PSYC388 - Module 3: Evolution & Adaptive Significance of Circadian Rhythms & Clocks
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
in biology and psychology, scientists distinguish between 2 types of causality:
1. proximate
2. ultimate
what is proximate causality?
the "how"
mechanisms behind processes
ie. how brain cells generate circadian rhythms
ie. how LD cycles sync our internal clocks
how brain cells generate circadian rhythms
a) proximate causality
b) ultimate causality
a) proximate causality
what is ultimate causality?
the "why"
function or purpose of processes
ie "why circadian rhythms evolved and what advantages they provide"
"why circadian rhythms evolved and what advantages they provide"
a) proximate causality
b) ultimate causality
b) ultimate causality
this module (3) focuses on which?
a) proximate causality
b) ultimate causality
b) ultimate causality
circadian rhythms help organisms align with the 24 hour ____________
solar day
circadian rhythms help organisms align with the 24 hour solar day, which are _____________ encoded and have evolved because they provide ______________________
1. encoded
2. survival advantages
t or f: global environmental features are unstable and affect all life on earth
f: they're stable
natural selection favours traits like internal clocks that help organisms....
adapt to both local and global environments
Life began ______ billion years ago
a) 3.5
b) 4.5
c) 5.5
3.5
true circadian clocks are found across all 3 domains of life
what are these domains?
1. Eukaryotes
2. Bacteria
3. Archaea
true circadian clocks possess rhythms that...
persist in constant conditions with 24h periodicity
true circadian clocks are found across all 3 domains of life (eukaryotes, bacteria, archaea) and also across all major kingdoms like....
plants, animals, fungi, protists, chromists, archaebacteria, eubacteria
Circadian clocks are universal across life. They're present in multicellular eukaryotes like...
1. humans
2. mice
3 .fruitflies
4. worms
5. plants
6. fungi
Circadian clocks are universal across life. They're present in unicellular eukaryotes like...
1. algae
2. Euglena
Circadian clocks are universal across life. They're present in prokaryotes like...
1. cyanobacteria
2. human gut bacteria
3. extremophile archaea
what is proof that clocks are ancient and evolved early?
1. primitive organisms like cyanobacteria and archaea have circadian rhythms
2. their widespread across domains and kingdoms = ancient
what is proof that circadian clocks evolved multiple times?
1. different organisms use different clock genes
2. no shared clock genes between bacteria, plants, and animals = independent (convergent) evolution
what is proof that circadian clocks are vital for survival?
their continued presence in organisms implies they play big roles in survival
adapting to the 24 hrs day/night cycle
in regards to the escape from light hyp, what were the 2 main challenges that drove circadian evolution?
1. external coordination
2. internal coordination
in regards to the escape from light hyp, what do we mean by external coordination?
1/2 main challenges that drove circadian evolution
aligning biological functions with day-night cycles of light and temperature
in regards to the escape from light hyp what do we mean by internal coordination?
