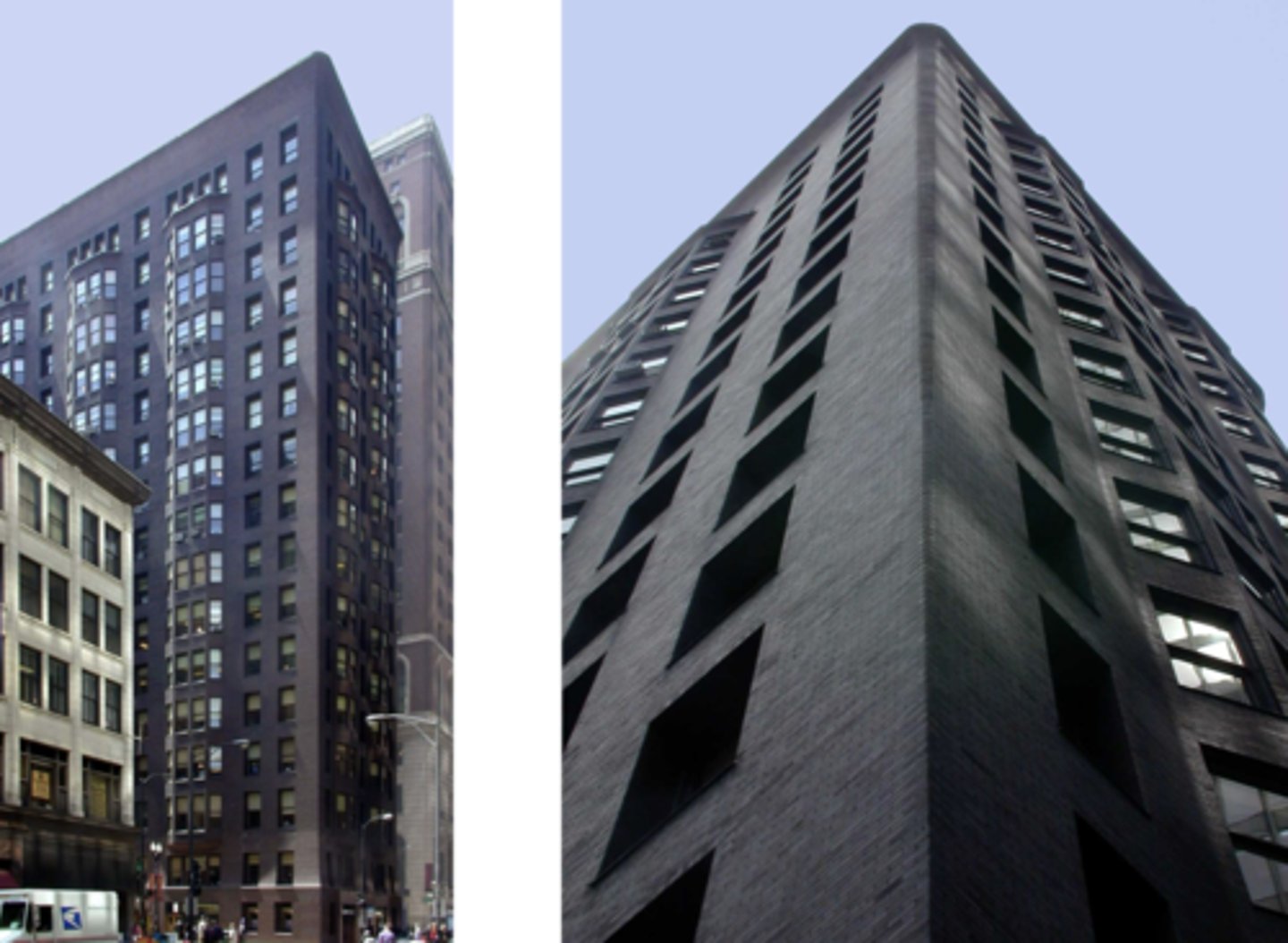

What shape was the site and its dimensions for Monadnock Block? Why was it "perfect"?
rectangular block about 66 feet wide by 200 feet long;
space for a double-loaded corridor plan that has maximum rental space
Which building is characterized by a simple exterior design, no skeleton framing or ornamentation, and a load-bearing structure extending from top to bottom across 17 stories?
Monadnock Block
What is Monadnock Block named after?
a mountain in Vermont
Who were the clients for the Monadnock Block?
