BUSINESS 3.6 - HR Management
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is human resource management?
activities relating to the labour of workers
What are the 6 human resource objectives?
employee engagement, talent development, training, diversity, aligning values, number/location/skill of employees
Why do managers value human resource objectives?
enhanced reputation, improves employee performance, increases customer satisfaction
What are internal influences on HR objectives?
overall objectives, attitudes of managers, type of product
What are external factors of HR objectives?
PESTLE
How do managers achieve HR objectives?
hard HR/soft HR approaches
What is hard HR management?
employees being treated as a resource and earning low pay
What is soft HR management?
employees treated as valuable assets
What is labour turnover?
the proportion of the workforce that leave within a certain time period
What is the formula for labour turnover?
number of leavers/average number of employees x 100
What are disadvantages of high labour turnover?
negative brand image, increased training costs, decreased customer service
Why is high labour turnover not always bad?
firms with seasonal demand/ firms with younger/temporary workers will have a high labour turnover
What is labour productivity?
amount of output produced by a certain amount of workers in a certain time period
why does labour productivity matter?
business performs better, higher profitability, lower unit costs, competitive advantage
What are employee costs?
how much is paid for staff
How do you calculate employee costs as a percentage of turnover?
employee costs/revenue x 100
What are influences on employee costs as a percentage of turnover?
productivity, wages, other employment costs, capacity utilisation
What is retention?
the proportion of the workforce that stays in their jobs over a certain time period
What is the formula for retention?
workers staying/total workforce x 100
Why does labour retention matter?
lower costs, increased motivation, better customer service
What is HR planning?
using staff to meet corporate objectives, working out how to use staff to achieve objectives
How do HR managers use data?
tracking absence, performance management systems
What is job design?
the way tasks and responsibilities are organised, and the relationship between job holders, subordinates, superiors and colleagues
What is a subordinate?
a lower ranking level individual
What is a superior?
a higher ranking individual
What does job design involve?
job enlargement, job rotation, job enrichment, empowerment
What is job enlargement?
giving employees extra tasks
What is job rotation?
engaging in different roles each day
What is job enrichment?
giving employees more challenging tasks
What are influences on job design?
objectives, employee performance, legal issues, customer needs, (training) resources
What is an organisational structure?
the way a business is arranged to carry out activities
What are the types of organisational structures?
functional, product based, regional, matrix structure
What is a functional structure?
businesses being organised into departments and carrying out different functions
What is a product based structure?
businesses being organised into departments with a specific function
What is a regional structure?
businesses seperated by geographic locations
What is a matrix structure?
employees reporting back to multiple managers
What are influences on organisational design?
authority, span of control, hierarchy, delegation, centralisation and decentralisation
What is centralisation?
decisions being made by senior management
What is decentralisation?
decisions being made by employees
What is a span of control?
the amount of subordinates a manager has responsibility for
Why might businesses change their organisational design?
objectives, reduced costs, competition
What is the HR flow?
The employee’s life cycle in an organisation
What does the HR flow include?
HR plan, recruitment, training, redeployment, redundancy
What is redoployment?
businesses allocating workers a different job
What are the advantages of motivation and employee engagement?
increased productivity, increased reputation, improved customer service
What was taylor’s scientific management theory?
believed that individuals are only motivated by money
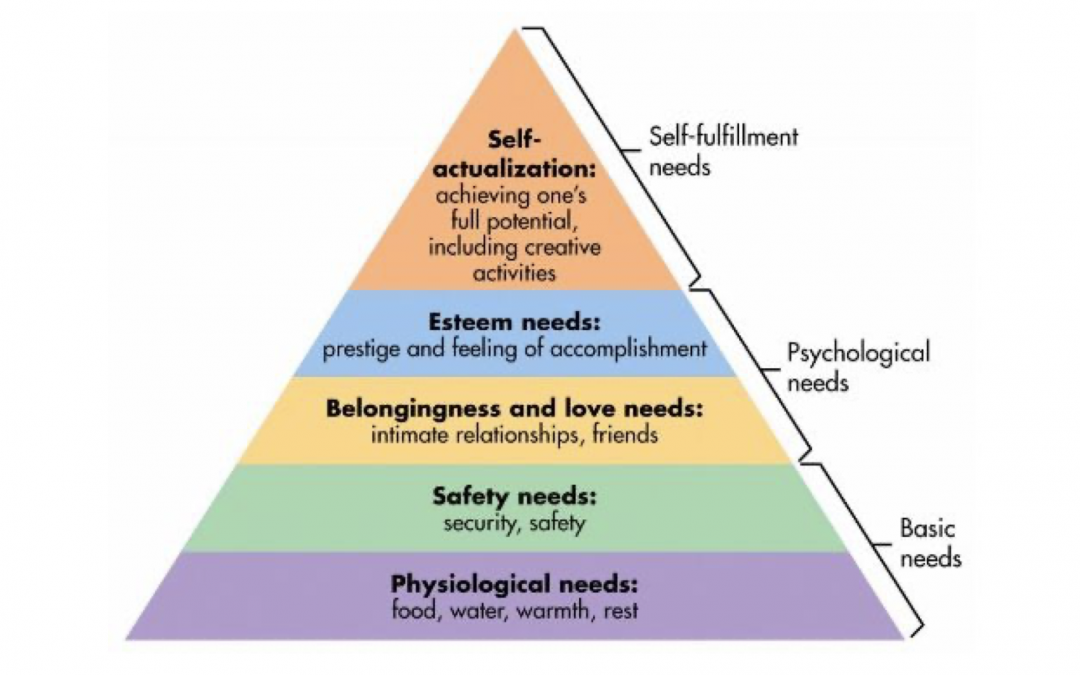
What was maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
belief that individuals need to fulfil all levels of hierarchy to increase motivation
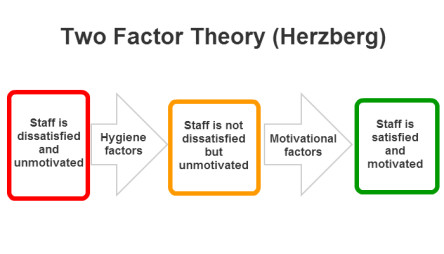
What was herzberg’s two factor theory?
belief that hygiene and motivation factors influence employee motivation
What are examples of hygiene factors?
wages, working conditions
What are examples of motivation factors?
recognition, promotion
What are financial methods of motivation?
piece rate, commission, salary scheme, performance related pay (PRP)
What is piece rate?
employees being paid for the amount they produce
What are the advantages of piece rate?
increases productivity, increases motivation
What are the disadvantages of piece rate?
may decrease quality of products
What is a salary scheme?
pension benefits (income after retirement)
What is PRP?
employees only getting paid if targets are reached
What are non-fanancial methods of motivation?
delegation, empowerment, consultation, team working, flexible working, job enrichment, job rotation
What is delegation
giving someone else the authority to carry out a task
What are advantages of delegation?
increases motivation
What are disadvantages of delegation?
can cause stress on workers
What is empowerment?
giving employees greater control over work
What is consultation?
asking for workers’ opinions
What is team working?
giving small teams of staff tasks to complete
What is flexible working?
workers can adjust their working hours
What are the types of employee representation methods?
trade unions, work councils, work committees, staff associations
What is a trade union?
organisation of employees working to protect their rights
What role do unions play in labour markets?
collective bargaining, lobbying and advocacy, provision of support and advice, education and training
What is lobbying?
workers influencing government to to support a policy/campaign
What are the impacts of unions?
power of group protest (strikes), partnerships between unions and firms
What is a work council?
an organisation representing shop floor employees which operates independently of trade unions
What do work councils do?
represent employee views in decision making
What is the difference between involvement and participation?
involvement is how much employees contribute to business choices, participation is the way employees are involved in business choices
What are legal issues in participation and involvement?
firms need to consult employees if 20 or more staff are redundant, or if the business is being bought
What are influences on employee involvement?
leadership styles, objectives, nature of work/employees, tradition, legal factors
How are employee relations managed?
no-strike agreements, single union agreements, external organisations
How are industrial disputes resolved?
arbitration, conciliation, tribunals
What is arbitration?
decision on how to solve worker disputes
What is conciliation?
individual helping both parties come to a mutual agreement
What is a tribunal?
specialist resolving worker conflict
What are benefits of good industrial relations?
better brand image, lower costs, motivated and productive workers, more competitive