Physiology Exam 4 Module 13
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
hydrogen
Integration of Homeostatic Controls:
\
•The ***kidneys and the respiratory system*** work together to regulate _______ ion concentrations.
\
•The ***kidneys and the respiratory system*** work together to regulate _______ ion concentrations.
2
New cards
ventilation, lowers
Respiratory can respond quickly-within minutes-to changes in H+ (pH) until the renal system can eliminate the imbalance in a period of hours or days
Ex. Increased arterial H+ stimulates _____ (air moves from atmosphere to alveoli),raises/lowers arterial PCO2, which reduces H+
3
New cards
faster
respiratory fixes faster/slower than renal (filter)
4
New cards
co2, hco3, urine
Sources of Hydrogen Ion (GAIN) \n - Finding pH homeostasis
1. generation of H+ from ___ (respiratory)
2. gain of H+ due to loss of ____ in diarrhea or other non gastric GI fluids (digestive)
3. gain of H+ due to loss of HCO3 in the ____ (urinary)
1. generation of H+ from ___ (respiratory)
2. gain of H+ due to loss of ____ in diarrhea or other non gastric GI fluids (digestive)
3. gain of H+ due to loss of HCO3 in the ____ (urinary)
5
New cards
vomit, hyper
Sources of Hydrogen Ion (LOSS) \n - Finding pH homeostasis
loss of H+ in ____ (digestive)
loss of H+ in urine (urinary)
____ventilation (respiratory
loss of H+ in ____ (digestive)
loss of H+ in urine (urinary)
____ventilation (respiratory
6
New cards
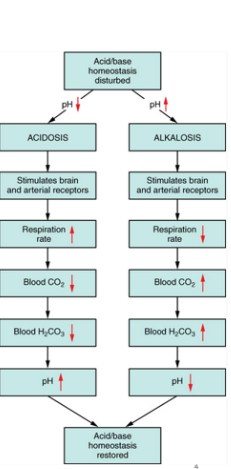
acidosis
metabolic _________
due to processes other than respiration, low blood pH
Examples:
•Lactic acid build-up due to severe exercise
•Diarrhea (This gets rid of bicarbonates-creating more acidic environment)
7
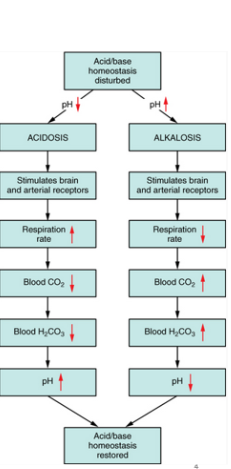
New cards
alkalosis
metabolic __________ due to processes other than respiration, rising blood pH
•Examples:
•Excessive vomiting (HCL)
•Intake of excess bases - antacids
8
New cards
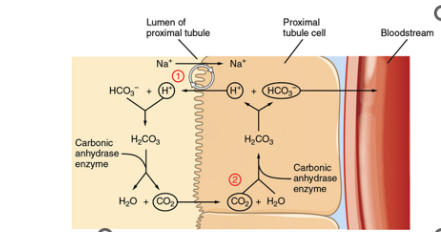
7\.4
•***Extracellular fluid*** should be at a pH of ___
•This pH value corresponds to the concentration of H+
•***Buffering*** reversibly binding H+
•The major extracellular buffer is the ***CO2/HCO3- system.***
•The kidneys eliminate or replenish hydrogen ions from the body by altering plasma bicarbonate concentration.