The Brooks brothers (Peter and Shepherd)
How many stories does the Monadnock Block have? Whats unique about the first one? What is the material of all?
17 stories; 6-foot-thick brick walls on first story; Load bearing masonry
The clients are known for being ornamental, so why is the Monadnock Block not?
Bet hypothesis, plain brick box hypothesis, Dwight Perkins hypothesis
What do the oriels pose for the Monadnock Block and how many stories do they inhabit?
15-story Oriels, extensions of the building, they get to steal space from the public and charge rent for it
Why were sheer walls added to the Monadnock Block, and which sides were they across?
were added across the short sides to strengthen against wind
Why was the Monadnock Block divided into 2 halves?
for the possibility of selling only half the building
Montauk Block
Burnham and Root
Chicago
1881-1882
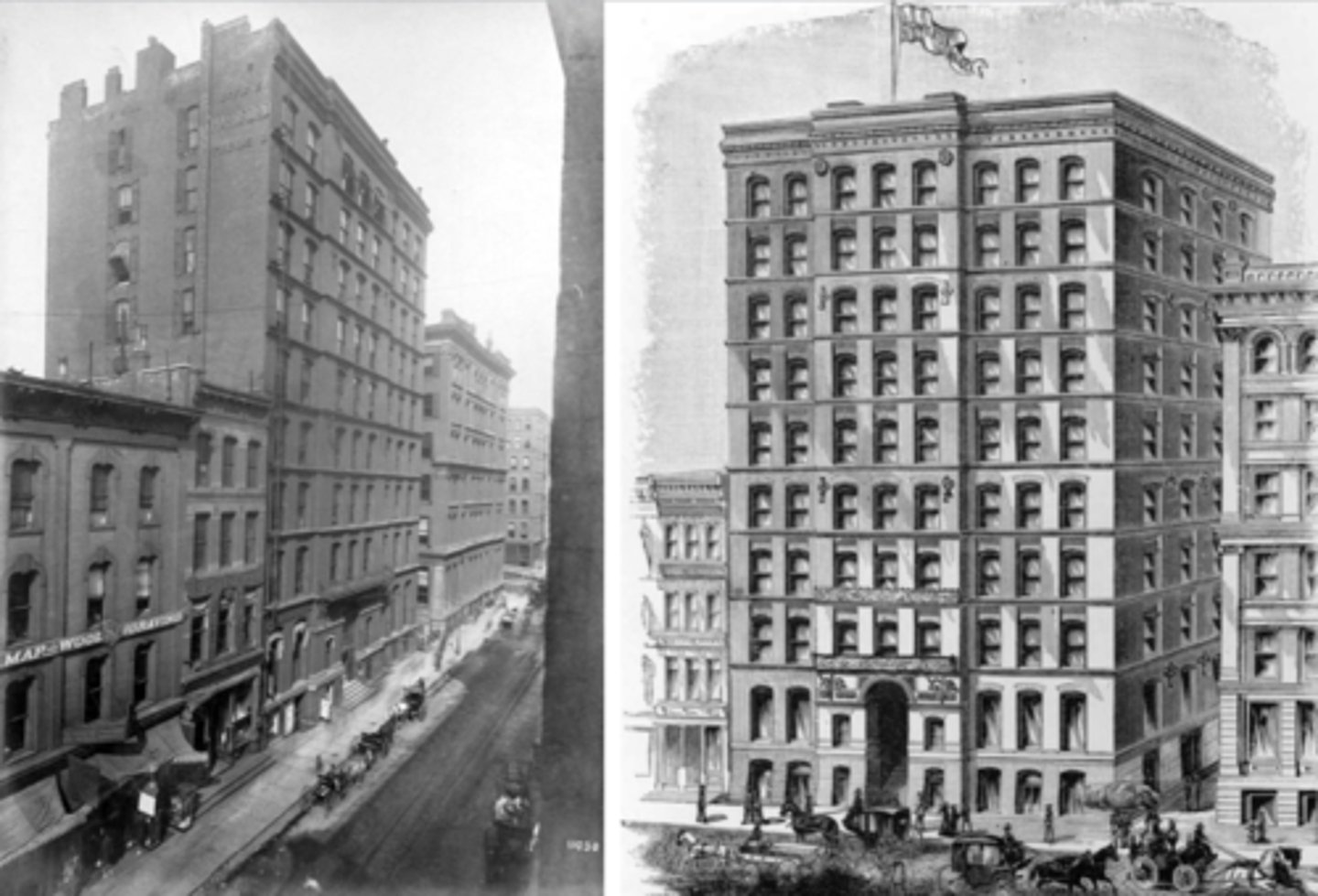

Should openings always be even or odd numbers? Supports?