1/2 main challenges that drove circadian evolution
organizing cellular processes so that incompatible functions happen at different times
explain how sunlight was both useful and harmful for early organisms according to the escape from light hypothesis
provided energy but contained UV radiation which
1. damaged DNA, disrupting transcription
2. was harmful for organisms w/o UV protection
Explain the 2 ways in which circadian clocks were used as a defence mechanisms in early life from light (escape from light hyp)
1. timing: early life restricted vulnerable processes to night time (cell div, gene transcription)
2. movement: mobile organisms could "escape from light" by relocating before sunrise
t or f: many species today still perform critical cellular functions at night (escape from light hyp)
true (evidence for the escape from light hypothesis)
t or f: According to the escape from light hypothesis, light exposure at night causes greater cellular damage, supporting the evolutionary role of circadian clocks in UV protection
true
What was the hypothesis the followed after the "escape from light" hypothesis? for the origin hypothesis of the evolution of circadian clocks
escape from oxygen (radicals)
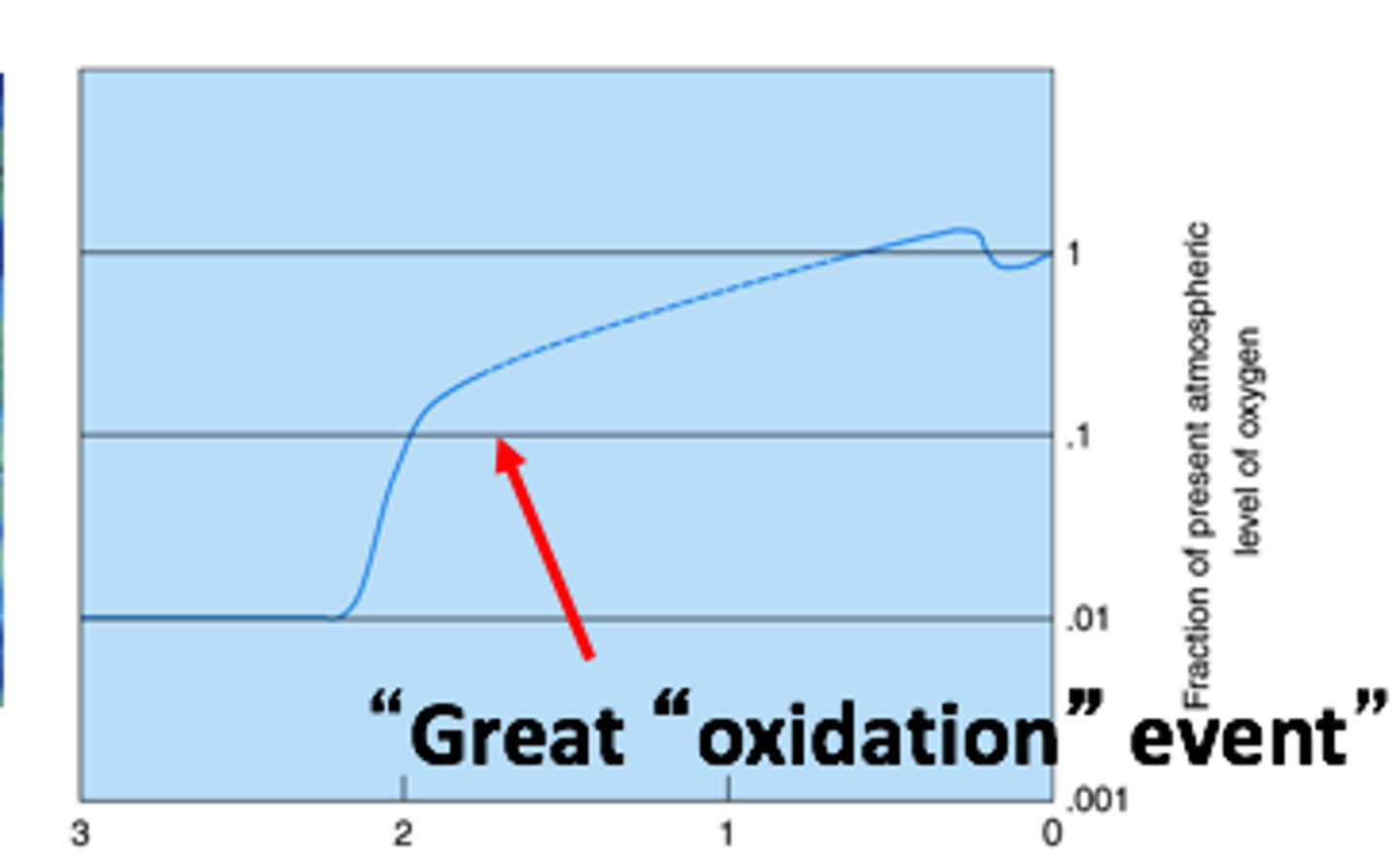
about ____b years ago, during the great oxidation event, cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of O2 through photosynthesis
a) 1.5b
b) 2.5b
c) 3.5b
b) 2.5b
about 2.5b years ago, during which event did cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of O2 through photosynthesis?