•For example: Reabsorption of bicarbonate leaves little H+ in the tubules, H+ is secreted into the tubule
9
New cards
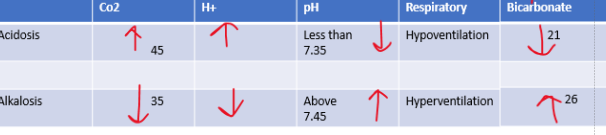
aciddosis, alkalosis
•Range for pH of blood: 7.35 – 7.45
•PCO2 was 40mmHg, Range: 35-45
Bicarbonate range: 21-26 mEq/
\
higher co2 is ___________
higher bicarbonate is _______
•PCO2 was 40mmHg, Range: 35-45
Bicarbonate range: 21-26 mEq/
\
higher co2 is ___________
higher bicarbonate is _______
10
New cards
full, not, partial
Ph is leaning to one category → co2 is in that category → co2 is respiratory = respiratory alk (b/c leaning to alk)
Though ph is leaning it is still considered normal so full compensation
________ compensation = ph is normal
______ → other variable is normal
________ → acid/alka each hold a variable, ph is not normal
11
New cards
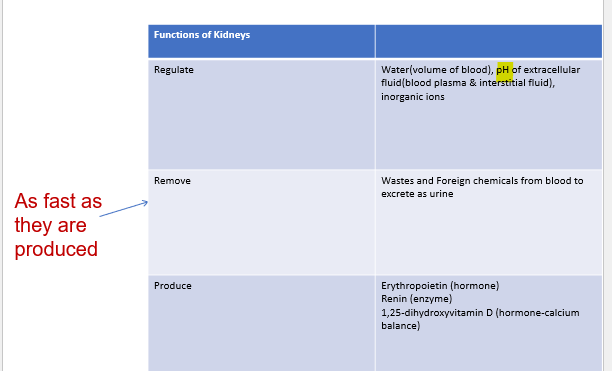
renal
_______ functions: Regulate by increasing or decreasing secretion
12
New cards
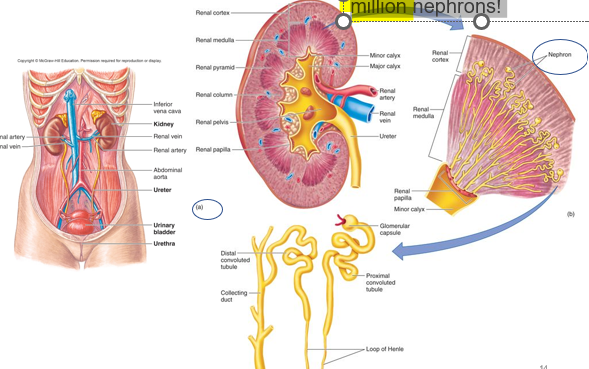
nephrons
Each kidney has approx. 1 million _________!
13
New cards
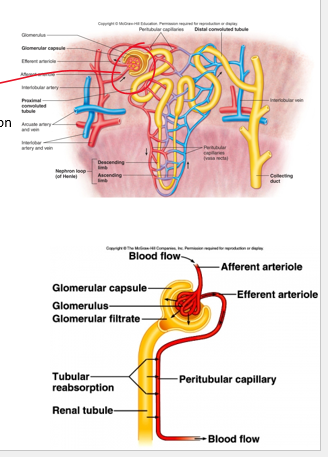
glomerular
renal blood vessels
•Two sets of capillaries
•___________ (ball of capillaries): filtration
14
New cards
peritubular
renal blood vessels
__________ : reabsorption of filtrate to blood supply
__________ : reabsorption of filtrate to blood supply
15
New cards
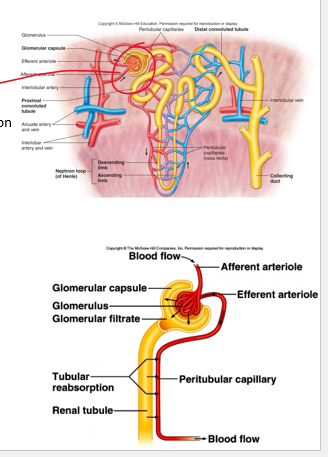
afferent , efferent
•Two sets of arterioles
•______ : where blood flows into glomerular capillaries
•__________ : where blood leaves the glomerulus
16
New cards
glomerulus, pct, loh, dct
order 1. 2. 3. 4.
