GI radiology (words)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What are the nine parts of the abdomen?
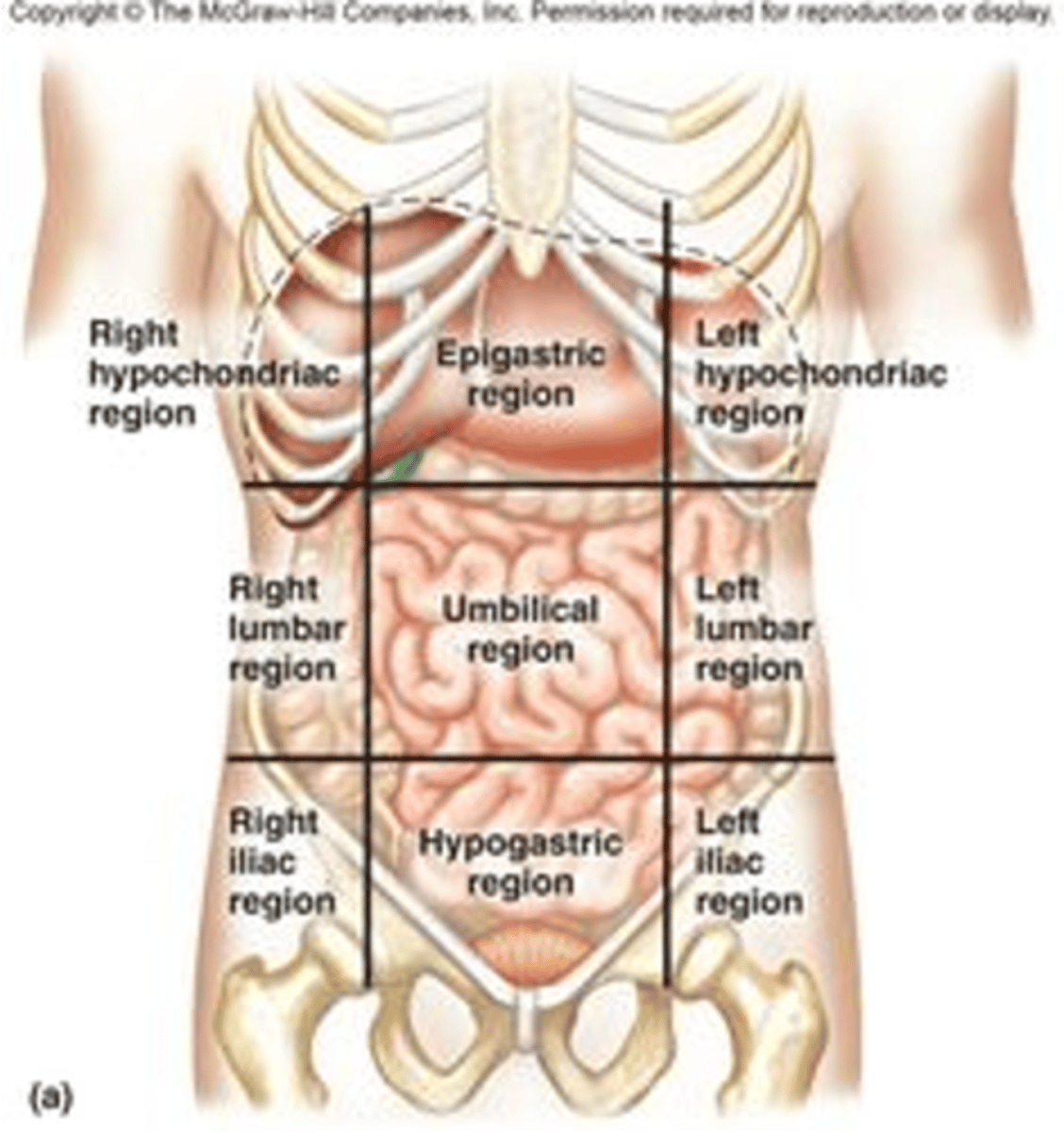
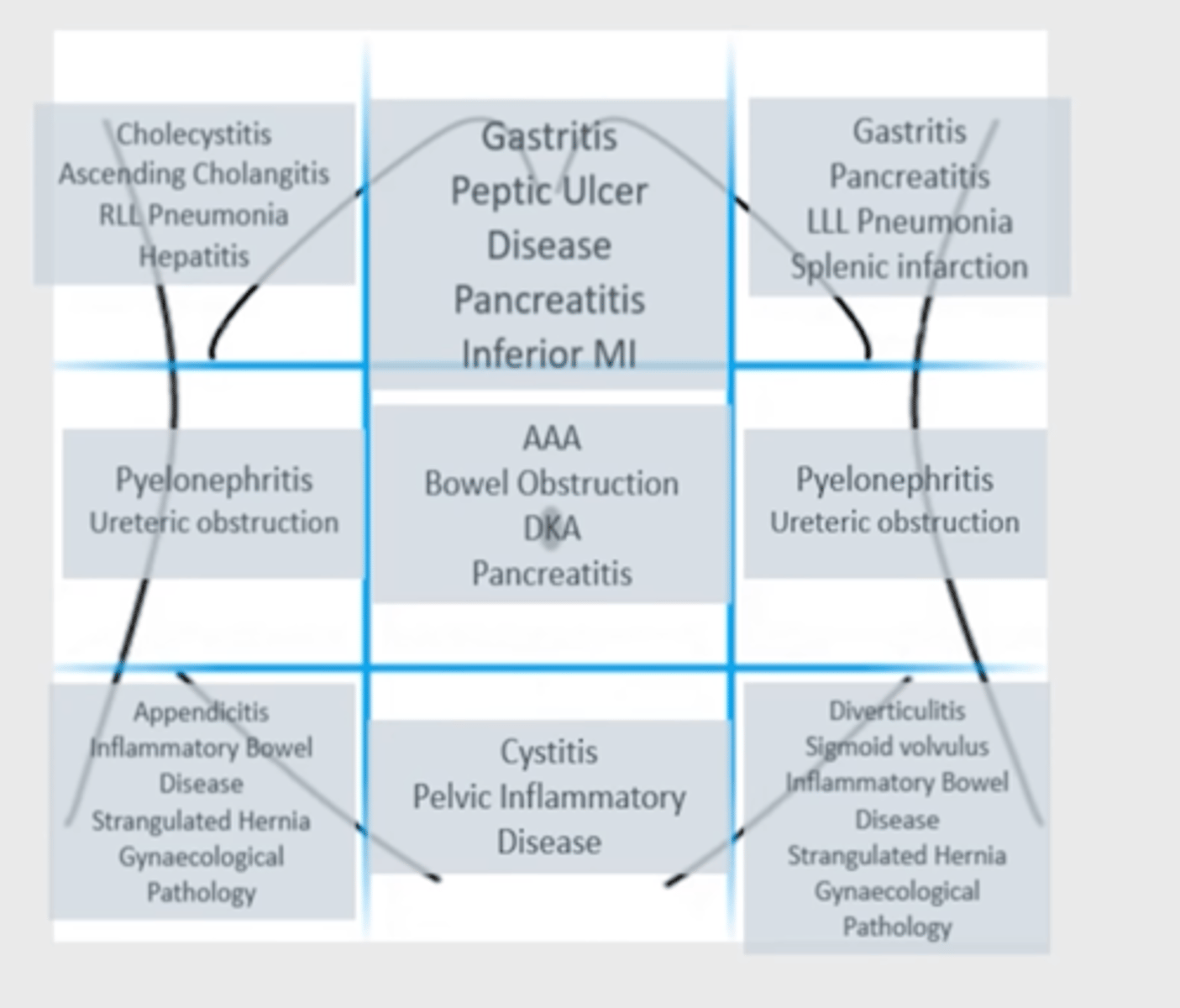
What diseases can be found in each of the nine parts?

