Stem Cells
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Stem Cell
Not terminally differentiated
Capable of unlimited division
Self renewing
Progenitor Cells
Divide a limited number of times
On a path to terminal differentiation
Not self renewing
Totipotent
Give rise to every cell of the body (embryonic)
Pluripotent
Give rise to cells in all 3 germ layers (placental)
Multipotent
Can become a subset of cells in the organism (organ)
Unipotent
Contributes to 1 cell type of the tissue (organ)
Terminally differentiated (not stem cell)
Divides a limited amount of time but does not change cell type
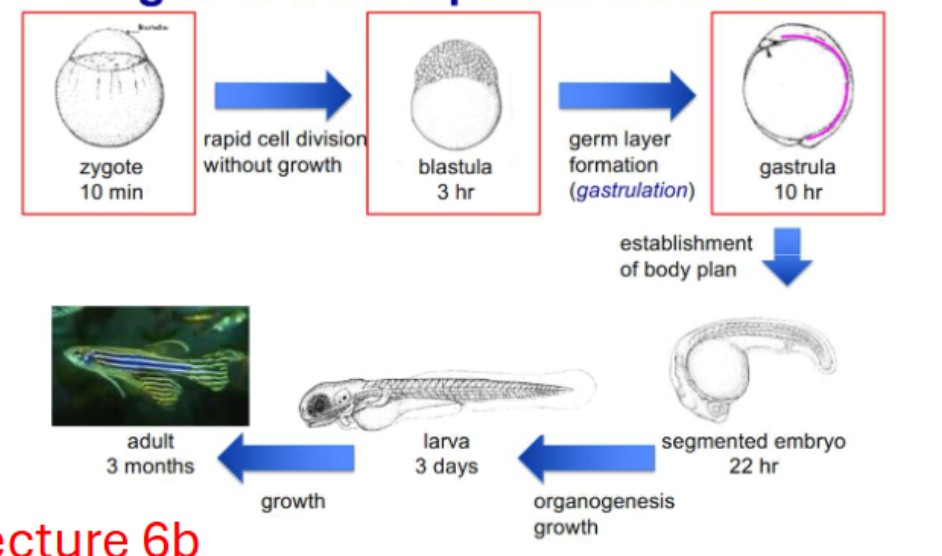
Stages of development in animals
zygote
blastula
gastrula
segmented embryo
larva
adult
Stem Cell Niche
Place often with unique adhesion (ECM or cell-cell) and work together
Niche
Distal tip expresses a delta ortholog lag-2
Cells under a distal tip express the notch receptor ortholog glp-2 and are senstive to notch signaling
cells divide in distal, pushing some cells out of niche
Once pushed out of niche, notch is no longer present and cells undergo meiosis to make oocytes
Normal Notch
Lots of small dividing nuclei around DTC
Cells properly develop into sperm and oocytes
Constitutatively active notch
Germline is full of cells that never enter oogenesis
Sterile
Develop germline tumors
Loss of function notch
Germline has few cells and lost stem cell niche
Sterile
Few germ cells are produced
Same phenotype as laser ablating DTC
Nuclear Transfer
1. Remove the nuclei for a verified stem cell.
2. Collect the Nuclei from a terminally differentiated cell.
3. Place the Nuclei into the stem cell.
The newly derived hybrid cell is Pluripotent like the original stem cell There is large-scale remodeling of the chromatin Chromatin decondenses (nuclei grows 50x) X-inactivation is reversed
iPSCs
A set of mRNAs that enrich stem cells yet did not confer stemness except for Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, Myc) and can revert to pluripotent stemcells and reduce the need for embryonic stem cells
What happens when stem cells lose niche
Develop a teratoma and be in any tissue
Organoids
An intermediate that depletes stem cell population that is artificially grown and have less function than the natural counterpart
Liver
• detoxification
• metabolism - glucose<->glycogen, non-essential amino acids
• synthesis of lipoproteins, cholesterol, and plasma serum proteins
• digestive functions
• biotransformation
• storage of glycogen
• largest organ
• endoderm that shares progenitors with stomach, intestine, colon, and pancreas
Liver regeneration
Adjusts to organism size large or smal;
Signalling molecules (EGF, HGF, etc.) and physical environmental cues
Insulin and bile acids
Homeostasis
the state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions
maintained by living systems.
Intestines and gastrointestinal tract
Absorb nutrients and secretes waste, acidic, proteases, environmental toxins, and lots of movement with a turnover of 3-5 days
Small intestine
single layered epithelium
• absorptive cells
• mucus secreting cells
• enteroendocrine cells
• paneth cells
Cre Recominase
• Cre-mediated excision of regions between LoxP sites.
• Permanent and inherited by all later generations of cells and mice.
• LacZ(β-galactosidase) turns the clear X-gal substrate Blue
Using promoters
Lgr5- promoter expresses in a wide range of stem cells
ROSA26 is expressed in nearly every cell type.
What controls Wnt?
Signals from surrounding tissue:
BMP4 inhibits Wnt
But: Wnt and Hh activate Bmp4
What controls migration?
Ephrin (ligand) and Eph (receptor) control of cell motility and the loss of migration control leads to disrupted villus structure
Notch
controls the balance in numbers of secretory cells (inactive notch) and absorptive cells.
Positive Selection
Select the presence of something
Negative Selection
You select against the presence of something