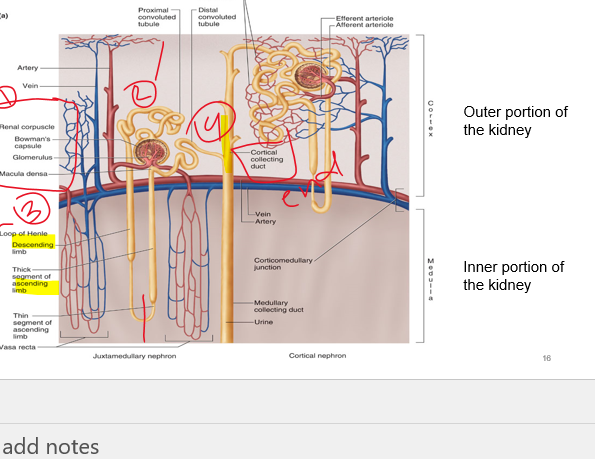
17
New cards
ureters
**__________** transport urine from kidneys to bladder (peristalsis of smooth muscle help move urine)
**Bladder**: store urine until voided from body
**Urethra**: carry urine from bladder to the outside of the body
filtrate: anything that you filter
filtrate (nephron) → urine (ureter)
18
New cards
smooth
•The bladder stores urine until it is excreted from the body by the ***micturition reflex***
•Micturition is initiated by a nervous reflex which causes the ______ muscle of the bladder walls (***detrusor muscle***) to contract and expel the urine. (innervated by neurons)
•Action potentials can exhibit automaticity in response to stretch but stimulation is required for bladder emptying
renal
19
New cards
shut
micturition:
As bladder fills, pressure increases stimulating receptors for control of muscle & sphincters
\
stimulate = contract = _________ (no role)
As bladder fills, pressure increases stimulating receptors for control of muscle & sphincters
\
stimulate = contract = _________ (no role)
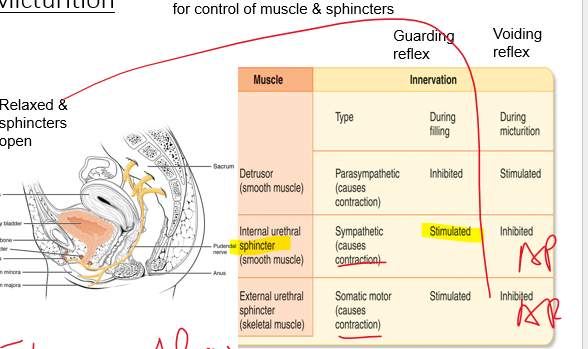
20
New cards
urinating
during voiding reflex, both sphincters are inhibited so we are doing what?
21
New cards
secretion
•A substance may enter tubules through glomerular filtration or tubular **______** (capillary to lumen).
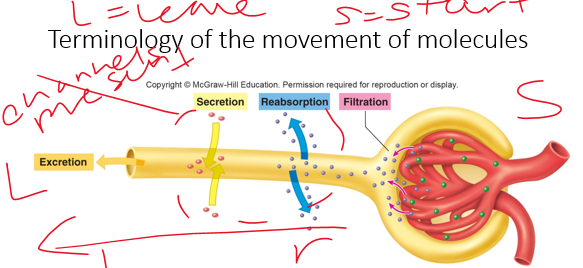
22
New cards
reabsorption
•A substance may leave the tubule through **__________** (passing of substances from the lumen (tubules) to the capillary) or **excretion** (out of the body)
•Reabsorption and secretion require a substance to move across a layer of epithelial cells
•Reabsorption and secretion require a substance to move across a layer of epithelial cells
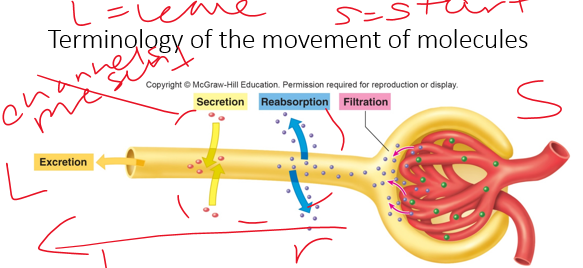
23
New cards
proximal
•Reabsorption occurs constantly in ***__________ and loop of Henle tubules*** and is not subject to hormonal control. Distal and collecting tubules *are* subject to this control.
