Part 6: Care of Site Specific Side Effects: VI. Bone Marrow Depression
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Bone Marrow Depression aka
Bone Marrow Suppression
Myelosuppression (fyi: myel/o = marrow)
/
Bone Marrow Depression can start at doses of ____
20 Gy and above
I got 2 Bones
Hematopoietic System includes:
bone marrow
circulating blood
lymph nodes
thymus
spleen
2 types of bone marrow
red marrow
yellow marrow
term. Yellow Marrow
def. consists primarily of fat cells BUT does not supply mature cells to the circulation (so not very important for our purposes)
term. red marrow
def. supplies mature cells to the circulating blood
What is the primary effect of radiation on bone marrow?
A decrease in the # of stem cells
term. Stem Cell
def.
Immature cells from which a variety of mature cells can arise
A precursor cell that can develop into one of many mature cells
BMD is generally not a problem unless what?
25% of Red (active) Marrow is in the tx field
or
RTT is combined with chemo
% of of Red Bone marrow that gets treated in the following fields
Skull
Ribs/ Sternum
Pelvic Bones
Vertebrae
Scapula
Proximal Femur & Humerus
Pelvic Bones- 30%
Vertebrae-25%
Ribs/Sternum-20%
Skull 10%
Scapula 10%
Proximal Femur & Humerus 5%
Although BMD is not usually a big problem unless the the RTT is combined with chemo___ is recommended as a wise precaution
weekly blood counts
term. Neutropenia
def. a decrease neutrophil count
Mature Blood cells in order of descending radiosensitivity ( most sensitive to least)
Little Monkeys Play Everywhere
Lymphocytes
White Cells
Platelets
Erythrocytes
Why are RBC (erythrocytes) not very radiosensitive?
They have a slow mitotic rate
Immature RBCs are called
erythroblasts
Are erythroblasts radiosensitive or radioresistant?
they are even more radiosensitive than any mature Mature Blood Cell
(Mature/ Stem) Cells are more radiosensitive
Stem Cells
True or False: Any stem cell is going to be VERY radiosenstive
True
What is the most radiosensitive Blood Stem Cell?
Erythroblast
term. Anemia
Def. ↓ in the # of RBC, HCT, HGB
a decrease in the number of Red Blood Cells, Hematocrit, and Hemoglobin
What is the most common symptom of anemia?
Fatigue
Why is fatigue a common symptom of anemia?
It is caused by the lack of circulating oxygen in the blood cell
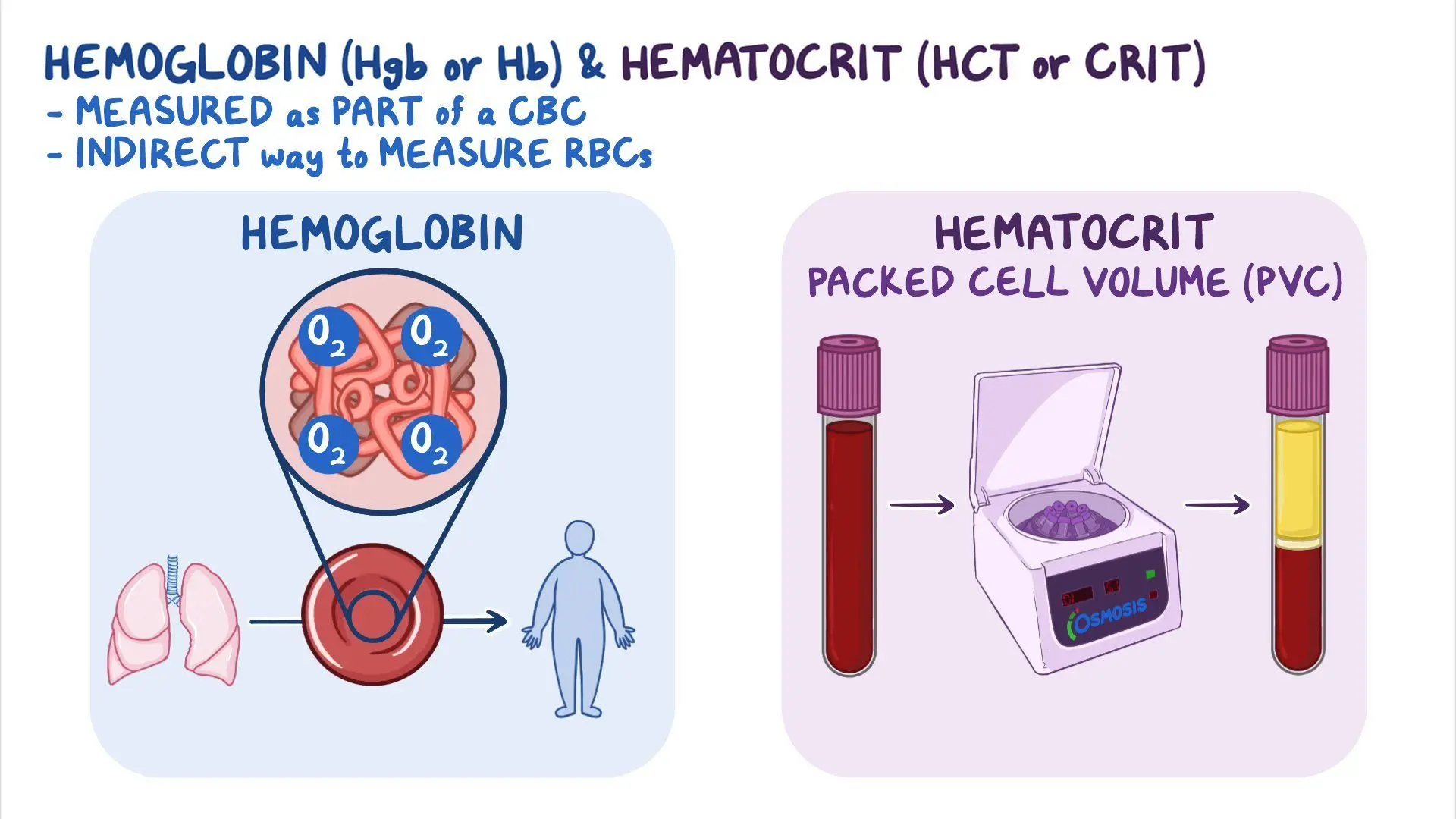
Interventions for anemia?
Maintain adequate hydration