What can we see in a Supine abdomen view XR?
-gas pattern
-calcification
-massess
What combination of views is largely obsolete?
abdominal 3 view, or acute abd series
What can we see in upright abdomen view XR?
free air
air-fluid levels (small bowel obstructions)
When do we use a CXR?
-pneumoperitoneum
-interthoracic conditions that can lead to referred abdomen pain
What views are included in acute abdominal series (AKA abdominal 3 view)?
-supine
-upright
-CXR
When do we use a left lateral decubitus view?
pts who can't stand
pneumoperitoneum
How can we use a left lateral decubitus view to identify pneumoperitoneum?
free air will go to the highest part of the abdominal cavity (the pts right side)
we will see the free air over the outside of the liver
What view is used to view the rectosigmoid colon?
prone abdomen (rarely done)
What are limitations of an abdominal XR?
-hard to differentiate between structures of similar densities
-only 5 basic densities
-poor for disease diagnosis

What is a scout film?
prelim image before imaging procedure to help position pt and locate areas of interest
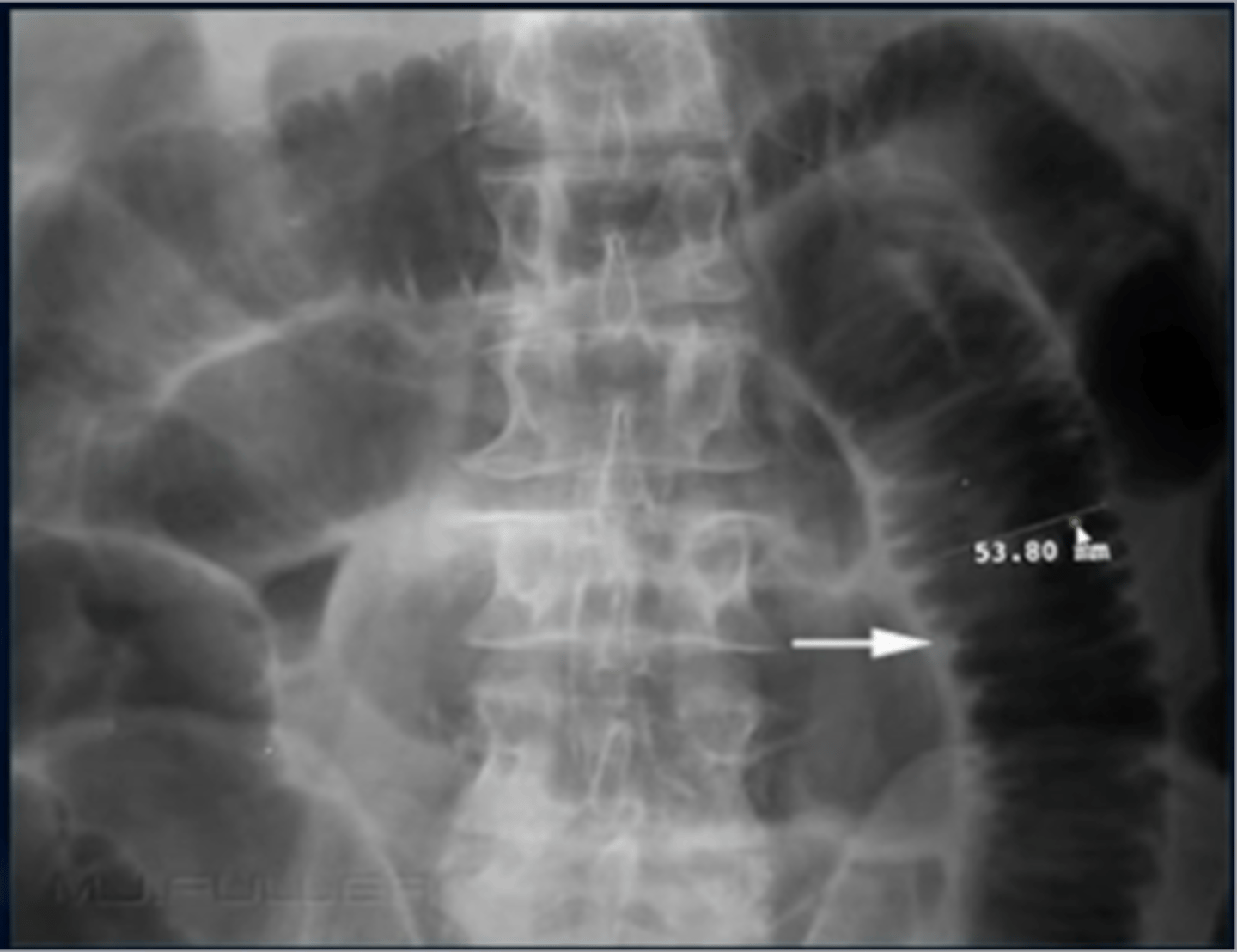
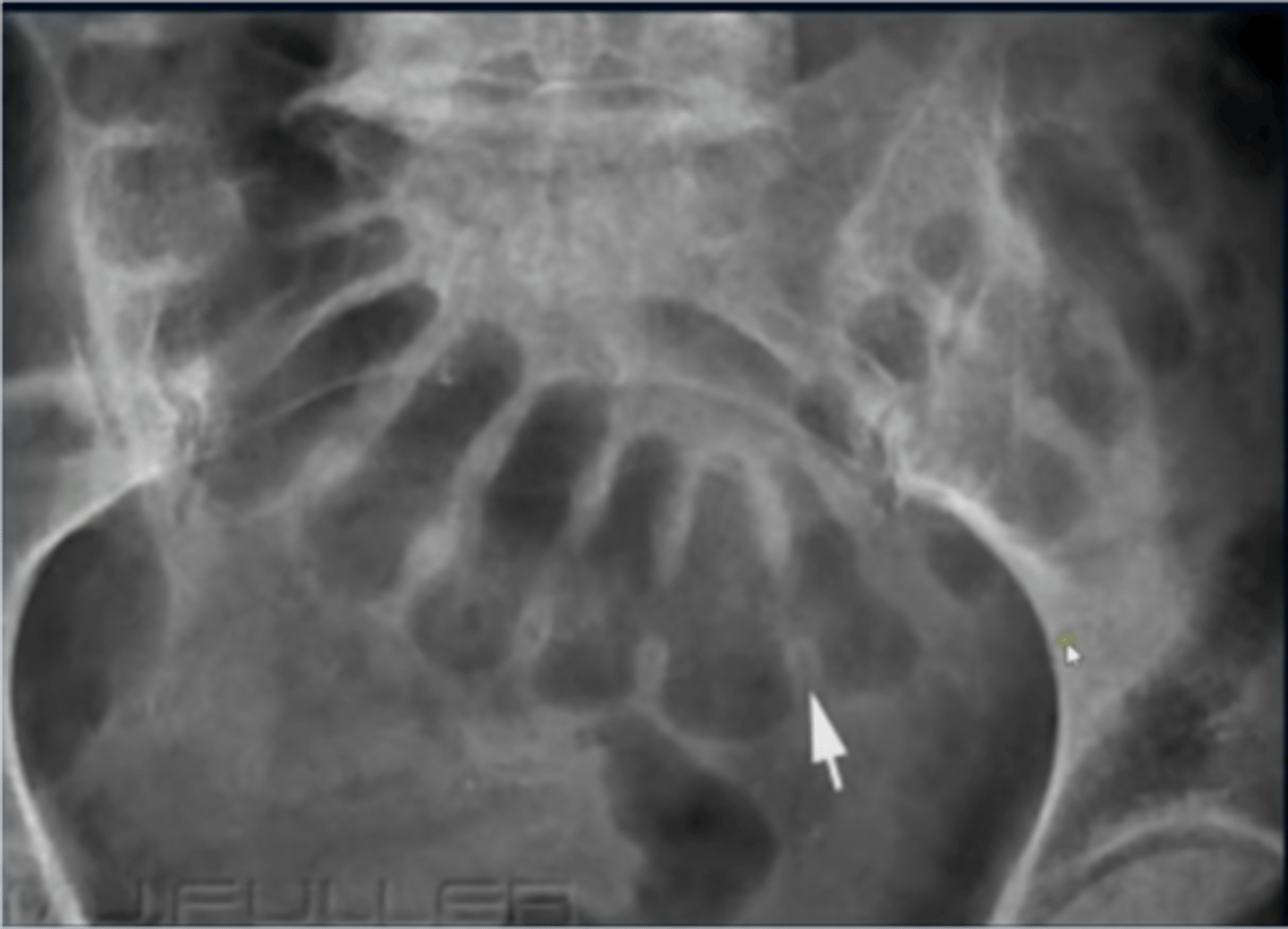
How can we differentiate between small and large bowel?
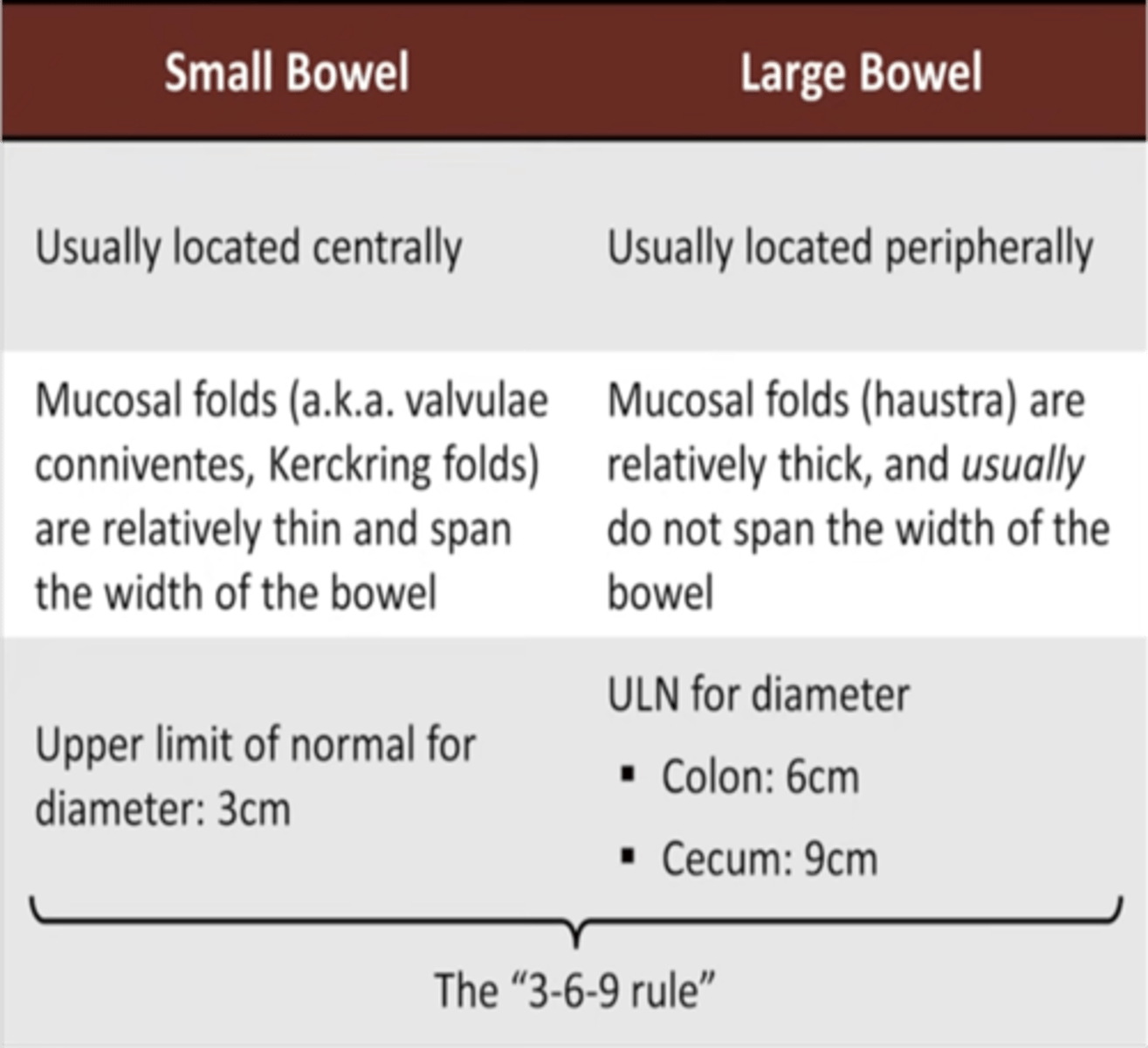
small bowel: valvulae conniventes
large bowel: haustra
How do valvulae appear on XR?