Openings should always be an odd number and the solid supports should always be an even number
What type of foundation did the Montauk Block introduce and why? What foundation did it replace?
Floating raft foundation helps distribute the building's weight more evenly; replaced isolated pier footings
What advantage did the Montauk Block's foundation provide for the basement design?
It allowed more room for vaults and storage by eliminating the need for multiple deep pier footings
Explain the projection (ressaut) in terms of the Montauk Block?
refers to the small step-like projections in the masonry façade that added depth and emphasized the building's vertical structure before the adoption of true steel-skeleton framing
How tall was Montauk Block?
10 stories high or 130 feet
What building was the first that people referred to as a skyscraper?
Montauk Block
What was Roots' sister-in-law's name, and what did she do?
Harriet Monroe; she wrote a biography of Root
What did the biography of Root say about the Montauk Building?
In one of the stories, it describes how no one likes the Montauk building
Rand-McNally Building
Burnham and Root
Chicago
1888-1889
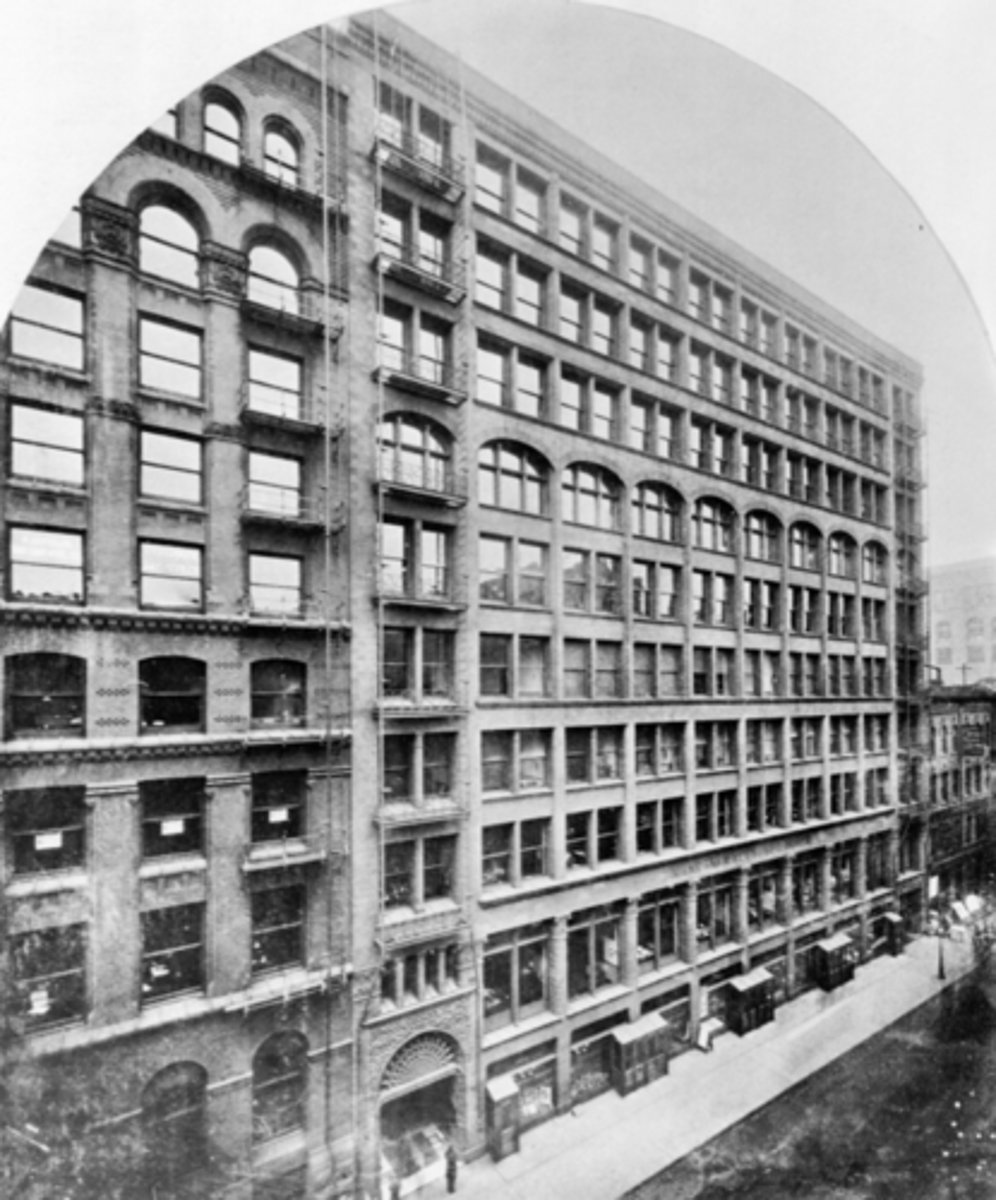

what did the Rand-McNally Building do?
