29. Diseases of upper gastrointestinal tract: oral cavity, pharynx, saliva glands
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are examples of diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract?
Oral cavity diseases
Dysphagia
Stomatitis
Gingivitis
Feline eosinophilic granuloma complex
Oral neoplasia
Diseases of the pharynx
Trauma
Pharyngitis
Tonsillitis
Neoplasia, tonsillar lymphosarcoma
Neuromuscular diseases
Diseases of the salivary glands
Sialocele
Sialadenitis
Sialoliths
Ptyalism
Hypoptyalism
What is dysphagia?
Difficulty or discomfort in swallowing. It is a clinical sign, not a specific disease.
What are the two main categories of causes of dysphagia?
Functional and structural
What are functional causes of dysphagia?
Secondary to a neurologic or muscular disturbance of the swallowing reflex, such as:
Eosinophilic myositis
Myasthenia gravis
Botulism
Cranial neuropathies (V - trigeminal nerve)
What are structural causes of dysphagia?
Secondary to plaque, calculus, gingivitis, inflammation, strictures, traumatic injury, foreign bodies, or neoplastic processes (SCC, epulis) involving the oropharyngeal region or oesophagus
What are the main types of dysphagia based on location?
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
Oesophageal dysphagia
Gastroesophageal dysphagia
What is a typical sign of oropharyngeal dysphagia?
Exaggerated swallowing movements
What are the three stages of oropharyngeal dysphagia based on the site of dysfunction?
Oral dysphagia, pharyngeal dysphagia, and cricopharyngeal dysphagia
What is oral dysphagia?
Difficulty in prehension and transport of food to the oropharynx
What is pharyngeal dysphagia?
Pharyngeal constriction
What is cricopharyngeal dysphagia?
Improper relaxation of the cricopharynx and passage of food into the proximal oesophagus
How does oesophageal dysphagia differ from oropharyngeal dysphagia?
It is associated with more delayed regurgitation and usually no exaggerated swallowing movements
How is dysphagia diagnosed?
Time from food ingestion to regurgitation (seconds for oral, minutes for oesophageal),
Level of exaggerated swallowing movements
Oral cavity examination
Endoscopy
X-ray with contrast
How is dysphagia treated?
By treating the underlying cause
What are some oral diseases?
Congenital (cleft palate)
Trauma (puncture, foreign body, chemical burns)
Acquired (broken teeth, feline eosinophilic granuloma complex (FEGC), labial granuloma, glossitis, gingival hyperplasia, oronasal fistula, and neoplasia (benign epulis, malignant squamous cell carcinoma))
What is stomatitis?
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth
What are some causes of stomatitis?
Primary (excessive inflammatory response to dental plaque)
Secondary (autoimmune disorder, internal organ failure (e.g., uraemic stomatitis due to kidney failure), infectious agents, and eosinophilic complex)
What are some clinical signs of stomatitis?
Contact ulcers (kissing ulcers), red, ulcerative lesions, dysphagia, and bad breath
How is stomatitis diagnosed?
Physical examination of mucous membranes
Laboratory examination (biochemistry to exclude secondary causes)
Imaging methods (radiography for dental abnormalities)
How is stomatitis treated?
Plaque control, antibiotics, NSAIDs, and dental extraction of teeth in contact with mucous membranes with plaque accumulation
What is gingivitis?
Inflammation of the gums
What is the most common cause of gingivitis?
Poor diet and lack of oral hygiene, leading to food and bacteria build-up between teeth and gums
What can untreated gingivitis progress to?
Periodontitis
What are some clinical signs of gingivitis?
Red gingival margin, swollen, red gums, bad breath, bleeding gums, mouth pain, reluctance to eat, drooling, and gum recession

How is gingivitis treated?
Cleaning teeth with a scaler (removing plaque/tartar from under the gingival margin) and using antibacterial gel (e.g., Stomodine gel)
What are some differentials for oral ulcerations?
Ingestion of caustic substances
Immune-mediated disease (lupus, pemphigus, ulcerative gingivitis/stomatitis)
Inflammatory conditions (FEGC)
Infectious causes (FIV, FeLV, Feline Herpesvirus (FHV), Feline Calicivirus (FCV), fungal infections (Candida))
Palatine ulcers (due to overgrooming)
What is Feline Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex (FEGC)?
A complex consisting of three forms of skin lesions in cats: eosinophilic plaque, eosinophilic granuloma, and indolent ulcers
What are some clinical signs of FEGC?
Ulcers on the lips (especially the upper lip), clearly demarcated ulcers with raised borders and marked swelling, eosinophilic granulomas in the mouth (especially gums and palate), ptyalism, oral bleeding, reluctance to eat hard food, and dysphagia
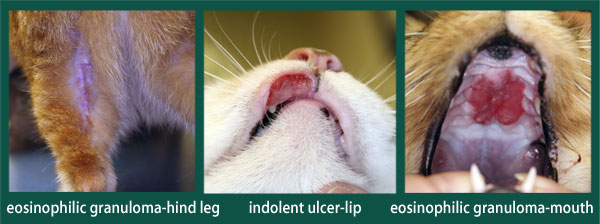
How is FEGC diagnosed?
Clinical signs, fine needle aspirate (FNA), and biopsy
How is FEGC treated?
Antibiotics (amoxicillin), corticosteroids (prednisone), and cyclosporine
What are some diseases of the pharynx?
Trauma, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, neoplasia, tonsillar lymphosarcoma, and neuromuscular diseases
What are salivary mucoceles/sialoceles?
Accumulation of saliva in surrounding tissue after damage to the salivary gland/duct
What is sialadenitis?
Inflammation of the salivary gland, which may form an abscess
How is sialadenitis treated?
Antibiotics and drainage of the abscess
What are sialoliths?
Calcified stones within the salivary duct
What is ptyalism/hypersalivation?
Excessive drooling/excessive production of saliva
What are some causes of ptyalism?
Drugs, toxins, stomatitis, glossitis, infectious diseases (rabies!), motion sickness, fear, nervousness, metabolic disorders, dysphagia/disorders interfering with swallowing, dental disorders, oral cavity injuries, and gastric reflux
How is ptyalism treated?
Glycopyrrolate
What is hypoptyalism?
Decreased secretion of saliva, which may lead to a dry mouth
How is hypoptyalism treated?
Pilocarpine
What does a dog look like when it has dysphagia due to trigeminal nerve (CN V) problems?
Problem with mastication since it regulates the jaw, so signs is dropping of affected side with saliva hanging down from one side of the mouth

What can cause laryngeal collapse and dysphagia?
Brachycephalic syndrome