Great Oxidation Event
about 2.5b years ago, during the great oxidation event, _______________ began producing large amounts of O2 through photosynthesis
cyanobacteria
about 2.5b years ago, during the great oxidation event, cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of O2 through photosynthesis
what are cyanobacteria?
ancient, photosynthetic bacteria that produce oxygen
live in various environments
play a key role in ecosystems
can also cause harmful algal blooms.
about 2.5b years ago, during the great oxidation event, cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of ______ through photosynthesis
oxygen
about 2.5b years ago, during the great oxidation event, cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of O2 through what process?
photosynthesis
the process where organisms make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, and it produces oxygen as a result.
about 2.5b years ago, during the great oxidation event, cyanobacteria began producing large amounts of O2 through photosynthesis
what did this lead to?
rise of aerobic metabolism, which produces harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) as byproducts
the Great Oxidation event led to the rise of aerobic metabolism
this process produced something a bit harmful, what was it?
harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) as byproducts (ie. H202)
the Great Oxidation event led to the rise of aerobic metabolism
what is this?
the process your cells use to make energy from food using oxygen, and it produces a lot of energy along with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
the Great Oxidation event led to the rise of aerobic metabolism, which produced ROS (bad)
how did organisms fight this?
circadian clocks evolved to anticipate daytime oxygen production and activate anti-oxidants in advance to neutralize ROS
evolutionary advantage, more efficient and resilient
in the "escape from oxygen hypothesis", the rise of aerobic organisms led to the extinction of many _______________
anaerobic organisms
Anaerobic organisms live and grow without oxygen and may even be harmed by it, while aerobic organisms need oxygen to survive and make energy.
Oxygen metabolism produces ______________ like hydrogen peroxide (H202)
ROS (reactive oxygen species)
Why are ROS (reactive oxygen species) harmful?
highly reactive and can damage cells - liked to aging and disease like cancer
what was needed to neutralize the effects of ROS?
anti-oxidant systems
photosynthesis and ROS production happen during
a) the day
b) night
a) day
Because photosynthesis and ROS production happen during, what did organisms evolve into to defend themselves against the harm of ROS?
1. activate anti-oxidant production in advance
2. shut it down at night when no longer needed
What was hypothesis 2? for the evolutionary origins of circadian clocks?
Internal biochemical coordination hypothesis
Explain how plants and cyanobacteria evolved using the Internal biochemical coordination hypothesis
Some organisms needed ammonia to keep them healthy
to make ammonia, they took nitrogen from the air and used nitrogen fixation to turn it into ammonia
this process required enzyme nitrogenase
the issue was oxygen, made during photosynthesis destroys nitrogenase
so these 2 processes cant happen at the same time
so as a solution, organisms used time: photosynthesis for the day, nitrogen fixation for the night
their circadian clock controls this switch
the process where cells take nitrogen from the air and turn it into ammonia:
nitrogen fixation
nitrogen fixation, the process where cells take nitrogen from the air and turn it into ammonia: requires an enzyme called:
nitrogenase
what was stopping organisms form producing ammonia?
the oxygen produced during photosynthesis destroys nitrogenase, which is required for nitrogen fixation, which is used to make ammonia
photosynthesis was basically stopping organisms from making ammonia and keeping themselves healthy
what did they do as a solution?
photosynthesis occur in day
nitrogen fixation for night (O2 production stops)
explain how humans use internal biochemical coordination as an evolutionary advancement
glucose storage in liver:
after eating, liver stores sugar using enzyme glycogen synthase
when not eating, body needs sugar back into blood, and it does this using enzyme glycogen phosphorylase
these enzymes do opposite jobs so they're made at diff times of the day based on circadian clock
humans and internal biochemical coordination:
after eating, the liver stores sugar using an enzyme called:
glycogen synthase
humans and internal biochemical coordination:
when not eating, our bodies need sugar back in blood and does this using an enzyme called;
a) glycogen synthase
b) glycogen phosphorylase
glycogen phosphorylase
"The only reason for time is so that everything doesn't happen at once" -Einstein
what does this mean?