produce maps (sold maps)
Why does the Rand-McNally Building have a blank wall?
it's surrounded by buildings on both sides, leaving one exposed wall blank
what street is Rand-McNally Building on?
La Salle Street
what is on the front and back of Rand-McNally Building? what about the sides?
skeleton-framed and terracotta curtain walls with parti walls on the sides
what happened to the Rand-McNally Building in 1912?
demolished
how tall was Rand-McNally Building and what bldg was it shorter than?
10 stories high or 125 feet, shorter than Rookery
Why is the Rand-McNally Building skeleton frame significant?
It was made entirely of steel, marking the start of the shift from iron to steel in building construction
What was the Rand-McNally Building façade made of and why was it important?
terra cotta and it provided excellent fireproofing and was a lighter/cheaper alternative to stone
Whats unique about the Rand McNally court?
it added two matching cutouts to enlarge its central light court and shared this court with the Insurance Exchange Bldg
What was typical about the Rand McNally Building's office layout?
it had a standard floor plan with double-loaded corridors placed along the parti walls (north & south)
Why did the Rand McNally Building need a cantilevered foundation on the east wall?
The last line of steel columns had to be cantilevered from the first line because the Insurance Building's foundation blocked the placement of the final steel columns
what helped Burnham and Root grow?
The structural developments of Rand McNally Bldg
The Rookery
Burnham and Root
Chicago
1885-1888
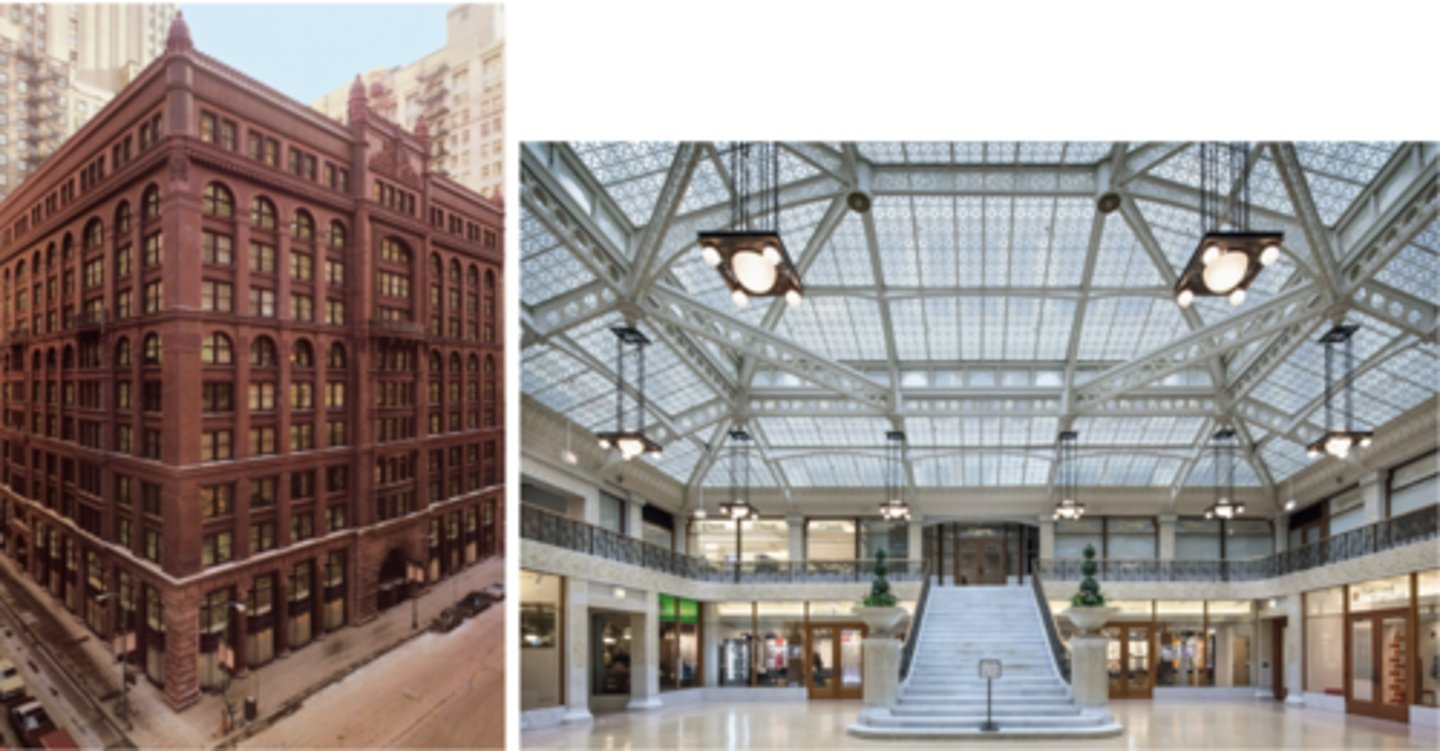

Whats the benefits of The Rookery on a corner?
Corner allows more surfaces to have windows for more light
Does the Rookery have a Skeleton frame?
Some elements of iron framing, but not a skeleton frame
What did the Rookery site used to be?
temporary city hall built around a water tank
How are the office spaces orientated in the Rookery and what do they have?
square donut with double-loaded corridors
Whats the difference between the bottom and upper floors?
Bottom floors constructed of stone while Upper floors constructed of brick with stone details
What style is the Rookery? Why?
Richardsonian Romanesque architecture style; Thick arch on the entrance with voussoirs and ornament, not a lot of vertical walls beneath the springing of the arch
Describe the Rookery entrance and its columns.