-stack of coins
-closely stacked and extend across the lumen of the small bowel
What do haustra look like on an XR?
-wide spread and do not traverse the whole diameter
Where does almost all gas in the bowel comes from?
swallowed air
What is bowel distention?
normal
loops of bowel that have sufficient amount of air to fill the lumen
What is bowel dilation?
abnormal
loops of bowel filled beyond their normal size
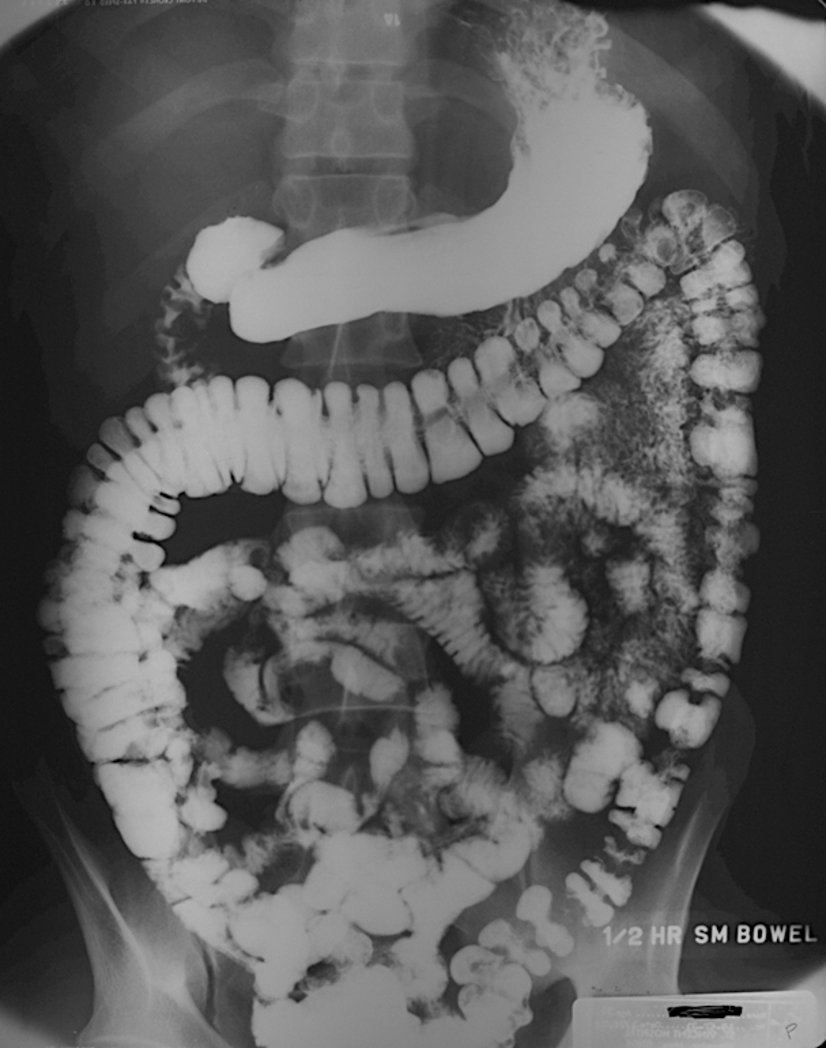
What is a barium enema study?
air and barium are both used as contrast agents
allows for excellent visualization of the mucosal surface of the colon
Explain how a barium swallow with follow through works
pt drinks barium contrast, and the barium goes though allow visiualiization of entire upper GI tract
What does constipation look like on XR?
-soft tissue like opacitites with interla mottled air in the large bowel
What does hepatomegaly look like on XR?
displacement of all bowel loops from RUQ down to the iliac crest and across the midline
What does splenomegaly look like on XR?
projects below 12th rib
displaces the stomach bubble toward or across the midline
What is a kidney intravenous pyelogram?
