sensation and perception
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
sensation
detection of raw, basic information from the outside world
perception
interpretation and organization of transmitted information into meaningful objects and concepts
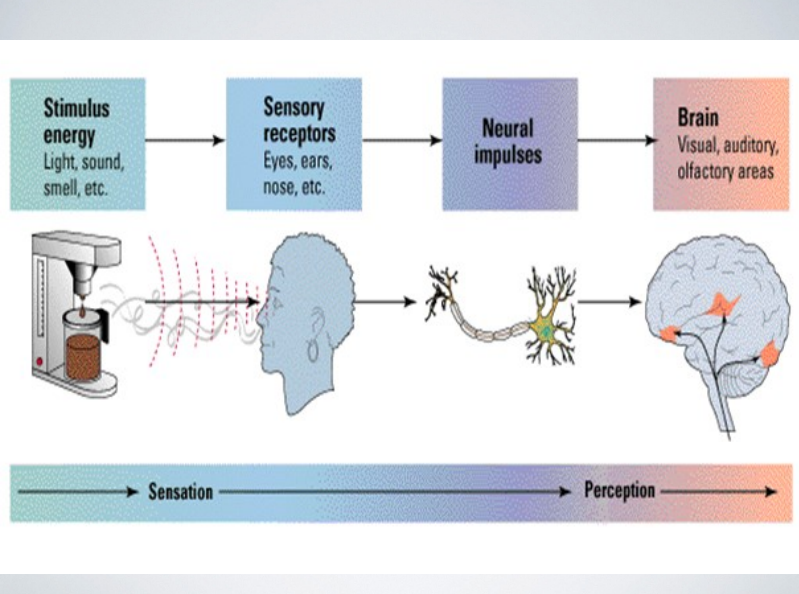
stimulus energy
sensory receptors
neural impulses
brain
sensation to perception
physical stage
action of one or more physical stimulus on a sense organ
physiological stage
internal processing of received stimulus, which operate within the receptor and the nervous system
absolute threshold
smallest amount of stimulus that must be present in order to be discerned
terminal threshold
maximum physical energy that can be still detected by a sense organ, anything beyond which already evokes a different sensation or no sensation at all
differential threshold
minimum amount of stimulus energy required to recognize the difference between two stimuli
sensory adaptation
reduction in sensitivity to stimulation as stimulation persists through time
modality
stimulus belongs based on the nature of the physical energy
quality
different experiences within the same modality
intensity
degree within the same quality
duration
length of time a sensation is experienced in the consciousness
reaction time
time between application of sensory stimulus and recognition of sensory experience
the riddle of separate sensations
sense receptors: specialized cells that convert physical energy in the environment or the body to electrical energy that can be transmitted as nerve impulses to the brain
doctrine of specific nerve energies
diff sensory modalities exist because signals received by the sense organ stimulate different nerve pathways leading to different areas of the brain
visual sense
shapes and colors, spatial arrangements, objects near and far away.
physical stage
stimuli that register as light in our eyes are electromagnetic radiation waves, our eyes happen to be sensitive and capable of responding
visible spectrum
rage of wavelengths that humans are sensitive to
hue
visual experience to specified by color names and related to wavelength of light
brightness
lightness and luminance; related to the amount of light emitted
saturation
vividness or purity of color; visual experience related to the complexity of light waves
cornea
protects eye and bends light toward lens
lens
focuses on objects by changing shape
iris
controls amount of light that gets into eye
pupil
widens or dilates to let in more light
retina
neural tissue lining the back of the eyeball’s interior, contains receptors for vision
rods
visual receptors that respond to dim light
cones
visual receptors involved in color vision. humans have 4 types of cones
form perception
gestalt principles describe the brains organization of sensory building blocks into meaningful units and patterns
gestalts view of perception
“the whole is more than a sum of its parts
law of pragnanz
individual organize their experience in as simple, concise, symmetrical, and complete manner as possible
simplicity
tendency to perceive patttern in the most basic manner possible
figure-ground
distinguishing between a figure and a background
proximity
elements tend to be grouped together according to their nearness
similarity
items similar in some respect tend to be grouped together
continuity
based on smooth continuity, preferred to abrupt changes of direction
closure
items are grouped tgt if they tend to complete a figure
symmetry
prefer to perceive objects as mirror images
monocular cues
visual cues to depth or distance that can be used by one eye alone
texture gradients
grain of item
relative size
bigger is closer
interposition
closer are in front of the other objects
linear perspective
parallel lines converge in distance
aerial perspective
images seem blurry father away
motion parallax
objects gets smaller at decreasing in speed in distance
ames room
room that makes people seem to change size as they move around to it, not rectangular
binocular cues
visual cues to depth or distance that require the use of both eyes
convergence
turning inward of the eyes, occurs when they focus on a nearby object
retinal disparity
slight difference in lateral separation between two objects as seen by the left and right eye
shape constancy
even tho images cast shadows of diff shapes, we still know the shape
visual illusions
muller-lyer illusion: tend to perceive the line as slightly longer than the other
ponzo illusion
linear perspective provides context
perceptual illusions
we cannot perceive what does exist
we perceive things that do not exist
we perceive what cannot be there
trichromatic theory
young and helmholtz proposed that the eye detects 3 primary colors
opponent process theory
assumes that the visual system treats pairs of colors as opposing or antagonistic. inhibited by a color, have a burst of activity when it is removed
hearing
what we hear; an ear on the world; constructing the auditory world
frequency
number of vibrations per second
amplitude
amount of contraction and expansion as represented by the amount which the curve departs from the base line
loudness
intensity of a pressure wave
pitch
frequency of pressure wave
timbre
complexity of pressure wave
taste
Gustation is the special sense associated with the tongue.
papillae
knoblike elevations on the tongue, containing tastebuds
tastebuds
nest of taste receptor cells
smell
airborne chemical molecules enter the nose and circulate through the nasal cavity.
gate-control theory of pain
Experience of pain depends (in part) on whether the pain impulse gets past neurological “gate” in the spinal cord and thus reaches the brain.
neuromatrix theory of pain
brain is capable of generating pain (and other sensations) in the absence of signals from sensory nerves
kinesthesis
sense of body position and movement of body parts; also called kinesthesia.
equilibrium
sense of balance
Semicircular Canals
organs in the inner ear, which contribute to equilibrium by responding to rotation of the head.
subliminal perception
perceiving without awareness
subliminal perception
perception vs persuasion
extrasensory perception
ability to perceive smth without ordinary sensory information
telepathy
mind to mind communication
clairvoyance
perception of remote events
precognition
ability to see future events
parapsychology
study of purported psychic phenomena such as ESP and mental telepathy.