Holding space for defying gravity
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
An object can be regarded as point mass when:
A body covers a very large distance as compared to its size, so, to study its motion, its size or dimensions can be neglected
Radial fields are considered _____ fields
non-uniform
What does this therefore mean?
g is different depending on how far object is from centre of mass of sphere
Gravitational are attractive and repulsive: T or F
Attractive only
What do gravitational field lines represent?
gravitational field
also direction of acceleration of test mass in field
Gravitational field lines around a point mass are ____ _____
radially inwards
equation for radial field strength:
g=-GM/r²
magnitude of g is plotted against the distance from the centre of a planet:
r < R (the radius of the planet), g is directly proportional to r
When r > R, g is inversely proportional to r2
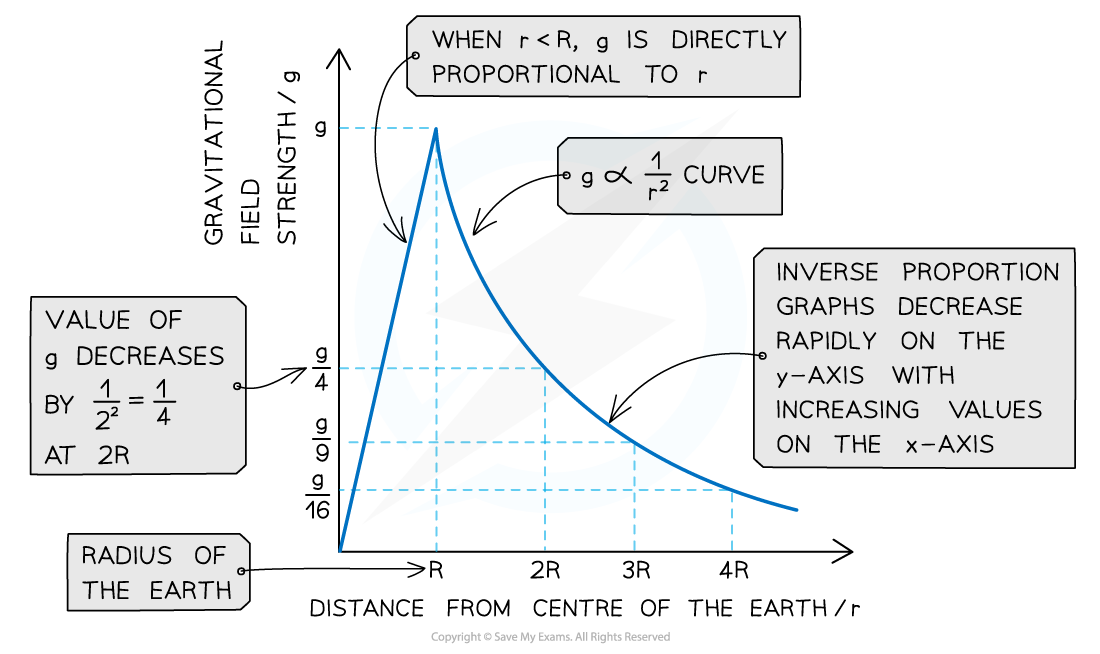
Near the Earth's surface, the gravitational field is ____
uniform
Newton’s Law of Gravitation states:
The gravitational force F between two masses m1 and m2 is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation, r
negative sign indicates what in newtons law of gravitation states?
that the gravitational force F between the two point masses m1 and m2 is attractive
radius of earth
6400km
What is Kepler’s first law?
