4. Democracy and Median Voter Theorem
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Median Voter Theorem: Equilibrium
parties choose the Median voter ideal policy point
median voter: half voters prefer lower policy point, half voters prefer higher policy point
median voter theorem: under certain assumptions, majority voting yields the policy outcome preferred by the median voter
Business analogy: Hotelling’s Model
consumers distributed uniformly along a street
2 ice cream trucks sell same ice cream for same price
consumers buy from closest truck
result: ice cream trucks converge to the middle of street
Median Voter model: Assumptions
single dimensional voting and single-peaked preferences
voters care about single issue
voters have bliss point and utility falls as you move away from that point
Two candidate or parties
no party ideology — parties only care about winning office
if they did care, median voter won’t hold bc. too se on personal beliefs
no selective voting — everyone votes
no money in politics
full information — politicians know voter preference, voters know party positions
what if we had multidimensional policy space?
problem because there is no clear equilibrium
if there were more (3) would parties have incentive to move away from MV policy position?
deviate because parties would have an incentive to move away bc they will ensure a win
What happened to Britain’s Median Voter?
1997 labour thought they needed to cater to mondeo man and the worcester woman
Tony bliar noticed that labors who had done well were now becoming tory and viewed labor as hindering him
convergence to the median depends on which issues are more salient
economic issues = parties closer
other issues like Brexit = ideological stance
mvt may hold within political groups — leave/remain in EU supporting parties
median voter can change over time and does not have to be in the middle of political spectrum
no full info: different parties can have different veliefs on median voter
2019 conservaties bet on MV being working class, leaving voting northern
evidence on MVT: how can we provide evidence on whether the median voter preferences rather than party/politician preferences determine policy?
having to different parties means the two parties are not equal and therefore have different median voters in each so against the MVT
to have MVT you need same median voter and same policy

Close races
we will see that MVT is still close even through different outcome
if you compare D1 and D2 they should vote the same, because same MV same policy
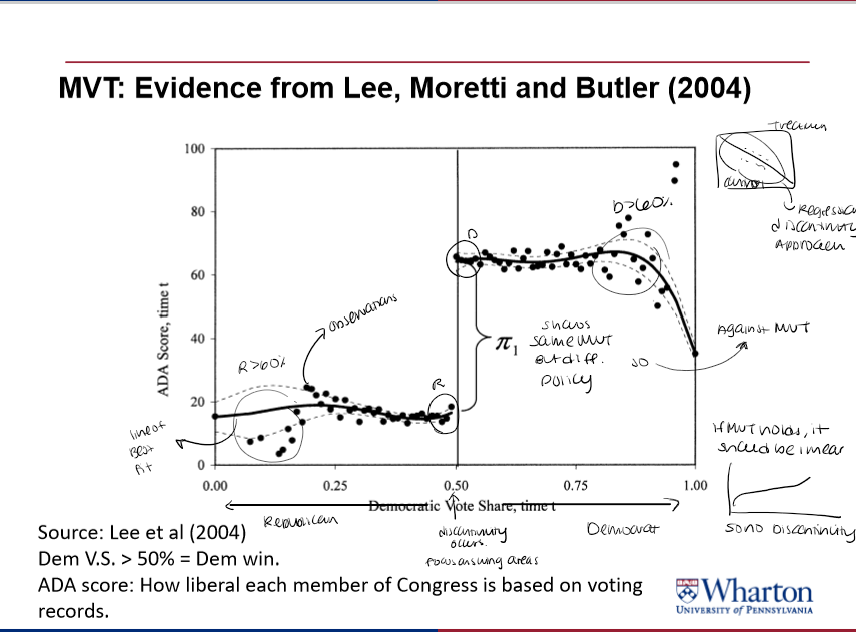
MVT: Evidence from Lee, Moretti, and Butler
shows when republicans barely won and when democrats barely won
provides evidence against MVT using regression D.
suggests party affiliation strongly determines policy outcomes rather than convergence to the MV preference
MVT: Evidence from gerber and Lewis
analyze voting record and legislator behavior in LA in 1990s
MV preference are better predictor of legislative behavior in homogenous than heterogenous districts
homogenous districts = more MV influence — voters have similar policy preferences, legislator will align with to get reelected
Heterogenous = more party influence — voters have polarized/different views, legislators will rely on party platform
big picture: whether there is convergence to the median depends on the context, MVT does not always predict legislator behavior
Lecture 4 Summary
MVT: majority voting yields the policy outcome preferred by the median voter
requires certain assumptions that may not hold
evidence on party policy convergence is mixed: depends on setting