APUSH Salad Bowl Terms - 1st Semester
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Mercantilism
Economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy, as trade increases wealth. It provides the idea that wealth is limited in the world, one side's gain will result in one side's loss.

Conquistadores
Spanish conquerors of the Native American lands, most notably the Aztec and Inca empires.
Puritans
A group of religious reformers who left England in the 16th and 17th centuries to establish a holy commonwealth in the New World.
Jamestown
Colonial settlement in Virginia, founded in 1607, being the first permanent English settlement in North America.
Metacom's War / King Philip's War
A conflict between the Wampanoag and other Native American tribes and the English colonists in New England from 1675 to 1678.
Great Awakening
A series of religious revivals in the American colonies and the British Isles that took place between the 1700s, and it was mainly impacted by the Enlightenment.

Anne Hutchinson
Considered one of the earliest American feminists who challenged male authority, also being a spiritual leader in Massachussets,

Navigation Acts
Restrictions on colonial trade to England enacted by Parliament to promote the self-sufficiency of the British Empire.
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
Chartered a government for the Northwest territory, provided a method of admitting new states to the Union, and listed a guarantee bill of rights.
Mexican-American War
A war stemming from the United States' seizure of Texas in 1845. The war resulted in the American acquisition of the land that later became New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, California, Texas, and western Colorado.
Emancipation Proclamation
Issued by Abraham Lincoln announcing that all persons held as slaves within the rebellious states 'are, and henceforward shall be free.'
Missouri Compromise
An act authorizing the people of Missouri and Maine territories to form a constitution and state government, being admitted on an equal footing with the original states. It also tried to address growing sectional tensions over the issue of slavery, banning it in all states and territories above the latitude running along Missouri's southern border.
Trail of tears
The forced Westward displacement of American Indian tribes from the South and Southeast guided by policies favored by Andrew Jackson. Thousands of Natives died.
Era of Good Feelings
A period that reflected a sense of national purpose and a desire for unity among Americans following the War of 1812.
Eli Whitney
American inventor who developed the cotton gin. Also contributed to the concept of interchangeable parts that were exactly alike and easily assembled or exchanged.
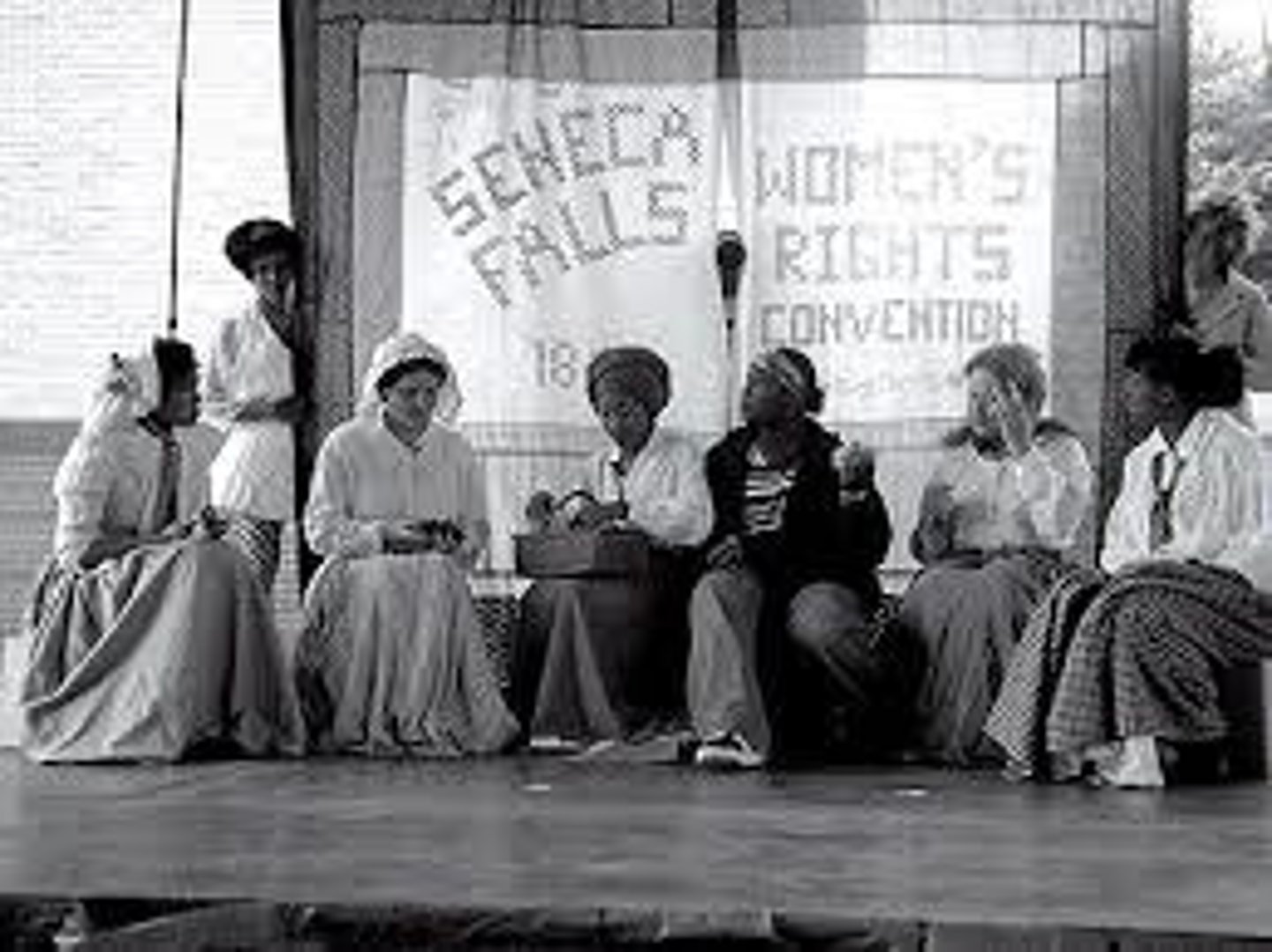
Seneca Falls Convention
Women's rights convention held in Seneca Falls, New York, in 1848. The Declaration of Sentiments was signed at that convention.