(more than secretion)
24
New cards
glucose
Products reabsorbed at high rates:
• **______ & most organic nutrients**
•For products like these, the kidneys just help in ***maintaining*** plasma levels of the nutrients
•**Water and many ions**
•Kidneys can aid in ***regulating*** these
•Ex. Water intake decreases, kidneys water reabsorption increases
• **______ & most organic nutrients**
•For products like these, the kidneys just help in ***maintaining*** plasma levels of the nutrients
•**Water and many ions**
•Kidneys can aid in ***regulating*** these
•Ex. Water intake decreases, kidneys water reabsorption increases
25
New cards
reabsorption
•Most ___________ occurs in proximal tubule, 65%
tubule/lumen (nephron) → blood
26
New cards
active
•Sodium reabsorption:
•_______ process
•occurs in all tubular segments
**except** the descending limb
•_______ process
•occurs in all tubular segments
**except** the descending limb
27
New cards
osmosis
•Water reabsorption:
•_______
•dependent upon sodium reabsorption
•_______
•dependent upon sodium reabsorption
28
New cards
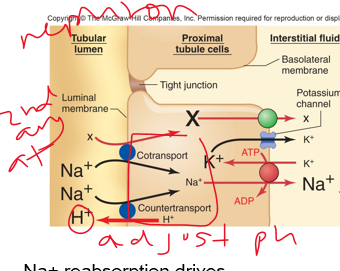
primary
Throughout tubule, Na+ is reabsorbed by ***__________ active transport***
29
New cards
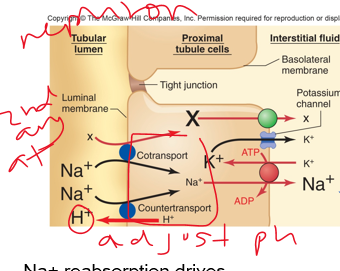
Na+
___ reabsorption drives reabsorption of cotransported substances (such as Cl-) and secretion of H+
30
New cards
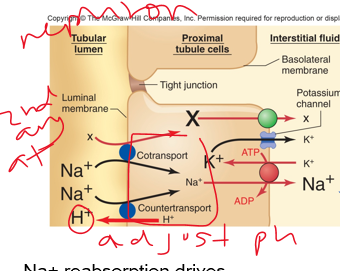
water
Na+ and Cl- combine to form NaCl in the interstitial fluid which will drive the reabsorption of ***________***
(then 2ndary at)
31
New cards
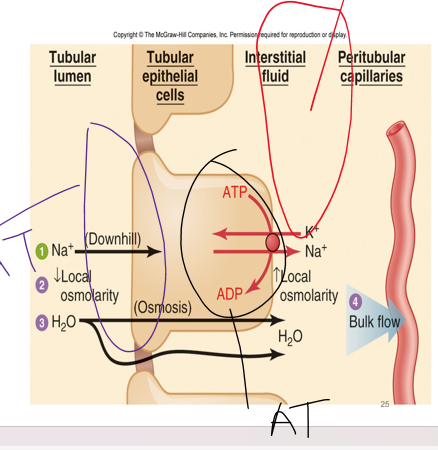
passive
Coupling of Water reabsorption to sodium reabsorption
***_______ process-*** water follows ions as they move
rewatch video for this part? slide 25
32
New cards
impermeable
•Na+ & water in proximal tubule is reabsorbed in the same proportions
\
But in the Loop of Henle…
•The descending loop of Henle is relatively ***__________*** to solutes and freely permeable to water.