supports the internal biochemical coordination:
Some important things your cells need to do can't happen at the same time because they interfere with each other, thus our clocks help solve this
Circadian clocks were thought to help organisms _____________________ for predictable daily environmental changes like transition from night to day. temp, & humidity
anticipate and prepare
circadian clocks were thought to help organisms anticipate and prepare for predictable changes
these close evolved independently in different organisms and are widely conserved across specied due to their survival benefits
what do we mean by "widely conserved"?
something (like a gene, trait, or system) has remained similar across many different species over time because it’s important for survival and evolution has kept it.
what are examples of organisms that use circadian clocks for anticipatory benefits
1. nematodes (worms)
2. fruit flies
3. photosynthetic organisms
explain how nematodes (worms) evolutionarily used circadian clocks for anticipatory benefits
use clocks to time vertical movement in soil, avoiding extreme heat or dryness
explain how fruit flies evolutionarily used circadian clocks for anticipatory benefits
they come out of their cocoons around dawn, when it's best for their wings to dry.
Their internal clock keeps working while they change into adults and stays in sync with light.
Explain how photosynthetic organisms evolutionarily used circadian clocks for anticipatory benefits
use clocks to produce enzymes ahead of sunrise, maximizing efficiency
explain the importance of the "reliability of dawn" in regards to how organisms evolutionarily used circadian clocks for anticipatory benefits
dawn is a consistent environmental cue
its more dependable than temp or humidity
which organisms use to time crucial behaviours
t or f: food availability isn't really a key rhythm animals adapt to
false: its a key daily rhythm they adapt to
What does FAA mean and why is it important?
Food-anticipatory activity
animals can learn and remember the time of day that food is provided if predicable from day to day
Rats/mice show increased activity _____ hours before predictable meals
a) 1-2h
b) 2-4h
c) 4-6h
a) 1-2h
t or f: FAA persists even when meals are skipped
true
FAA persists even when meals are skipped
what does this imply?
implies the use of internal clocks, not just hunger or external cues
t or f: animals can anticipate meals in constant light or darkness
true
t or f: animals can anticipate multiple meals per day, possibly up to 4
true
Provide evidence that animals can remember when and where food appears?
honey bees:
use circadian clocks like an alarm clock to start/stop foraging
use clocks like a wrist watch to remember specific times and places
can recall up to 9 meal times tied to distant locations even w/o time cues

honey bees can remember when and where food appears
what is this ability called? Why is this ability important?
zeitgedächtnis (memory for time)
enables efficient foraging
t or f: birds and rodents are the only organisms that cannot demonstrate time-place learning
false: Birds and rodents also demonstrate time-place learning, though rats require more training.
birds, bees, and butterflies navigate using the _____
sun
birds, bees, and butterflies navigate using the sun, which moves ___ degrees an hour
a) 12
b) 15
c) 20
b) 15
birds, bees, and butterflies navigate using the sun, which moves 15 degrees an hour
to navigate accurately, animals adjust their orientation based on:
time of day using a circadian clock
bees use the _________________ to communicate distance and direction of food relative to the sun
waggle dance
bees use the waggle dance to communicate distance and direction of food relative to the sun
and clocks help them do what?
compensate for sun movement
bees use the waggle dance to communicate distance and direction of food relative to the sun
and clock helps them compensate for sun movement
what does this all mean?
Bees perform a special movement called the waggle dance to tell other bees where to find food.
The dance shows:
1. Direction of the food (based on the angle to the sun).
2. Distance to the food (based on how long they "waggle").
bees also use an internal clock to adjust their dance if the sun moves across the sky.
ex. if sun has shifted since the bee found the food, the bee changes the angle of the dance accordingly.