-pt given IV contrast (excreted by kidneys)
-we can see kidneys, ureters, and bladder
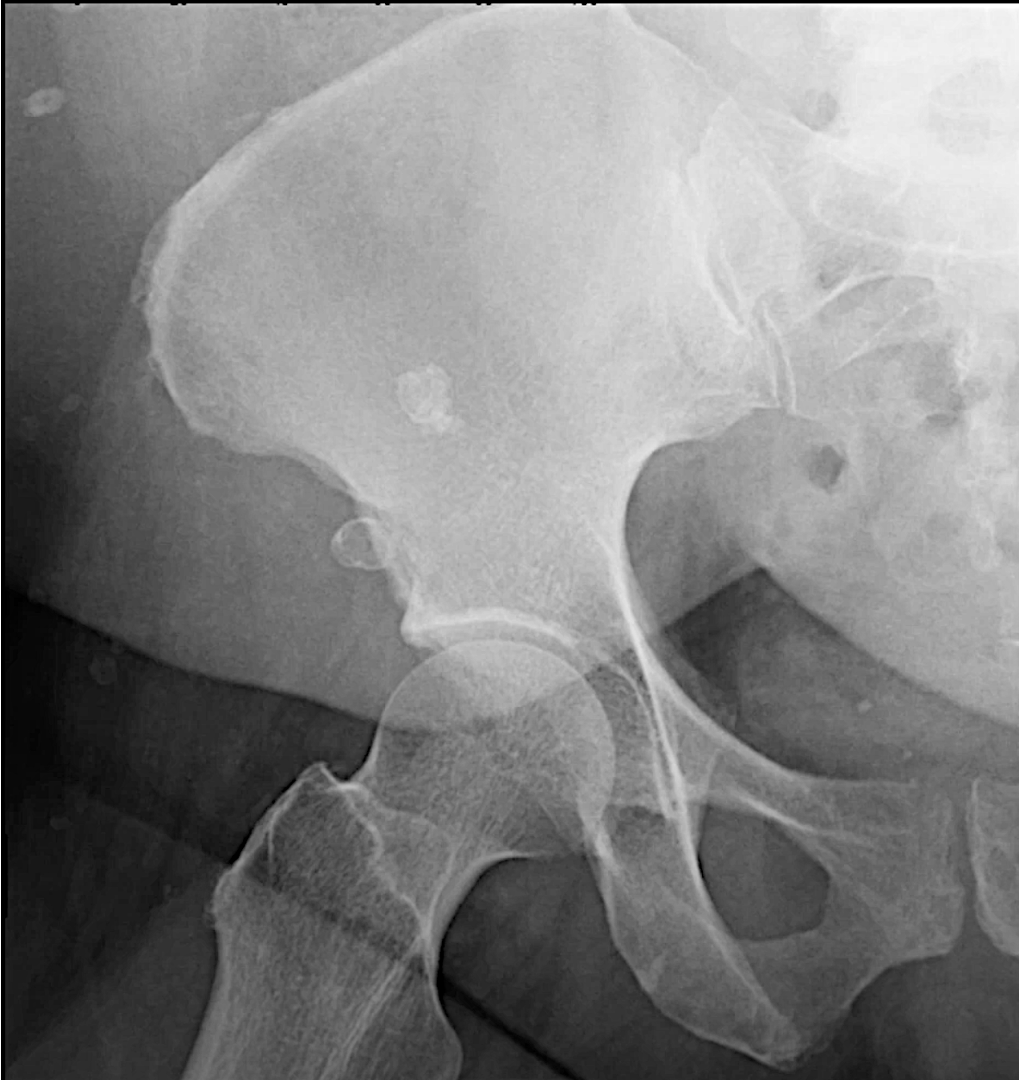
What are the 4 patterns of calcifications?
-rimlike
-linear
-lamellar
-cloudlike
What does nephrocalcinosis look like on XR?
-cloudlike calcifications within the kidney
What imaging is used for follow up of suspected small bladder stones?
US
What does nephocalcinosis suggest?
a significant metabolic issue with primary hyperparathyroidism
What does a calcified gallbladder wall look like on XR?
-rim seen around the gallbladder
What is a porcelain gallbladder?
occurs with chronic cholecystitis associated with gallstones (wall of gallbladder is calcified)
What are injection granulomas?
multiple calcified lesions overlying and next to the ileum
MC cause of calcifications in gluteal region
IM injection → fat necrosis and dystrophic calcifications → visible granulomas
When do we use IV contrast?
-cancer
-trauma
-acute abdomen
-aortic aneurysm/dissection
When do we use PO contrast?
-non traumatic abdominal pain
-IBD
-abscess
-bowel perforation
-hernia
-bowel obstruction
When do we not use contrast?
when we suspect a renal or ureteral stone
What kind of contrast do pts w acute abdomens receive?
both PO and IV
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
-enlargement of abdominal aorta
-Risk factors: HTN, atherosclerosis
-usually asymptomatic, but can cause pain
-large ones can rupture lead to hypotension and death
What imaging is used to follow an enlarged AAA?
US
If woried about a ruptured AAA, what imaging should you order?
CT, not US
What is the risk of an AAA rupturing?
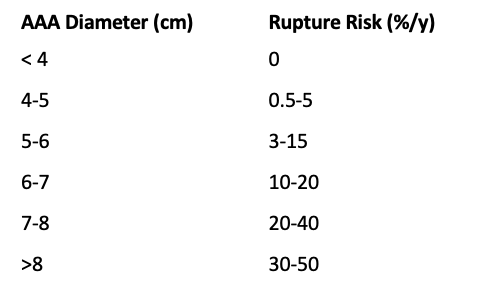
What is a calcified aortic aneurysm?
-common in those with DM and atherosclerosis
-aorta has rim like calcifications
-aneurysm is when normal diameter exceeds 50% of normal size
What is the difference between hyperecoic and hypecoic livers?
-hyperecoic: too bright=fatty liver
-hypecoic: starry sky=hepatitis
What is the best imaging for evaluating the pancreas?
CT or MRI
What does a normal pancreas look like?
-6 inches long and across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach
-head is on the right and connected to doudenum
-tail is on the left side
What is the function of the pancreas?
-make digestive enzymes our body uses to break down and process food
-makes insulin
What do the kidneys look like on imaging?
-renal pelvis in the central portion
-right renal artery is posterior to IVC
-left renal vein in anterior to left renal artery
What does a normal bowel look like on imaging?
-less than 2.5cm
-wall is so thin it is almost invisible
-terminal ileum has fat containing "lips" of the ileocecal value which is outlines with contrast
What does a normal bladder look like on imaging?
-has unopacified urine
-bladder wall is thin and equal thickness around the circumference of the bladder
-rectum is posterior
What is Zenkers diverticulum?
-pouch that forms in the throat where the esophagus and throat meet
-caused by over tightening of cricopharyngeus muscle
-MC in older adults
What is cricopharyngeal achalasia?
-upper esophageal sphincter does not open adequately during swallowing leading to dysphagia
-Use barium swallow to evaluate
What is Barrett's esophagus?
stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by simple columnar epithelium
most people have GERD
has risk of developing esophageal cancer
What is Achalasia?
-disease of lower esophageal body and sphincter
-sphincter fails to relax and open to let food pass
-caused by loss of inhibitory neurons in esophagus
-Sx: difficulty swallowing, chest pain, regurgitation
-complications: lung problems, loss of weight
-Dx: XR, endoscopy, esophageal manometry
What does achalsia look like on XR?