two-story cast-iron bay windows with stone columns made from granite on each side of the entrance, with the orders being unique because they don't resemble a specific one
Whats special about the Rookery's lobby?
its a two-story atrium
What architect was asked to help with the design of the Rookery, and which parts did they help with?
Frank Lloyd Wright; he designed the light fixtures in the courtyard and was was invited by the owners to renovate the building after it was built
Who did the restoration for the Rookery and what was added?
McClier architects; another glass roof was added to the top to help with water infiltration
What does the interior light court of the Rookery have?
a ton of iron structure with a brick and terracotta curtain wall
Burnham and Root had what saved/restored, and in what building?
Their offices (the library) were saved and restored in the building called The Rookery
Masonic Temple
Burnham and Root
Chicago
1890-1892

What was important about the time when it was being built?
Started while Monadnock was going up
What was the Masonic Temple later called?
Capitol Building
What's on the lower floors of the Masonic Temple?
theatre, restaurant, etc.
Whats on floors 4-10 in the Masonic Temple?
Originally designed as a vertical shopping mall (eventually turned to offices)
Whats unique about every floor under the 11th in the Masonic Temple?
Each floor had a name like a street name
Whats on floors 11-16 in the Masonic Temple? Why?
offices; Elevator service was considered too slow, so those floors were changed to offices
Whats on floors 17-20 in the Masonic Temple?
belonged to the free masons (owners, clients, developers of building)
What design elements are located on the clubrooms of the Masonic Temple?
Oriels and gables
What is on the roof floor of the Masonic Temple?
roof garden observatory
What's special about the roof of the Masonic Temple, and what was it used for?
it was an atrium roof with a hole that went for 21 stories and was used as a roof garden observatory (Glass skylight on top)
What design elements are on the roof of the Masonic Temple?
Iron cladding in the interior court with stone dormer windows that look like witch hats on the roof
What was in the basement of the Masonic Temple?
Restaurant
Who was the client and what did they want to do with the Masonic Temple?
The free masons; wanted a clubhouse in the
downtown area, then rent the rest of the building out to provide income
When and why was the Masonic Temple demolished?