Transcendentalism
Philosophical and literary movement in the mid 19th century that focused on the belief that every human has god-like qualities.
Boston Tea Party
To protest the British Parliament's tax on tea, the demonstrators boarded the ships and threw the chests of tea into the Boston Harbor. 'No taxation without representation.'
Republican Motherhood
Was considered a custodian of civic virtue responsible for upholding the morality of her husband and children.
Declaration of Independence
The founding document of the United States.
Shays' Rebellion
A series of protests in 1786 and 1787 by American farmers against state and local enforcement of tax collections and judgments for debt.
Constitutional Convention
Delegates from all states met and decided that the best solution to the young country's problems was to set aside the Articles of Confederation and write a new constitution.
Alien and Sedition Acts
Raised the residency requirements for citizenship from 5 to 14 years, authorized the president to deport 'aliens,' and permitted their arrest, imprisonment, and deportation during wartime.
Louisiana Purchase
The US purchased 828,000 square miles of land west of the Mississippi River for $15 million.
Corrupt Bargain
During the election of 1824, the House elected John Quincy Adams over rival Andrew Jackson. It was widely believed that Clay, the Speaker of the House, convinced Congress to elect Adams, who then made Clay his Secretary of State. Jackson's supporters denounced this as a 'corrupt bargain'.
Manifest Destiny
The idea that white Americans were divinely ordained to settle the entire continent of North America.
Nullification Crisis
A result of southern states resistance to imposed, protective tariffs on foreign goods to guard emerging industries.
Spoils system
A practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its supporters as a reward for working toward victory.
John Winthrop
He was a puritan leader and the first governor of the Massachusetts bay colony. He is known for the vision he had of the colony 'city upon the hill'. Winthrop's leadership helped set a foundation for self government and community in New England.
Stamp Act Congress
It occurred in 1765 which included nine American colonies and their representatives to protest against the British stamp act which tried to raise American taxes. It caused colonial unity as it brought colonial unity as the declaration of right appeared due to the raise of taxes.
2nd Great Awakening
A religious movement in the United States during the late 18th and early 19th century. It was big on personal salvation and emotional faith, widespread of social reforms were created as for abolition, women's rights, shaping American society and culture.
William Bradford
The governor of the Plymouth colony (first permanent colony in New England) for 30 years, and helped shape and stabilize the political institutions.
War of 1812
A war between the U.S. and Great Britain caused by American outrage over the impressment of American sailors by the British, the British seizure of American ships, and The war strengthened American nationalism and encouraged the growth of industry.
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the exchange of diseases, ideas, food crops, and populations between the New World and the Old World following the voyage to the Americas by Christopher Columbus in 1492.
Declaratory Act
The Declaratory Act, passed by Parliament on the same day the Stamp Act was repealed, stated that Parliament could make laws binding the American colonies 'in all cases whatsoever'.
John Adams
John Adams was an American Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before his presidency, he was a leader of the American Revolution that achieved independence from Great Britain.
Daughters of Liberty
The Daughters of Liberty was known as the formal female association that was formed in 1765 to protest the Stamp Act, and later the Townshend Acts, and was a general term for women who identified themselves as fighting for liberty during the American Revolution.
Indentured servant
Laborer who agreed to work without pay for a certain period of time in exchange for passage to America.
James Madison
James Madison was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817.
Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord was the first major military campaign of the American Revolutionary War, resulting in an American victory and outpouring of militia support for the anti-British cause. "The Shot Heard 'Round the World"
Headright system
The Headright system was a system in which fifty acres of land was granted to those who sponsored the immigration of Indentured Servants. Some plantation owners used this system to buy passage for slaves to come to the Americas, gaining more land for doing so, as well as gaining slaves.
Pueblo Revolt
A rebellion in 1680 in which the indigenous Pueblo people revolted against Spanish colonizers, largely successful, driving the Spanish away for twelve years.