-birds beak
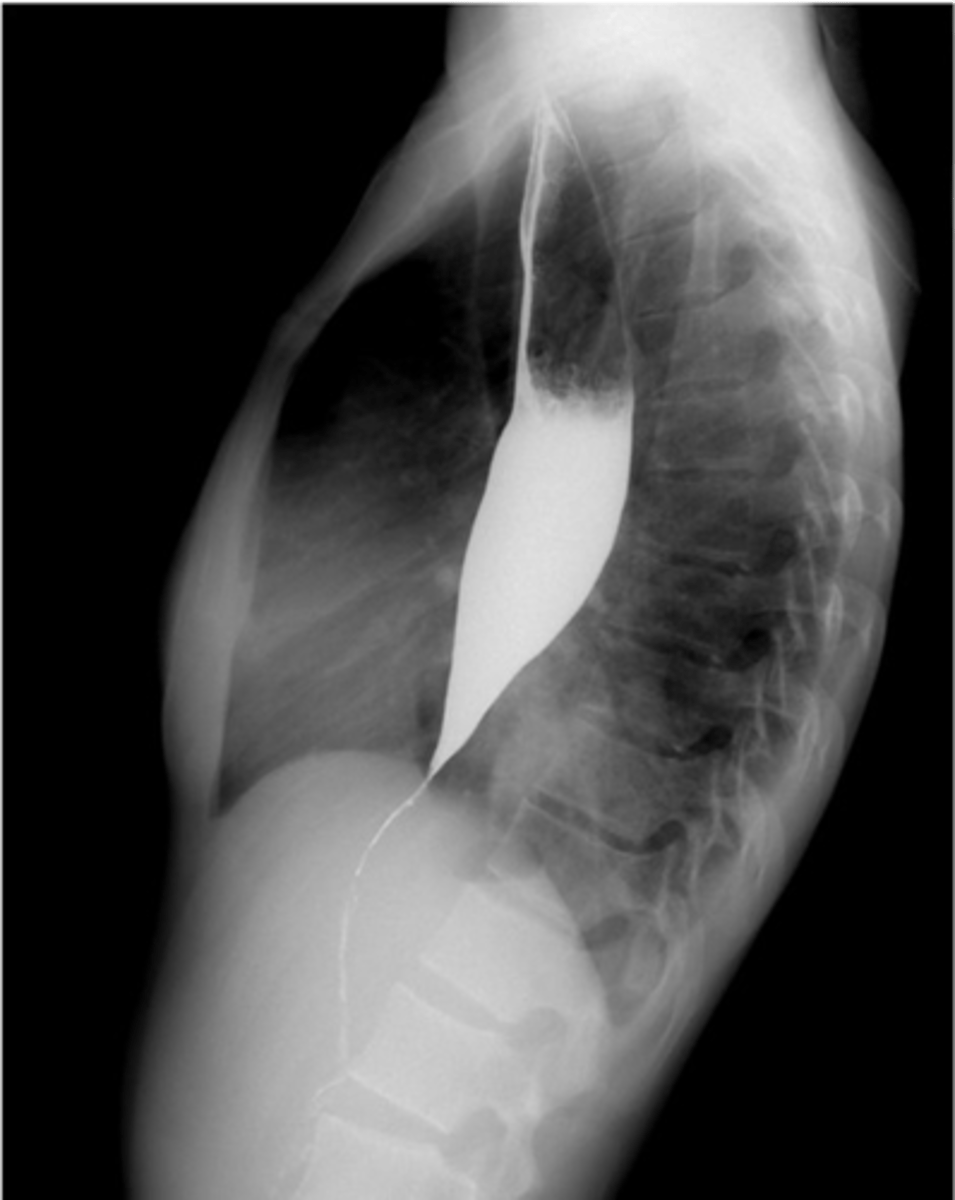
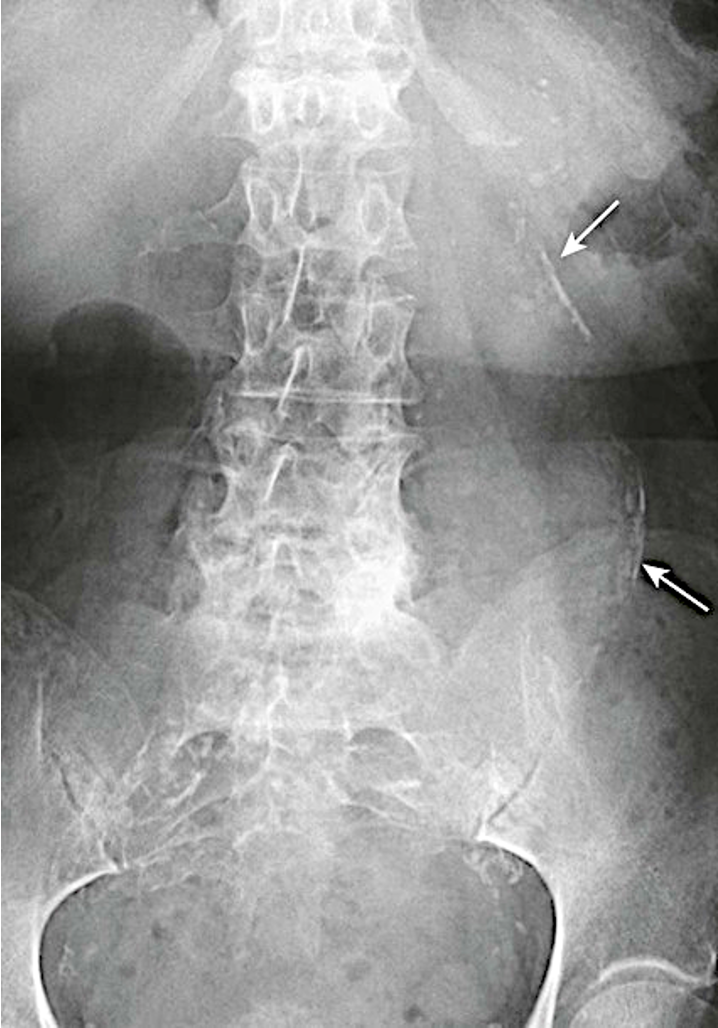
What is a sliding esophageal hernia?
-top part of the stomach pushes through the top part of the diaphragm
-GERD, heartburn, belching, nausea, chest pain
What is a paraesopahgeal hernia?
-stomach pushed up into the chest beside the esophagus
-incarceration: hernia stuck and squeezed
-strangulation: lack of blood supply
What are risk factors for hernia?
