chemical analysis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
pure susbtance
a single element or compound not mixed with any other substance
mixture ( a substance that contains 2 or more different substances that aren’t joined together)
element ( one type of atom)
compound (2 or more types of atoms chemically bonded 4
pure elements and compounds melt at specif temps
measure the melting point
pure substances have a sharp melting substances
and impure melt over a broader range of temperatures
formulations
a mixture designed as a useful product (paint, medicine, makeup, alloys, NPK fetilliser)
mix together components that have a particular purpose in carefully measured quantaties to make sure the product has the desired characteristics
impure substacnes
lowers melting point
and raises the BP
The more impurity the greater the difference in MP and BP
in liquids, an impurity dillutes the conc of a liquid, decreasing the number of molecules that can vaporise at any given temp
decreasng vol increases the pressure as a higher temp required to get enough molecules to vaporise to allow boiling to occur
impurities in a solid disrupt the repeating pattern of forces that holds a solid togethere, smaller amounts of energy is requird to melt the part of the solid surrounding the impurity so the melting point isn’t as high
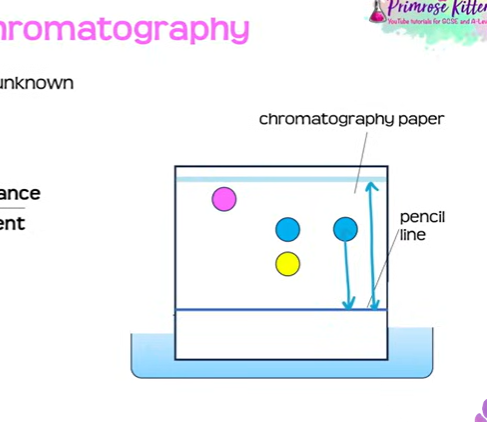
chromatogrpahy
method used to separate mixtures
also useful in indentifying certain substances
chromotogprahy paper
pencil line
dyes across the line
placed into solvent
solute- what dissolves
solvent- does the dissolving
solubility- how easy it dissolves
2 phases of chromatogrpahy
mobilephase- the solvent that carries the different substances
stationary- non moving phase ( the paper _
RF VALUE to identify unknown val
measure distance moved by substances / distance moved my solvent
both measured from pencil line (one to dye) and (one to the paper)
value always between 0 and 1
mixtures separate into different spots depending on the solvent , but pure compounds produce a single spot
draw a pencil line across the chromatography paper, 1 - 2 cm from the bottom
use a pipette or capillary tube to add small spots of each ink to the line on the paper
place the paper into a container with a suitable solvent in the bottom
allow the solvent to move through the paper, but remove the chromatogram before it reaches the top
allow the chromatogram to dry, then measure the distance travelled by each spot and by the solvent
hydrogen test oxygen
lit splint at neck of test tube containing gas, presence of hydrogen is a squeaky pop sound
glowing spliint, 02 presence the splint re lits
carbon, buble gas through aq solution of lime water, if present lime water turns cloudy
chlorine, damp blue litmus paper onto gas, if bleached turns white
flame tests
identifies some metal ions
dip nichrome wire into hcl (nichrome is unreactive
heat the wire in a blue bunsen flame until it ives no colour (reomve contaminant metal ions)
dip wire into water
dip wet wire into substance being dissolved
put into blue bunsen flame (note colour)
lithium - crimson
na- yellow
potassium - lilac
calcium- orange-red
copper- green
when metal compounds heated electrons in metal ions absorb energy
electrons promoted to higher energy level
electrons drop back to their ground state and release excess energy but as light and not heat
different amounts of energy released produces different colours of light
identifying metal ions
mixture of different ions, and the flame colours can be masked because of the different colours being mixed together (problems in flame test)
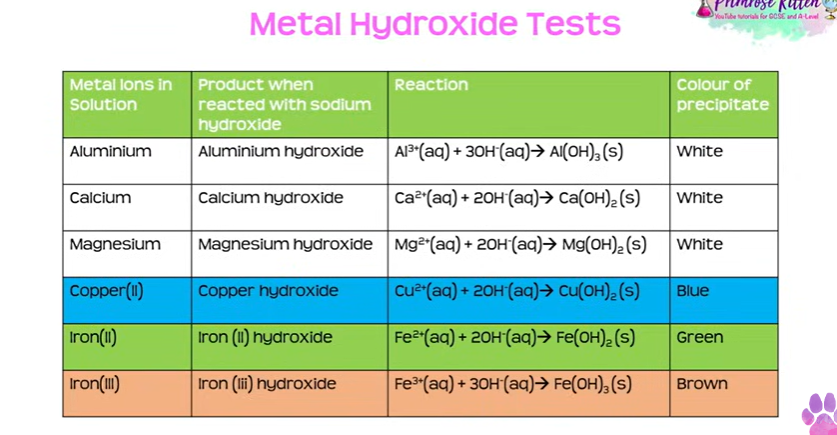
metal hydroxide tests
add sodium hydroxide to solution
observe the colour of the precipitate that forms
aluminium- white
calcium- white
magnesium- white
copper- blue
iron 2 - green
iron 3 - brown
the 3 that form white, add more sodium hydroxide so its excess, only aluminium dissolves again, and calcium and magnesium dont
carbonate ions
react carbonates with dilute acid, forming co2 gas
now bubble the gas through limewater
if present limewwater turns cloudt
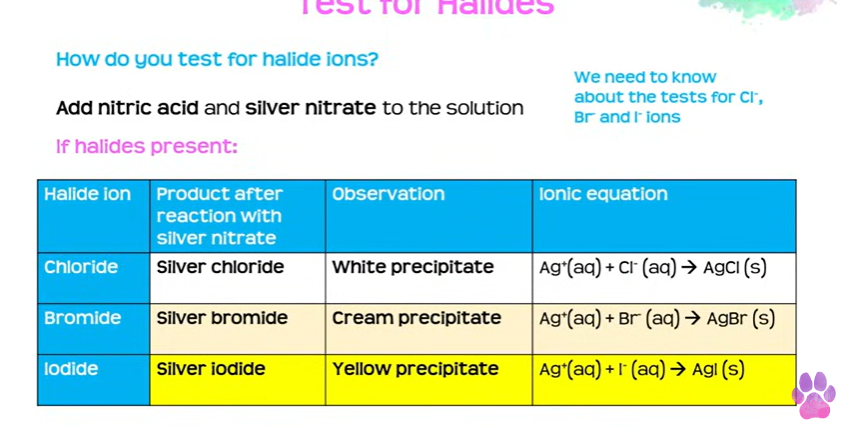
halide ions
add nitric acid and silver nitrate to the solution (nitric because hcl has chloride ions in it)
precipitates
silver chloride - white
silver bromide - cream
silver iodide- yellow
remeber trend of colours
testing sulfate ions
barium chloride solution and dilute hcl
white precip forms
baso4
insturmenta methods
-more accurate than flame tests
-more sensitive
-rapid tests
Flame emission spectroscopy analyses metal ions in solutions
-expensive
-special training to use them
sample put into flame
light passed through spectroscope
spectroscope gives a line spectrum thats analaysed to identify the metal ions in the solution
the concentration of the metal ions in the solution can also be found