Encomienda system
A Spanish labour system that rewarded Spanish people who took indigenous people as slaves and attempted to turn them to Catholicism.
Mayflower Compact
The first governing document of Plymouth Colony, signed in 1620, containing rules for self governance as established by the settlers aboard the Mayflower.
Seven Years' War
A war from 1756 to 1763 fought mainly in Europe and the Americas, primarily between Britain and Prussia vs France, Austria, Russia, Sweden, and Spain, leaving Great Britain weakened.
Mutiny (Quartering) Act
An act in 1765 that required the colonists of the Thirteen Colonies to provide housing and food to British soldiers, causing outrage among the colonists.
Tobacco
A plant that can be smoked or chewed, and was a major cash crop in the US.
Thomas Paine
Founding Father and author who wrote Common Sense.
Massachusetts Bay Colony
A large colony in Massachusetts founded by Puritans, with John Winthrop as the first governor.
Boston Massacre
A violent confrontation on March 5th, 1770, where British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists, killing five, inciting a violent riot.
Alexander Hamilton
Founding Father and first Secretary of the treasury, who organized the National Bank and wrote 51 of the 85 essays in the Federalist papers.
George Washington
The first president of the United States.
Salutary neglect
An unofficial British policy of not enforcing parliament's laws or taxes in the American colonies, which ended with new restrictions.
Bacon's Rebellion
A resistance made by Virginian settlers from 1676-1677, led by Nathaniel Bacon against Governor William Berkeley, in response to Berkeley's refusal to remove Native Americans.
Navigation Acts
Passed in 1651 and 1660 to promote British trade by restricting colonial trade to England and prohibiting trade with other foreign powers.
Virginia House of Burgesses
An assembly of elected officials from Virginia that met from 1643 to 1776, recognized as the first democratic government in the American colonies.
Sugar Act
Passed in 1764, it taxed sugar from the French and Dutch West Indies to end illegal smuggling and maintain British control.
Compromise of 1850
Included the Fugitive Slave Act allowing escaped slaves to be returned to slavery, banned the slave trade in Washington DC, and admitted California as a free state.
Market Revolution
A period that contributed to the economic growth of the United States, characterized by lower-class Americans working in factories for low wages, leading to poverty.
George III
King of Great Britain during the American Revolution, whose policies and taxes on the colonies contributed to the tensions that led to the American War of Independence.
Sons of Liberty
A secret group of American colonists who protested British taxation and policies, which played a significant role in the Boston Tea Party.
Coercive/Intolerable Acts
A series of punitive laws were passed by Britain in 1774 to punish Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party. This escalated colonial resistance.
Democratic-Republican Party
A political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison, advocating for states rights and limited federal government in opposition to federalists.
Tariff of Abominations
A nickname for the 1823 tariff, which angered many southern states by imposing high taxes on imported goods. This benefited northern industry but hurt the southern economies.
Proclamation of 1763
The British government said that no American colonists could go west of the Appalachian Mountains and that colonists who had already gone west of the Appalachian Mountains had to return to the eastern side of the mountains.
Townshend Duties
Taxes imposed by the British government on the colonists that taxed things like paper and tea. The colonists protested 'no taxation without representation' and that the British did not have the right to tax the colonists since they had no representation in the British government.
Committees of Correspondence
A group of American colonists that wanted to coordinate opposition to the British government, and the committee was used as a way of communicating throughout the American Colonies in order to provide for rapid communication between colonial governments.
Anti-Federalists
A political group lead by Thomas Jefferson that wanted a strict interpretation of the constitution but a weak central government, Power to state governments, Agrarian economy, and admired France rather than Great Britain.
Valley Forge
Where the Continental Army that was lead by George Washington camped for the Winter in the Revolutionary war, but it was poorly equipped to spend a long, freezing winter. Hundreds of men died and over a thousand deserted.
Hartford Convention
A group of New England colonies created a list of demands for the federal government, including that the President should only have one term and that there shouldn't be two presidents in a row from the same state.
1st Continental Congress
Declared that Americans have the same rights as Englishmen.
Articles of Confederation
Created a sovereign national government, serving as the United States' first constitution, until the actual Constitution went into effect
Marbury v Madison
Supreme Court decision that said that the Supreme Court has the power to decide whether or not something is constitutional.
The American System
Henry Clay's 3 part plan made in the 1820's meant to promote American Industry, consisting of a strong banking system, a protective tariff, and a federally implaced transportation system.
Andrew Jackson
The seventh president from 1829-1837, representative of the 'Common Man' and won the popular vote by a lot, partially because he came from 'Humble beginnings.'
Whigs
A political party created in the 1830s to oppose Andrew Jackson, made up of sections from different political parties such as former members of the National Republican Party, the Anti-Masonic Party, and disaffected Democrats.
Mexican-American War
From 1846-1848 when the US invaded Mexico to claim Texas, resulting in the US acquiring land that makes up what is now New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, California, Texas, and western Colorado.
Stamp Act
The British government put a tax on goods for colonists such as specific documents, papers, and playing cards, which upset the colonists.