-pregnancy
-obesity
-family history
-increased age
What is a schatzki ring?
-thin, weblike filling defect just above the hernia
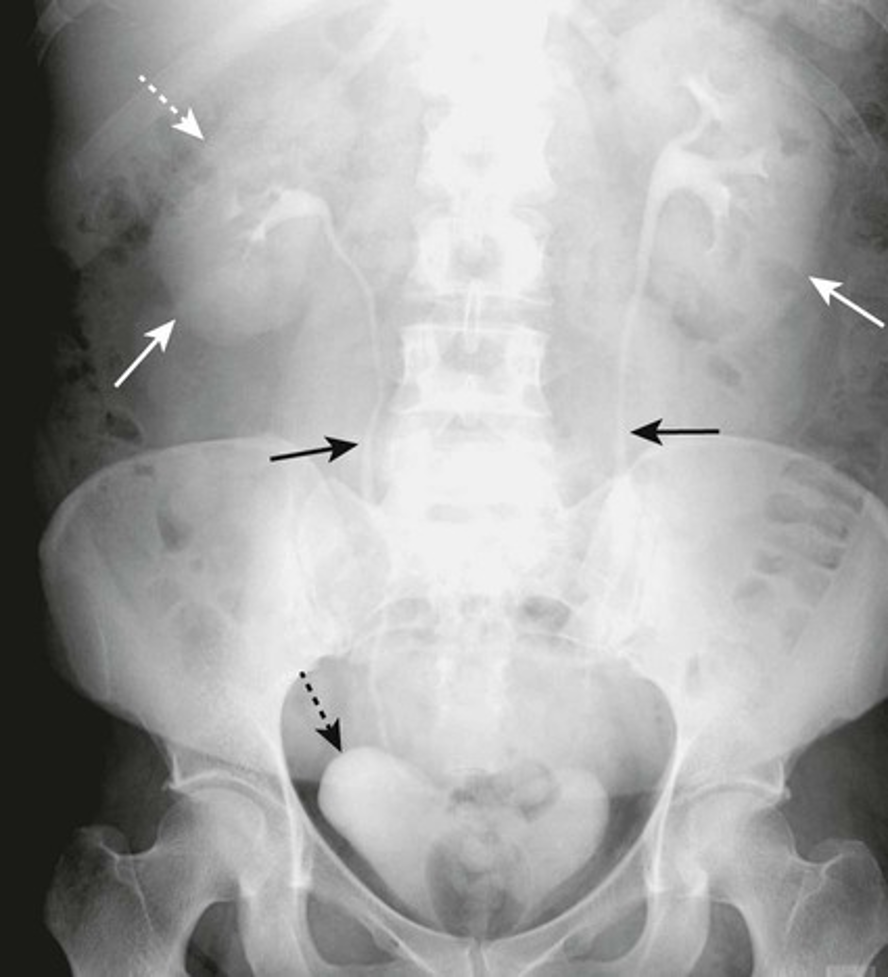
What is a small bowel obstruction?
-physical blockage in small intestine (adhesion, tumor, hernia)
-mostly due to adhesion
-Tx: NG tube
-Complications: sepsis, bowel ischemia, death
What is an ileus?
-functional, non mechanical obstruction where bowel muscle fails to contract properly
-due to nerve damage or med SE
-TX: NG tube
What is a localized ileus?
-from focal inflammation from adjacent organs
What is an adynamic ileus?
-post operative state
-electrolyte imbalance
-gas filled bowel distention, many bowel loops dilated
What are Localized ileus (sentinel loops) from pancreatitis?
-single, persistently dilated loop of small bowel in LUQ
What are the XR findings of an adynamic ileus?
-air filled loops of large + small bowels
-large and small bowel equally distented
-equal air fluid levels
-bowel can be distented
What are examples of mechanical small bowel obstruction?
-postsurgical adhesions
-tumor
-hernia
-gallstones
-intussusception
-IBD
What are examples of mechanical large bowel obstructions?
-tumor
-hernia
-volvulus
-diverticulitis
-intussusception
What are adhesions?
-band of scar tissue that cause internal organs and tissues to stick together
-MC in abdomen
-Cause by surgery, infection, and inflammatory conditions
What does SBO look like on an XR?
-step ladder appearance
What is a volvulus?
when the cecum or sigmoid twists upon itself
Coffee bean appearance
considered a LBO
massively dilated colon and haustra are absent
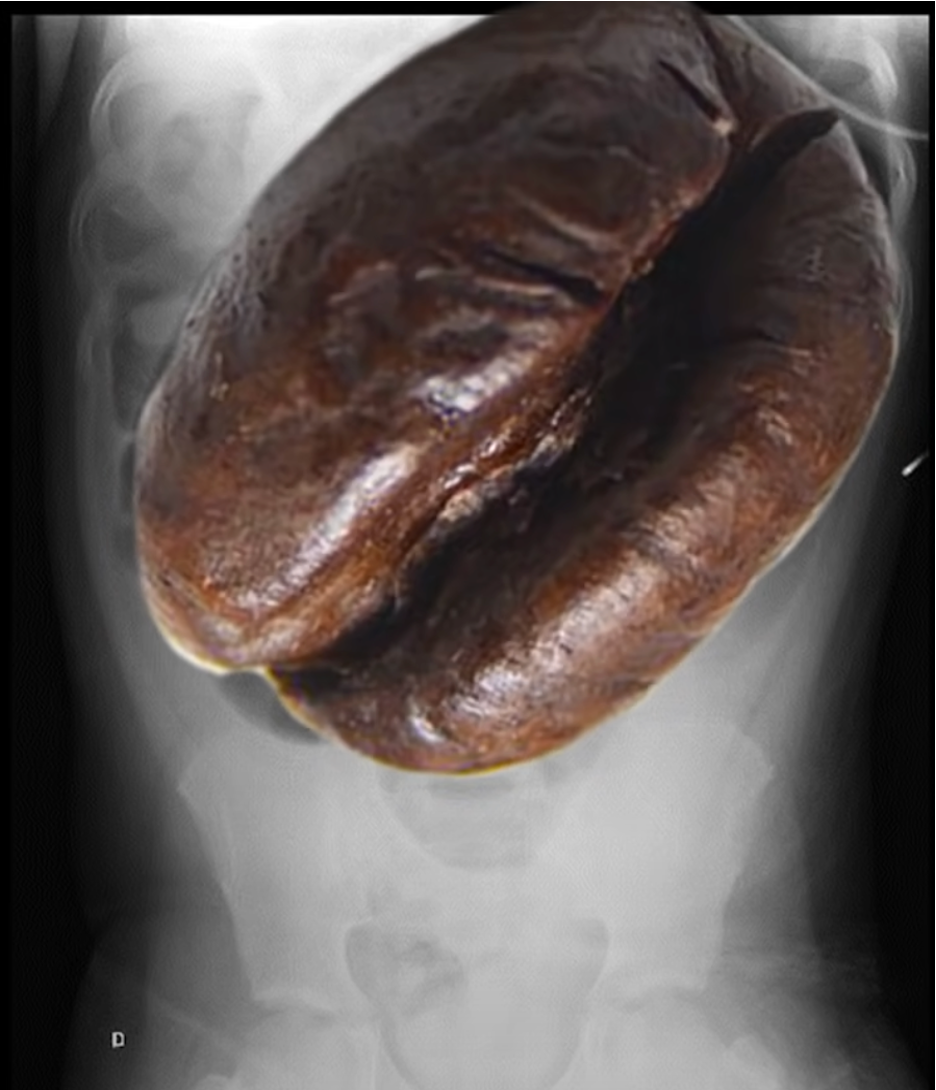
What is a sigmoid volvulus?