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse, with the sun at one the two foci

Kepler’s second law:
A line segment joining the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals
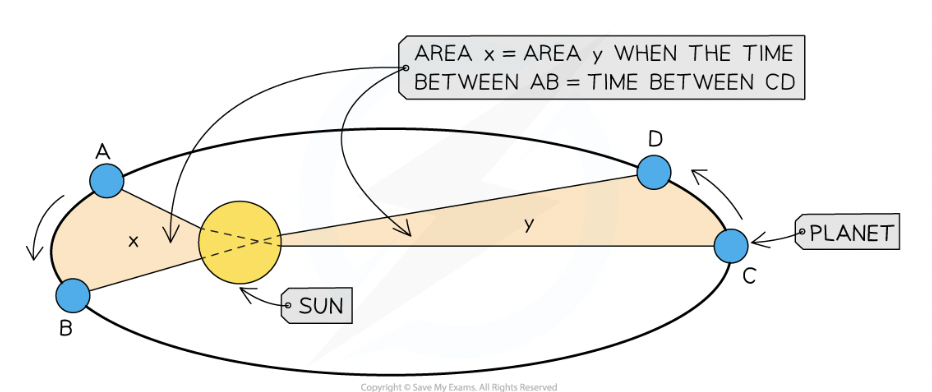
What does this therefore mean?
Planets closer to the sun travel faster and further away travel slower
Keplers 3rd law
Square of orbital time period T is directly proportional to cube of orbital radius r
How do we say planets move?
In circular motion
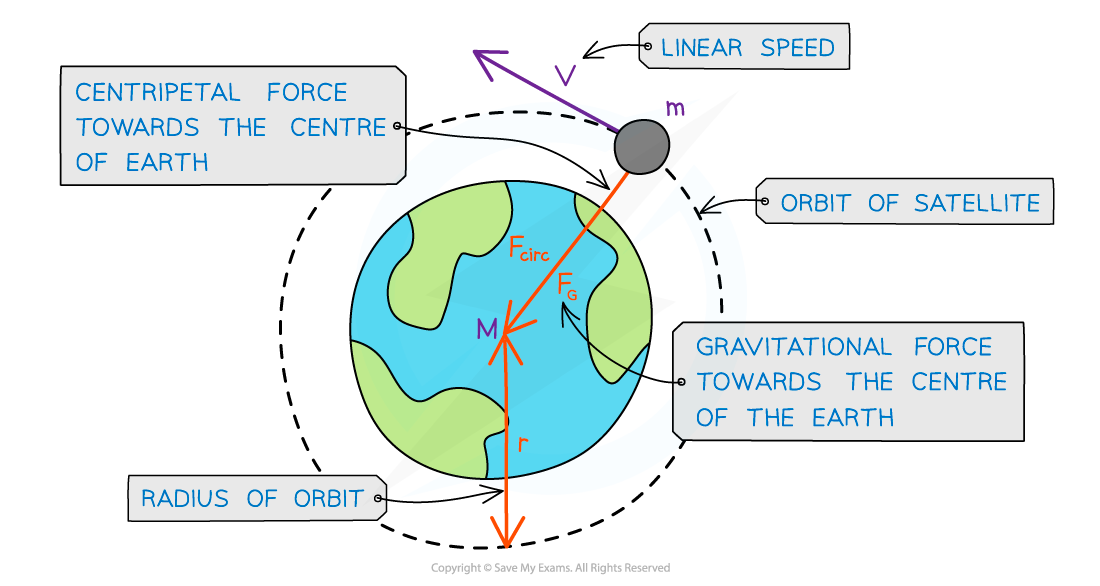
gravitational force is centripetal, so it is perpendicular to the direction of travel of the planet
gravitational force F on the satellite is centripetal
F=Fcentripetal
How to find orbital speed?
GMm/r² = mv²/r
What does this therefore mean?
all satellites, whatever their mass, will travel at the same speed v in a particular orbit radius r
equation for speed of orbiting planet
v=2πr/ T
How to derive T²=4PI²r³/ GM
V=2 PI r/ T
V²=GM/r ( GMm/r²=mv²/r )
specific type of orbit in which the geostationary orbit satellite
Remains directly above the equator
Is in the plane of the equator
Always orbits at the same point above the Earth’s surface
Moves from west to east (same direction as the Earth spins)
Has an orbital time period equal to Earth’s rotational period of 24 hours
What are geostationary satellites used for?
telecommunication transmissions (e.g. radio) and television broadcast
How do geostationary satellites works?