1939; was not successful economically so it lost money
What frame, material, and qualities did the Masonic Temple have?
skeleton frame skyscraper, built of steel; it has several elevators, it is very tall, and meets all the requirements to be a skyscraper
How many, what type, and how were the elevators arranged in the Masonic Temple?
14 elevators, 2 freight elevators, and the elevators were
arranged in a horseshoe form
What store replaced the Masonic Temple after it was demolished?
2 story Walgreens (drug) store replaced it
What building is known by its street and took inspiration from the Masonic Temple? What qualities did it have? Who were the architects?
La Salle Street (190 S. La Salle Street); the first-floor lobby is very large, with direct implementation of the orders; Johnson/Burgee Architects
How is Arthur Rubloff connected to the Masonic Temple?
he was the one who decided to demolish the building and proposed to replace it with the Walgreens
What are the 4 ways to count the height of buildings?
Bottom to architectural top
Bottom to highest occupiable floor
Bottom to height of the roof
Bottom to height of the tip of the building
Describe W.L.B. Jenny
Born 1832, Fairhaven, Massachusetts
Went to school in the USA, then went to France to study engineering at the Ecole Centrale
Joined the army, became Major Jenney
Gifted engineer
Louis Sullivan worked under him
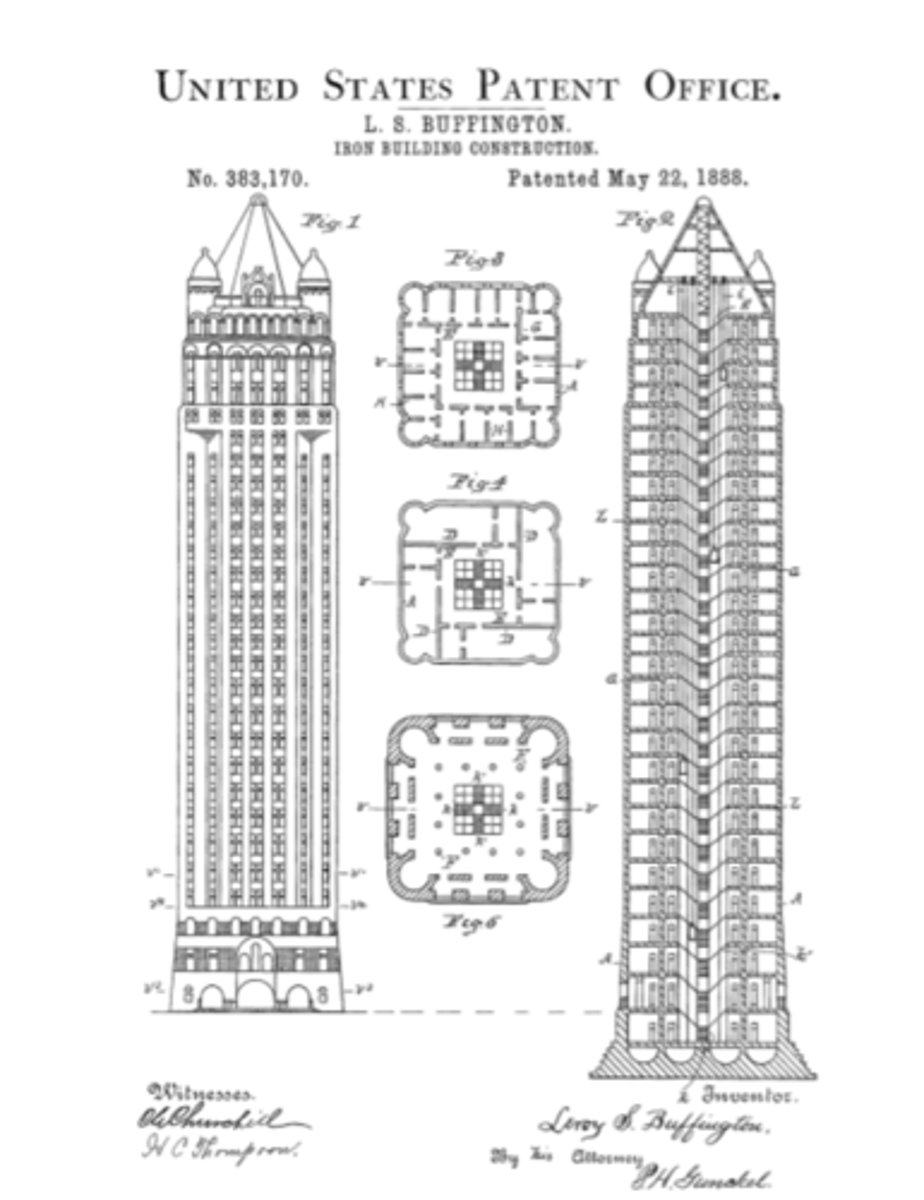
Leroy Buffington Skyscraper Designs of 1888: Patent drawings
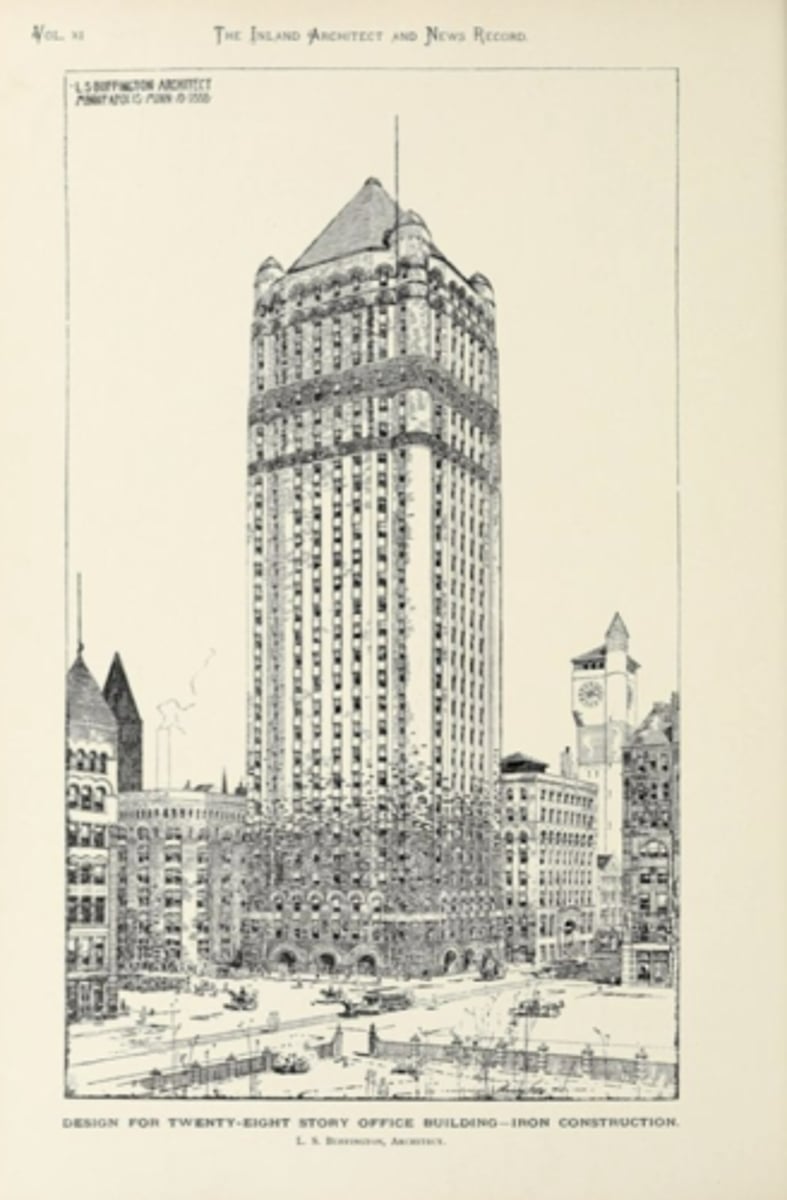
Leroy Buffington Skyscraper Designs of 1888: "Cloudscraper" Project, Harvey Ellis Drawing

Daniel H. Burnham
Born into the Swedenborgian Church
Started working for Carter, Drake, and Wight after failing at getting into Harvard and being a cowboy
John Wellborn Root
Worked for architects in England to get out of the Civil War
Ended up working in NYC for James Renwick
Then worked for J.B. Snook
Then Peter Bonnett Wight
Cover Illustration of Scientific American Magazine had what buildings on the front of it?
Church Spire of Trinity Church
Statue of liberty
Dome of U.S. Capitol
World's First Ferris Wheel