-when last part of large bowel twists on itself
-chronic constipation
What is pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie syndrome)?
-in older hospitalized pt
-ascosiated with anticholinergic drugs
-loss of peristalsis
-TX: meds or bowel decompression
What are the 4 most common locations?
-intraperitoneal (free air): MC
-retroperitoneal air
-air in bowel wall (pneumatosis)
-air in biliary system (pneumobilia)
Etiologies of free air (pneumperitoneum)
-peptic ulcer disease
-bowel ischemia
-appendicitis
-colitis
-diverticulitis
-penetrating abdominal trauma
-foreign body ingestion
-endoscopic complications
-post surgery
What is pneumatosis intestinal?
-cluster of air containing cysts in the left colon
What is a rigler sign?
-double wall sign
-sign of pneumoperitoneum
-gas is outling both sides of the bowel wall
What is pneumobilia?
-air is present in biliarty system
-caused by abnormal connection between biliary tract and intestines
What is Crohns disease?
-skip lesions
-MC in terminal ileum
-affects all bowel wall layers (transmural inflammation)
What is ulcerative colitis?
-begins in rectum and spreads to colon
-long last inflammation and ulcers in digestive tract
-intermost lining only affected
-can lead to colon cancer
What is diverticulosis?
-outpouchings in the weakened colon walls
-MC in sigmoid colon
What is diverticulitis?
-one or more inflammed diverticula
-Sx: LLQ and fever
-complications: bowel obstruction, fistual, abscesses
-TX: Bowel rest, Abx, drainage, surgery
What are polyps?
-persistent filling defects in the colon
-barium is displaced by polyp
What is a virual colonoscopy?
-uses CT to contruct virual images of the colon
-Advantages: noninvasive, no sedation, can find polyps, can see outsisde of bowel
-Disadvantage: radiation, no biopsy available, have to inject air into colon, hard to see small or flat polyps
What is intussusception?
-part of the intestine folds into itself, blocking food and blood flow
What are risk factors for colorectal cancers?
-family history
-colon polyps
-long standing ulcerative colitis
what is the difference between left and right sided cancers?
-right: grow large before causing symptoms, cause iron deficiency=fatigue, weakness, SOB
-left: narrower part of colon so more likely to cause obstruction
Signs and symptoms of colon cancer include
-change in bowel habits
-bleeding/blood in stool
-persistant abdominal pain
-feeling that your bowel doesn't completely empty
-weakness, fatigue
-weight loss
What does colonic carcinoma look like on imaging?
-apple core lesion
What is colitis?
inflammation of the colon
-infectious
-ischemic
-IBD
What are the signs and symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis?
-diarrhea
-abdomainal cramps, pain, tenderness
-fever
-pus/mucus in stool
-nausa
-dehydration
What is appendicitis?
-inflammation caused by blockage of the appendix secondary to calcified stool or tumor of the cecum/appendix
-mid abdominal pain that migrates to RLQ (mcburneys point)
CT findings of appendicitis
->6mm
-enhancement and thickening of the wall
-infiltration of the fat
-appendicolith
-ascites
what is Pancreatitis?
-occurs when digestive enzymes produced in your pancreas become activated while inside the pancreas
-Sx: Upper abdominal pain, pain that radiates to your back, pain that is worse after eating, N/V, tenderness
-elevated amylase and lipase
What are the signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
-normally occur in advanced disease
-upper abdominal pain, jaundice, loss of appetite, weight loss
-CT and MRI best
What is fatty liver?
-reversible
-caused by alcholism and obesity
-asymptomatic, can cause pain and enlarged liver
-MC cause of elevated LFT
What is cirrhosis?
-when healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue
-MC Cause: hepatitis B and C, fatty liver, alcohol abuse
-complications: High bloop pressure in veins supplying liver, swelling in legs/abdomen, ascites, splenomegaly, bleeding from varices hepatic encephalopathy, jaundice, hepatocellular carcinoma
What is metastatic disease?
-MC malignant tumor of liver
-MC tumors that spread to liver: breast, colorectal, esophageal, lung, melanoma, pancreatic, stomach
-CT with IV contrast
What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
-primary malignancy of the liver (most pts have undering chronic liver disease and cirrhosis)
-Elevated AFT
-TX: chemo, radio frequency, surgery, chemo ablation
What are cysts?
-abnormal sacs filled with fluid in the liver
-can be present at birth, grow slowly
-most asymptomatic, large can cause bloating or RUQ pain
-most do not need Tx, large and painfully can be drained or removed
-associated with polycystic kidney disease
Cysts on imaging
-XR: well circumscribed, lobulated; black, good through transmission, no vascularity
-CT: round and well circumscribed, dark, do not enhance, no internal architecture
-MRI: T2 bright, well circumscribed, lobulated, T1 hypotense
What is a hemangioma?
-noncancerous mass on liver
-no signs or symptoms normally
What is the best study for evaluating the gallbladder, except when its the distal common bile duct?
-US (pt should be fasting 6-8hrs)
What study is used to evaluate the distal common bile duct?
-MRCP