Chem 102 Exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
Organic Chemistry
Hydrocarbons & their derivatives
2
New cards
Inorganic Chemistry
Everything other than hydrocarbons
3
New cards
Saturated hydrocarbon
Single bonds
4
New cards
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Double or triple bonds or both
5
New cards
Hydrocarbon derivatives
Hydrocarbon + one additional element
6
New cards
Cyclic
continuous chain of hydrocarbons
7
New cards
Acyclic
No ring/continuous structure
8
New cards
Alkane formula
CnH2n+2
9
New cards
Alkene forumla
CnH2n
10
New cards
Alkyne forumla
CnH2n-2
11
New cards
Constitutional isomers
isomers with different connectivity of atoms
12
New cards
Stereoisomers
same molecular and structural formula but different orientation
13
New cards
Cis
same side
14
New cards
Trans
opposite side
15
New cards
Physical properties of cycloalkanes
* nonpolar
* denisty: lighter than water
* denisty: lighter than water
16
New cards
Does boiling point increase or decrease with increase in chain length
Increase
17
New cards
Combustion
reaction with oxygen that produces heat and light/ CO2, H2O and energy
18
New cards
Halogenation
Substitution reaction
* Halogens replace hydrogens
* Halogens replace hydrogens
19
New cards
Halogenated alkanes name
Haloalkens/ Alkyl Halides
20
New cards
Halogenated cycloalkanes name
Halocycloalknes/ cycloalkyl halides
21
New cards
Physical properties of Halogenated Alkanes
* Density: heavier than water
* Polar
* Limited water solubility
* Polar
* Limited water solubility
22
New cards
Functional group
reactive end of a molecule
23
New cards
2 simplest alkenes
Propene & ethene
24
New cards
Shape of alkanes
tetrahedral
25
New cards
Shape of alkenes
trigonal planar
26
New cards
Simplest cycloalkene
cyclopropene
27
New cards
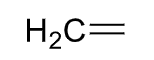
Methylene
\
28
New cards
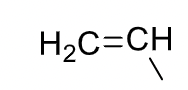
Vinyl
29
New cards
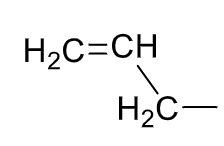
Allyl
30
New cards
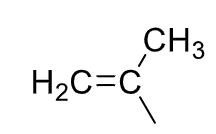
Isopropenyl
31
New cards
Positional isomers
(constitutional)
* same carbon chain arrangement but different C=C position
* same carbon chain arrangement but different C=C position
32
New cards
Skeletal isomers
(constitutional)
* different carbon chain arrangements
* different carbon chain arrangements
33
New cards
Pheromones
Alkenes or alkane derivatives
34
New cards
Terpenes
isoprene structural units
35
New cards
Isoprene
2-methylbutane
36
New cards
Physical properties of alkenes
* Gases = 2-4 Carbons
* Liquids = 5-17 Carbons
* Solids = >17 Carbons
* Liquids = 5-17 Carbons
* Solids = >17 Carbons
37
New cards
Dehydrogenation
Taking out 2 H’s
38
New cards
Hydrogenation
Adding 2 H’s
39
New cards
Halogenation
Halogen atom is added (Example: Br2)
40
New cards
Hydration
Addition of Water
* H2SO4 = catalyst
* H2SO4 = catalyst
41
New cards
Hydrohalogenation
Addition of Hydrogen and a Halogen (such as Cl)
42
New cards
Marovnikovs’s Rule
The hydrogen atom of HQ attaches to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms
43
New cards
Polymers
Macromolecules made up of repeating subunits (monomers)
44
New cards
Copolymer
polymer in which 2 different monomers are present
45
New cards
Physical properties of Alkynes
* nonpolar
* insoluble in water
* Boiling point increases with molecular mass
* Gases when low molecular mass
* insoluble in water
* Boiling point increases with molecular mass
* Gases when low molecular mass
46
New cards
Aromatic hydrocarbons
6 Carbon ring with alternation single and double bonds
47
New cards
Toluene (benzene)
CH3 on top of benzene
48
New cards
Styrene (benzene)
CH=CH2 on top of benzene
49
New cards
Phenol (benzene)
OH on top of benzene
50
New cards
Aniline (benzene)
NH2 on top of benzene
51
New cards
Ortho
1,2
52
New cards
Meta
1,3
53
New cards
Para
1,4
54
New cards
Physical properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
* nonpolar
* insoluble in water
* flammable (combustion)
\
* insoluble in water
* flammable (combustion)
\
55
New cards
What are the two types of bonds Oxygens can make?
Two single bonds
or
One double bond
or
One double bond
56
New cards
Alcohol
An organic compound in which an -OH group is bonded to a saturated carbon atom
57
New cards
Polyhydroxy alcohols
diol at the end
58
New cards
Methanol
Simplest alcohol
* CH3OH
* Good solvent
* CH3OH
* Good solvent
59
New cards
Ethanol
Drinking alcohol
* CH3CH2OH
* Formation of sugars
* Hydration of Ethene
* CH3CH2OH
* Formation of sugars
* Hydration of Ethene
60
New cards
Isopropanol
Rubbing alcohol
* (CH3)2CHOH
* rapid evaporation
* Really bad if ingested
* (CH3)2CHOH
* rapid evaporation
* Really bad if ingested
61
New cards
Glycols
\-Diols with -OH groups on adjacent carbon atoms
* high boiling point
* soluble in water
* high boiling point
* soluble in water
62
New cards
Triol
three -OH groups attached on 3 adjacent carbon atoms
63
New cards
Physical Properties of alcohols
* polar and nonpolar
* Increased carbon chain length = decrease in polarity, increase in boiling point, and decrease in solubility
* Increased carbon chain length = decrease in polarity, increase in boiling point, and decrease in solubility