A base station on Earth sends the TV signal up to the satellite where it is amplified and broadcast back to the ground to the desired locations
The satellite receiver dishes on the surface must point towards the same point in the sky
Since the geostationary orbits of the satellites are fixed, the receiver dishes can be fixed too
Gravitational potential near surface of earth:
G.P.E = mgΔh
When using this equation, the G.P.E on the surface of the Earth is taken to be zero
This means work is done to lift the object
Why can GPE= mgh only be used when objects are near earths surface?
This is because, near Earth's surface, the gravitational field is approximated to be uniform
Far away from the Earth's surface, the gravitational field is radial because the Earth is a sphere
In a radial field what is GPE defined as:
energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field
Definition of gravitational potential at a point:
gravitational potential energy per unit of mass for an object at that point
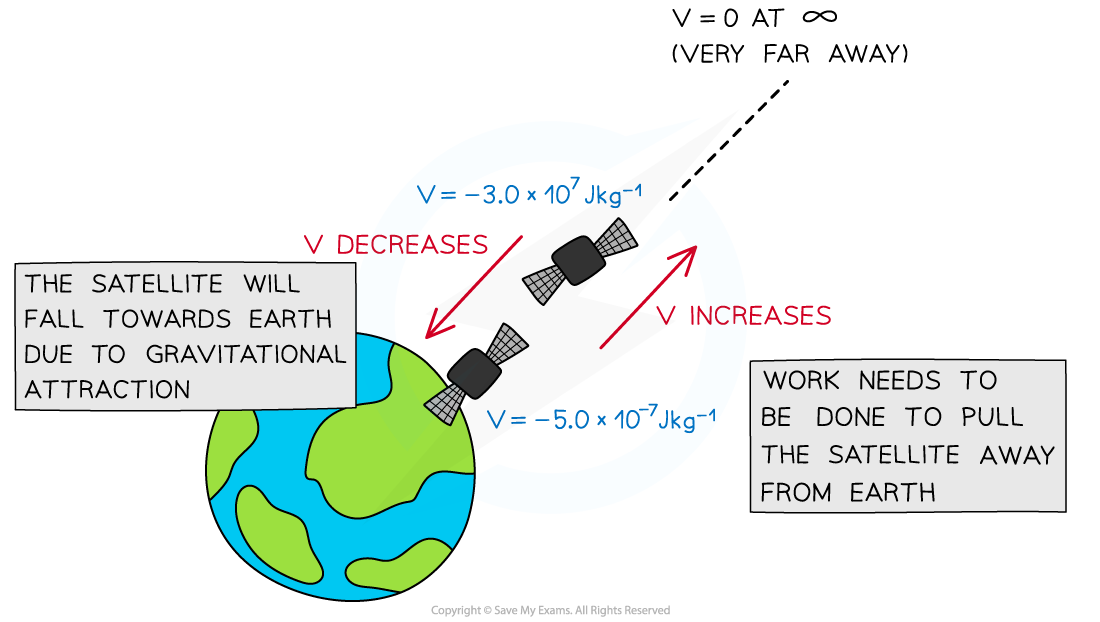
Gravity is always attractive, so work must be done on a mass to move it away to a point infinitely far away from every other mass
Why is gravitational energy always attractive?
'Infinity' is the point at which the gravitational potential is zero
Therefore, since the potential energy of all masses increases as work is done on them to move them infinitely far away, the value of the potential is always negative
Since the potential energy of a mass therefore increases as it moves toward infinity (where V = 0), the value of the potential everywhere else must be negative.