This keeps the directions accurate even as time passes.
t or f: birds and butterflies, like bees, use time-compensated navigation during long-distance migrations
true
circadian clocks allow for complex behaviours like:
timing, memory, and spatial navigation
t or f: humans are the best at circadian clock complex behaviours like timing, memory, and spatial navigation
false: bees outperform humans here
overall, internal clocks enhance survival by allowing animals to
optimize behaviour without relying solely on external cues
mating success increases when males and females:
are active at the same time
mating success increases when males and females are active at the same time
this is achieved by:
aligning rest-activity cycles to shared environmental cues
explain how blind mole rats, despite living underground, have true circadian rhythms entrained to LD cycles
light-sensitive eyes under their skin that detect light and connect to brain's circadian clock
exposed to light when digging
15 mins of light per day is enough to entrain their rhythms
despite living underground, they have true circadian rhythms entrained to LD cycles
Even in animals that live underground (like blind and naked mole rats), circadian rhythms can still be entrained by very limited light exposure—especially in individuals with specific roles (like digging).

explain how naked mole rats entrain their clocks
tunnel digging workers get occasional light exposure which may help them entrain their clocks
Even in animals that live underground (like blind and naked mole rats), circadian rhythms can still be entrained by very limited light exposure—especially in individuals with specific roles (like digging).
explain how dispersers maintain genetic diversity through outbreeding
Dispersers are a special type of individual in some eusocial animals (like naked mole rats) whose job is to leave their home colony and go find a new one—or even start a new one themselves.
Workers = day-active
Dispersers = night-active
Likely because dispersal occurs at night when it’s safer for vulnerable individuals.
“You don’t belong here anymore—it’s your job to go out, find new mates, and keep the species strong.”

t or f: circadian clocks synchronize behaviour across sexes/species for optimal survival and reproduction
true
t or f: circadian clocks synchronize behaviour across sexes/species for optimal survival and reproduction, and even blind or underground species rely on light cues to regulate these rhythms
true
how do naked mole rats' social roles support division of labour and maintain survival strategies?
they align with distinct circadian patterns
Explain how Guillemot chicks survive with circadian clocks (demonstrating avoidance)
they leave the nest when mature (fledge) which is risky due to predators
they fledge in large groups at night when light is low
this behaviour is regulated by circadian clock
this strategy is known as swamping which overwhelms predators

what is swamping?
strategy where prey fledge (leave the nest) in large groups to overwhelm predators
this behaviour is controlled by circadian clock
another ie. fruit flies emerge at down
explain how desert rats use circadian rhythms to avoid competition, not predators (demonstrating temporal niche segregation)
only the dominant larger species stay nocturnal
smaller ones become dinural to avoid conflict
temporal niche segregation: sharing the same space but using different times to reduce competition
what is temporal niche segregation?
sharing the same space but using different times to reduce competition
demonstrates how animals use circadian rhythms to avoid competition
explain how malaria parasites use circadian timing to maximize transmission and avoid immune attack
-live in mosquito vectors infect hosts during bites
-after maturing in liver cells, they enter bloodstream in evening when mosquitoes are active
-return to liver in morning to hide from immune system
what are the 2 benefits that circadian control offers for malaria parasites?
1. maximizes transmission to mosquitoes (evening emergence)
2. swamps the hosts immune system (which cant kill them all at once)

releasing many at once to overwhelm predators or immune defenses
swamping
what are the 3 ways circadian clocks help animals in avoidance
1. timing predator avoidance (fledging)
2. avoiding competition (temporal niche segregation)
3. timing transmission and immune evasion
t or f: even tiny organisms like parasites rely on circadian rhythms for survival strategies
true
What is photoperiodism?
1. tracking day length to anticipate seasonal changes
2. relies on circadian clock as internal calendar
3. common in both plants and animals
t or f: photoperiodism is a unique feature only found in plants
f: plants and humans