AP Psychology Unit 0; Scientific Foundations of Psychology
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yay get hypeee
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms

Psychodynamic Perspective
Our unconscious mind draws conclusions from the past (specifically negative childhood memories) influencing our behaviors.

Behavioral Perspective
All behavior is learned. Conditioning, almost influenced by a reward system. Observable traits.

Social-Cultural Perspective
Behavior is based on someone’s social and cultural norms, or what they think is normal.
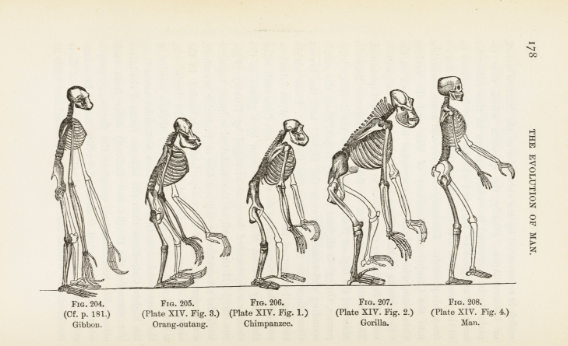
Evolutionary Perspective
Behavior is intrinsically motivated by survival instincts. Survival of the fittest of personality traits and behaviors.
Biological Perspective
Human behavior is explained by biological factors such as genetics, hormones, and neurotransmitters
Humanistic Perspective
Behavior is explained by what people do to meet their individual needs and reach their full potential. Everyone has different needs, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow.
Cognitive Perspective
To understand someone’s actions you must understand their predispositions and how they perceive/interpret actions. Largely based on memory, Interpretation, and perception.
Biopsychosocial approach
An integrate approach incorporating biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis. Ex: Similar style to others because it is learned when we see others wear it, culturally/socially normal, and we don’t want to stick out (unconscious mind wants others to like yourself).
Cultural Norms
Shared expectations, rules, beliefs, values, and behaviors that are considered typical in a specific group.
Confirmation Bias
Ignoring what doesn’t go along with what you believe, tendency to search for information supporting our preconceptions etc.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that we would have fore seen it. I knew it all along thing, after learning something our brains make connections.
Overconfidence
Tendency to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements.
Experimental
Research method involving manipulation of variables to observe effects. Random assignment, experiment, control, variables.
Key words of experiment
Experiment, Variables, Control, Manipulate, Random Assignment
Case Study (non-experimental)
A descriptive technique where an individual or group is studied in the hope of revealing universal principles. Specifically used when manipulation of the thing being tested is unethical or impossible. Ex; pole in head guy
Correlation (non-experimental)
A measure of the extent two variables influence each other, how well one predicts the other. Uncontrolled, statistical relation.
Meta-Analysis
Combining multiple studies to form one conclusion.
Key words of Meta-Analysis
Combine, conclusion, multiple studies
Naturalistic Observation (non-experimental)
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without manipulation or control. ABSOLUTELY NO OUTSIDE INFLUENCE.
8 Psychology Perspectives
Humanistic, Behavioral, Biological, Evolutionary, Cognitive, Psychodynamic, Social-Cultural, Biopsychosocial
4 Types of Bias
Cultural Norms, Confirmation Bias, Hindsight Bias, Overconfidence
5 Research Methodologies
Experimental, Case Study, Correlation, Meta Analysis, Naturalistic Observation
Falsifiable
A hypothesis must be able to be proven false through evidence or experimentation. Must be a possible scenario that could prove the theory incorrect. Not falsifiable, cannot be rigorously tested or scientifically supported.
Operational Definitions
Carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study.
Experimental Group
Group exposed to treatment, version of independent variable or independent variable.
Control Group
Group not exposed to treatment, contrasts to serve as comparison to experimental group
Confounding Variables
Cannot be controlled but could influence results
Single Blind
Participants unaware of the experimental conditions under which they are operating
Double Blind
Pateints and experimenters unaware of experimental conditions, especially strong with drug evaluation, eliminates expectation bias
Sample
Subset of population selected for study with aim of making inferences to the population, important to assure representative/generalizability of group.
Population
All those eligible for the sample
Representative Sample
Selection of study units from a larger group in an unbiased way to accurately reflect total population. Focused on quality of people (making sure representative)
Random Sampling
So that all in representative sample have equal probability of being chosen for sample
Sampling Bias
Systematic/directional error, choice of units affects validity of experiment due to things like convenience sampling or choosing a group with all the same preexisting differences.
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, diff from random sampling as it is only in experiments.
Peer Review
Evaluation of scientific and academic work by other experts in same field
Variables in NON experimental methodology
not controlled
factors contributing to result
Institutional Review Board
Committee named by an agency or institution to review research proposals for ethical acceptability. Like the UN of ethical research
Informed consent
A participant knows enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate or not, legally binding.
Informed Assent
Obtaining agreement from participants not legally able to provide informed consent by providing them with information about study to comprehend what their participation involves, potential risks, etc.
Protection from Harm
Ethical principle requiring researchers to protect and create safeguards to avoid any kind of harm.
Confidentiality
Ethical principle requiring a limitation on the disclosure of a participant’s identifiable information.
Deception
Distortion or withholding of fact with the purpose of misleading. Not disclosed true purpose of experiment, etc.
Research Confederates
Aides of experimenter, like moles of an experiment, their behavior is rehearsed and they pose as a participant.
Debriefing
At the end of an experiment, providing participants with fuller explanation, including any deceptions and the purpose.