Gravitational potential definition:
The work done per unit of mass in bringing a mass from infinity to a defined point
What does area of gravitational force against distance from planet equal?
work done
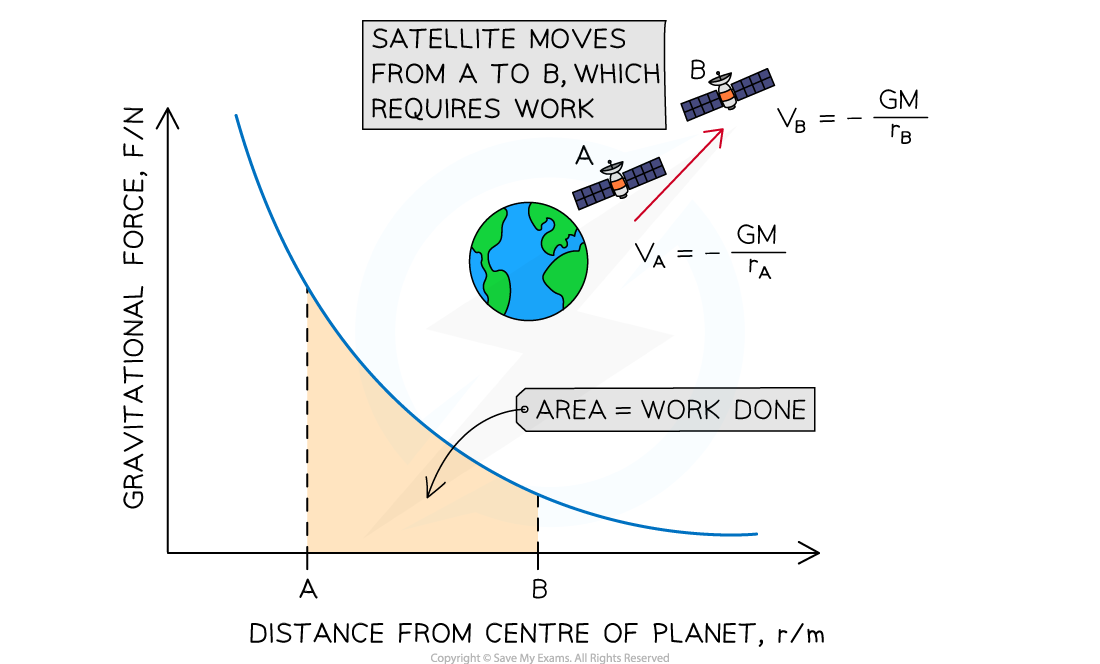
In the case of a mass m moving further away from a mass M, the potential increases
Since gravity is attractive, this requires work to be done on the mass m
The area between two points under the force-distance curve therefore gives the change in gravitational potential energy of mass m
When a mass is moved against the force of gravity, work is required
This is because gravity is attractive, therefore, energy is needed to work against this attractive force
Equation for change in GPE:
M = mass that is producing the gravitational field (e.g., a planet) (kg)
m = mass that is moving in the gravitational field (e.g., a satellite) (kg)
r1 = initial distance of m from the centre of M (m)
r2 = final distance of m from the centre of M (m)
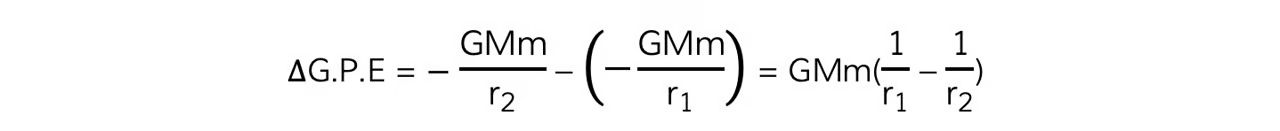
escape velocity definition:
The minimum speed that will allow an object to escape a gravitational field with no further energy input
escape velocity is ____ for all masses in same gravitational field
same
What needs to be transferred when object reaches escape velocity and what equation does this make?
KE —> gravitational potential energy
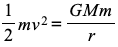
Units of equation
m = mass of the object in the gravitational field of mass M (kg)
v = escape velocity of the object (m s-1)
G = Newton's Gravitational Constant
M = mass of the object to be escaped from, causing the gravitational field (i.e., a planet) (kg)
r = distance from the centre of mass of M (m)
Why do rockets launched from earth’s surface not need to achieve escape velocity to teach orbit around earth?
They are given energy through fuel continuously to provide thrust
Less energy is needed to achieve orbit than to escape from Earth's gravitational field
UNITS OF VG
J KG^-1