33
New cards
permeable
•The ascending limb is ***_________*** to solutes, but not water.
34
New cards
hypertonic
Urine Concentration: The Countercurrent Multiplier System
__Descending loop__: Water is drawn out by osmosis
The interstitial fluid is ***_________*** (water will move to the higher concentration of solutes)
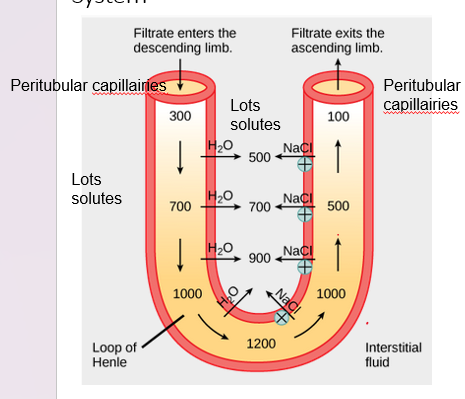
35
New cards
osmolality
at the bottom of the loop, __________ is at its max
hypertonic environment keeps returning
hypertonic environment keeps returning
36
New cards
cl and k
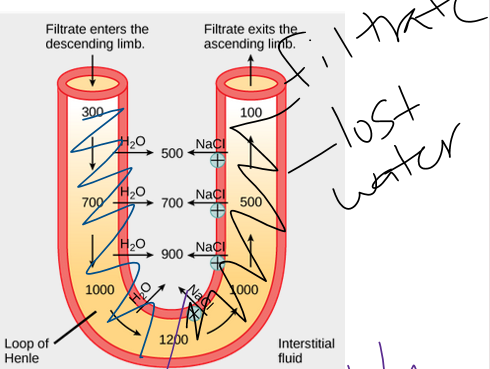
Urine Concentration: The Countercurrent Multiplier System
__Ascending loop__:
•Na+ moves across the epithelial cells of the thick portion of the tubule via the electrochemical gradient, this drives the secondary active transport of and ___
•K+ diffuses back into filtrate, Na+ is pumped into interstitial fluid, Cl- passively follow
urea = solute
37
New cards
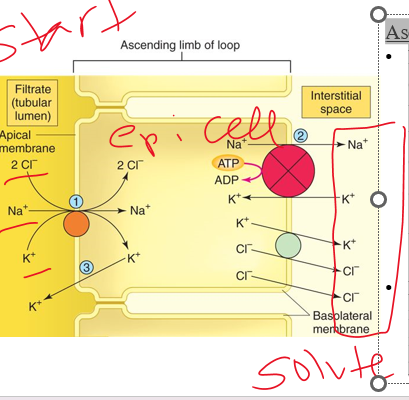
positive
Urine Concentration: The Countercurrent Multiplier System
\
•A ***_______ feedback system*** is generated.
The system sets up a concentration favoring water reabsorption ;
Water leaves and immediately goes to bloodstream (doesn’t stay) that’s why hypertonic (increased osmolality)
\
•A ***_______ feedback system*** is generated.
The system sets up a concentration favoring water reabsorption ;
Water leaves and immediately goes to bloodstream (doesn’t stay) that’s why hypertonic (increased osmolality)
38
New cards
atp pumps
•Max concentration (the end to the positive feedback) is determined by the **number of** __**_______**__
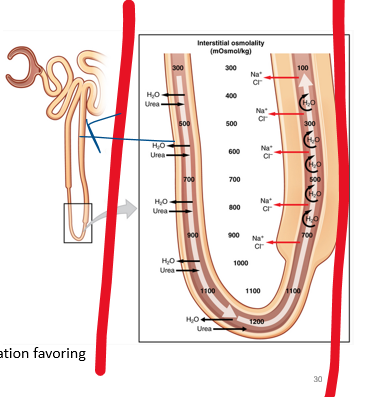
39
New cards
channels
Regulation of reabsorption and/or secretion of many substances is achieved by regulating the activity or concentrations of the appropriate ***transport proteins or ion ________*** .
