Lecture 4: Covalent and non-covalent bonding
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
How do atoms with nearly empty/nearly full shells interact together?
ionise easily to form salts
energy gain is from the electrostatic interaction between charged species
ionic bonding
what is ionic bonding
Strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
structure of ionic lattices and why is it stable?
regular arrangements with each positively charged ion surrounded by a negatively charged ion
stability comes from electrostatic forces of attraction
what is covalent bonding?
a shared pair of electrons between atoms to have a full outer shell(valency)
the orbitals of 2 atoms overlap to form a sigma bond
paired
what is bond dissociation energy?
formation of the bond releases energy. Energy required to break the bond = bond dissociation energy (higher = stronger bond)
The greater the orbital overlap, the stronger the bond
what are sigma bonds?
strongest type of covalent bond
form when atomic orbitals overlap
e- can be found anythwere in the orbital as electron density
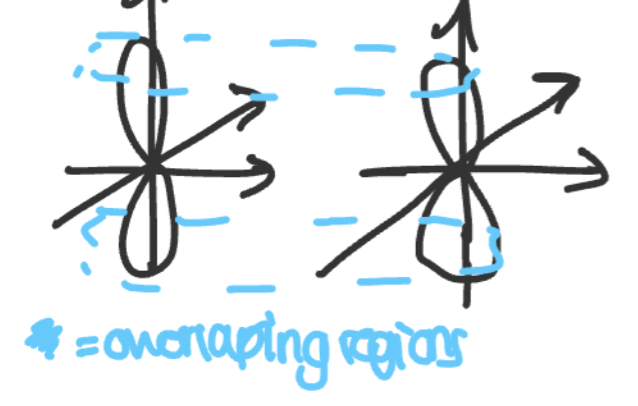
what are pi bonds?
covalent bonds which form due to overlap of 2 orbitals laterally
the node between the lobes has no electron density
the plane has no electron density
why are pi bonds weaker than sigma bonds?
due to less overlap between orbitals due to parallel orientation
what does restricted rotation in pi bonds allow?
stereoisomerism
what are lone pairs on molcules seen as
they take up an orbital e.g.
oxygen is a tetrahedral sp3 shape due to 2 lone pairs
ammonia is a tetrahedral sp3 shape due to one lone pair
what does the lone pair do?
Lone pair generates more repulsion and reduces the bond angle by 2.5
what is electronegativity?
the ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons towards itself in a covalent bond
what are the most electronegative elements?
F, O, N
what does delta plus delta minus acc mean?
in a bond, an electronegative atom pulls the bond more towards itself, its not shared evenly
what is hydrogen bonding?
electrostatic force of attaction between a hydrogen bound to an electronegative element (O,N,F) which is bound to an adjacent atom w lone pairs of electrons
lone pairs are Hydrogen bond __________
acceptors
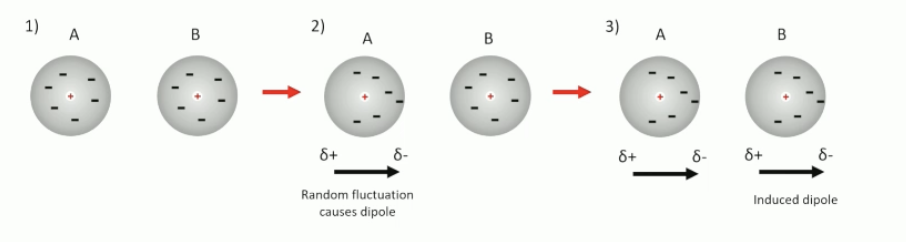
what are VDWs?
large differences in electronegativity which result in permanent dipoles
weaker than H bonding
can induce dipoles in neighbouring molecules
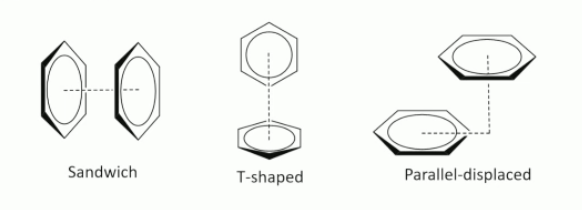
what is pi stacking?
non-covalent interactions between aromatic rings in large molecules e.g proteins
what are the different types of pi stacking?
sandwich(opposite rings)
T-shaped( one perpendicular to another, 90 degrees)
parallel displaced
what are amphiphiles?
molecules containing hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
how do amphiphilic molecules work as micelles?
hydrophilic regions are facing the water and the hydrophobic regions are tucked away inside form the water. it allows transport of oils etc
what is the primary protein structure?
a sequence of AA joined together by peptide bonds
what is the secondary protein structure?
defined by hydrogen bonding patterns. Alpha helix and Beta sheets
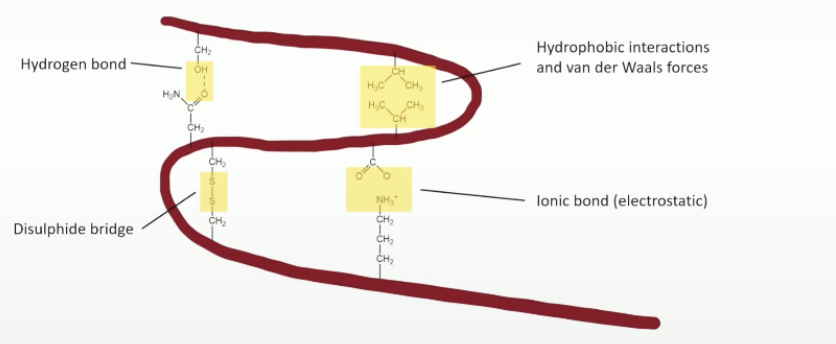
what is the tertiary protein structure
the sheets further bond, the 3d globular structure
involves hydrophobic interactions, salt bridges, hydrigen bonding, disulphide bridges
what is the quaternary structure
2 or more polypeptide chains combining into one functional protein
how do biomolecules fold(protein)
through various interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding.