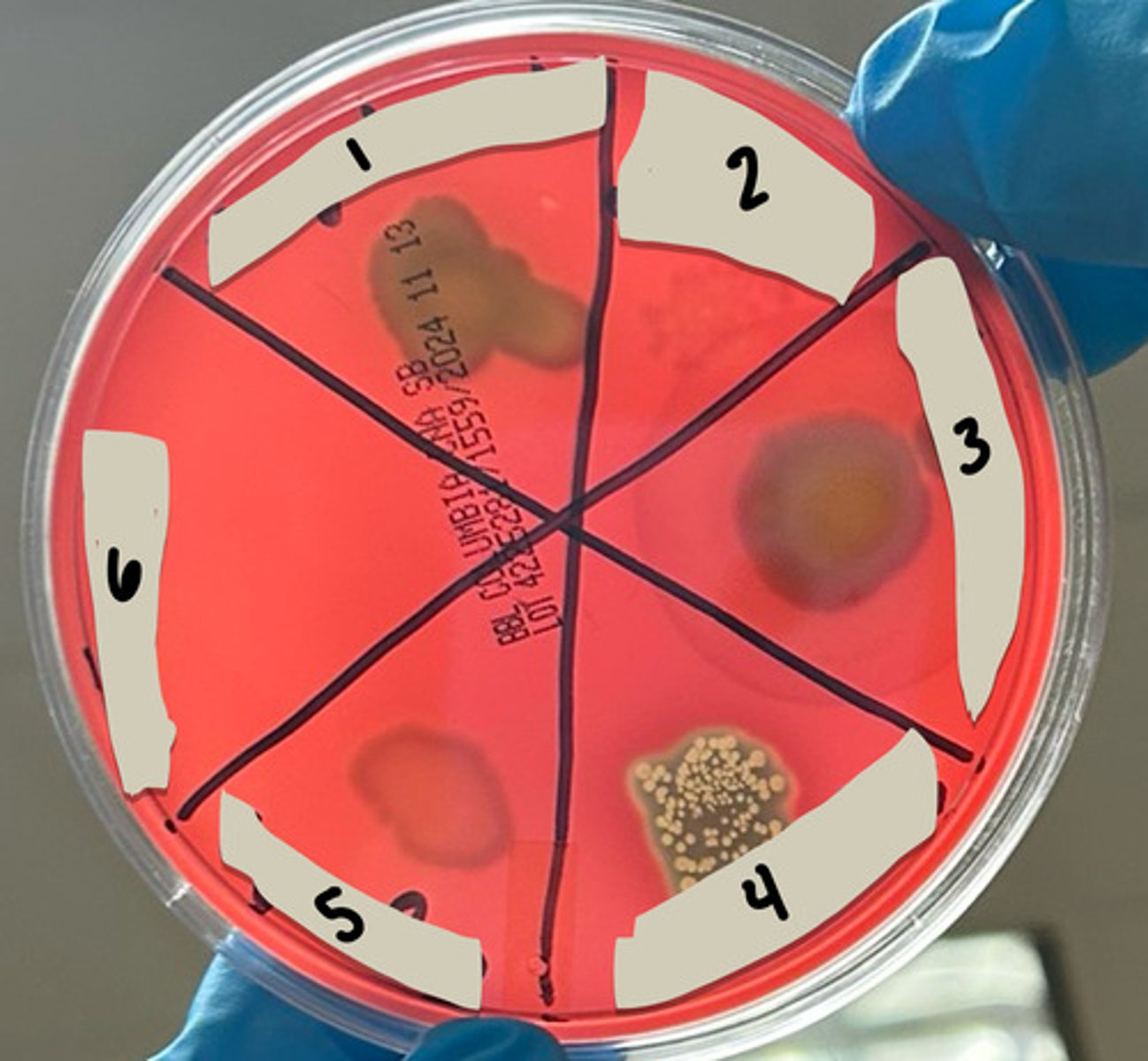
4-2: Columbia CNA with 5% SBA
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
- Colistin and Nalidixic acid with sheep blood agar
- CNA is selection, SBA is differentiation
state what CNA with SBA means; which part is selection and which is differentiation
the two antibiotics (colistin and nalidixic acid) synergize to inhibit gram- growth (selects for gram+ growth)
what does CNA do
- colistin attacks plasma membrane integrity
- nalidixic acid blocks DNA replication
how does CNA inhibit gram- growth
Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci
state 3 examples of gram+ microbes that grow on CNA/SBA
tests for the presence of hemolysin (a virulence factor)
describe how SBA is used for differentiation
- alpha hemolysis: partial hemolysis (looks green)
- beta hemolysis: complete hemolysis (looks clear)
- gamma-hemolysis: non-hemolytic (no effect)
alpha and beta hemolysis indicate a presence of hemolysin
state and describe the 3 types of hemolysis seen on SBA
- would grow because its gram+
- beta hemolytic because it does complete hemolysis (looks clear)
describe what Streptococcus pyogenes would do on CNA/SBA
- would grow because its gram+
- either alpha or gamme hemolytic because strains can either do partial hemolysis or no hemolysis (look green or have no effect)
describe what Streptococcus gallolyticus would do on CNA/SBA
- would grow because its gram+
- gamma hemolytic because it cannot do hemolysis (no effect)
describe what Staphylococcus epidermidis would do on CNA/SBA
- would not grow because its gram-
describe what E. coli would do on CNA/SBA
1. Staphylococcus epidermidis (alpha hemolysis)
2. Streptococcus gallolyticus (gamma hemolysis)
3. Staphylococcus aureus (beta hemolysis)
4. Streptococcus pyogenes (beta hemolysis)
5. Enterococcus faecalis (gamma hemolysis)
6. Escherichia coli (non-hemolytic)
state what microbe is in each section based on the reaction