if channels aren’t present, nothing moves
40
New cards
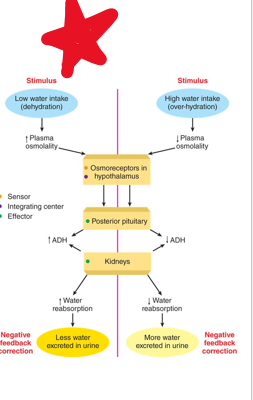
vasopressin, ADH
Na + H2O
Must ingest these substances to replace your loss, kidneys will minimize excretion until you do so
•Thirst is triggered by ***increase in plasma osmolality and decrease in ECF*** (extracellular fluid)
•These are the two factors that stimulate ***______ (?)***
•More vasopressin - more aquaporins - more water retained - less water excreted
•Most mammals like Salt-we consume more than we need
41
New cards
hormones
______ in charge of binding and inserting more channels
42
New cards
proximal
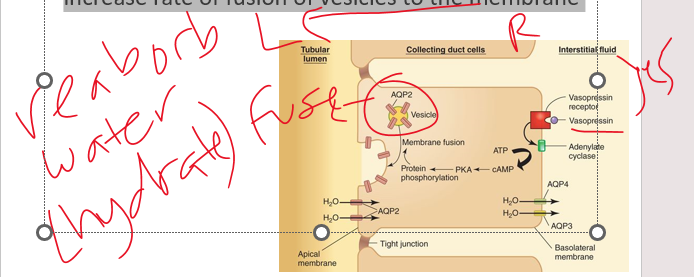
•Permeability varies depending on location in tubule and presence of ***aquaporins***
•***______ tubule*** location for highest water permeability (ie highest # of aquaporins)
•Vasopressin stimulates presence of aquaporins in the collecting ducts, without it permeability is low
43
New cards
diuresis
water ____
•large amounts of water in urine due to low vasopressin
•large amounts of water in urine due to low vasopressin
44
New cards
ach
vasopressin
•After vasopressin locks in, a secondary messenger activates an enzyme that causes proteins to increase rate of fusion of vesicles to the membrane
if we go L
•After vasopressin locks in, a secondary messenger activates an enzyme that causes proteins to increase rate of fusion of vesicles to the membrane
if we go L
45
New cards
K+
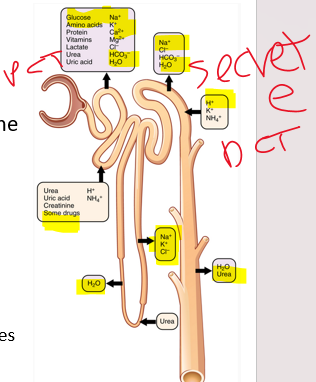
what is secreted into the renal tubules
•Substances such as hydrogen ion, potassium, and organic anions move from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular lumen.
•Tubular secretion is an important mechanism for:
1\.Excess __
2\. controlling blood ph (H+)
3\.Disposing of drugs and drug metabolites
\*this is why most drug tests are urine tests
•Substances such as hydrogen ion, potassium, and organic anions move from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular lumen.
•Tubular secretion is an important mechanism for:
1\.Excess __
2\. controlling blood ph (H+)
3\.Disposing of drugs and drug metabolites
\*this is why most drug tests are urine tests
46
New cards
okay
How do I know if the cause is metabolic (renal) or respiratory
1\.Look at ph (ph reflects H+ concentrations) both systems influence ph
2\.Look for if the H+ changes (ph) aligns to CO2 or HCO3 changes outside of normal. When ph aligns to one, that variable is causing the changes (both leaning acidic, bicarbonate is responsible for ph changes à metapholic acidosis)
3\.Since both systems influence pH, if one causes a condition then the other should fix (compensate)
Co2 not regulated by renal system (respiratory only) , bicarbonate is not respiratory